Why do patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection develop hepatocellular carcinoma after HBsAg seroclearance?
-
Abstract: This article summarizes the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection after HBsAg seroclearance, as well as its mechanism and implications.
-
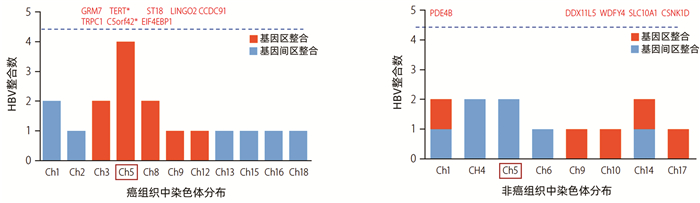
图 2 在癌和非癌组织中HBV整合位点分布(根据参考文献[16]绘制)
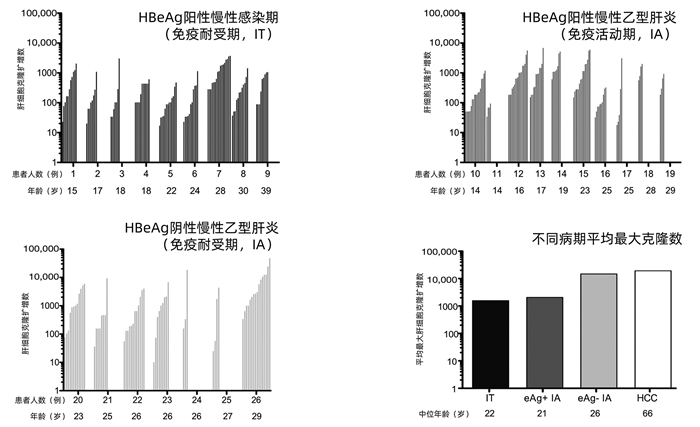
图 3 慢性HBV感染不同病期肝细胞克隆扩增数比较(根据参考文献[19]绘制)
图 4 HBeAg阳性和阴性黑猩猩的肝细胞内HBV cccDNA与整合的HBV DNA分布(根据参考文献[21]绘制)
-
[1] HUO TI, WU JC, LEE PC, et al. Sero-clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen in chronic carriers does not necessarily imply a good prognosis[J]. Hepatology, 1998, 28(1): 231-236. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510280130. [2] CHEN YC, SHEEN IS, CHU CM, et al. Prognosis following spontaneous HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients with or without concurrent infection[J]. Gastroenterology, 2002, 123(4): 1084-1089. DOI: 10.1053/gast.2002.36026. [3] YUEN MF, WONG DK, FUNG J, et al. HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B in Asian patients: Replicative level and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 135(4): 1192-1199. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.008. [4] KIM JH, LEE YS, LEE HJ, et al. HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B: Implications for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2011, 45(1): 64-68. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181dd558c. [5] PARK Y, LEE JH, SINN DH, et al. Risk and risk score performance of hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2021, 12(1): e00290. DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000290. [6] MOUCARI R, KOREVAAR A, LADA O, et al. High rates of HBsAg seroconversion in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients responding to interferon: A long-term follow-up study[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 50(6): 1084-1092. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.01.016. [7] FATTOVICH G, GIUSTINA G, SANCHEZ-TAPIAS J, et al. Delayed clearance of serum HBsAg in compensated cirrhosis B: Relation to interferon alpha therapy and disease prognosis. European Concerted Action on Viral Hepatitis (EUROHEP)[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 1998, 93(6): 896-900. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00272.x. [8] ARASE Y, IKEDA K, SUZUKI F, et al. Long-term outcome after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Am J Med, 2006, 119(1): 71. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2005.02.033. [9] LIU F, WANG XW, CHEN L, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43(12): 1253-1261. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13634. [10] KUANG XJ, JIA RR, HUO RR, et al. Systematic review of risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2018, 25(9): 1026-1037. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12905. [11] SONG A, WANG X, LU J, et al. Durability of hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance and subsequent risk for hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2021, 28(4): 601-612. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13471. [12] KIM GA, LEE HC, KIM MJ, et al. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma after HBsAg seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B patients: A need for surveillance[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(5): 1092-1099. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.031. [13] GOUNDER PP, BULKOW LR, SNOWBALL M, et al. Nested case-control study: Hepatocellular carcinoma risk after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 43(11): 1197-1207. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13621. [14] SIMONETTI J, BULKOW L, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(5): 1531-1537. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23464. [15] PARK YM, LEE SG. Clinical features of HBsAg seroclearance in hepatitis B virus carriers in South Korea: A retrospective longitudinal study[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(44): 9836-9843. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i44.9836. [16] JANG JW, KIM JS, KIM HS, et al. Persistence of intrahepatic hepatitis B virus DNA integration in patients developing hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2021, 27(1): 207-218. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0115. [17] BONILLA GUERRERO R, ROBERTS LR. The role of hepatitis B virus integrations in the pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2005, 42(5): 760-777. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2005.02.005. [18] BUDZINSKA MA, SHACKEL NA, URBAN S, et al. Cellular genomic sites of hepatitis B virus DNA integration[J]. Genes (Basel), 2018, 9(7): 365. DOI: 10.3390/genes9070365. [19] MASON WS, GILL US, LITWIN S, et al. HBV DNA integration and clonal hepatocyte expansion in chronic hepatitis B patients considered immune tolerant[J]. Gastroenterology, 2016, 151(5): 986-998. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.012. [20] YANG W, SUMMERS J. Integration of hepadnavirus DNA in infected liver: Evidence for a linear precursor[J]. J Virol, 1999, 73(12): 9710-9717. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.12.9710-9717.1999. [21] WOODDELL CI, YUEN MF, CHAN HL, et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(409): eaan0241. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aan0241. -



 PDF下载 ( 3098 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3098 KB)


 下载:
下载: