胆汁酸膜受体TGR5在胆道疾病中的研究进展
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.03.047
Research advances in the bile acid membrane receptor TGR5 in biliary tract diseases
-
摘要: TGR5是一种胆汁酸激活的G蛋白偶联受体,在胆道系统生理及病理过程中发挥着重要作用。本文简述了在正常生理情况下,TGR5在肝脏及胆管中的正常表达情况,及发挥调节胆汁酸分泌、代谢,细胞保护作用等功能。归纳了在病理生理情况下,TGR5表达及功能的变化通过炎症反应、细胞增殖、凋亡等途径来影响疾病的发生与发展的机制。TGR5可能是未来治疗胆道疾病的潜在靶点。
-
关键词:
- 胆道疾病 /
- 胆酸类 /
- 受体, G-蛋白偶联
Abstract: TGR5 is a bile acid-activated G protein-coupled receptor and plays an important role in the physiological and pathological processes of the biliary system. This article describes the normal expression of TGR5 in the liver and bile duct under normal physiological conditions and its functions including the regulation of bile acid secretion and metabolism and cytoprotection. This article also summarizes the changes in the expression and function of TGR5 under pathophysiological conditions and the mechanism of TGR5 in affecting the development and progression of biliary tract diseases through inflammatory response and cell proliferation and apoptosis. TGR5 may be a potential target for the treatment of biliary tract diseases in the future.-
Key words:
- Biliary Tract Diseases /
- Cholic Acids /
- Receptors, G-Protein-Coupled
-
HBV慢性感染是肝细胞癌(HCC) 发生的最常见病因,HCC的发病率和病死率在恶性肿瘤中分别占第6位和第4位,严重威胁着人类健康[1]。HCC细胞异常增殖可使血清糖蛋白N-糖链组成和结构发生改变,因此,血清糖蛋白的N-聚糖可作为HCC诊断标志物和HCC治疗的分子靶点[2]。N-聚糖改变的基础在于肝细胞内糖基转移酶活性的变化,其中多数糖基转移酶表达与肝脏功能密切相关。当肝细胞发生癌变时,某些糖基转移酶基因被激活,其表达异常增加,或基因表达受抑制而含量下降,从而导致一些蛋白质异常糖基化修饰。大量研究[3]表明,这种异常糖基化修饰与肿瘤细胞恶性侵袭行为密不可分。笔者前期研究[4]发现,与健康对照相比,HBV相关HCC(HBV-HCC)患者血清中N-聚糖图谱发生一系列特征改变,其中二天线N-聚糖峰1(peak1, NGA2F)丰度升高;三天线N-聚糖峰9(peak9, NA3Fb)丰度特异性升高;其他三天线和四天线N-聚糖峰(peak10 NA3Fc、peak11 NA4、peak12 NA4Fb)丰度也有不同程度的升高。但目前HBV-HCC患者血清N-聚糖变化机制尚未完全阐明。本研究中,通过检测HBV-HCC患者癌组织与癌旁组织中8种重要的糖基转移酶基因(包括岩藻糖基转移酶FUT3、FUT4、FUT6、FUT7、FUT8和N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖转移酶Gn-TⅢ、Gn-TⅣa、Gn-TⅤ)表达水平变化并比较其差异,探索HBV-HCC患者血清N-聚糖变化的可能机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 肝组织标本和血清标本的收集
收集解放军总医院2018年9月—2019年11月HBV-HCC行手术患者的肝癌和癌旁组织及正常肝组织标本,同时采集血清标本,置于-80 ℃冰箱保存。患者符合以下入选标准: (1)均为感染HBV的HCC患者;(2)排除HAV、HCV、HDV、HEV等肝炎病毒感染;(3)患者术后病理标本均经医院病理科确诊为HCC,肝癌诊断符合原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[5]。同时收集HCC患者临床资料。另外选取20例健康成年人血清作为对照。
1.2 DSA-FACE法检测HBV-HCC患者血清N-聚糖图谱
应用SPSS 20.0软件从34例HCC患者中随机选择8例HCC患者血清标本作为HCC试验组,20例健康成年人血清标本作为对照组。采用DSA-FACE法检测和分析血清N-聚糖图谱[6],具体步骤如下:
(1) 寡糖的释放:取3 μl血清,加入含有2 μl 10 mmol/L NH4HCO3缓冲液和3 μl去离子水的PCR反应板中, 反应板放入PCR仪器,95 ℃加热5 min后冷却至4 ℃, 然后加入3 μl PNGaseF(2.2 U/μl),37 ℃孵育3 h,之后加入100 μl去离子水终止反应,标记为D板。
(2) 标记寡糖:从D板吸取10 μl溶液加入一新的PCR反应板中,开盖在60 ℃条件下烘干90 min,加入3 μl标记溶液(20 mmol/L APTS∶ 1 mol/L NaCNBH3=1∶ 1),90 ℃反应2 h,加入100 μl去离子水终止反应,标记为L板。
(3) 去唾液酸:从L板中取2 μl溶液加入一新的PCR反应板,加入0.25 μL 100 mmol/L NH4Ac(pH=5.0)、0.2 μl唾液酸酶(2.5 U/μl)和1.55 μl去离子水, 震荡混匀后42 ℃孵育4 h,加40 μl去离子水终止反应,标记为DE板。
(4) DNA测序仪上机检测:取DE板10 μl溶液加入ABI测序仪专用96孔板,放入ABI 3500测序仪进行N-聚糖图谱分析,数据经GeneMapper软件分析。
1.3 荧光定量PCR法检测患者癌组织与癌旁组织中的糖基转移酶mRNA表达水平
冻存的肝组织放入超声震荡仪研磨后,用Trizol试剂提取总RNA,用Nano Drop One检测总RNA的浓度和纯度。将总RNA逆转录为cDNA后,用荧光定量PCR仪(ABI 7500 FAST)进行cDNA扩增,反应体系为20 μl。反应条件为:(1)95 ℃ 30 s;(2)95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 34 s共40个循环;(3)溶解曲线:95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 1 min, 95 ℃ 15 s。
以RPS11作为内参基因,目的基因的相对表达量用2-△△CT表示。癌组织和癌旁组织糖基转移酶mRNA相对表达量检测分析的对照均是正常肝组织。FUT3、FUT4、FUT6、FUT7、FUT8、Gn-TⅢ、Gn-TⅣa和Gn-TⅤ基因的特异引物由生工生物工程股份有限公司合成,引物序列见表 1。
表 1 荧光定量PCR检测糖基转移酶基因引物序列表基因 序列号 引物序列(5′→3′) FUT3 NM_001374740.1 F: CAA CAG AGA AAG CAG GCA
R: AAG AAA CAC ACA GCC ACC[7]FUT4 XM_032167182.1 F: TCC TAC GGA GAG GCT CAG
R: TCC TCG TAG TCC AAC ACG[7]FUT6 XM_011527879.3 F: CAT TTC TGC TGC CTC AGG
R: GGG CAA GTC AGG CAA CTC[7]FUT7 NM_004479.4 F: CCA CGA TCA CCA TCC TTG
R: AGG CTT CGG TTG GCA CTC[7]FUT8 XM_032180460.1 F: TCT AGC CGA GAA CTG TCC
R: GCT GCT CTT CTA AAA CGC[7]Gn-TⅢ XM_019018480.2 F: CCG CCA CAA GGT GCT CTA T
R: GAT CTC GTC CGC ATC GTC A[8]Gn-TⅣa XM_032178740.1 F: ACC AAG GGC ATA CGC TGG AG
R: GTT CTT GGT TGC CGC TAT GGA[9]Gn-TV XM_032411636.1 F: GCT GCC CAA CTG TAG GAG AC
R: GAA TCA AGG ACT CGG AGC AT[10]RPS11 XM_032159559.1 F: GCC GAG ACT ATC TGC ACT AC
R: ATG TCC AGC CTC AGA ACT TC[11]1.4 蛋白印迹法检测癌组织和癌旁组织中FUT8、Gn-TⅤ和Gn-Ⅳa的蛋白表达水平
冻存的肝组织放入超声震荡仪研磨后,用含cOmplete蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液提取蛋白,用BCA蛋白试剂盒来测定蛋白浓度。电泳分离不同分子量蛋白后,15 V恒压下用半干转电转仪将蛋白转移至PVDF膜,于5%的脱脂奶粉中室温封闭1 h,加入抗-FUT8(1∶ 1000)、抗-Gn-TⅣa(1∶ 1000)、抗-Gn-TⅤ(1∶ 1000)、抗-β-actin(1∶ 4000)一抗,4 ℃过夜,TBST溶液洗膜3次,分别加入抗鼠或抗兔的二抗(1∶ 5000),室温下孵育2 h,TBST溶液洗膜3次,加入增强型ECL化学发光试剂,凝胶成像仪扫描显影的条带,ImageJ软件分析条带灰度。以β-actin作为内参,目的蛋白的相对表达量用目的蛋白灰度值与内参蛋白灰度值的比值来表示。
1.5 统计学方法
应用SPSS 20.0软件对数据进行统计分析。计量资料用x ±s表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验。所有统计学分析均采用双侧检验,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 HBV-HCC患者临床特征
34例HBV-HCC患者临床特征见表 2。
表 2 34例HBV-HCC患者临床特征临床特征 数值 男性[例(%)] 29 (85.29) 年龄(岁) 54.85±8.20 HBV DNA(×106IU/ml) 2.35±7.15 AFP(ng/ml) 556.82±1995.22 ALT(U/L) 44.34±60.72 AST(U/L) 40.71±44.25 肿瘤直径(例) ≤5 cm 21 5~10 cm 9 ≥10 cm 4 2.2 HBV-HCC患者血清N-聚糖图谱特征
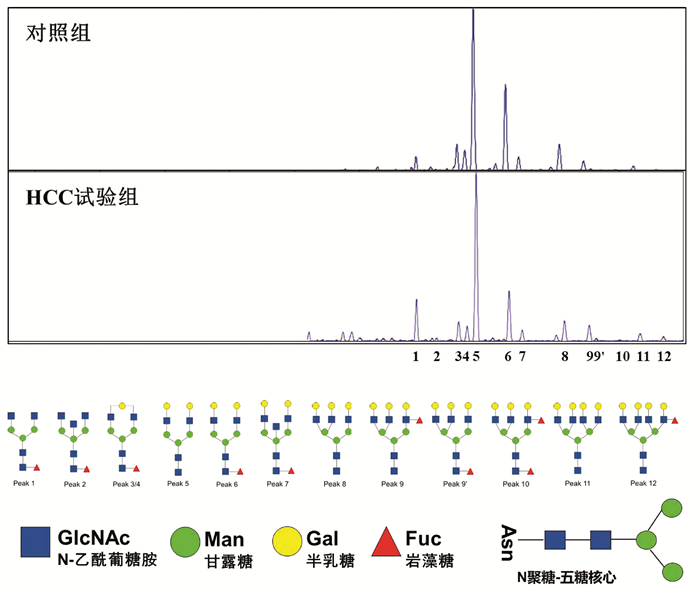
应用DSA-FACE法分析HCC试验组8例HBV-HCC患者与对照组20例健康成年人血清N-聚糖图谱(图 1),其特征改变与笔者前期研究发现的特征改变相同[4]。
 图 1 HCC试验组与对照组血清N-聚糖图谱注:a,血清中12种N-聚糖丰度比较;b,12种N-聚糖结构。Peak1-Peak12图引自文献[4],Peak1: 二天线无半乳糖基核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NGA2F);Peak2: 二天线无半乳糖基核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化平分型N聚糖(NGA2FB);Peak3/Peak4: 二天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化单支链半乳糖基N聚糖(NG1A2F);Peak5: 二天线N聚糖(NA2);Peak6: 二天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA2F);Peak7: 二天线平分型核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA2FB);Peak8: 三天线N聚糖(NA3);Peak9: 三天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fb);Peak9’: 三天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fc);Peak10: 三天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化与核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fbc);Peak11: 四天线N聚糖(NA4);Peak12: 四天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA4 Fb)。
图 1 HCC试验组与对照组血清N-聚糖图谱注:a,血清中12种N-聚糖丰度比较;b,12种N-聚糖结构。Peak1-Peak12图引自文献[4],Peak1: 二天线无半乳糖基核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NGA2F);Peak2: 二天线无半乳糖基核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化平分型N聚糖(NGA2FB);Peak3/Peak4: 二天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化单支链半乳糖基N聚糖(NG1A2F);Peak5: 二天线N聚糖(NA2);Peak6: 二天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA2F);Peak7: 二天线平分型核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA2FB);Peak8: 三天线N聚糖(NA3);Peak9: 三天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fb);Peak9’: 三天线核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fc);Peak10: 三天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化与核心ɑ-l, 6岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA3Fbc);Peak11: 四天线N聚糖(NA4);Peak12: 四天线支链ɑ-l, 3岩藻糖基化N聚糖(NA4 Fb)。与对照组相比,HCC试验组患者三天线N-聚糖峰9(peak9,NA3Fb)丰度明显升高(t=-2.514,P<0.05);血清二天线N-聚糖峰1(peak1,NGA2F)和四天线N-聚糖峰(peak11 NA4、peak12 NA4Fb)的丰度在两组间差异无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)。
2.3 癌组织与癌旁组织8种糖基转移酶mRNA表达水平比较
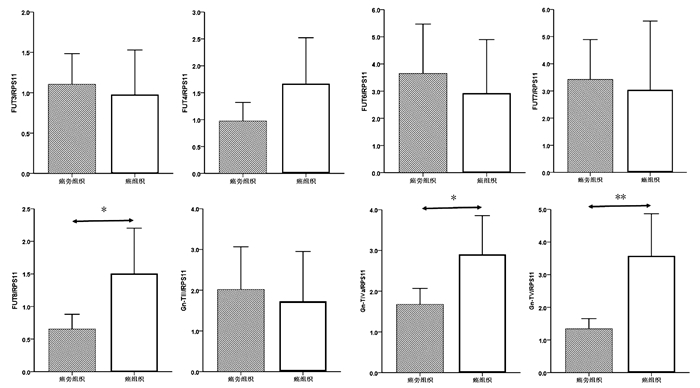
癌组织中FUT8、Gn-TⅣa和Gn-TⅤ基因mRNA表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(1.50±0.34 vs 0.65± 0.11, t=-2.354,P=0.022; 2.90±0.47 vs 1.68±0.19, t=-2.403,P=0.019; 3.57±0.64 vs 1.33±0.16, t=-3.384,P=0.001),差异均有统计学意义。FUT3、FUT4、FUT6、FUT7和Gn-TⅢ mRNA的表达水平在癌组织与癌旁组织间比较差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)(图 2)。
进一步比较了HCC试验组中8例患者癌组织与癌旁组织中8种糖基转移酶mRNA表达水平。与癌旁组织相比,8例HCC试验组患者癌组织中Gn-TⅤ mRNA表达明显升高(Gn-TⅤ: 5.26±1.70 vs 1.49±0.33, t=-2.173, P=0.047);Gn-TⅢ、Gn-TⅣa、FUT4和FUT8 mRNA表达在癌组织与癌旁组织间无显著性差异(Gn-TⅢ: 1.03±0.46 vs 1.55±0.62, t=0.663, P=0.518;Gn-TⅣa: 5.15±1.50 vs 2.39±0.46, t=-1.752, P=0.102; FUT4: 1.56±1.12 vs 0.81±0.27, t=-0.653, P=0.524; FUT8: 2.61±1.26 vs 1.01±0.41, t=-1.213, P=0.245)。
2.4 癌组织和癌旁组织FUT8、Gn-TⅣa和Gn-TⅤ基因的蛋白表达水平比较
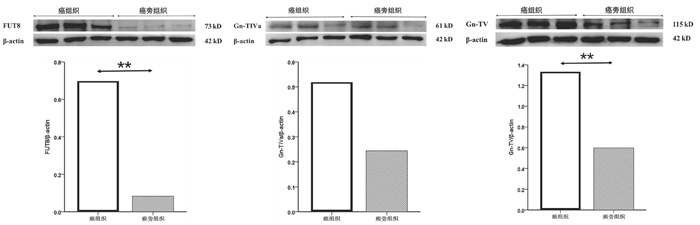
选取mRNA表达有显著性差异的3个糖基转移酶基因FUT8、Gn-TⅣa和Gn-TⅤ作为蛋白印迹实验的检测因子。结果如图 3所示,癌组织中FUT8与Gn-TⅤ的蛋白表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(0.70±0.11 vs 0.083±0.017, t=9.555, P=0.001; 1.33 ±0.19 vs 0.60±0.15, t=5.097, P=0.007);Gn-TⅣa的蛋白表达水平在癌组织与癌旁组织间比较差异无统计学意义(0.52±0.24 vs 0.24±0.11, t=1.833, P=0.141)。
3. 讨论
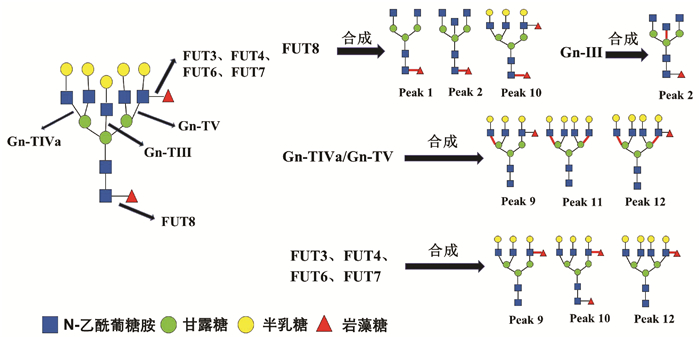
HCC患者血清中常出现大量异常糖基化N-糖蛋白,分离糖蛋白的N-聚糖链进行表达图谱分析,可发现支链与核心岩藻糖基化N-聚糖和多天线N-聚糖含量增加,这些N-聚糖与HCC发生发展密切相关,可作为筛查和诊断HCC的特异性标志[12]。研究[4, 13]发现在HBV-HCC患者血清中支链岩藻糖基化三天线N-聚糖(peak9, NA3Fb)丰度显著升高,且核心岩藻糖基化二天线N-聚糖(peak1, NGA2F)、核心岩藻糖基化平分型二天线N-聚糖(peak2, NGA2FB)、支链与核心岩藻糖基化三天线N聚糖(peak10, NA3Fc)、四天线N-聚糖(peak11, NA4)和支链岩藻糖基化四天线N-聚糖(peak12, NA4Fb)丰度也有不同程度的升高(N-聚糖结构如图 4)。本研究通过对HBV-HCC患者癌组织与癌旁组织相关糖基转移酶基因表达检测分析,探寻HCC患者特异性血清N-聚糖变化的可能机制。
糖基转移酶Gn-TⅤ与Gn-TⅣa催化形成三天线及三天线以上N-聚糖的N-乙酰葡糖胺(GlcNAc)糖链结构[14-15],而Gn-TⅢ催化合成N-聚糖的平分型GlcNAc结构,Gn-TⅢ与Gn-TⅤ、Gn-TⅣa有拮抗作用(图 4)[16]。本研究发现,在癌组织中Gn-TⅤ与Gn-TⅣa mRNA表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05),蛋白印迹实验也显示,在癌组织中Gn-TⅤ蛋白表达显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05)。而Gn-TⅢ mRNA表达水平在癌组织与癌旁组织间无统计学差异(P=0.711)。本研究结果可以解释HCC试验组患者血清中N-聚糖变化:与对照组相比,8例HCC患者血清中三天线N-聚糖(peak9)丰度显著升高(P<0.05),而且这8例HCC患者癌组织Gn-TⅤ表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05)。说明HCC患者血清中多天线N-聚糖丰度升高可能与糖基转移酶Gn-TⅤ高水平表达密切相关,促进含GlcNAc多分支(三天线及以上)N-聚糖的合成(图 4)。
以往研究[4, 13]表明,在HBV-HCC患者血清中核心岩藻糖基化N-聚糖(peak1、peak2、peak10)丰度较高。本研究发现,在癌组织中核心岩藻糖基转移酶FUT8 mRNA与蛋白表达水平显著高于癌旁组织(P<0.05)。FUT8表达上调会导致核心岩藻糖基化修饰结构的N-聚糖增加,可能与癌细胞高转移潜能有关[17]。另外,AFP是临床上最常用的HCC血清学检测指标,有研究[18]发现HCC患者血清中AFP经FUT8催化作用下可形成核心岩藻糖基化AFP(AFP-L3),其与肿瘤的发展速度、肿瘤大小和肿瘤转移密切相关,且诊断HCC效力优于AFP。除了α-1, 6核心岩藻糖基化N-聚糖,α-1, 3分支岩藻糖基化N-聚糖的丰度在HBV-HCC患者血清也特异性升高。α-1, 3分支岩藻糖基化结构是三天线N-聚糖(peak9)中Lewis X结构形成的关键[4],参与合成α-1, 3分支岩藻糖基化结构且与HCC密切相关的糖基转移酶有FUT3、FUT4、FUT6、FUT7[19]。本研究显示,在34例HCC患者癌组织与癌旁组织间FUT3、FUT4、FUT6和FUT7 mRNA表达水平没有显著性差异(P>0.05),不能解释血清N-聚糖水平异常改变。结合以往研究报道分析FUT基因表达的检测结果,可能因为多种岩藻糖基转移酶参与合成α-1, 3分支岩藻糖基化结构,而目前对于这些酶相互作用机制尚未明确,较难判断岩藻糖基转移酶中那一种亚类起主导作用。本研究主要检测8种与HCC密切相关的糖基转移酶基因表达,初步阐述HBV-HCC患者血清中N-聚糖变化的可能机制。但对于不同糖基转移酶之间相互作用的具体机制以及其他血清N-聚糖(如异常唾液酸化修饰的N-聚糖等)变化机制,还有待于进一步研究。
-
[1] PERINO A, DEMAGNY H, VELAZQUEZ-VILLEGAS L, et al. Molecular physiology of bile acid signaling in health, disease, and aging[J]. Physiol Rev, 2021, 101(2): 683-731. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00049.2019. [2] YANG F, MAO C, GUO L, et al. Structural basis of GPBAR activation and bile acid recognition[J]. Nature, 2020, 587(7834): 499-504. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2569-1. [3] KEITEL V, REINEHR R, GATSIOS P, et al. The G-protein coupled bile salt receptor TGR5 is expressed in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells[J]. Hepatology, 2007, 45(3): 695-704. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21458. [4] GUO C, CHEN WD, WANG YD. TGR5, Not only a metabolic regulator[J]. Front Physiol, 2016, 7: 646. DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00646. [5] HOLTER MM, CHIRIKJIAN MK, BRIERE DA, et al. Compound 18 improves glucose tolerance in a hepatocyte TGR5-dependent manner in mice[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(7): 2124. DOI: 10.3390/nu12072124. [6] MASYUK AI, HUANG BQ, RADTKE BN, et al. Ciliary subcellular localization of TGR5 determines the cholangiocyte functional response to bile acid signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2013, 304(11): G1013-G1024. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00383.2012. [7] NAKHI A, WONG HL, WELDY M, et al. Structural modifications that increase gut restriction of bile acid derivatives[J]. RSC Med Chem, 2021, 12(3): 394-405. DOI: 10.1039/d0md00425a. [8] VASSILEVA G, HU W, HOOS L, et al. Gender-dependent effect of Gpbar1 genetic deletion on the metabolic profiles of diet-induced obese mice[J]. J Endocrinol, 2010, 205(3): 225-232. DOI: 10.1677/JOE-10-0009. [9] WANG YD, CHEN WD, YU D, et al. The G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor, Gpbar1 (TGR5), negatively regulates hepatic inflammatory response through antagonizing nuclear factor κ light-chain enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(4): 1421-1432. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24525. [10] BIAGIOLI M, MARCHIANÒ S, CARINO A, et al. Bile acids activated receptors in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(6): 1281. DOI: 10.3390/cells10061281. [11] YANG H, ZHOU H, ZHUANG L, et al. Plasma membrane-bound G protein-coupled bile acid receptor attenuates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via the inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling in mice[J]. Liver Transpl, 2017, 23(1): 63-74. DOI: 10.1002/lt.24628. [12] GUO C, QI H, YU Y, et al. The G-Protein-Coupled Bile Acid Receptor Gpbar1 (TGR5) inhibits gastric inflammation through antagonizing NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2015, 6: 287. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00287. [13] SU J, ZHANG Q, QI H, et al. The G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor Gpbar1 (TGR5) protects against renal inflammation and renal cancer cell proliferation and migration through antagonizing NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(33): 54378-54387. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17533. [14] YANG H, LUO F, WEI Y, et al. TGR5 protects against cholestatic liver disease via suppressing the NF-κB pathway and activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(14): 1158. DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-2631. [15] ZHAO X, LI H, LYU S, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals heterogeneous progression and EGFR activation in pancreatic adenosquamous carcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(10): 2590-2605. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.58886. [16] REICH M, DEUTSCHMANN K, SOMMERFELD A, et al. TGR5 is essential for bile acid-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation in vivo and in vitro[J]. Gut, 2016, 65(3): 487-501. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309458. [17] LIU X, CHEN B, YOU W, et al. The membrane bile acid receptor TGR5 drives cell growth and migration via activation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 412: 194-207. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.017. [18] PATHAK P, LIU H, BOEHME S, et al. Farnesoid X receptor induces Takeda G-protein receptor 5 cross-talk to regulate bile acid synthesis and hepatic metabolism[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(26): 11055-11069. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.784322. [19] BIDAULT-JOURDAINNE V, MERLEN G, GLÉNISSON M, et al. TGR5 controls bile acid composition and gallbladder function to protect the liver from bile acid overload[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3(2): 100214. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100214. [20] PÉAN N, DOIGNON I, GARCIN I, et al. The receptor TGR5 protects the liver from bile acid overload during liver regeneration in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2013, 58(4): 1451-1460. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26463. [21] DONEPUDI AC, BOEHME S, LI F, et al. G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor plays a key role in bile acid metabolism and fasting-induced hepatic steatosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(3): 813-827. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28707. [22] KEITEL V, CUPISTI K, ULLMER C, et al. The membrane-bound bile acid receptor TGR5 is localized in the epithelium of human gallbladders[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(3): 861-870. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23032. [23] KEITEL V, REICH M, HÄUSSINGER D. TGR5: pathogenetic role and/or therapeutic target in fibrosing cholangitis?[J]. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2015, 48(2-3): 218-225. DOI: 10.1007/s12016-014-8443-x. [24] LI T, HOLMSTROM SR, KIR S, et al. The G protein-coupled bile acid receptor, TGR5, stimulates gallbladder filling[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2011, 25(6): 1066-1071. DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0460. [25] SHI Y, SU W, ZHANG L, et al. TGR5 regulates macrophage inflammation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 609060. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.609060. [26] KANG JH, KIM M, YIM M. FXR/TGR5 mediates inflammasome activation and host resistance to bacterial infection[J]. Biochem Biophys Rep, 2021, 27: 101051. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101051. [27] FRANKE A, BALSCHUN T, KARLSEN TH, et al. Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility[J]. Nat Genet, 2008, 40(11): 1319-1323. DOI: 10.1038/ng.221. [28] KARLSEN TH, FRANKE A, MELUM E, et al. Genome-wide association analysis in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 138(3): 1102-1111. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.11.046. [29] DEUTSCHMANN K, REICH M, KLINDT C, et al. Bile acid receptors in the biliary tree: TGR5 in physiology and disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864(4 Pt B): 1319-1325. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.021. [30] REICH M, SPOMER L, KLINDT C, et al. Downregulation of TGR5 (GPBAR1) in biliary epithelial cells contributes to the pathogenesis of sclerosing cholangitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(3): 634-646. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.029. [31] ZHANG R, MA WQ, FU MJ, et al. Overview of bile acid signaling in the cardiovascular system[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2021, 9(2): 308-320. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.308. [32] FRYER RM, NG KJ, NODOP MAZUREK SG, et al. G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 stimulation mediates arterial vasodilation through a K(Ca)1.1 (BK(Ca))-dependent mechanism[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2014, 348(3): 421-431. DOI: 10.1124/jpet.113.210005. [33] YUSTA B, MATTHEWS D, FLOCK GB, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-2 promotes gallbladder refilling via a TGR5-independent, GLP-2R-dependent pathway[J]. Mol Metab, 2017, 6(6): 503-511. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.006. [34] ERICE O, LABIANO I, ARBELAIZ A, et al. Differential effects of FXR or TGR5 activation in cholangiocarcinoma progression[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2018, 1864(4 Pt B): 1335-1344. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.016. [35] XU L, HAUSMANN M, DIETMAIER W, et al. Expression of growth factor receptors and targeting of EGFR in cholangiocarcinoma cell lines[J]. BMC Cancer, 2010, 10: 302. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-302. [36] LAVOIE B, BALEMBA OB, GODFREY C, et al. Hydrophobic bile salts inhibit gallbladder smooth muscle function via stimulation of GPBAR1 receptors and activation of KATP channels[J]. J Physiol, 2010, 588(Pt 17): 3295-3305. DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.192146. [37] BRIERE DA, RUAN X, CHENG CC, et al. Novel small molecule agonist of TGR5 possesses anti-diabetic effects but causes gallbladder filling in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(8): e0136873. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0136873. [38] VASSILEVA G, GOLOVKO A, MARKOWITZ L, et al. Targeted deletion of Gpbar1 protects mice from cholesterol gallstone formation[J]. Biochem J, 2006, 398(3): 423-430. DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060537. [39] MASYUK TV, MASYUK AI, LORENZO PISARELLO M, et al. TGR5 contributes to hepatic cystogenesis in rodents with polycystic liver diseases through cyclic adenosine monophosphate/Gαs signaling[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(4): 1197-1218. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29284. [40] LARUSSO NF, MASYUK TV, HOGAN MC. Polycystic liver disease: The benefits of targeting cAMP[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2016, 14(7): 1031-1034. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.03.008. [41] SUSSMAN CR, WANG X, CHEBIB FT, et al. Modulation of polycystic kidney disease by G-protein coupled receptors and cyclic AMP signaling[J]. Cell Signal, 2020, 72: 109649. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109649. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 唐飞,梁静,景丽,刘刚,王凤梅. 重组人血小板生成素对D-氨基半乳糖诱导急性肝衰竭大鼠血小板的影响. 中华危重病急救医学. 2024(02): 189-194 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 闫盼盼,胡兆东,李秀敏,苗明三. 基于中西医临床病症特点的急性肝衰竭动物模型分析. 中华中医药杂志. 2023(10): 5023-5028 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 黄晓光,林灿峰,林连兴,文之斐,张晓平. 聚乙二醇化重组人粒细胞刺激因子注射液对癌症患者粒细胞的作用. 实用癌症杂志. 2020(07): 1166-1169 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2268 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2268 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术