以慢加急性肝衰竭起病的自身免疫性肝炎1例报告
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.025
-
-
Key words:
- Liver Failure /
- Hepatitis, Autoimmune /
- Diagnosis
-
表 1 AIH综合诊断积分系统(1999年)评估此例患者积分
参数/临床特征 结果 实际积分 性别 女性 +2 ALP(ULN倍数):AST
(或ALT)(ULN倍数)0.297 +2 血清IgG∶正常值 2.1 +3 ANA、SMA或LKM-1滴度 ANA+(1∶100颗粒型) +1 AMA 阴性 0 肝炎标志物 阴性 +3 药物史 阴性 +1 平均乙醇摄入量 <25 g/d +2 肝脏组织学检查 未进行 0 其他免疫性疾病 抗SSA抗体(+);
抗Ro-52抗体(+)+2 其他可用参数 无 0 其他特异性自身抗体(SLA/LP、LC-1、
ASGPR、pANCA)阳性 +2 HLA-DR3或DR4 无 总计 - 16 注:此表反应该患者治疗前水平。AIH综合诊断积分系统(1999年)诊断标准(治疗前):明确的AIH,≥16分; 可能的AIH,10~15分; 治疗后:明确的AIH,≥18分; 可能的AIH,12~17分。ULN,正常值上限。 表 2 AIH简化诊断标准评估该患者积分
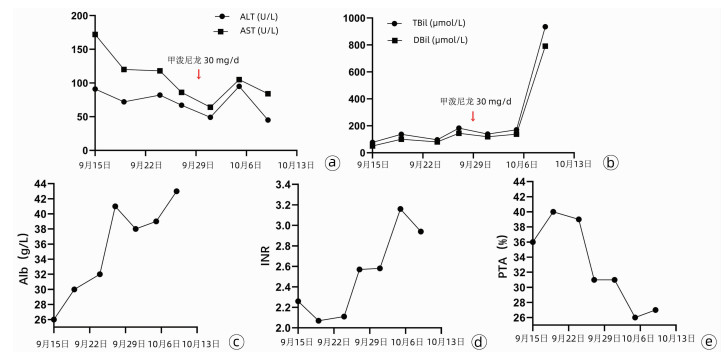
变量 结果 分值 ANA或ASMA ANA阳性(1∶100颗粒型) 1 LKM-1 阴性 0 SLA阳性 阴性 0 IgG 2.1 2 肝组织学 未做 0 排除病毒性肝炎 阴性 2 总计 - 5 注:AIH可能,6分; 确诊AIH,≥7分。 表 3 激素治疗前后肝酶、胆红素及凝血功能变化
时间 体温(℃) WBC
(×109/L)ALT
(U/L)AST
(U/L)TBil
(μmol/L)DBil
(μmol/L)INR PTA
(%)甲泼尼龙30 mg/d 使用前1天 36.3 8.06 67 86 182.8 144.6 2.57 31 使用后3天 36.8 10.54 49 64 139.0 119.1 2.58 31 甲泼尼龙24 mg/d 使用后1天 38.8 8.79 95 105 170.8 137.5 3.16 26 使用后4天 36.9 13.10 45 84 935.5 791.5 2.94 27 -
[1] MANNS MP, LOHSE AW, VERGANI D. Autoimmune hepatitis-Update 2015[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 62(1 Suppl): S100-S111. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.03.005. [2] ZHANG HP, YAN HP. Research advances in autoantibodies in autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 749-753. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.007.张海萍, 闫惠平. 自身免疫性肝炎自身抗体的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(4): 749-753. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.007. [3] ANAND L, CHOUDHURY A, BIHARI C, et al. Flare of autoimmune hepatitis causing acute on chronic liver failure: Diagnosis and response to corticosteroid therapy[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(2): 587-596. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30205. [4] ALVAREZ F, BERG PA, BIANCHI FB, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: Review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 1999, 31(5): 929-938. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80297-9. [5] HENNES EM, ZENIYA M, CZAJA AJ, et al. Simplified criteria for the diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48(1): 169-176. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22322. [6] Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007.中华医学会感染病学分会肝衰竭与人工肝学组, 中华医学会肝病学分会重型肝病与人工肝学组. 肝衰竭诊治指南(2018年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(1): 38-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. [7] MONTANO-LOZA AJ, SHUMS Z, NORMAN GL, et al. Prognostic implications of antibodies to Ro/SSA and soluble liver antigen in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Liver Int, 2012, 32(1): 85-92. DOI: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2011.02502.x. [8] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis(2015)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(1): 9-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.01.002. [9] WANG QX, MA X. Current status and perspectives of autoimmune hepatitis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(4): 721-723. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.001.王绮夏, 马雄. 自身免疫性肝炎的研究现状与展望[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(4): 721-723. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.04.001. [10] MIELI-VERGANI G, VERGANI D, CZAJA AJ, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 18017. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.17. [11] ABE M, HIASA Y, MASUMOTO T, et al. Clinical characteristics of autoimmune hepatitis with histological features of acute hepatitis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2001, 21(3): 213-219. DOI: 10.1016/s1386-6346(01)00109-7. [12] MONTANO-LOZA AJ, CARPENTER HA, CZAJA AJ. Features associated with treatment failure in type 1 autoimmune hepatitis and predictive value of the model of end-stage liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 46(4): 1138-1145. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21787. [13] van DEN BRAND FF, van DER VEEN KS, de BOER YS, et al. Increased mortality among patients with vs without cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 17(5): 940-947. e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.09.046. -



 PDF下载 ( 2483 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2483 KB)

 下载:
下载:


