五种肝硬化无创诊断方法对代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化患者中医证型的诊断价值分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.01.016
Value of five noninvasive diagnostic methods for liver cirrhosis in diagnosis of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types in patients with compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨5种肝硬化无创诊断[FibroScan肝脏硬度值(LSM值)、AST和PLT比值指数(APRI)、肝纤维化4因子指数(FIB-4)、GGT-PLT比值(GPR)、红细胞体积分布宽度-PLT比值(RPR)]在乙型肝炎肝硬化代偿期中与中医证型的相关性。 方法 回顾性分析2017年1月—2020年1月河南中医药大学第一附属医院确诊为乙型肝炎肝硬化代偿期的327例患者临床相关资料,分为肝郁脾虚证(n=160)、肝胆湿热证(n=84)、肝肾阴虚证(n=13)、脾肾阳虚证(n=5)、瘀血阻络证(n=65),采集临床相关资料以及血常规、肝功能、LSM值、肝胆脾胰彩超等信息,并对患者进行中医辨证分型,建立APRI、FIB-4、GPR、RPR模型。符合正态分布的计量资料多组间均数比较用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t法;不符合正态分布的计量资料多组间比较用多个独立样本Kruskal-Wallis H秩和检验,采用Kruskal-Wallis单因素ANOVE(k样本)进行多重比较;采用二元logistic回归分析进行进中医证型与肝硬化无创诊断的关系;使用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)评价5种肝硬化无创诊断方法预测乙型肝炎肝硬化代偿期中医证型的诊断能力。 结果 logistic回归分析结果显示,在肝胆湿热证中,AST(OR=1.981,95%CI:1.8225~2.139,P<0.05)、LSM(OR=2.002,95%CI:1.840~2.160,P<0.05)是代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化的影响因素;在肝郁脾虚证中,门静脉宽度(OR=4.402,95%CI:4.050~4.754,P<0.05)、LSM值(OR=3.901,95%CI:3.589~4.213,P<0.05]、APRI[OR=1.891,95%CI:1.740~2.042,P<0.05]、FIB-4(OR=1.845,95% CI:1.697~1.993,P<0.05)是代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化的影响因素;在瘀血阻络证中,LSM值(OR=2.465,95%CI:2.268~ 2.662, P<0.05]、APRI(OR=1.298,95%CI:1.194~1.402, P<0.05)、FIB-4(OR=1.849,95%CI:1.701~1.997, P<0.05)是代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化的影响因素;ROC曲线显示,LSM值与RPR模型评估肝胆湿热证的诊断价值明显优于其他诊断方法;LSM值与FIB-4模型评估肝郁脾虚证的诊断价值明显优于其他诊断方法;5种无创诊断方法均能较好地评估瘀血阻络证。 结论 5种无创诊断方法可对不同证型具有不同评估优势,对乙型肝炎肝硬化代偿期患者中医证型诊断提供参考价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the association of five noninvasive diagnostic methods for liver cirrhosis, i.e., liver stiffness measurement (LSM) on FibroScan, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index (APRI), fibrosis-4 (FIB-4), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-to-platelet ratio (GPR), and red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio (RPR), with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome types in patients with compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 327 patients who were diagnosed with compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis in The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine from January 2017 to January 2020, and based on their TCM syndrome type, they were divided into liver depression and spleen deficiency group with 160 patients, liver-gallbladder damp-heat syndrome group with 84 patients, liver-kidney Yin deficiency group with 13 patients, spleen-kidney Yang deficiency group with 5 patients, and blood stasis obstructing the collaterals group with 65 patients. Related data were collected, including clinical data, routine blood test results, liver function, LSM, and color Doppler ultrasound findings of liver, gallbladder, spleen, and pancreas. TCM syndrome differentiation was performed, and the models of APRI, FIB-4, GPR, and RPR were established. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups; the multiple independent samples Kruskal-Wallis H rank sum test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between multiple groups, and the one- way Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA (k-sample) was used for multiple comparison; the binary logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the association between TCM syndrome types and non-invasive diagnosis of liver cirrhosis; the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the diagnostic capability of five noninvasive methods for predicting TCM syndrome type in compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis. Results The logistic regression analysis showed that in the liver-gallbladder damp-heat syndrome group, aspartate aminotransferase OR=1.981, 95%CI: 1.8225-2.139, P < 0.05), and LSM (OR=2.002, 95%CI: 1.840-2.160, P < 0.05) were influencing factors for compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis; in the liver depression and spleen deficiency group, portal vein width (OR=4.402, 95%CI: 4.050-4.754, P < 0.05), LSM (OR=3.901, 95%CI: 3.589-4.213, P < 0.05), APRI (OR=1.891, 95%CI: 1.740-2.042, P < 0.05), and FIB-4 (OR=1.845, 95%CI: 1.697-1.993, P < 0.05) were influencing factors for compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis; in the blood stasis obstructing the collaterals group, LSM (OR=2.465, 95%CI: 2.268-2.662, P < 0.05), APRI (OR=1.298, 95%CI: 1.194-1.402, P < 0.05), and FIB-4 (OR=1.849, 95%CI: 1.701-1.997, P < 0.05) were influencing factors for compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis. The ROC curve analysis showed that LSM and RPR had a significantly better diagnostic value than the other methods in evaluating liver-gallbladder damp-heat syndrome, and LSM and FIB-4 had a significantly better diagnostic value than the other methods in evaluating liver depression and spleen deficiency; all five noninvasive diagnostic methods had a good value in evaluating the syndrome of blood stasis obstructing the collaterals. Conclusion The five noninvasive diagnostic methods have their own advantages in evaluating different syndrome types, which provide a reference for the diagnosis of TCM syndrome types in patients with compensated hepatitis B cirrhosis. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Hepatitis B /
- TCM syndrome /
- Diagnosis
-
表 1 中医证型分布情况
证型 例数 性别 年龄(岁) 男(例) 女(例) 肝郁脾虚证 160 120 40 42.96±10.74 肝胆湿热证 84 60 24 43.17±11.12 肝肾阴虚证 13 8 5 45.46±10.41 脾肾阳虚证 5 4 1 46.60±9.74 瘀血阻络证 65 46 19 47.80±10.92 统计值 χ2=1.569 F=2.451 P值 0.814 0.056 表 2 代偿期乙型肝炎肝硬化患者主要中医证型基线资料比较
相关指标 肝郁脾虚证(n=160) 肝胆湿热证(n=84) 瘀血阻络证(n=65) 统计量 P值 PLT(×109/L) 138.00(85.25~177.25) 110.50(92.25~142.75) 44.00(34.00~55.50)1)2) χ2=155.337 <0.05 ALT(U/L) 34.00(21.95~43.63) 68.85(48.75~109.43)1) 29.50(17.95~39.75)2) χ2=123.210 <0.05 AST(U/L) 28.95(23.60~39.63) 61.40(40.15~94.03)1) 27.60(21.55~38.05)2) χ2=86.659 <0.05 Alb(g/L) 44.97±3.13 46.25±3.331) 31.41±2.461)2) F=542.512 <0.05 GLB(g/L) 29.04±4.46 28.76±4.71 29.09±4.62 F=0.128 0.88 GGT(U/L) 31.20(20.83~53.13) 39.10(27.33~65.15)1) 27.70(21.70~44.05)2) χ2=13.079 <0.05 门静脉主干宽度(mm) 12.79±0.76 12.18±0.991) 13.40±0.581)2) F=43.373 <0.05 LSM值(kPa) 16.00(13.40~18.08) 18.65(16.63~25.00)1) 24.40(22.30~26.50)1)2) χ2=131.312 <0.05 APRI 1.10(0.62~1.35) 1.30(0.88~2.00)1) 1.55(1.26~2.31)1) χ2=54.280 <0.05 FIB-4 1.90(1.38~2.74) 2.66(1.99~3.54)1) 6.19(4.66~8.37)1)2) χ2=129.893 <0.05 GPR 0.67(0.27~1.18) 0.81(0.49~1.27)1) 1.52(0.94~2.46)1)2) χ2=57.485 <0.05 RPR 0.37±0.16 0.39±0.10 1.10±0.341)2) F=351.219 <0.05 注:与肝郁脾虚证相比,1)P<0.05;与肝胆湿热证相比, 2)P<0.05。 表 3 各无创诊断评估肝郁脾虚证比较
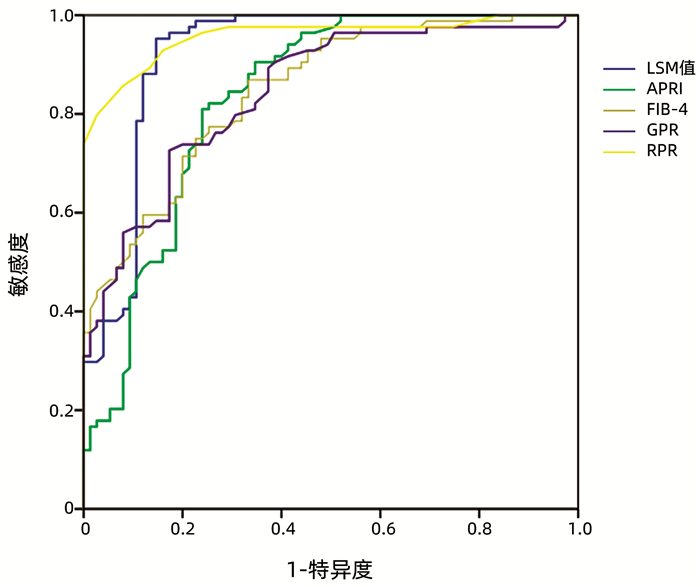
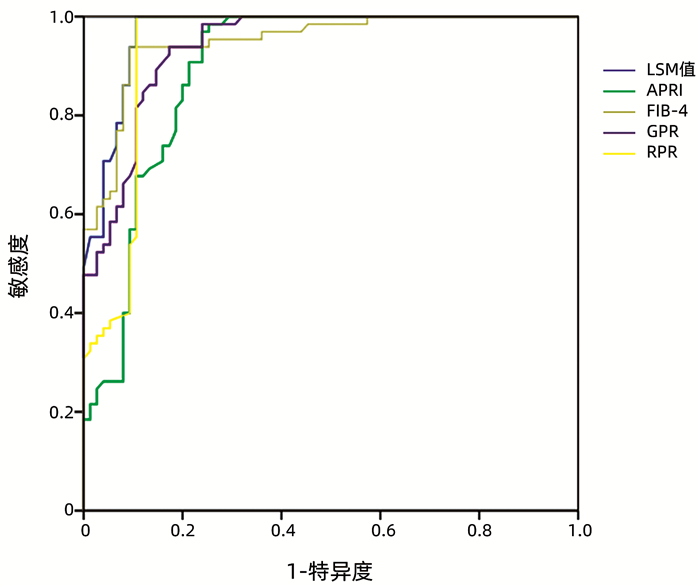
无创诊断方法 AUC(95%CI) cut-off值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 阳性似然比 阴性似然比 LSM值 0.982(0.955~0.995) 0.875 98.12 89.33 95.2 95.7 9.20 0.02 APRI 0.899(0.853~0.934) 0.629 86.87 76.00 88.5 73.1 3.62 0.17 FIB-4 0.950(0.913~0.974) 0.776 85.62 92.00 95.8 75.0 10.70 0.16 GPR 0.618(0.553~0.680) 0.303 55.63 74.67 82.4 44.1 2.20 0.59 RPR 0.752(0.692~0.806) 0.533 61.25 92.00 94.2 52.7 7.66 0.42 表 4 各无创诊断评估肝胆湿热证比较
无创诊断方法 AUC(95%CI) cut-off值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 阳性似然比 阴性似然比 LSM值 0.922(0.868~0.958) 0.806 95.24 85.33 87.9 94.1 6.49 0.06 APRI 0.834(0.767~0.888) 0.570 80.95 76.00 79.1 78.1 3.37 0.25 FIB-4 0.848(0.783~0.900) 0.536 86.90 66.67 74.5 82.0 2.61 2.61 GPR 0.844(0.778~0.896) 0.553 72.62 82.67 82.4 72.9 4.19 0.33 RPR 0.958(0.914~0.983) 0.777 85.71 92.00 92.3 85.2 10.71 0.16 表 5 各无创诊断评估瘀血阻络证比较
无创诊断方法 AUC(95%CI) cut-off值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 阳性似然比 阴性似然比 LSM值 0.969(0.925~0.991) 0.893 100.00 89.33 89.0 100.0 9.37 0.00 APRI 0.895(0.831~0.940) 0.731 98.46 74.67 77.1 98.2 3.89 0.02 FIB-4 0.949(0.899~0.979) 0.845 93.85 90.67 89.7 94.4 10.05 0.07 GPR 0.941(0.888~0.973) 0.765 93.85 82.67 82.4 93.9 5.41 0.07 RPR 0.935(0.880~0.969) 0.893 100.00 89.33 89.0 100.0 9.37 0.00 -
[1] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [2] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. The guidelines of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007.中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2648-2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. [3] FATTOVICH G, BORTOLOTTI F, DONATO F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(2): 335-352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.011. [4] XU LM, LIU P, SHEN XZ, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis in integrative medicine practice(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007.徐列明, 刘平, 沈锡中, 等. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007. [5] LIU CH, WEI BH, YAO SK. Consensus statements on the integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine diagnosis and treatment of liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Integr Trad West Med Dig, 2011, 19(4): 277-279. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2011.04.025.刘成海, 危北海, 姚树坤. 肝硬化中西医结合诊疗共识[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2011, 19(4): 277-279. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2011.04.025. [6] DONG XQ, WU Z, ZHAO H, et al. Evaluation and comparison of thirty noninvasive models for diagnosing liver fibrosis in chinese hepatitis B patients[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2019, 26(2): 297-307. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13031. [7] SONNEVELD MJ, BROUWER WP, CHAN HL, et al. Optimisation of the use of APRI and FIB-4 to rule out cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results from the SONIC-B study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(7): 538-544. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30087-1. [8] LEMOINE M, SHIMAKAWA Y, NAYAGAM S, et al. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio (GPR) predicts significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(8): 1369-1376. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309260. [9] CHEN YP, HU XM, LIANG XE, et al. Stepwise application of fibrosis index based on four factors, red cell distribution width-platelet ratio, and aspartate aminotransferase-platelet ratio for compensated hepatitis B fibrosis detection[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(1): 256-263. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13811. [10] LI ZH, ZHANG XL, GUO YQ, et al. Effect of Anluohuaxian Pills combined with Entecavir in the treatment of hepatitis B cirrhosis and its influence on liver function[J]. China Med Herald, 2020, 558(28): 151-154.李朝晖, 张晓龙, 郭彦清, 等. 安络化纤丸联合恩替卡韦治疗乙肝肝硬化的效果及对肝功能的影响[J]. 中国医药导报, 2020, 558(28): 151-154. [11] YE YAN, LIU RJ, YANG XZ, et al. Literature study on chracteristics of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome types and syndrome elements distribution of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocirrhosis[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 61(4): 346-350. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2020.04.016.叶永安, 刘蕊洁, 杨先照, 等. 乙型肝炎肝硬化中医证型、证素分布特点文献研究[J]. 中医杂志, 2020, 61(4): 346-350. DOI: 10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2020.04.016. [12] JIN TY, LIU W. Research progress on the correlation between TCM syndromes and biological indicators of cirrhosis in recent 10 years[J]. Global Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 13(1): 163-168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2020.01.043.靳天怡, 刘汶. 肝硬化中医证型与生物学指标相关性近10年研究进展[J]. 环球中医药, 2020, 13(1): 163-168. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1749.2020.01.043. [13] WANG Y, WANG M, ZHANG GH, et al. Clinical diagnosis, staging, and therapeutic principles of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 17-21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.004.王宇, 王民, 张冠华, 等. 肝硬化的诊断、分期及治疗原则[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 17-21. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.004. [14] LIAO W, SHI L, LIU BY, et al. Diagnostic value of ultrasonic contrast and virtual touch tissues quantification on liver cirrhosis[J/CD]. Chin J Liver Dis (Electronic Version), 2020, 12(2): 25-30. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2020.02.005.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2020.02.005.廖卫, 石莉, 刘秉彦, 等. 超声造影与声触诊组织量化技术在肝硬化诊断中的价值[J/CD]. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2020, 12(2): 25-30. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2020.02.005. [15] KIM WR, BERG T, ASSELAH T, et al. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(4): 773-780. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.012. [16] SONNEVELD MJ, BROUWER WP, CHAN HL, et al. Optimisation of the use of APRI and FIB-4 to rule out cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Results from the SONIC-B study[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 4(7): 538-544. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30087-1. [17] LEMOINE M, SHIMAKAWA Y, NAYAGAM S, et al. The gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase to platelet ratio (GPR) predicts significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic HBV infection in West Africa[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(8): 1369-1376. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309260. [18] DING YY, WANG HJ, LIAO SP, et al. Value of red blood cell distribution width-to-platelet ratio in diagnosing and predicting the severity of hepatitis B liver fibrosis[J]. Chin J Lab Med, 2017, 40(7): 532-534. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2017.07.012.丁予昀, 王海军, 廖昭平, 等. RPR在乙型肝炎性肝纤维化诊断和预测严重程度中应用价值的评价[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2017, 40(7): 532-534. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-9158.2017.07.012. [19] European Association for Study of Liver; Asociacion Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Higado. EASL-ALEH clinical practice guidelines: Non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease severity and prognosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(1): 237-264. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.006. [20] SHI RY, ZHEN Z, CHEN YP, et al. Value of FibroScan, aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index, and fibrosis-4 in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2018, 38(23): 5719- 5721. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.23.034.石荣亚, 甄真, 陈宇萍, 等. FibroScan、APRI、FIB-4对肝纤维化及肝硬化的诊断价值[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(23): 5719-5721. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.23.034. [21] XU FM, SHENG QS. Research advances in serum markers and transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(3): 618-622. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.040.许峰铭, 盛庆寿. 血清标志物与瞬时弹性成像技术评估肝纤维化的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(3): 618-622. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.040. [22] LU Q, LU C, LI J, et al. Stiffness value and serum biomarkers in liver fibrosis staging: Study in large surgical specimens in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Radiology, 2016, 280(1): 290-299. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2016151229. [23] AN HJ, GENG H, GE ZS, et al. Value of transient elastography combined with serological indexes in diagnosis of liver fibrosis and assessment of prognosis of patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Nosocomiol, 2020, 30(22): 3443-3447. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ni.2020-200197.安红杰, 耿华, 葛志胜, 等. 瞬时弹性成像技术在慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化诊断及预后评估中的价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2020, 30(22): 3443-3447. DOI: 10.11816/cn.ni.2020-200197. [24] XU FM, SHENG QS. Research advances in serum markers and transient elastography in the evaluation of liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(3): 618-622. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.040.许峰铭, 盛庆寿. 血清标志物与瞬时弹性成像技术评估肝纤维化的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(3): 618-622. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.03.040. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 赵远红,陈茂艳,杨瑞雪,吕强. 隐源性肝癌与病毒性肝癌临床特征比较. 中西医结合肝病杂志. 2020(02): 107-110 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 赵远红,吕强,杨瑞雪,陈茂艳. 14例病理诊断明确的隐源性肝癌临床资料分析. 中医肿瘤学杂志. 2020(02): 19-23+38 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 张杨,孙立哲,刘宝刚,耿翠翠,董妙,李磊强,李欣. 颅内血管外皮细胞瘤MRI影像学特征与ki67因子表达相关性研究. 临床军医杂志. 2017(12): 1267-1269 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2578 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2578 KB)


 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

