2例关节挛缩-肾功能不全-胆汁淤积综合征患儿的临床特征及遗传学分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.029
Clinical features and genetic analysis of two children with arthrogryposis, renal insufficiency, and cholestasis syndrome
-
-
Key words:
- Cholestasis, Intrahepatic /
- Arthrogryposis /
- Renal Insufficiency /
- Signs and Symptoms /
- Genetic Testing
-
表 1 2例ARC综合征患儿入院后初次肝功能指标检查结果
患儿 TBil (μmol/L) DBil (μmol/L) 总蛋白(g/L) 白蛋白(g/L) ALT (U/L) AST (U/L) 总胆汁酸(μmol/L) GGT (U/L) 病例1 163.7 129.4 55.8 32.6 70.3 86.7 97.3 25.0 病例2 225.8 147.7 46.7 32.3 135.2 134.8 68.3 23.5 正常值 3.4~17 0~6 55~80 35~55 0~40 0~40 0~9.67 0~50 表 2 2例ARC综合征患儿基因检测结果
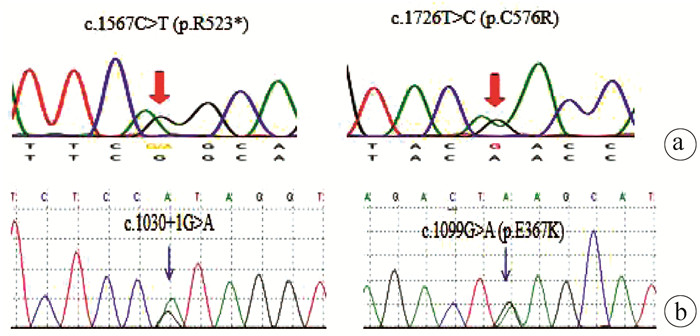
患儿 染色体位置 核苷酸改变 氨基酸改变 状态 来源 文献报道 变异类型 病例1 chr15∶91543734 c.1567C>T p.R523* 杂合 母亲 有 无义突变 病例1 chr15∶91542955 c.1726T>C p.C576R 杂合 新发 有 错义突变 病例2 chr15∶91548923 c.1030+1G>A - 杂合 母亲 无 剪切位点 病例2 chr15∶91548616 c.1099G>A p.E367K 杂合 父亲 无 错义突变 -
[1] FAWAZ R, BAUMANN U, EKONG U, et al. Guideline for the evaluation of cholestatic jaundice in infants: Joint Recommendations of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2017, 64(1): 154-168. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001334. [2] LI AQ, DONG Y, XU ZQ, et al. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3: A report of two cases in one pedigree[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(7): 1601-1604. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.032.李爱芹, 董漪, 徐志强, 等. 进行性家族性肝内胆汁淤积症3型一家系2例报告[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(7): 1601-1604. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.07.032. [3] QIU YL, LIU T, ABUDUXIKUER K, et al. Novel missense mutation in VPS33B is associated with isolated low gamma-glutamyltransferase cholestasis: Attenuated, incomplete phenotype of arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction, and cholestasis syndrome[J]. Hum Mutat, 2019, 40(12): 2247-2257. DOI: 10.1002/humu.23770. [4] BRETSCHER-DUTOIT C. Familial bile duct malformations associated with tubular renal insufficiency: A.R. Lutz-Richner and R. F. Landolt. Helv. Paediatr. Acta 28: 1-12 (March), 1973[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 1974, 9(4): 577. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-3468(74)80079-5. [5] HUANG DG, LIU JJ, GUO L, et al. Clinical features and VPS33B mutations in a family affected by arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction, and cholestasis syndrome[J]. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2017, 19(10): 1077-1082. DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.10.009.黄大桂, 刘佳佳, 郭丽, 等. 关节挛缩、肾功能不全和胆汁淤积综合征一家系临床特点及VPS33B基因突变分析[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2017, 19(10): 1077-1082. DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2017.10.009. [6] RICHARDS S, AZIZ N, BALE S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology[J]. Genet Med, 2015, 17(5): 405-424. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. [7] RIGGS ER, ANDERSEN EF, CHERRY AM, et al. Technical standards for the interpretation and reporting of constitutional copy-number variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen)[J]. Genet Med, 2020, 22(2): 245-257. DOI: 10.1038/s41436-019-0686-8. [8] SMITH H, GALMES R, GOGOLINA E, et al. Associations among genotype, clinical phenotype, and intracellular localization of trafficking proteins in ARC syndrome[J]. Hum Mutat, 2012, 33(12): 1656-1664. DOI: 10.1002/humu.22155. [9] FU K, WANG C, GAO Y, et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics reveal the effect of hepatic Vps33b deficiency on bile acids and lipids metabolism[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 276. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00276. [10] GISSEN P, JOHNSON CA, MORGAN NV, et al. Mutations in VPS33B, encoding a regulator of SNARE-dependent membrane fusion, cause arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis (ARC) syndrome[J]. Nat Genet, 2004, 36(4): 400-404. DOI: 10.1038/ng1325. [11] WANG JS, ZHAO J, LI LT. ARC syndrome with high GGT cholestasis caused by VPS33B mutations[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(16): 4830-4834. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4830. [12] DUONG MD, ROSE CM, REIDY KJ, et al. An uncommon case of arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction, and cholestasis (ARC) syndrome and review of the renal involvement: Answers[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2020, 35(2): 249-251. DOI: 10.1007/s00467-019-04338-z. [13] LEE MJ, SUH CR, SHIN JH, et al. A novel VPS33B variant identified by exome sequencing in a patient with arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis syndrome[J]. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr, 2019, 22(6): 581-587. DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2019.22.6.581. [14] GISSEN P, TEE L, JOHNSON CA, et al. Clinical and molecular genetic features of ARC syndrome[J]. Hum Genet, 2006, 120(3): 396-409. DOI: 10.1007/s00439-006-0232-z. [15] AGAKIDOU E, AGAKIDIS C, KAMBOURIS M, et al. A novel mutation of VPS33B gene associated with incomplete arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis phenotype[J]. Case Rep Genet, 2020, 2020: 8872294. DOI: 10.1155/2020/8872294. [16] ROSALES A, MHIBIK M, GISSEN P, et al. Severe renal Fanconi and management strategies in arthrogryposis-renal dysfunction-cholestasis syndrome: A case report[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2018, 19(1): 144. DOI: 10.1186/s12882-018-0926-1. [17] FOKKEMA IF, TASCHNER PE, SCHAAFSMA GC, et al. LOVD v. 2.0: The next generation in gene variant databases[J]. Hum Mutat, 2011, 32(5): 557-563. DOI: 10.1002/humu.21438. [18] LI LT, ZHAO J, CHEN R, et al. Two novel VPS33B mutations in a patient with arthrogryposis, renal dysfunction and cholestasis syndrome in mainland China[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(1): 326-329. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.326. [19] DEL BRÍO CASTILLO R, SQUIRES JE, MCKIERNAN PJ. A novel mutation in VPS33B gene causing a milder ARC syndrome phenotype with prolonged survival[J]. JIMD Rep, 2019, 47(1): 4-8. DOI: 10.1002/jmd2.12027. -



 PDF下载 ( 2204 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2204 KB)

 下载:
下载:


