达芬奇机器人与传统腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除术近期疗效及安全性比较的Meta分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.025
Short-term efficacy and safety of Da Vinci robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy versus traditional laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: A meta-analysis
-
摘要:
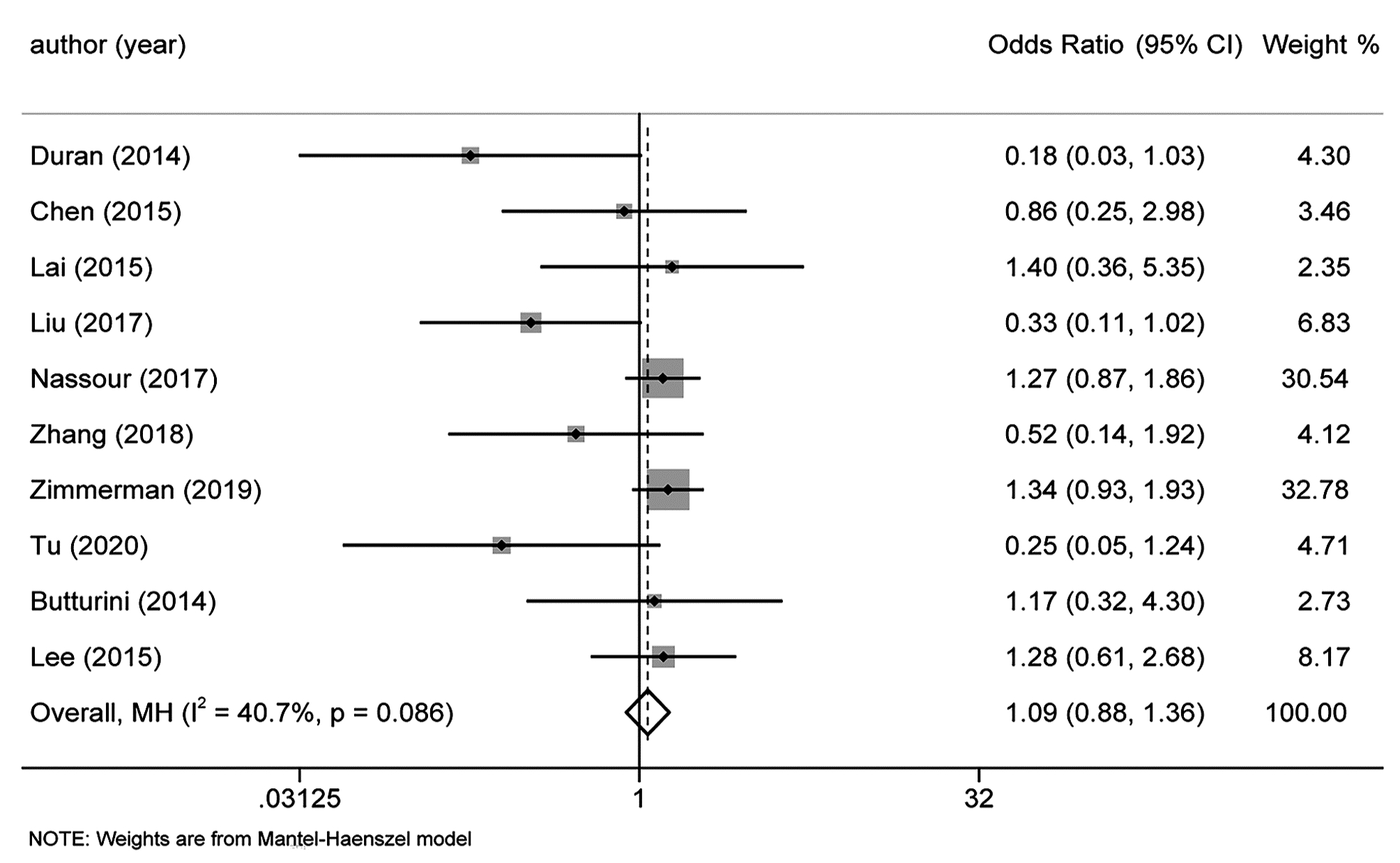
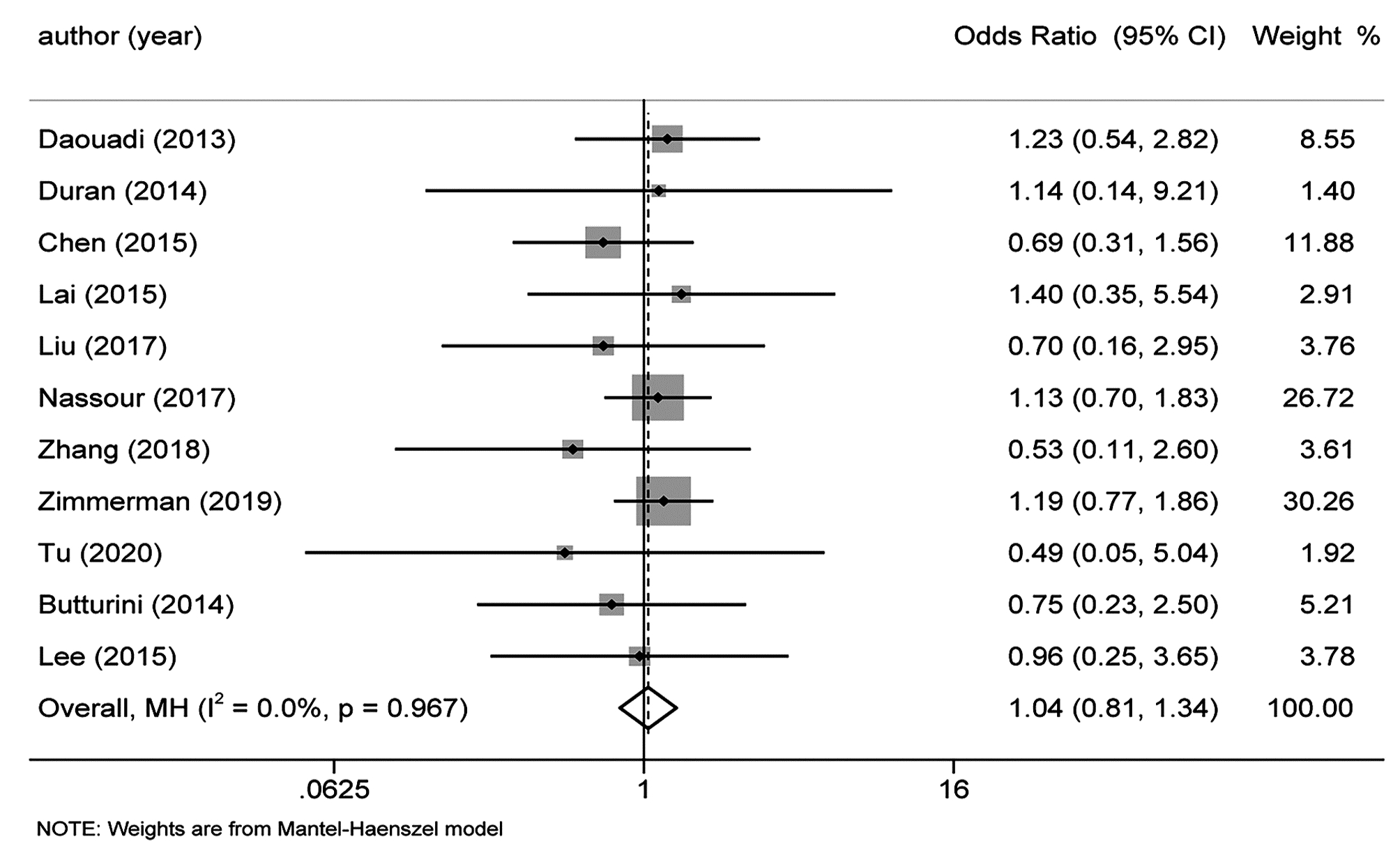
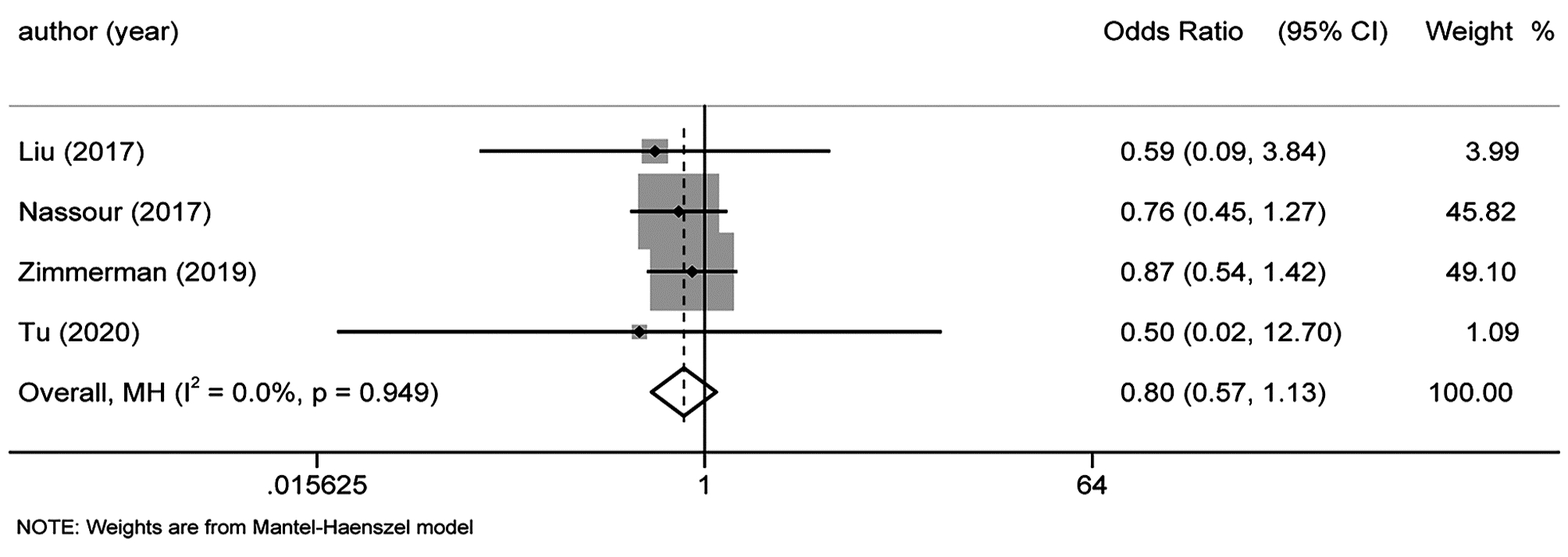
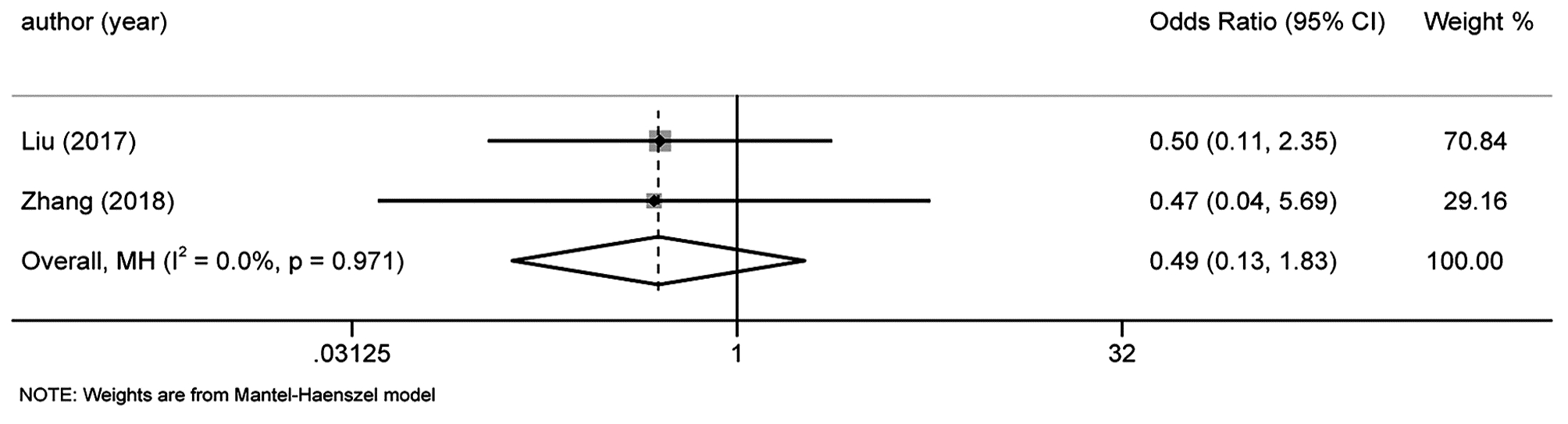
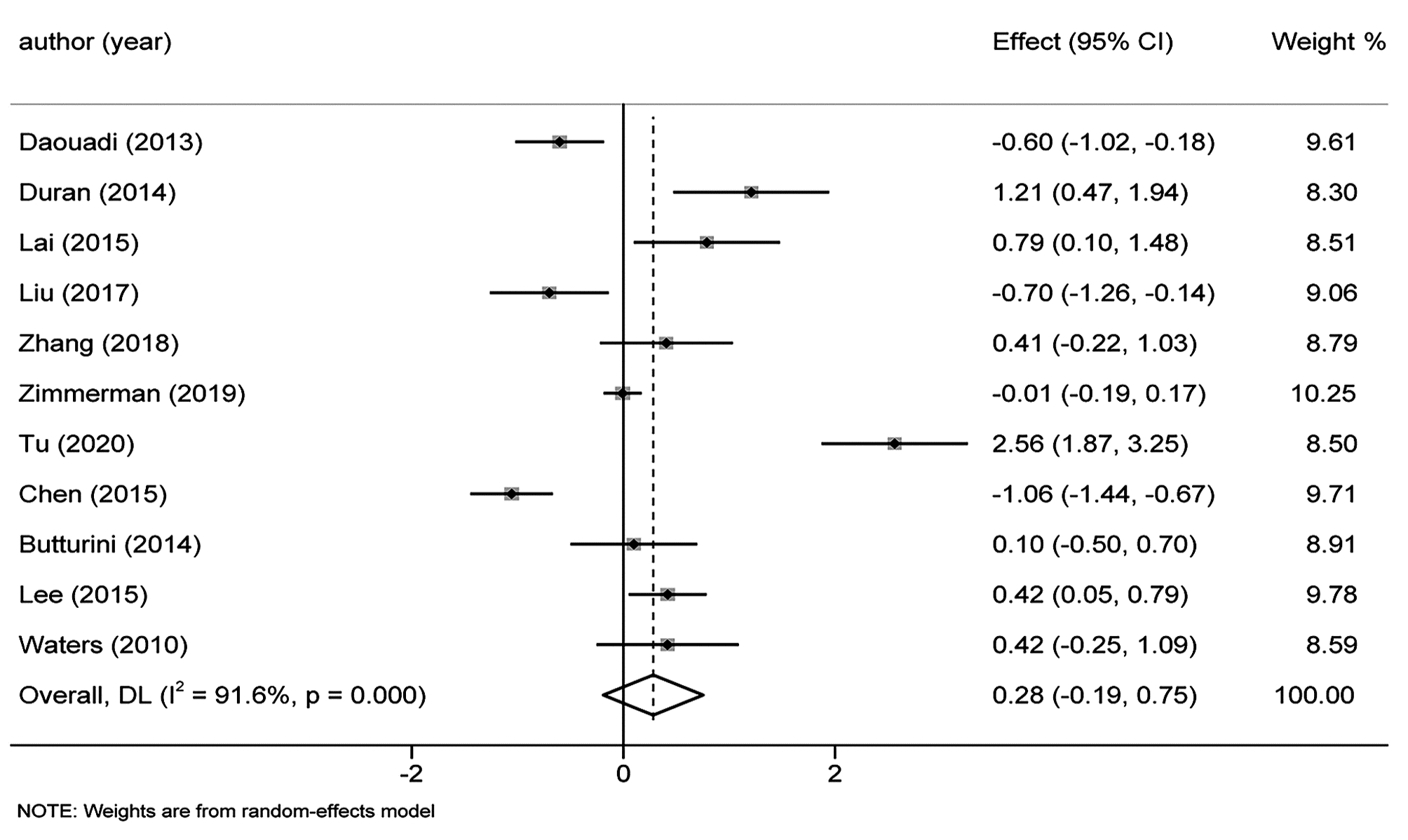
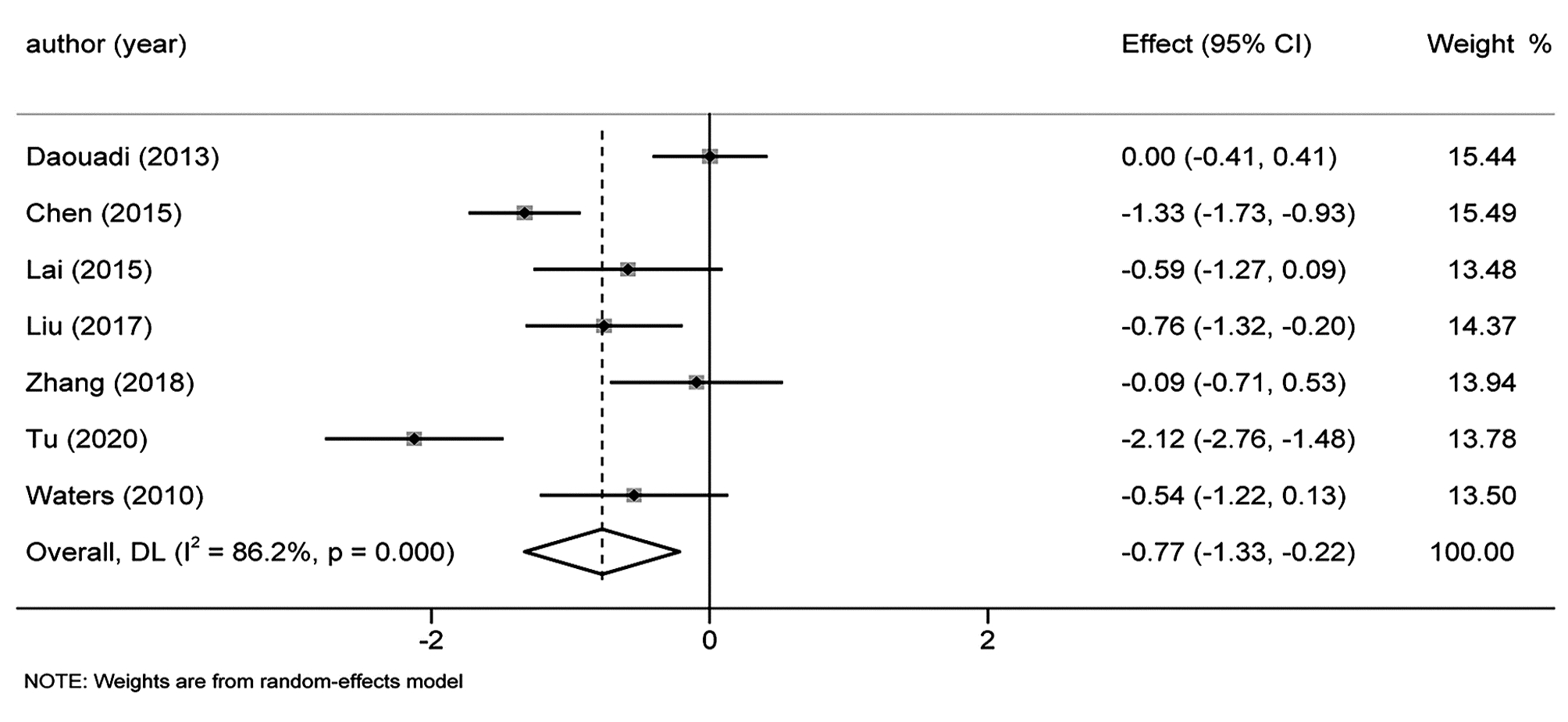
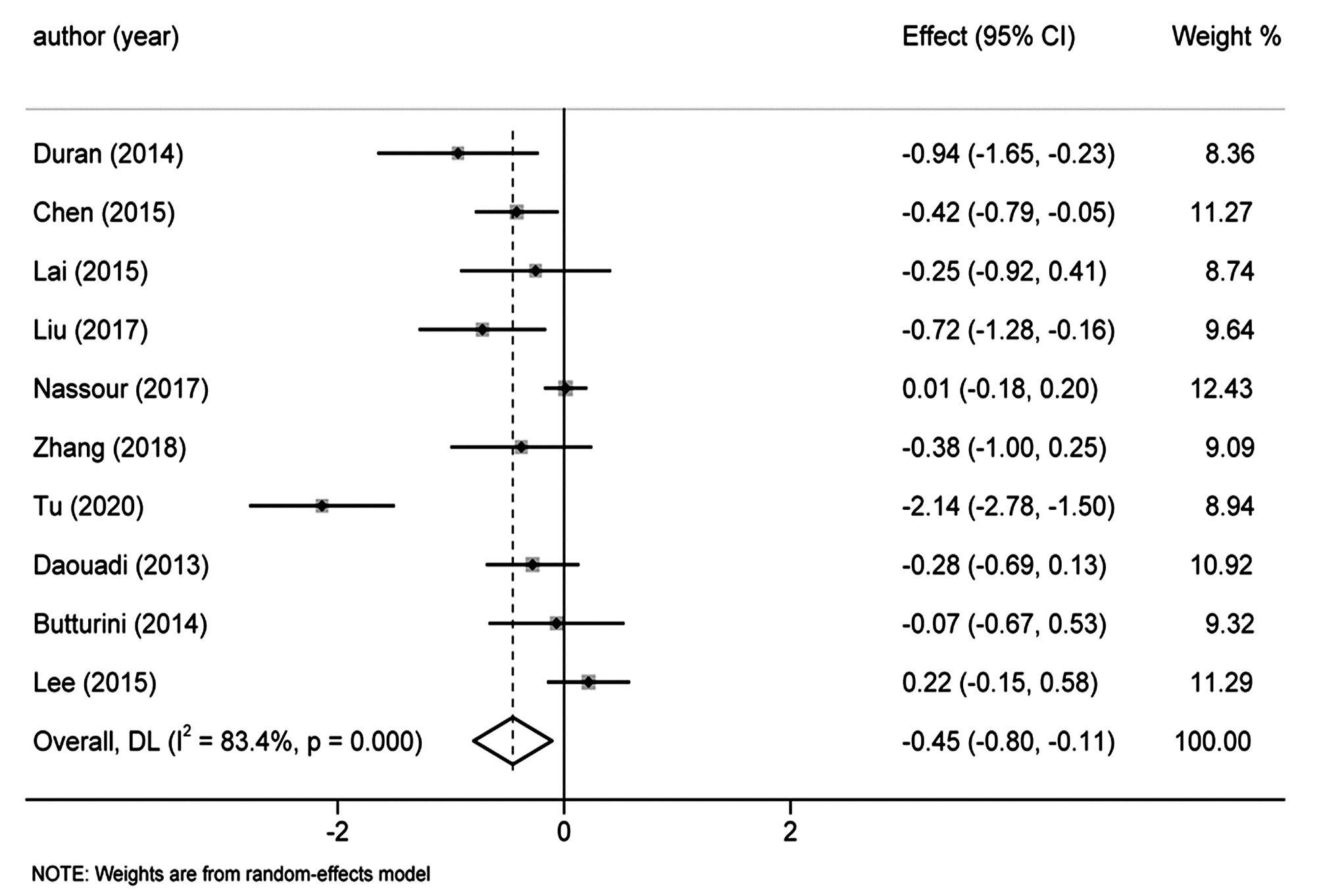
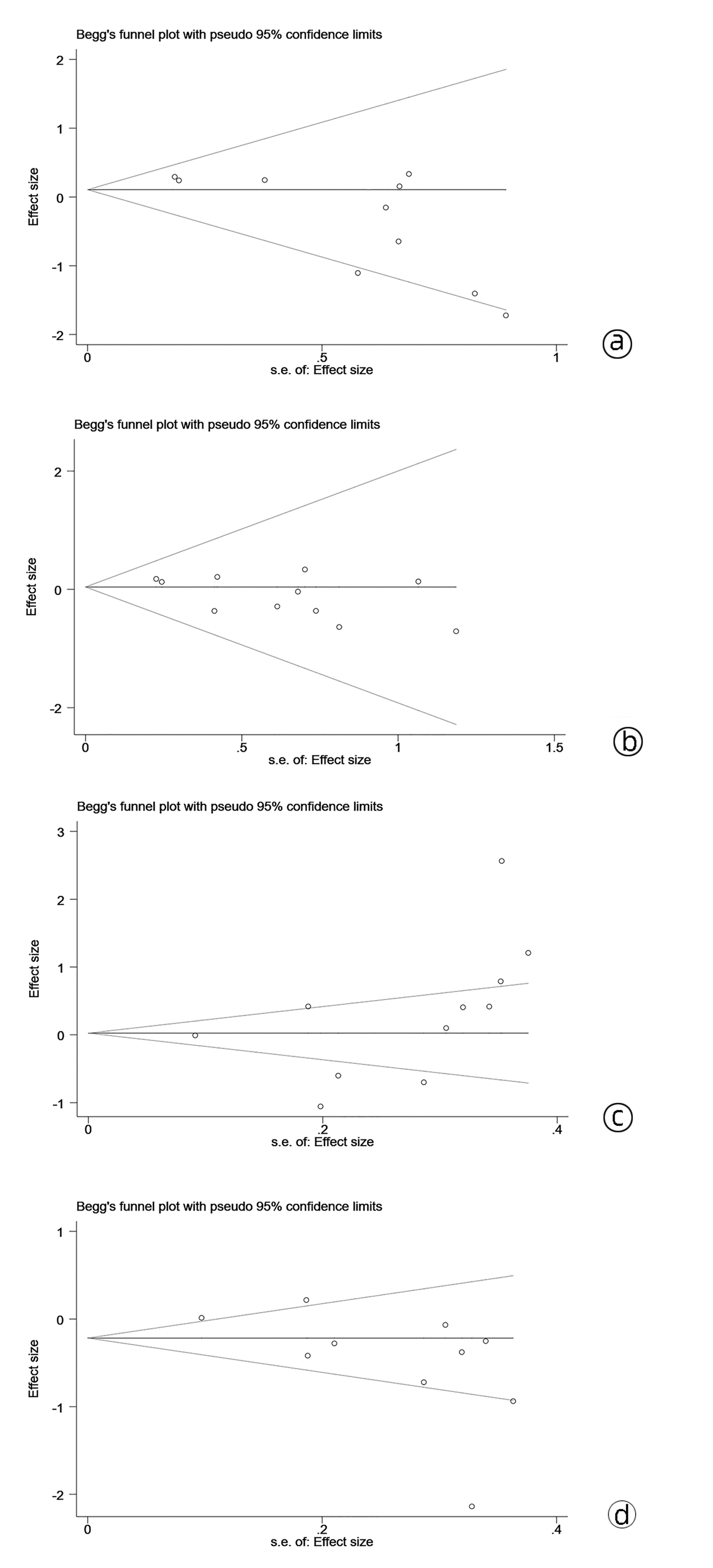
目的 本研究旨在系统评价机器人手术系统与传统腹腔镜手术在胰十二指肠切除术中应用的近期疗效与安全性,为临床研究与实践提供参考。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、Embase、Cochrane Library、中国知网、万方和维普等中英文期刊服务平台,纳入所有对比机器人辅助腹腔镜和传统腹腔镜应用于胰十二指肠切除术临床疗效的队列研究。按照Cochrane系统评价纳入文献的质量,使用Stata 15.1软件对提取的相关结局指标进行Meta分析。 结果 最终纳入12篇合格的队列研究,共计1630例患者,RPD(机器人胰十二指肠切除术)组患者683例,LPD(腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除术)组患者947例。Meta分析结果显示:RPD组与LPD组患者术后出血率(OR=0.66, 95%CI: 0.48~0.91)、中转开腹率(OR=0.41, 95%CI: 0.30~0.56)、预估手术出血量(WMD=-0.77, 95%CI: -1.33~-0.22)、术后住院时间(WMD=-0.45, 95%CI: -0.80~-0.11)比较,差异均具有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。发表国家这一因素可能是术后总体并发症发生率亚组间异质性的来源之一(P<0.05)。 结论 达芬奇机器人手术系统相较于传统LPD,可降低术后出血率、术中出血量、中转开腹率,缩短术后住院时间,且不增加手术时间和术后总体并发症发生率,两种手术方式均同样安全可行。 -
关键词:
- 胰十二指肠切除术 /
- 机器人手术 /
- 腹腔镜 /
- Meta分析(主题)
Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the short-term efficacy and safety of robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy (RPD) versus traditional laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy (LPD), and to provide a reference for clinical research and practice. Methods Chinese and English databases such as PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, CNKI, Wanfang Data, and VIP were searched to include the cohort studies comparing the clinical efficacy of robot-assisted laparoscopy and traditional laparoscopy in pancreaticoduodenectomy. The quality of included articles was evaluated based on Cochrane systematic review, and Stata15.1 software was used to perform a meta-analysis of related outcome measures extracted. Results A total of 12 cohort studies were included, with 1630 patients in total, and there were 683 patients in the RPD group and 947 patients in the LPD group. The meta-analysis showed that there were significant differences between the RPD group and the LPD group in postoperative bleeding rate (odds ratio [OR]=0.66, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.48-0.91, P < 0.05), rate of conversion to laparotomy (OR=0.41, 95%CI: 0.30-0.56, P < 0.05), estimated intraoperative blood loss (weighted mean difference [WMD]=-0.77, 95%CI: -1.33 to -0.22, P < 0.05), and length of postoperative hospital stay (WMD=-0.45, 95%CI: -0.80 to -0.11, P < 0.05). Country of publication might be one of the sources of heterogeneity in the incidence rate of postoperative complications between subgroups (P < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with traditional LPD, da Vinci RPD can reduce postoperative bleeding rate, intraoperative blood loss and rate of conversion to laparotomy and shorten postoperative hospital stay, and meanwhile, it does not increase the operation time and the incidence rate of postoperative complications. Both surgical procedures are safe and feasible. -
表 1 纳入文献基本特征
Table 1. Including the basic characteristics of the literature
作者 年份 国家 样本量 研究类型 RPD组(例) LPD组(例) Daouadi[14] 2013 美国 124 回顾性队列研究 30 94 Duran[4] 2014 西班牙 34 回顾性队列研究 16 18 Chen[5] 2015 中国 119 回顾性队列研究 69 50 Lai[6] 2015 中国 35 回顾性队列研究 17 18 Liu[7] 2017 中国 52 回顾性队列研究 27 25 Nassour[8] 2017 美国 428 回顾性队列研究 193 235 Zhang[9] 2018 中国 40 回顾性队列研究 20 20 Zimmerman[10] 2019 美国 491 回顾性队列研究 211 280 Tu[11] 2020 中国 61 回顾性队列研究 24 37 Butturini[12] 2014 意大利 43 前瞻性队列研究 22 21 Lee[13] 2015 美国 168 前瞻性队列研究 37 131 Waters[15] 2010 美国 35 前瞻性队列研究 17 18 表 2 纳入文献质量评价
Table 2. Including literature quality evaluation
作者 年份 国家 对象的选择 可比性 结局评估 得分 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Daouadi[14] 2013 美国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Duran[4] 2014 西班牙 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ _ 7 Chen[5] 2015 中国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Lai[6] 2015 中国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ _ 7 Liu[7] 2017 中国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ _ 7 Nassour[8] 2017 美国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Zhang[9] 2018 中国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Zimmerman[10] 2019 美国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Tu[11] 2020 中国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Butturini[12] 2014 意大利 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Lee[13] 2015 美国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 Waters[15] 2010 美国 ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ ★ 8 表 3 亚组分析
Table 3. Subgroup analysis
纳入指标 中国 其他国家 P值 合并效应值 95%CI 合并效应值 95%CI 中转开腹率 0.16 0.02~1.25 0.14 0.31~0.58 0.10 术后总体并发症发生率 0.55 0.31~0.97 1.24 0.97~1.57 0.01 术后胰漏 0.74 0.42~1.30 1.13 0.85~1.51 0.18 术后出血率 0.37 0.14~0.98 0.71 0.51~1.00 0.21 术后胃瘫 0.46 0.08~2.80 0.82 0.57~1.16 0.54 保脾率 3.52 1.23~10.05 1.49 0.42~5.29 0.31 手术时间 0.38 -0.85~1.62 0.19 -0.19~0.58 0.77 术后住院时间 -0.77 -1.38~-0.16 -0.12 -0.39~0.16 0.06 预估手术出血量 -0.99 -1.61~-0.36 -0.2 -0.72~0.32 0.06 淋巴结清扫 1.27 -1.07~3.60 0.43 -0.30~1.16 0.50 注:P为亚组间的异质性。 -
[1] GAGNER M, POMP A, et al. Laparoscopic pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy[J]. Surg Endosc, 1994, 8(5): 408-410. DOI: 10.1007/bf00642443. [2] GIULIANOTTI PC, CORATTI A, ANGELINI M, et al. Robotics in general surgery: Personal experience in a large community hospital[J]. Arch Surg, 2003, 138(7): 777-784. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.138.7.777. [3] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9): 603-605. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z. [4] DURAN H, IELPO B, CARUSO R, et al. Does robotic distal pancreatectomy surgery offer similar results as laparoscopic and open approach? A comparative study from a single medical center[J]. Int J Med Robot, 2014, 10(3): 280-285. DOI: 10.1002/rcs.1569. [5] CHEN S, ZHAN Q, CHEN JZ, et al. Robotic approach improves spleen-preserving rate and shortens postoperative hospital stay of laparosc opic distal pancreatectomy: A matched cohort study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2015, 29(12): 3507-3518. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-015-4101-5. [6] LAI EC, TANG CN. Robotic distal pancreatectomy versus conventional laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy: A comparative study for short-term outcomes[J]. Front Med, 2015, 9(3): 356-360. DOI: 10.1007/s11684-015-0404-0. [7] LIU R, ZHANG T, ZHAO ZM, et al. The surgical outcomes of robot-assisted laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy versus laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy for periampullary neoplasms: A comparative study of a single center[J]. Surg Endosc, 2017, 31(6): 2380-2386. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-016-5238-6. [8] NASSOUR I, WANG SC, POREMBKA MR, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: A nsqip analysis[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2017, 21(11): 1784-1792. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-017-3543-6. [9] ZHANG Y, HONG D, ZHANG C, et al. Total laparoscopic versus robot-assisted laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Biosci Trends, 2018, 12(5): 484-490. DOI: 10.5582/bst.2018.01236. [10] ZIMMERMAN AM, ROYE DG, CHARPENTIER KP. A comparison of outcomes between open, laparoscopic and robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2018, 20(4): 364-369. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2017.10.008. [11] TU GP, SUN JC, NIE WP, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of robotic-assisted versus laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer[J]. Chin J Gen Surg, 2020, 3(29): 269-275. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.03.003.涂广平, 孙吉春, 聂晚频, 等. 机器人辅助与腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除术治疗胰腺癌的效果与安全性比较[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2020, 3(29): 269-275. DOI: 10.7659/j.issn.1005-6947.2020.03.003. [12] BUTTURINI G, DAMOLI I, CREPAZ L, et al. A prospective non-randomised single-center study comparing laparoscopic and robotic distal pancreatec tomy[J]. Surg Endosc, 2015, 29(11): 3163-3170. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-014-4043-3. [13] LEE SY, ALLEN PJ, SADOT E, et al. Distal pancreatectomy: A single institution's experience in open, laparoscopic, and robotic approaches[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2015, 220(1): 18-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.10.004. [14] DAOUADI M, ZUREIKAT AH, ZENATI MS, et al. Robot-assisted minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is superior to the laparoscopic technique[J]. Ann Surg, 2013, 257(1): 128-132. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31825fff08. [15] WATERS JA, CANAL DF, WIEBKE EA, et al. Robotic distal pancreatectomy: Cost effective?[J]. Surgery, 2010, 148(4): 814-823. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2010.07.027. [16] ZHANG C, AN L, WANG Y, et al, Impact of different operative approaches for laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy on short-term treatment outcomes[J]. Chin J Hepatobiliary Surg, 2020, 4(26): 286-289. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113884-20190926-00318.张成, 安琳, 王羊, 等. 腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除不同手术入路的近期疗效[J]. 中华肝胆外科杂志, 2020, 4(26) : 286-289. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113884-20190926-00318. [17] ALIP S, KOUKOURIKIS P, HAN WK, et al. Comparing revo-i and da vinci in retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: A preliminary propensity score analysis of outcomes[J]. J Endourol, 2022, 36(1): 104-110. DOI: 10.1089/end.2021.0421. [18] WU CJ, CHEN HH, CHENG PW, et al. Outcome of robot-assisted bilateral internal mammary artery grafting via left pleura in coronary bypa ss surgery[J]. J Clin Med, 2019, 8(4): 502. DOI: 10.3390/jcm8040502. [19] GAVRIILIDIS P, LIM C, MENAHEM B, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy-the first meta-analysis[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2016, 18(7): 567-574. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2016.04.008. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 程玉鑫,刘亮,董适毓,李胜超,张萌. 外泌体蛋白、mRNA及非编码RNA调节肝癌发生和发展的研究进展. 实用医学杂志. 2024(06): 748-755 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 王玲,曹信宇,商伟芳,丁秀婷. 慢性乙型肝炎患者外泌体miR-335-5p与肝硬化严重程度的相关性. 中国热带医学. 2024(03): 326-332 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 窦金萍,高维崧,韦双,高新桃,李轶女. 外泌体MicroRNA在抗病毒免疫中的功能分析. 生物技术通报. 2024(05): 48-57 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3979 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3979 KB)


 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术

