Risk factors for rebleeding after endoscopic selective variceal devascularization in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis and acute variceal bleeding
-
摘要:
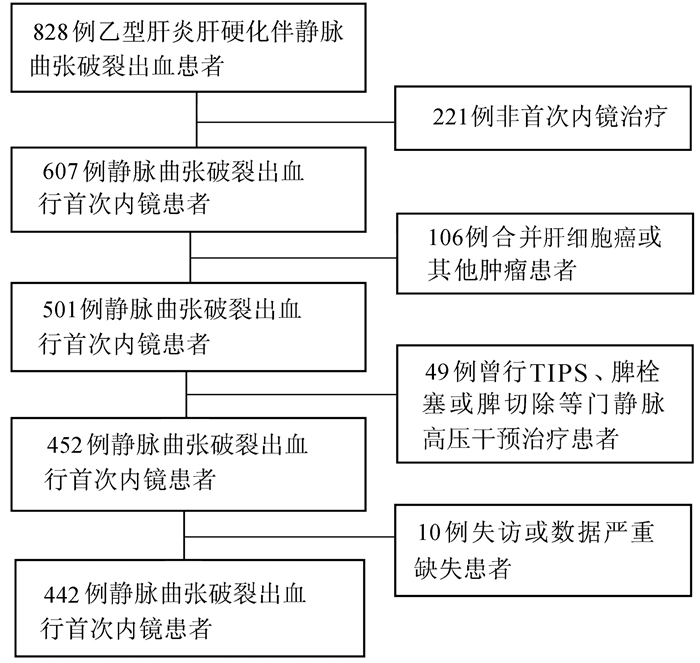
目的 明确乙型肝炎肝硬化伴食管胃静脉曲张破裂出血(EVB)患者行内镜下精准食管胃静脉曲张断流术(ESVD)后的再出血率及再出血的预测因素。 方法 纳入2010年10月—2019年12月因乙型肝炎肝硬化伴EVB,于首都医科大学附属北京地坛医院就诊,并行首次ESVD治疗的患者,根据纳入和排除标准共筛选出患者442例。对患者的常规临床、实验室、影像学及内镜等指标进行比较,随访患者的再出血情况。正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用t检验,非正态分布的计量资料两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。采用Kaplan-Meier法描述再出血和生存情况,采用Cox回归明确静脉曲张再出血的独立危险因素。 结果 首次ESVD治疗后1、2、3、4、5年累积再出血率分别为25.11%、33.94%、39.82%、42.08%和45.02%。单因素分析结果显示,年龄、收缩压、抗病毒疗程≥1年、腹水、WBC、中性粒细胞、直接胆红素与再出血相关(P值均<0.05);多因素分析结果显示,抗病毒疗程≥1年(HR=0.504,95%CI:0.357~0.711,P<0.001)和腹水(HR=1.424,95%CI:1.184~1.714,P<0.001)是静脉曲张再出血的独立影响因素。 结论 ESVD治疗乙型肝炎肝硬化伴EVB,再出血率低,合并腹水或抗病毒时间短是治疗后再出血的独立危险因素。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the rebleeding rate after endoscopic selective variceal devascularization (ESVD) and the predictive factors for rebleeding in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis and esophageal variceal bleeding (EVB). Methods The patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis and EVB who attended Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, from October 2010 to December 2019 and underwent ESVD for the first time were enrolled, and a total of 442 patients were screened out based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. Routine clinical indices, laboratory markers, imaging findings, and endoscopic findings were compared between patients, and the patients were followed up to observe rebleeding. The t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups; the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to describe rebleeding and survival status, and a Cox regression analysis was used to determine the independent risk factors for variceal rebleeding. Results The 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5-year cumulative rebleeding rates after first ESVD treatment were 25.11%, 33.94%, 39.82%, 42.08%, and 45.02%, respectively. The univariate analysis showed that age, systolic pressure, duration of antiviral therapy ≥1 year, ascites, white blood cell count, neutrophil, and direct bilirubin were associated with rebleeding (all P < 0.05), and the multivariate analysis showed that duration of antiviral therapy ≥1 year (hazard ratio [HR]=0.504, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.357-0.711, P < 0.001) and ascites (HR=1.424, 95%CI: 1.184-1.714, P < 0.001) were independent influencing factors for variceal rebleeding. Conclusion ESVD has a low rebleeding rate in the treatment of hepatitis B cirrhosis with EVB, and presence of ascites and a short duration of antiviral therapy are independent risk factors for rebleeding after treatment. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Esophageal and Gastric Varices /
- Hemorrhage /
- Risk Factors
-
原发性肝癌是肝脏最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,其在我国发病率居恶性肿瘤的第4位,肿瘤相关死亡第2位[1]。肝细胞癌(HCC)是肝癌中的最常见的类型,是目前全球第五大恶性肿瘤。慢性肝脏疾病患者,如患有病毒性肝炎、酒精性肝病、非酒精性脂肪性肝炎等,是HCC的主要高危人群。中国的新发病例数及死亡病例数均占了全球的50%左右,因此HCC严重影响我国人民的健康[2]。
对于肝癌患者的根治性治疗,目前主要有肝切除术(liver resection, LR)和肝移植术(liver transplantation, LT)两种方法[3-4],2种方法的选择取决于医院和医生的水平、患者的意愿及身体状况等。为了提高对这2种治疗方法结果的认识,更好的指导临床,本文回顾性分析了首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院171例HCC患者治疗后3年的随访资料,比较LR和LT 2种方法的临床治疗效果。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2009年3月—2014年3月在本院首次接受LR或LT的HCC患者171例,依据治疗方式的不同分为LR组(n=83)和LT组(n=88)。LT组患者肝癌的分期依照UICC/AJCC第7版及巴塞罗那分期(BCLC)进行。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:(1)病理确诊符合HCC的诊断标准;(2)LR及LT治疗均在适应证内。排除标准:(1)既往有恶性肿瘤病史;(2)术前曾行抗肿瘤治疗;(3)术后有肿瘤残留;(4)合并严重糖尿病、高血压、心脏病、肾脏病等可能影响生存期的疾病。
1.3 随访情况
患者经过门诊及电话随访,随访主要终点为死亡或随访满3年(36个月),次要终点为检测到肿瘤复发。
1.4 伦理学审查
本研究获得首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院伦理委员会审批,批号:LL-2018-031-K。受试者均签署知情同意书。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 25.0统计学软件进行数据分析。分类资料组间比较使用χ2检验。比较亚组间无瘤生存期和总生存期的差异使用Kaplan-Meier和log-rank检验。检测影响预后的因素使用单因素和多因素Cox比例风险模型。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
171例HCC患者中男142例(83.04%),女29例(16.96%)。95例(55.56%)患者在50岁以下。3年随访期间共有20例(11.70%)患者失访。3年随访结束时,69例(40.35%)患者肿瘤复发,32例(18.71%)患者发生HCC相关死亡(表 1)。
表 1 肝癌患者的基本资料指标 例数(n=171) 手术类型 χ2值 P值 LR组(n=83) LT组(n=88) 性别(例) 0.192 0.661 男 142 70 72 女 29 13 16 年龄(例) 0.117 0.732 ≤50岁 95 45 50 >50岁 76 38 38 潜在肝病(例) 2.333 0.311 HBV 153 76 77 HCV 17 6 11 其他 1 1 0 肿瘤位置(例) 1.161 0.281 右叶 119 61 58 非右叶或多叶 52 22 30 肿瘤数目(例) 29.649 <0.001 单发 113 38 75 多发 58 45 13 肿瘤大小(例) 46.383 <0.001 <3 cm 72 13 59 3~5 cm 62 43 19 >5 cm 37 27 10 AFP (例) 3.350 0.187 <20 ng/ml 82 42 40 20~400 ng/ml 52 20 32 >400 ng/ml 37 21 16 TNM分期(例) 0.174 0.677 Ⅰ+Ⅱ 117 57 63 Ⅲ+Ⅳ 54 26 25 BCLC肝癌分期(例) 0.057 0.972 A 87 42 45 B 44 22 22 C 40 19 21 Child-Pugh分级(例) 7.833 0.005 C 140 75 65 B+C 31 8 23 病理分级(例) 2.573 0.276 低分化 29 18 11 中分化 113 52 61 高分化 29 13 16 肿瘤复发(例) 4.121 0.042 否 102 43 59 是 69 40 29 HCC所致死亡(例) 0.937 0.333 否 139 65 74 是 32 18 14 从基础数据上可以看出,LT组较LR组的单发肿瘤比例更多、肿瘤更小、Child-Pugh分期更高、复发率更低(P值均<0.05),而其他的指标如性别、年龄、潜在肝病、肿瘤位置、AFP水平、TNM分期、BCLC肝癌分期和病理分级2组间比较差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)(表 1)。
2.2 无瘤生存期和总生存期
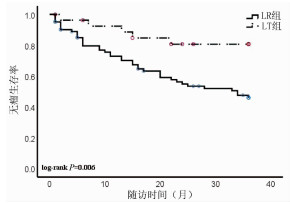
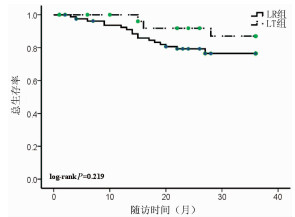
随访3年,LR组患者无瘤生存率是46.02%,而LT组患者的无瘤生存率为80.71%,两组差异具有统计学意义(P=0.006)(图 1);LR组患者的总生存率是76.44%,LT组患者的总生存率为86.99%,两组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.219)(图 2)。
2.3 HCC患者结局的影响因素分析
使用Cox生存分析方法分析无瘤生存期、总生存期和临床特征之间的相关性。在无瘤生存期的单因素分析中,治疗方法和TNM分期是无瘤生存期的影响因素(P值均<0.05)(表 2)。多因素分析结果显示,治疗方法和TNM期是HCC患者无瘤生存期的独立预后因素[RR(95% CI)分别为0.239(0.093~0.612)、4.834(2.598~8.993),P值分别为0.003、<0.001]。在总生存期的单因素分析中,TNM分期是无瘤生存期的影响因素(P<0.001)(表 2)。多因素分析发现TNM分期是HCC患者总生存期的独立预后因素[RR(95% CI):4.970(2.052~12.037),P<0.001]。
表 2 肝癌患者无瘤生存期和总生存期的单因素分析指标 无瘤生存期 总生存期 RR 95%CI P值 RR 95%CI P值 性别 男 1.000 1.000 女 0.539 0.213~1.367 0.193 0.474 0.110~2.034 0.315 年龄 ≤50岁 1.000 1.000 >50岁 1.023 0.570~1.838 0.939 0.678 0.281~1.636 0.387 肝病 HBV 1.000 1.000 HCV/其他 0.380 0.092~1.569 0.181 0.872 0.203~3.747 0.854 肿瘤位置 肝右叶 1.000 1.000 其他位置 0.816 0.422~1.581 0.548 0.693 0.254~1.893 0.475 肿瘤数目 单发 1.000 1.000 多发 1.513 0.833~2.751 0.174 1.491 0.628~3.542 0.365 肿瘤大小 <3 cm 1.000 1.000 <3 cm 1.000 1.000 3~5 cm 1.360 0.647~2.860 0.418 2.956 0.890~9.819 0.077 >5 cm 3.877 1.924~7.812 <0.001 5.595 1.721~18.189 0.004 AFP <20 ng/ml 1.000 1.000 20~400 ng/ml 1.862 0.861~4.025 0.114 0.982 1.699~12.123 0.003 >400 ng/ml 3.625 1.804~7.285 <0.001 4.539 1.699~12.123 0.003 TNM分期 Ⅰ-Ⅱ 1.000 1.000 Ⅲ 4.084 2.237~7.455 <0.001 4.985 2.058~12.076 <0.001 BCLC HCC分期 A 1.000 1.000 B 1.778 0.887~3.564 0.003 1.235 0.349~4.378 0.001 C 3.008 1.453~6.230 0.105 0.003 5.566 2.052~15.101 0.001 Child-Pugh分级 A 1.000 1.000 B+C 0.446 0.160~1.245 0.123 1.886 0.731~4.864 0.189 病理分期 低分化 1.000 1.000 中/高分化 0.813 0.378~1.750 0.597 0.524 0.203~1.350 0.181 治疗方法 LR 1.000 1.000 LT 3.383 1.334~8.579 0.010 0.474 0.140~1.610 0.232 3. 讨论
肝癌的治疗需要多学科协同、多种方法综合进行。目前临床上常用的肝癌治疗方法包括:LR、LT、局部消融治疗(射频消融治疗术为主)、经导管肝动脉化疗栓塞术、放射治疗、全身治疗(包括分子靶向治疗、免疫治疗、化疗、中医治疗等)等[3-5]。既往认为LT治疗的肝癌患者生存结局更好[5]。但是随着对HCC发生发展的探索、影像诊断水平的提高、局部和全身治疗方法的完善、手术技术的进步和术后多学科诊疗模式的形成,不同治疗下患者的最终结局,也随之而改善,有学者[6-7]提出目前LR治疗肝癌与LT同样取得理想效果。金子铮等[8]研究发现LT较LR治疗肝癌患者的5年生存率的优势,2005年—2011年较1989年—2004年明显缩小(73% vs 61%,77% vs 36%),他们认为这种优势的缩小是由于手术水平的进步、围手术期对肝硬化治疗的优化和对于复发肿瘤多手段的治疗。除了总体变化趋势外,治疗的结果还和医院的水平、患者的状况等多个因素相关。本研究发现LT较LR治疗肝癌3年后肿瘤的复发率明显降低,而总生存率差别不显著。Shen等[9]回顾分析了1218例LT和2068例LR治疗肝癌的患者得出结论,LT比LR在无瘤生存率和总生存率上都有优势。矫学黎等[7]对352例LR和37例LT治疗的患者进行了统计分析后也得到了相似的结论。本研究中LT组较LR组的肿瘤复发率明显降低,与文献一致。另一项纳入9篇关于LT和LR治疗HCC效果研究的Meta分析[10]结果显示,HCC患者术后第1年两种治疗方法的总生存率相似,术后第5年LR组较LT组总生存率明显降低。这与本研究中两组总生存率的结果稍有差别。该研究还认为,与LR组相比,HCC患者术后3年LT组的获益才开始表现出来,而本研究的随访截点正好是3年,因此本研究结果与其他中心的研究结果并不矛盾。肿瘤复发才是病死率增加的开始,如果延长随访时间,本研究的总生存率也将出现显著性差异。故本研究数据结合文献检索的结果,支持LT较LR治疗肝癌更有优势。
从笔者的基础数据上可以看出,LT组较LR组的单发肿瘤更多、肿瘤更小、Child-Pugh分期更高,而其他的指标如性别、年龄、潜在肝病、肿瘤位置、AFP水平、TNM分期、BCLC肝癌分期和病理分级2组比较差异均无统计学差异,这是因为在选择LT治疗的时候,兼顾疗效与公平,平衡考虑肿瘤患者预后,主观限制了总体的肿瘤数目和大小。LT较LR治疗肝癌患者的另一优势是不用考虑患者的肝功能,可以同时解决肿瘤和肝功能衰竭两大问题,本研究入组的LT患者中有2例是Child-Pugh C级。综上所述,LT更倾向于选择肝功能储备较差的早期肝癌患者,3年无瘤生存率令人满意。
LT也存在一定的缺点,比如供体的缺乏、术中并发症多、药物排异等,为了弥补这些缺点,目前已有较多研究在推动LT的进步,包括移植方法上的改进、治疗适应证的拓展、新型抗排异药物的研发和围手术期处理的优化等[11-14]。
本研究结果还得出TNM分期是无瘤生存期和总生存期的独立预测因素,支持TNM分期在临床上的重要作用,不但可以用于指导治疗方法的选择,还能预测术后结果。但是TNM分期也有缺点,淋巴结或远处脏器转移有时术前和术中难以准确评估,因此更好的判断预后的指标和方法也是研究的热点。
另外,本研究是单中心研究,基于现有的临床资料,还存在着样本量较小、随访时间短、纳入因素不全面等因素,而且对于手术切除范围、肝移植方法、供体类型、术后治疗、医疗成本、并发症情况等因素未纳入其中,局限了研究的意义。希望将来设计多中心、样本量更大的研究来弥补以上不足, 将更有利于临床工作的不断提升。
-
表 1 患者基线人口学及临床数据
参数 再出血组(n=203) 无再出血组(n=239) 统计值 P值 年龄(岁) 49.38±10.40 49.54±10.21 t=-0.163 0.870 男性(例) 157 168 χ2=2.801 0.105 SBP (mmHg) 110(80~160) 110(72~120) Z=-0.724 0.469 输血量(U) 0(0~14) 0(0~22) Z=-1.024 0.306 并发症(例) 腹水 159 172 χ2=2.360 0.152 肝性脑病 17 23 χ2=0.208 0.704 门静脉栓塞 58 52 χ2=2.726 0.122 现症吸烟(例) 66 57 χ2=4.102 0.044 现症饮酒(例) 46 42 χ2=1.781 0.220 胃静脉曲张出血(例) 64 52 χ2=5.413 0.023 首次组织胶注射量(mL) 1(0~10) 1(0~6) Z=-0.364 0.716 首次聚桂醇注射量(mL) 20(0~60) 20(0~70) Z=-0.129 0.898 抗病毒治疗(例) 157 196 χ2=1.488 0.236 门静脉内径(mm) 12(8~20) 12(7~19) Z=-0.667 0.505 脾脏厚度(mm) 53.63±9.51 52.83±9.99 t=0.728 0.435 WBC(×109/L) 3.75(1.10~26.87) 3.50(0.81~26.22) Z=-1.274 0.203 NEU(×109/L) 2.64(0.43~23.67) 2.57(0.38~23.47) Z=-0.883 0.377 LYM(×109/L) 0.79(0.15~4.20) 0.70(0.19~3.37) Z=-1.704 0.088 HCT 27.01±7.70 28.17±7.65 t=-1.575 0.116 Hb(g/L) 90.10±27.46 94.64±27.68 t=-1.723 0.086 Hb下降>30 g/dL(例) 62 79 χ2=0.319 0.609 PLT(×109/L) 60.40(18.00~314.40) 57.00(18.20~258.00) Z=-0.793 0.428 ALT(U/L) 26.90(8.20~363.60) 29.20(0.00~641.20) Z=-1.527 0.127 AST(U/L) 32.50(10.40~572.80) 37.10(9.20~917.60) Z=-2.452 0.014 TBil(μmol/L) 20.10(4.50~470.30) 20.10(5.20~615.60) Z=-1.492 0.136 DBil(μmol/L) 8.00(1.30~308.30) 8.10(1.90~483.10) Z=-1.554 0.120 TBA(μmol/L) 6.80(0.00~379.30) 11.25(0.10~336.60) Z=-2.485 0.013 Cr(μmol/L) 65.00(19.00~277.00) 64.00(17.00~1 296.00) Z=-0.126 0.900 TP(g/L) 58.65±10.31 59.99±10.31 t=0.977 0.181 Alb(g/L) 32.02±6.22 31.73±5.62 t=0.509 0.611 GLO(g/L) 26.69±6.36 28.29±7.52 t′=-2.3871) 0.017 A/G 1.20(0.50~2.20) 1.20(0.40~2.20) Z=1.787 0.074 GGT(U/L) 27.40(6.40~207.70) 29.30(2.90~369.90) Z=-0.609 0.543 ALP(U/L) 64.80(18.60~226.10) 69.55(20.90~270.00) Z=-1.897 0.058 ChE(U/L) 3 229.00(795.00~9 297.00) 2 899.50(705.00~8 306.00) Z=-1.678 0.093 TC(mmol/L) 2.68±0.84 2.74±0.89 t=-0.675 0.500 TG(mmol/L) 0.59(0.00~9.10) 0.60(0.00~1.70) Z=-0.476 0.634 PA(g/L) 84.36±33.78 77.66±39.27 t=1.786 0.075 PTA (%) 60.65±13.00 59.86±14.66 t=0.596 0.552 CRP (mg/L) 2.25(0.00~56.40) 3.15(0.00~49.30) Z=-1.941 0.052 Child-Pugh评分(分) 8(5~14) 8(5~15) Z=-0120 0.905 Child-Pugh分级(A/B/C,例) 49/108/46 61/112/66 χ2=1.969 0.374 MELD评分 6.54(-6.00~25.00) 6.88(-6.00~31.00) Z=-1.282 0.200 注:LYM,淋巴细胞;HCT,红细胞压积;TP,总蛋白;A/G,白球比;PA,前白蛋白;CRP,C反应蛋白;1)方差不齐,采用t′检验。 表 2 ESVD术后静脉曲张再出血的影响因素
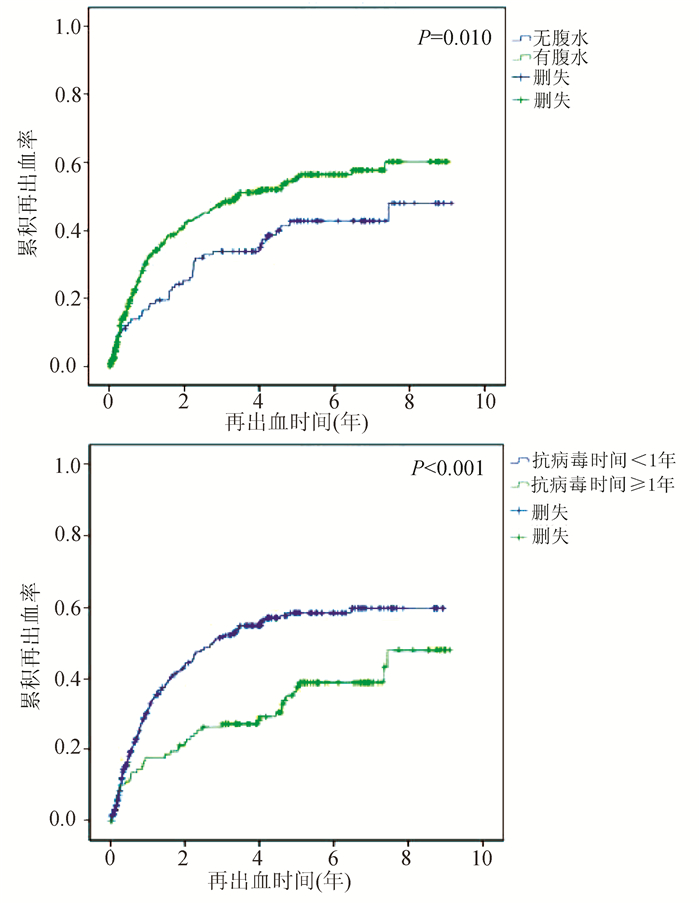
变量 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95%CI) P值 HR (95%CI) P值 年龄(岁) 1.014(1.000~1.028) 0.045 收缩压(mmHg) 0.988(0.978~0.998) 0.024 抗病毒疗程≥1年 0.523(0.373~0.731) <0.001 0.504(0.357~0.711) <0.001 腹水 1.442(1.210~1.719) <0.001 1.424(1.184~1.714) <0.001 WBC(×109/L) 1.049(1.009~1.092) 0.017 NEU(×109/L) 1.049(1.004~1.096) 0.031 DBil(μmol/L) 1.005(1.000~1.010) 0.049 -
[1] GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. [2] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会内镜学分会. 肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002. [3] MA JL, HE LL, LI P, et al. Prognosis of endotherapy versus splenectomy and devascularization for variceal bleeding in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35(6): 2620-2628. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-020-07682-6. [4] MERCADO MA. Surgical treatment for portal hypertension[J]. Br J Surg, 2015, 102(7): 717-718. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.9849. [5] NETT A, BINMOELLER KF. Endoscopic management of portal hypertension-related bleeding[J]. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 2019, 29(2): 321-337. DOI: 10.1016/j.giec.2018.12.006. [6] de FRANCHIS R. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 743-752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. [7] ZHENG J, PAN ZG, SU DX. Clinical effect of ESVD in treatment of portal hypertension and esophagogastric varices[J]. Int J Dig Dis, 2020, 40(5): 339-342. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2020.05.012.郑捷, 潘志刚, 苏东星. ESVD用于门脉高压食管胃静脉曲张破裂出血治疗的临床效果研究[J]. 国际消化病杂志, 2020, 40(5): 339-342. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-534X.2020.05.012. [8] LI P, WEI HS, JIANG Y, et al. Endoscopic selective varices devascularization: Effects of once endotherapy for esophageal and gastric varices[J]. J Inter Int Med, 2017, 23(4): 284-288. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20170407.李坪, 魏红山, 蒋煜, 等. 精准贲门胃静脉曲张断流术: 一次性治疗食管胃连通型静脉曲张的近期疗效[J]. 内科急危重症杂志, 2017, 23(4): 284-288. DOI: 10.11768/nkjwzzzz20170407. [9] MA JL, JIANG Y, AI ZL, et al. Analysis of the prognosis and survival of patients undergoing endoscopic selective varices devascularization[J]. Mod Digest Interv, 2019, 24(6): 578-582. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2019.06.004.马佳丽, 蒋煜, 艾正琳, 等. 内镜下精准食管胃静脉曲张断流术患者预后及生存状况分析[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2019, 24(6): 578-582. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2159.2019.06.004. [10] MA JL, HE LL, LI P, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of repeated endoscopic therapy for esophagogastric variceal hemorrhage in cirrhotic patients: Ten-year real-world analysis[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2020, 2020: 5747563. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5747563. [11] Spleen and Portal Hypertension Surgery Group, Chinese Medical Association of Surgery. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis portal hypertension(2015)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2015, 35(10): 1086-1090. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.12.01.中华医学会外科学分会门静脉高压症学组. 肝硬化门静脉高压症食管、胃底静脉曲张破裂出血诊治专家共识(2015)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2015, 35(10): 1086-1090. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.12.01. [12] MA JL, CHEN X, HONG S, et al. Metal clips combined with endoscopic histoacryl injection in the treatment of gastric varices with spontaneous portosystemic shunts (with video)[J]. Chin J Dig Endosc, 2020, 37(2): 111-114. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-5232.2020.02.007.马佳丽, 陈旭, 洪珊, 等. 金属夹联合组织胶注射治疗胃静脉曲张伴自发性门体分流的临床研究[J]. 中华消化内镜杂志, 2020, 37(2): 111-114. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn. 1007-5232.2020.02.007. [13] D'AMICO G, PAGLIARO L, BOSCH J. The treatment of portal hypertension: A meta-analytic review[J]. Hepatology, 1995, 22(1): 332-354. DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840220145. [14] CHEN J, ZENG XQ, MA LL, et al. Long-term efficacy of endoscopic ligation plus cyanoacrylate injection with or without sclerotherapy for variceal bleeding[J]. J Dig Dis, 2016, 17(4): 252-259. DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.12331. [15] RÍOS CASTELLANOS E, SERON P, GISBERT JP, et al. Endoscopic injection of cyanoacrylate glue versus other endoscopic procedures for acute bleeding gastric varices in people with portal hypertension[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2015, 5: CD010180. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010180.pub2. [16] ROCKEY DC. Liver fibrosis reversion after suppression of hepatitis B virus[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2016, 20(4): 667-679. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2016.06.003. [17] GOYAL SK, DIXIT VK, SHUKLA SK, et al. Prolonged use of tenofovir and entecavir in hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol, 2015, 34(4): 286-291. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-015-0576-1. [18] HE L, YE X, MA J, et al. Antiviral therapy reduces rebleeding rate in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis with acute variceal bleeding after endotherapy[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2019, 19(1): 101. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-019-1020-2. [19] BAMBHA K, KIM WR, PEDERSEN R, et al. Predictors of early re-bleeding and mortality after acute variceal haemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gut, 2008, 57(6): 814-820. DOI: 10.1136/gut.2007.137489. [20] AMITRANO L, GUARDASCIONE MA, BENNATO R, et al. MELD score and hepatocellular carcinoma identify patients at different risk of short-term mortality among cirrhotics bleeding from esophageal varices[J]. J Hepatol, 2005, 42(6): 820-825. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.01.021. [21] HOLSTER IL, TJWA ET, MOELKER A, et al. Covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic therapy + β-blocker for prevention of variceal rebleeding[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63(2): 581-589. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28318. [22] LV Y, QI X, HE C, et al. Covered TIPS versus endoscopic band ligation plus propranolol for the prevention of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic patients with portal vein thrombosis: A randomised controlled trial[J]. Gut, 2018, 67(12): 2156-2168. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314634. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 宋林泉,梁志宏. 肝门再阻断法在肝切除术后胆漏中的预防效果. 吉林医学. 2024(02): 364-367 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3002 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3002 KB)

 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术