Advances in the treatment of acute intermittent porphyria
-
摘要:
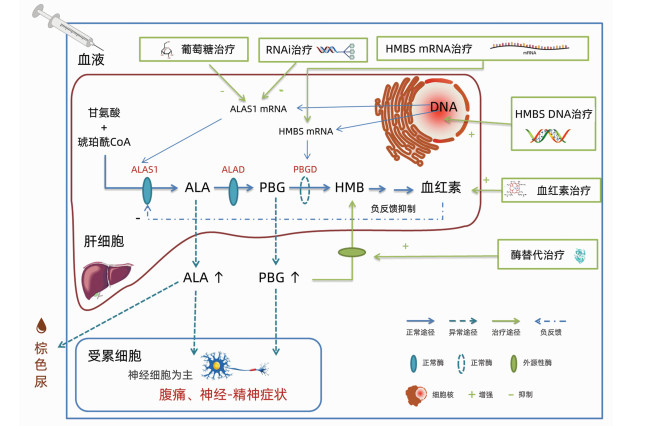
急性间歇性卟啉病(AIP)是一种HMBS基因突变而导致酶缺陷的罕见病,急性发作时常危及生命。介绍了AIP的高碳水化合物疗法和静脉输注血红素等传统治疗,以及一些针对病因的新兴疗法,包括酶替代治疗和DNA基因增补、mRNA基因增补、RNAi基因沉默等多个策略的基因治疗。其中基于RNAi基因沉默的药物吉佛西兰(Givosiran)已取得了突破进展,已经应用于临床。未来针对病因的基因治疗可能会成为罕见病治疗的新趋势。
-
关键词:
- 卟啉病, 急性间歇性 /
- 治疗学 /
- 吉佛西兰
Abstract:Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) is a rare disease caused by enzyme deficiency due to HMBS gene mutation and is often life-threatening during acute attack. This article introduces the traditional treatment methods for AIP, such as high-carbohydrate therapy and intravenous heme infusion, as well as several emerging therapies targeting the etiology of AIP, including enzyme replacement therapy and gene therapy with multiple strategies of DNA gene augmentation, mRNA gene augmentation, and RNAi gene silencing. It is worth noting that breakthroughs have been made in Givosiran, a drug based on RNAi gene silencing, and it has been used in clinical practice. Gene therapy targeting the etiology of AIP may become a new trend in the treatment of rare diseases in the future.
-
Key words:
- Porphyria, Acute Intermittent /
- Therapeutics /
- Givosiran
-
[1] BISSELL DM, ANDERSON KE, BONKOVSKY HL. Porphyria[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(9): 862-872. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1608634. [2] BONKOVSKY HL, MADDUKURI VC, YAZICI C, et al. Acute porphyrias in the USA: Features of 108 subjects from porphyrias consortium[J]. Am J Med, 2014, 127(12): 1233-1241. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.06.036. [3] CHEN Y, LI XQ. An excerpt of acute hepatic porphyrias: Recommendations for evaluation and long term management of the NCATS Rare Diseases Clinical lksearch Network[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(11): 2083-2086. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.11.006.陈洋, 李晓青. 《2017年美国推进转化科学中心罕见疾病临床研究网络卟啉病联合会: 急性肝卟啉病的评估和长期管理建议》摘译[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(11): 2083-2086. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.11.006. [4] FONTANELLAS A, ÁVILA MA, ANDERSON KE, et al. Current and innovative emerging therapies for porphyrias with hepatic involvement[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(2): 422-433. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.05.003. [5] WANG B, RUDNICK S, CENGIA B, et al. Acute hepatic porphyrias: Review and recent progress[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2019, 3(2): 193-206. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1297. [6] GOMÁ-GARCÉS E, PÉREZ-GÓMEZ MV, ORTÍZ A. Givosiran for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(20): 1989. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMc2026458. [7] BUNG N, ROY A, PRIYAKUMAR UD, et al. Computational modeling of the catalytic mechanism of hydroxymethylbilane synthase[J]. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2019, 21(15): 7932-7940. DOI: 10.1039/c9cp00196d. [8] RAMANUJAM VS, ANDERSON KE. Porphyria diagnostics-part 1: A brief overview of the porphyrias[J]. Curr Protoc Hum Genet, 2015, 86: 17.20.1-17.20.26. DOI: 10.1002/0471142905.hg1720s86. [9] BALWANI M, WANG B, ANDERSON KE, et al. Acute hepatic porphyrias: Recommendations for evaluation and long-term management[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1314-1322. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29313. [10] BISSELL DM, LAI JC, MEISTER RK, et al. Role of delta-aminolevulinic acid in the symptoms of acute porphyria[J]. Am J Med, 2015, 128(3): 313-317. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.10.026. [11] OLIVERI LM, DAVIO C, BATLLE AM, et al. ALAS1 gene expression is down-regulated by Akt-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of FOXO1 by vanadate in diabetic mice[J]. Biochem J, 2012, 442(2): 303-310. DOI: 10.1042/BJ20111005. [12] ANDERSON KE. Acute hepatic porphyrias: Current diagnosis & management[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2019, 128(3): 219-227. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2019.07.002. [13] SCASSA ME, VARONE CL, MONTERO L, et al. Insulin inhibits delta-aminolevulinate synthase gene expression in rat hepatocytes and human hepatoma cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 1998, 244(2): 460-469. DOI: 10.1006/excr.1998.4206. [14] FONTANELLAS A, ÁVILA MA, BERRAONDO P. Emerging therapies for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Expert Rev Mol Med, 2016, 18: e17. DOI: 10.1017/erm.2016.18. [15] ZHANG J, HU Y, ZHENG J, et al. Treatment of acute intermittent porphyria during pregnancy and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after delivery: A case report[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(6): 5554-5556. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.5212. [16] YARRA P, FAUST D, BENNETT M, et al. Benefits of prophylactic heme therapy in severe acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Mol Genet Metab Rep, 2019, 19: 100450. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.01.002. [17] BLAYLOCK B, EPSTEIN J, STICKLER P. Real-world annualized healthcare utilization and expenditures among insured US patients with acute intermittent porphyria (AIP) treated with hemin[J]. J Med Econ, 2020, 23(6): 537-545. DOI: 10.1080/13696998.2020.1724118. [18] WILLANDT B, LANGENDONK JG, BIERMANN K, et al. Liver fibrosis associated with iron accumulation due to long-term heme-arginate treatment in acute intermittent porphyria: A case series[J]. JIMD Rep, 2016, 25: 77-81. DOI: 10.1007/8904_2015_458. [19] SCHMITT C, LENGLET H, YU A, et al. Recurrent attacks of acute hepatic porphyria: Major role of the chronic inflammatory response in the liver[J]. J Intern Med, 2018, 284(1): 78-91. DOI: 10.1111/joim.12750. [20] PISCHIK E, KAUPPINEN R. An update of clinical management of acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Appl Clin Genet, 2015, 8: 201-214. DOI: 10.2147/TACG.S48605. [21] Study Group of Red Blood Cell Disease (Anemia), Chinese Society of Hematology, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of porphyria in China(2020)[J]. Natl Med J China, 2020, 100(14): 1051-1056. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200219-00349.中华医学会血液学分会红细胞疾病(贫血)学组. 中国卟啉病诊治专家共识(2020年)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2020, 100(14): 1051-1056. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200219-00349. [22] CARDENAS JL, GUERRERO C. Acute intermittent porphyria: General aspects with focus on pain[J]. Curr Med Res Opin, 2018, 34(7): 1309-1315. DOI: 10.1080/03007995.2018.1435521. [23] GONZALEZ-MOSQUERA LF, SONTHALIA S. Acute Intermittent Porphyria[A]. Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [24] GOUYA L, VENTURA P, BALWANI M, et al. EXPLORE: A prospective, multinational, natural history study of patients with acute hepatic porphyria with recurrent attacks[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(5): 1546-1558. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30936. [25] SCHULENBURG-BRAND D, GARDINER T, GUPPY S, et al. An audit of the use of gonadorelin analogues to prevent recurrent acute symptoms in patients with acute porphyria in the United Kingdom[J]. JIMD Rep, 2017, 36: 99-107. DOI: 10.1007/8904_2017_2. [26] MARSDEN JT, GUPPY S, STEIN P, et al. Audit of the use of regular haem arginate infusions in patients with acute porphyria to prevent recurrent symptoms[J]. JIMD Rep, 2015, 22: 57-65. DOI: 10.1007/8904_2015_411. [27] SINGAL AK, PARKER C, BOWDEN C, et al. Liver transplantation in the management of porphyria[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60(3): 1082-1089. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27086. [28] LISSING M, NOWAK G, ADAM R, et al. Liver transplantation for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Liver Transpl, 2021, 27(4): 491-501. DOI: 10.1002/lt.25959. [29] D'AVOLA D, LÓPEZ-FRANCO E, SANGRO B, et al. Phase I open label liver-directed gene therapy clinical trial for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 65(4): 776-783. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.05.012. [30] NAULT JC, DATTA S, IMBEAUD S, et al. Recurrent AAV2-related insertional mutagenesis in human hepatocellular carcinomas[J]. Nat Genet, 2015, 47(10): 1187-1193. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3389. [31] SERRANO-MENDIOROZ I, SAMPEDRO A, SERNA N, et al. Bioengineered PBGD variant improves the therapeutic index of gene therapy vectors for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2018, 27(21): 3688-3696. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy283. [32] SERRANO-MENDIOROZ I, SAMPEDRO A, ALEGRE M, et al. An Inducible Promoter responsive to different porphyrinogenic stimuli improves gene therapy vectors for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2018, 29(4): 480-491. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2017.056. [33] JIANG L, BERRAONDO P, JERICÓ D, et al. Systemic messenger RNA as an etiological treatment for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Nat Med, 2018, 24(12): 1899-1909. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-018-0199-z. [34] PARRA-GUILLEN ZP, FONTANELLAS A, JIANG L, et al. Disease pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling in acute intermittent porphyria to support the development of mRNA-based therapies[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2020, 177(14): 3168-3182. DOI: 10.1111/bph.15040. [35] de PAULA BRANDÃO PR, TITZE-DE-ALMEIDA SS, TITZE-DE-ALMEIDA R. Leading RNA interference therapeutics part 2: Silencing delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase 1, with a focus on givosiran[J]. Mol Diagn Ther, 2020, 24(1): 61-68. DOI: 10.1007/s40291-019-00438-6. [36] SARDH E, HARPER P, BALWANI M, et al. Phase 1 trial of an RNA interference therapy for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(6): 549-558. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807838. [37] SCOTT LJ. Givosiran: First approval[J]. Drugs, 2020, 80(3): 335-339. DOI: 10.1007/s40265-020-01269-0. [38] BALWANI M, SARDH E, VENTURA P, et al. Phase 3 trial of RNAi therapeutic givosiran for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 382(24): 2289-2301. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1913147. [39] AGARWAL S, SIMON AR, GOEL V, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the small interfering ribonucleic acid, givosiran, in patients with acute hepatic porphyria[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 108(1): 63-72. DOI: 10.1002/cpt.1802. [40] RAY K. Interfering with acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(8): 452. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-0335-3. [41] BUSTAD HJ, TOSKA K, SCHMITT C, et al. A pharmacological chaperone therapy for acute intermittent porphyria[J]. Mol Ther, 2020, 28(2): 677-689. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.11.010. -



 PDF下载 ( 2834 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2834 KB)

 下载:
下载:


