附脐静脉开放对肝硬化食管静脉曲张发生及出血的影响:保护因素还是危险因素?
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.04.036
Influence of patent paraumbilical vein on the development of esophageal varices and esophageal variceal bleeding in liver cirrhosis: A protective factor or a risk factor?
-
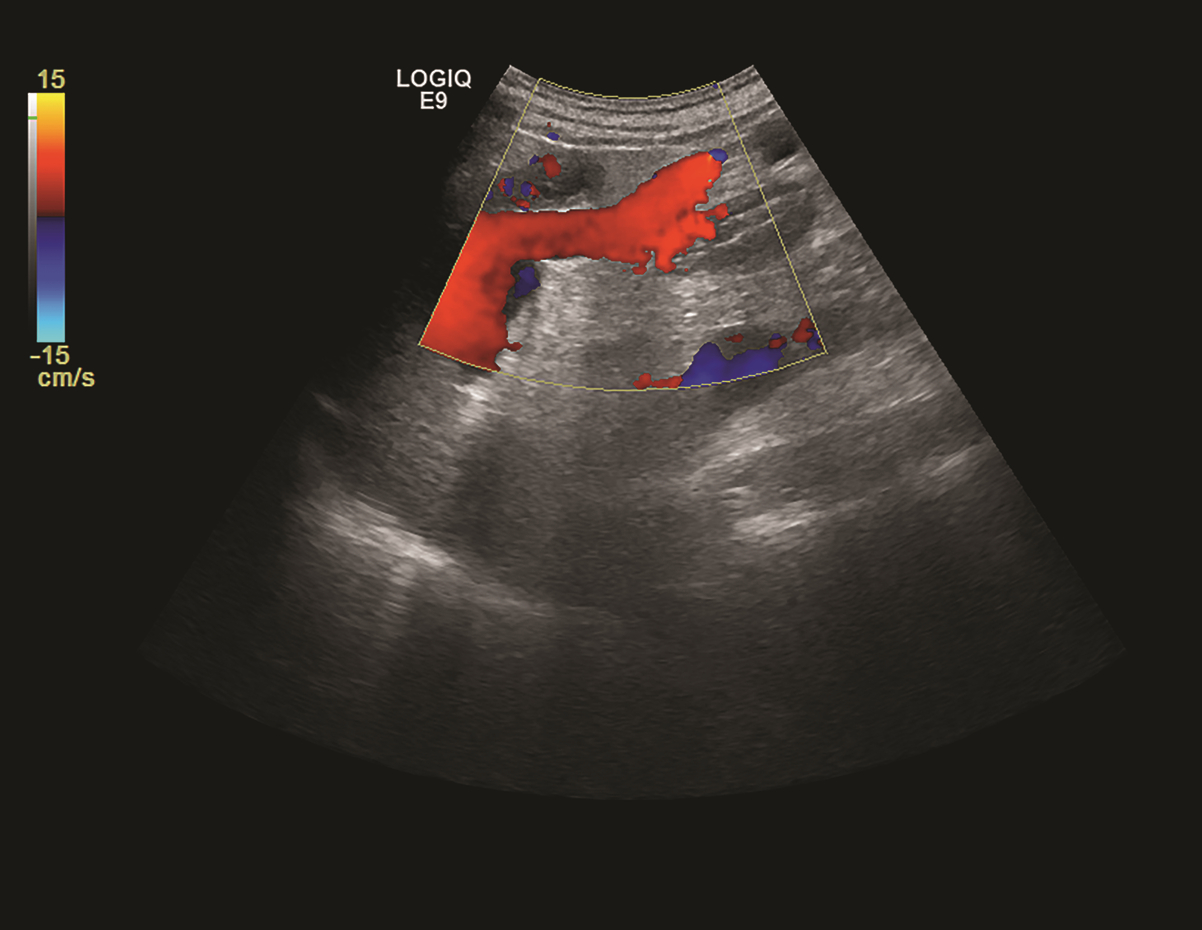
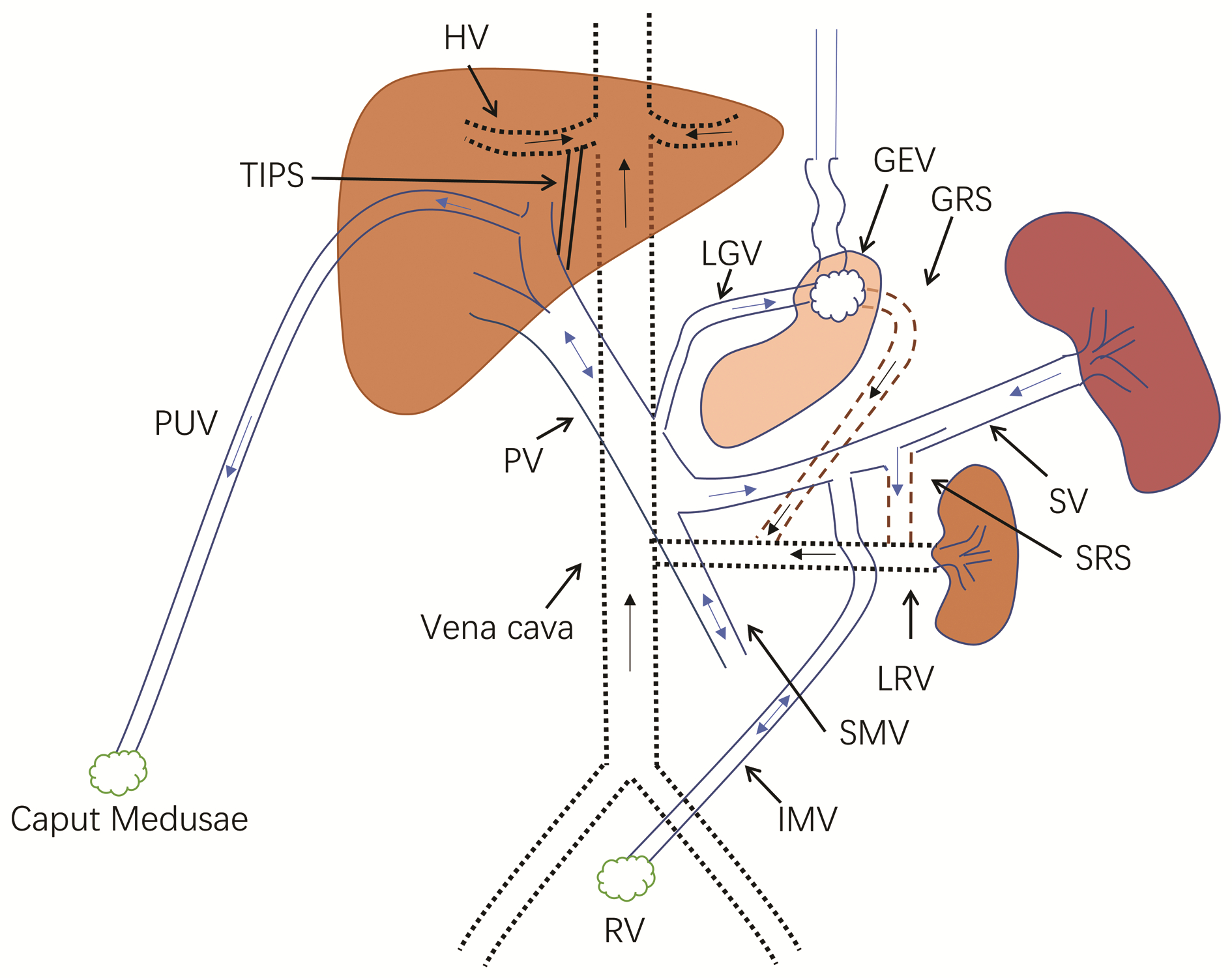
摘要: 既往研究认为,肝硬化门静脉高压时附脐静脉开放能够减少门静脉血流,降低门静脉压力,减少食管静脉曲张及出血的发生,但临床上对此尚存争论。本文从门静脉侧支循环形成及附脐静脉特点、附脐静脉开放定义及诊断、附脐静脉开放对食管静脉曲张发生及出血的影响等3个方面回顾总结,认为附脐静脉开放并不能够减少食管静脉曲张及出血的发生。与既往观点相反,附脐静脉开放更应作为肝硬化门静脉高压进展的一个表现,易导致肝性脑病的发生,临床上应注意针对性预防。Abstract: Previous studies believe that patent paraumbilical vein in cirrhotic portal hypertension can reduce portal venous flow, portal venous pressure, and the development of esophageal varices and esophageal variceal bleeding, but there are still controversies over this issue in clinical practice. This article reviews the formation of portal systemic collateral circulation, the characteristics of the paraumbilical vein, the definition and diagnosis of patent paraumbilical vein, and the influence of patent paraumbilical vein on the development of esophageal varices and esophageal variceal bleeding, and it is believed that patent paraumbilical vein may not reduce the development of esophageal varices and esophageal variceal bleeding. Contrary to the previous points of view, patent paraumbilical vein should be regarded as a manifestation of the progression of cirrhotic portal hypertension, which can lead to the complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, and therefore, targeted prevention measures should be adopted in clinical practice.
-
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Hypertension, Portal /
- Esophageal and Gastric Varices /
- Umbilical Veins
-
表 1 不同研究中附脐静脉开放组Child-Pugh分级情况
Table 1. Child-Pugh classification of the patent paraumbilical vein group in different studies
年份 作者 样本量(例) 附脐静脉开放组
Child-Pugh A/B/C比例1989 Mostbeck等[29] 11 1992 Morin等[33] 55 34.5%1)/65.5% 1994 Caturelli等[14] 20 45%/40%/15% 1995 Sacerdoti等[34] 184 26.5%/29.6%/56.8% 2000 Gupta等[31] 50 2009 Zardi等[21] 326 24.7%/66.7%/8.6% 2012 邝乃乐等[35] 738 21%/54.9%/24.1% 2014 Kondo等[23] 181 27.6%/53.2%/19.2% 2017 Calame等[32] 172 注:1)包括Child-Pugh A、B级。 -
[1] SEO YS. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2018, 24(1): 20-42. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2017.0064. [2] HUANG D, CAO JG, YE HY, et al. Occurrence and progression of hemodynamic dysfunction in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(10): 1117-1122. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210813-00394.黄登, 曹君贵, 叶航羊, 等. 肝硬化门静脉高压血流动力学紊乱发生及发展机制[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(10): 1117-1122. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210813-00394. [3] GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. [4] NARDELLI S, RIGGIO O, GIOIA S, et al. Spontaneous porto-systemic shunts in liver cirrhosis: Clinical and therapeutical aspects[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(15): 1726-1732. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1726. [5] PHILIPS CA, RAJESH S, AUGUSTINE P, et al. Portosystemic shunts and refractory hepatic encephalopathy: Patient selection and current options[J]. Hepat Med, 2019, 11: 23-34. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S169024. [6] BOREGOWDA U, UMAPATHY C, HALIM N, et al. Update on the management of gastrointestinal varices[J]. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 10(1): 1-21. DOI: 10.4292/wjgpt.v10.i1.1. [7] IWAKIRI Y. Pathophysiology of portal hypertension[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2014, 18(2): 281-291. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2013.12.001. [8] SHARMA M, RAMESHBABU CS. Collateral pathways in portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2012, 2(4): 338-352. DOI: 10.1016/j.jceh.2012.08.001. [9] VERMA SK, MITCHELL DG, LAKHMAN Y, et al. Paraumbilical collateral veins on MRI as possible protection against portal venous thrombosis in candidates for liver transplantation[J]. Abdom Imaging, 2008, 33(5): 536-541. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-007-9333-y. [10] ARORA A, RAJESH S, MEENAKSHI YS, et al. Spectrum of hepatofugal collateral pathways in portal hypertension: An illustrated radiological review[J]. Insights Imaging, 2015, 6(5): 559-572. DOI: 10.1007/s13244-015-0419-8. [11] MICHAUD M, RANAIVOJAONA S, LIVIDEANU C, et al. Umbilical vein recanalization[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2021, 361(5): e41. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjms.2020.07.012. [12] LEITE AF, MOTA A Jr, CHAGAS-NETO FA, et al. Acquired portosystemic collaterals: Anatomy and imaging[J]. Radiol Bras, 2016, 49(4): 251-256. DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2015.0026. [13] GARBAR V, NEWTON BW. Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, falciform ligament[M]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2021. [14] CATURELLI E, POMPILI M, SQUILLANTE MM, et al. Cruveilhier-Baumgarten syndrome: An efficient spontaneous portosystemic collateral preventing oesophageal varices bleeding[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 1994, 9(3): 236-241. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1994.tb01716.x. [15] BANDALI MF, MIRAKHUR A, LEE EW, et al. Portal hypertension: Imaging of portosystemic collateral pathways and associated image-guided therapy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(10): 1735-1746. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i10.1735. [16] MOUBARAK E, BOUVIER A, BOURSIER J, et al. Portosystemic collateral vessels in liver cirrhosis: A three-dimensional MDCT pictorial review[J]. Abdom Imaging, 2012, 37(5): 746-766. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-011-9811-0. [17] LAFORTUNE M, CONSTANTIN A, BRETON G, et al. The recanalized umbilical vein in portal hypertension: A myth[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1985, 144(3): 549-553. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.144.3.549. [18] SADDEKNI S, HUTCHINSON DE, COOPERBERG PL. The sonographically patent umbilical vein in portal hypertension[J]. Radiology, 1982, 145(2): 441-443. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.145.2.7134450. [19] HORTON KM, FISHMAN EK. Paraumbilical vein in the cirrhotic patient: Imaging with 3D CT angiography[J]. Abdom Imaging, 1998, 23(4): 404-408. DOI: 10.1007/s002619900369. [20] GIBSON RN, GIBSON PR, DONLAN JD, et al. Identification of a patent paraumbilical vein by using Doppler sonography: Importance in the diagnosis of portal hypertension[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1989, 153(3): 513-516. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.153.3.513. [21] ZARDI EM, UWECHIE V, CACCAVO D, et al. Portosystemic shunts in a large cohort of patients with liver cirrhosis: Detection rate and clinical relevance[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2009, 44(1): 76-83. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-008-2279-1. [22] ITO K, MATSUTANI S, MARUYAMA H, et al. Study of hemodynamic changes in portal systemic shunts and their relation to variceal relapse after endoscopic variceal ligation combined with ethanol sclerotherapy[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2006, 41(2): 119-126. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-005-1730-9. [23] KONDO T, MARUYAMA H, SEKIMOTO T, et al. Influence of paraumbilical vein patency on the portal hemodynamics of patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2014, 48(2): 178-183. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182a46d84. [24] CHEN CH, WANG JH, LU SN, et al. Comparison of prevalence for paraumbilical vein patency in patients with viral and alcoholic liver cirrhosis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2002, 97(9): 2415-2418. DOI: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05996.x. [25] BOLOGNESI M, VERARDO A, DI PASCOLI M. Peculiar characteristics of portal-hepatic hemodynamics of alcoholic cirrhosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(25): 8005-8010. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8005. [26] BOLOGNESI M, SACERDOTI D, MESCOLI C, et al. Different hemodynamic patterns of alcoholic and viral endstage cirrhosis: Analysis of explanted liver weight, degree of fibrosis and splanchnic Doppler parameters[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2007, 42(2): 256-262. DOI: 10.1080/00365520600880914. [27] OHHIRA M, OHTA H, OHHIRA M, et al. Altered intrahepatic pathway of para-umbilical vein in portal hypertension[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 1998, 13(7): 691-695. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1998.tb00715.x. [28] GIBSON PR, GIBSON RN, DONLAN JD, et al. Duplex Doppler ultrasound of the ligamentum teres and portal vein: A clinically useful adjunct in the evaluation of patients with known or suspected chronic liver disease or portal hypertension[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 1991, 6(1): 61-65. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01147.x. [29] MOSTBECK GH, WITTICH GR, HEROLD C, et al. Hemodynamic significance of the paraumbilical vein in portal hypertension: Assessment with duplex US[J]. Radiology, 1989, 170(2): 339-342. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.170.2.2643137. [30] CANNELLA R, GIAMBELLUCA D, PELLEGRINELLI A, et al. Color doppler ultrasound in portal hypertension: A closer look at left gastric vein hemodynamics[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2021, 40(1): 7-14. DOI: 10.1002/jum.15386. [31] GUPTA D, CHAWLA YK, DHIMAN RK, et al. Clinical significance of patent paraumbilical vein in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2000, 45(9): 1861-1864. DOI: 10.1023/a:1005505522151. [32] CALAME P, RONOT M, BOUVERESSE S, et al. Predictive value of CT for first esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: Value of para-umbilical vein patency[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2017, 87: 45-52. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2016.12.006. [33] MORIN C, LAFORTUNE M, POMIER G, et al. Patent paraumbilical vein: Anatomic and hemodynamic variants and their clinical importance[J]. Radiology, 1992, 185(1): 253-256. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.185.1.1523319. [34] SACERDOTI D, BOLOGNESI M, BOMBONATO G, et al. Paraumbilical vein patency in cirrhosis: effects on hepatic hemodynamics evaluated by Doppler sonography[J]. Hepatology, 1995, 22(6): 1689-1694. [35] KUANG NL, PAN CZ, LIN N, et al. Clinical significance of recanalized paraumbilical vein in hepatitis cirrhosis with portal hypertension[J/CD]. Chin J Hepat Surg: Electronic Edition, 2012, 1(1): 42-45. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2012.01.010.邝乃乐, 潘楚芝, 林楠, 等. 肝炎后肝硬化门静脉高压症患者附脐静脉开放的临床意义[J/CD]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2012, 1(1): 42-45. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2012.01.010. [36] VOROBIOFF JD, GROSZMANN RJ. Prevention of portal hypertension: From variceal development to clinical decompensation[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(1): 375-381. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27249. [37] SALAHSHOUR F, MEHRABINEJAD MM, RASHIDI SHAHPASANDI MH, et al. Esophageal variceal hemorrhage: The role of MDCT characteristics in predicting the presence of varices and bleeding risk[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2020, 45(8): 2305-2314. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-020-02585-5. [38] CARAIANI C, PETRESC B, POP A, et al. Can the computed tomographic aspect of porto-systemic circulation in cirrhotic patients be associated with the presence of variceal hemorrhage?[J]. Medicina (Kaunas), 2020, 56(6): 301. DOI: 10.3390/medicina56060301. [39] WAN SZ, NIE Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Assessing the prognostic performance of the Child-Pugh, model for end-stage liver disease, and albumin-bilirubin scores in patients with decompensated cirrhosis: A large asian cohort from gastroenterology department[J]. Dis Markers, 2020, 2020: 5193028. DOI: 10.1155/2020/5193028. [40] SOGA K, KASSAI K, KONISHI H, et al. Prediction of large esophageal variceal bleeding and subsequent mortality[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2014, 61(131): 678-682. [41] SIMÓN-TALERO M, ROCCARINA D, MARTÍNEZ J, et al. Association between portosystemic shunts and increased complications and mortality in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(6): 1694-1705. e4. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.028. [42] DÖMLAND M, GEBEL M, CASELITZ M, et al. Comparison of portal venous flow in cirrhotic patients with and without paraumbilical vein patency using duplex-sonography[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2000, 21(4): 165-169. DOI: 10.1055/s-2000-6928. [43] WACHSBERG RH, OBOLEVICH AT. Blood flow characteristics of vessels in the ligamentum teres fissure at color Doppler sonography: findings in healthy volunteers and in patients with portal hypertension[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1995, 164(6): 1403-1405. DOI: 10.2214/ajr.164.6.7754882. -



 PDF下载 ( 2602 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2602 KB)

 下载:
下载: