急性胰腺炎发生急性肾损伤的早期预测指标
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.046
-
摘要: 急性胰腺炎(AP)是消化系统常见的急腹症之一,尽早治疗避免加重至重症急性胰腺炎(SAP)是保证预后的关键,AP合并急性肾损伤(AKI),使胰腺炎死亡率显著增加。早诊断AP并发AKI,是降低病死率的重中之重。本文综述了现有关于AP发生AKI早期预测指标的相关研究,相互比较,简述了中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比率、胱抑素C、肾血管阻力指数、中性粒细胞明胶酶相关性脂质运载蛋白等常用指标以及其他有价值的指标,认为依据不同标志物的敏感度和特异度,多标志物联合诊断AP早期AKI是一大前景。
-
关键词:
- 胰腺炎, 急性坏死性 /
- 急性肾损伤 /
- 炎症 /
- 早期诊断
Abstract: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is one of the common acute abdominal diseases of the digestive system, and early treatment to avoid aggravation to severe pancreatitis (SAP) is the key to guaranteeing prognosis. AP with acute kidney injury (AKI) can significantly increase the mortality rate of pancreatitis. Early diagnosis of AP with AKI is a top priority to reduce mortality rate. This article reviews the current studies on the early predictors for AKI in AP and briefly describes commonly used indicators (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, cystatin C, renal vascular resistance index, and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) and other valuable indicators. It is pointed out that a combination of various markers based on their sensitivity and specificity has a promising future in the diagnosis of AKI in AP.-
Key words:
- Pancreatitis, Acute Necrotizing /
- Acute Kidney Injury /
- Inflammation /
- Early Diagnosis
-
肝组织病理学检查是疑难肝病诊治的关键技术,获得肝组织的活检方法常规为经皮肝穿刺活检(percutaneous liver biopsy, PLB),此外,在一些特殊患者中,还可以通过经颈静脉肝穿刺活检(transjugular liver biopsy, TJLB)、腹腔镜下肝活检等方式获得。对于凝血机制障碍或肝硬化腹水患者,TJLB是一种更安全的选择[1]。本研究拟通过对实施TJLB患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,探讨TJLB在疑难重症肝病诊治中的应用。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
收集2016年1月-2021年5月在本院实施TJLB患者的临床资料。所有患者在入院后行血常规、凝血酶原活动度(PTA)、国际标准化比值(INR)、肝脏生化指标、肝炎病毒学指标等化验,行肝胆脾彩超或CT/MRI检查。所有患者因肝衰竭或肝硬化合并腹水不宜行PLB检查,符合TJLB适应证[2-3]。
1.2 仪器与设备
LABS-200肝内穿刺活检针套装购自美国Cook公司; Fogarty 5.5F球囊导管购自美国爱德华公司; 10F血管鞘组、0.035inch-183超滑导丝、Terumo 5F导管购自日本Terumo公司; 心电测压仪购自美国飞利浦公司。
1.3 TJLB检测过程
术前充分询问病史,排除既往心脏病史患者,仔细阅览患者影像资料,确认肝静脉及下腔静脉无明显狭窄或阻塞。告知患者手术适应证及可能风险,签署知情同意书。按照TJLB标准操作流程实施肝穿刺[2, 4],并行肝静脉压力梯度测定。每次穿刺后观察组织标本完整程度,必要时反复穿刺,直至获取到满意组织标本。术中均行心电监护。所有肝穿刺标本直接放入4%甲醛溶液中,送至病理科进行组织病理检查。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入31例患者,男15例,女16例,中位年龄44(22~74)岁。其中8例因肝衰竭凝血机制障碍、13例因肝硬化合并腹水、10例因肝硬化合并血小板减少(<50×109/L)不宜行PLB,符合实施TJLB适应证。相关化验指标见表 1。
表 1 患者相关化验指标指标 数值 Alb(g/L) 33.00(28.00~37.00) ALT(U/L) 33.00(18.00~63.00) AST(U/L) 49.00(35.00~140.00) ALP(U/L) 149.00(84.00~266.00) GGT(U/L) 98.00(27.00~156.00) TBil(μmol/L) 57.30(18.10~164.60) PTA(%) 52.90(42.90~70.60) INR 1.37(1.13~1.58) WBC(×109/L) 3.38(2.14~5.30) Hb(g/L) 105.00(93.00~124.00) PLT(×109/L) 68.00(47.00~118.00) 注:数据描述方式为M (P25~P75)。 2.2 行TJLB的情况
30例患者顺利实施TJLB,1例因肝静脉与下腔静脉夹角过小,穿刺进针阻力较大,击发困难,手术时间延长。穿刺针次为2~4次不等,获取肝组织2~4条,其中最长单条长度为20 mm,满足完整汇管区数量>6个的病理检测要求[5]。术中患者疼痛表现,按长海痛尺评分,5分以下的15例(48.39%),5~8分16例(51.61%),无高于8分或不可耐受患者。术中一过性心律失常8例(25.81%)。所有患者给予肝穿刺术后常规护理,监测生命体征及血氧饱和度未见异常。术后复查血常规、凝血、生化指标与术前相比没有明显变化。术后穿刺部位无瘀斑、血肿情况发生,肝区不适5例(16.13%),一周内均可自行恢复。
22例(70.97%)患者在穿刺前进行肝静脉压力梯度测定,肝静脉楔压为15.0~52.8 cmH2O,肝静脉自由压为7.0~23 cmH2O,计算肝静脉压力梯度(hepatic venous pressure gradient,HVPG)为8.2~34.3 cmH2O。
2.3 疾病诊断情况
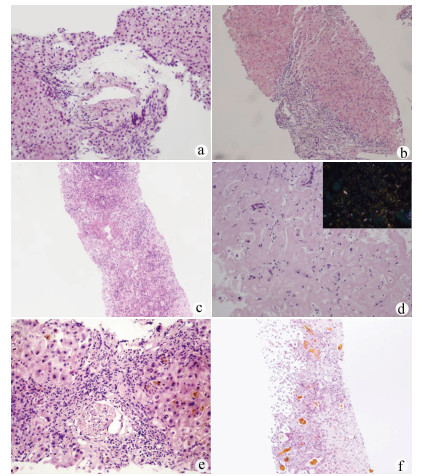
在肝穿刺病理诊断辅助下,患者出院明确诊断26例(83.87%),其中特发性门静脉高压(idiopathic portal hypertension,IPH)5例,代表病例1:女,39岁,入院诊断“门静脉高压、腹水”(图 1a),结合临床诊断IPH。药物性肝衰竭或肝硬化9例,代表病例2:男,34岁,入院诊断“肝硬化失代偿期”(图 1b),结合临床诊断药物性肝衰竭肝损伤。自身免疫性肝脏疾病包括原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)、自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)、重叠综合征,以及小胆管型原发性硬化性胆管炎(PSC)共5例,代表病例3:女,33岁,入院诊断“乙型肝炎肝衰竭”(图 1c),结合临床诊断AIH慢加急性肝衰竭、乙型肝炎肝硬化。其他原因肝硬化或肝衰竭患者7例,包括肝豆状核变性1例、甲状腺功能减退相关肝硬化1例、肝淀粉样变2例、阻塞性胆管炎1例、酒精性肝衰竭合并溶血性疾病1例,辅助排除肝脏肿瘤1例,代表病例4:男,74岁,入院诊断“肝硬化,布加综合征?”(图 1d),结合临床诊断肝淀粉样变性。尚不能明确病因患者5例(16.13%),代表病例5:男,72岁,入院诊断“肝功能异常,原因待查,腹水”,无明确药物应用史(图 1e)。病理会诊不能明确病因,治疗无效。临床诊断不明原因肝衰竭。此外,为证实诊断及决策是否肝移植患者3例,代表病例6:男,23岁,入院诊断“急性肝衰竭”。结合临床诊断急性药物性肝衰竭,3次人工肝治疗,病情无好转拟行肝移植,肝穿刺后结合病理结果决定保守治疗(图 1f),后经治疗病情好转。
3. 讨论
临床工作中约有20%的肝衰竭或肝硬化患者由于凝血机制障碍或腹水不能实施经PLB获取肝组织行病理检查[6],从而影响疾病的诊治。全球范围内不明原因肝衰竭的占比为10%~50%[7-8]。随着我国人民生活水平的提高,乙型肝炎肝衰竭占比逐年下降,不明原因肝衰竭的占比呈逐年升高趋势,迫切需要病理检查辅助提高疑难重症肝病的确诊率。TJLB因其可克服出血的优势,提供了重症肝病患者病理检测手段。
本研究纳入的31例患者中5例明确诊断IPH。IPH的发病机制目前未完全清楚,缺乏特异的检测指标,临床诊断较困难,肝活检对于IPH的诊断尤为重要[9-11]。IPH患者一般以肝硬化致门静脉高压合并腹水、消化道出血等起病,失去实施PLB时机,而临床无病理检查诊断较为困难。该组患者16.13%明确诊断为IPH,提示TJLB为隐源性肝硬化患者中IPH的诊断提供了重要手段。药物性肝炎诊断中,肝脏病理检查并不是必要条件,但需要排除其他疾病,特别是需与自身免疫性肝病进行鉴别,而非典型AIH的诊断,肝脏病理检查是必需的[12],因此对于药物性肝损伤的患者病理检查有时格外重要。该组9例患者经病理协助明确诊断药物性肝炎(29.03%),为后续治疗提供帮助。非典型自身免疫性肝脏疾病包括PBC、AIH、重叠综合征、PSC等,这类疾病的诊断依赖病理检查,同时,相关重症患者是否启用激素治疗是救治成功的关键,而激素治疗方案的制订需要病理辅助。该组患者协助明确诊断2例非典型PBC、2例非典型AIH及1例小胆管型PSC,并指导治疗获得较好的临床疗效。肝衰竭的早期精准预后相当重要,特别是指导选择内科保守治疗还是肝移植方面对患者尤为关键,且肝移植的时机也是术后良好恢复的重要参考指标。虽然临床上有较多的模型及指标进行预后判定,但肝脏病理在肝衰竭精准预后方面发挥重要作用,该组患者经过检查有3例患者改变了治疗方式的选择,精准指导肝移植治疗方案的制定。另外,通过肝穿刺病理检查可协助肝硬化晚期或肝衰竭患者确诊罕见病例,包括肝豆状核变性、甲状腺功能减退相关肝硬化、肝淀粉样变性等。
TJLB在获取肝组织行病理检查协助诊断的同时,可进行HVPG测定,获得血液动力学参数,对于确定是否存在门静脉高压,以及属于窦前、窦性、窦后哪一种类型,有较好的提示意义[13]。本组患者进行HVPG测量对门静脉高压的诊断起到了辅助作用,但HVPG的测量受体位、管路、肝内分流、导管位置等因素影响[14],测量数据可能欠精确,因此测量数值偏差较大,在今后的扩大研究中应注意对同类患者探索对应的分级标准,以便更好的协助诊断和评估预后。
病理检查在评价肝脏病理严重程度方面较为精准,在医学诊断中俗有“金标准”的地位[15],但是在病因确认方面尚有一定的局限性。一方面缘于病理损害缺乏特征性改变,对于某些肝硬化患者,肝组织病理检查可明确肝纤维化及肝脏炎症程度,但可能无法观察到疾病典型病理特征,不能提出明确的临床诊断。另一方面可能与临床医师及病理医师的知识面不够全面有关。有时肝组织病理检查只是起到排除诊断和提供诊断线索的作用,因此,病理检查只是提供诊断依据的辅助手段,而非临床最终诊断。疑难肝病的诊断需要临床医师具有全面的医学知识和丰富的临床经验,提供病理科医师更全面的信息,并结合其他检查方法,如骨髓穿刺、基因检测、血管成像等才能最终明确。TJLB费用相对较高,且也许不能获得良好预期,临床医师应严格掌握适应证,避免医疗纠纷。
该组患者肝组织获取成功率为100%,无明显不良反应,且获取肝组织基本符合病理检测要求,提示TJLB手术成功率较高。据文献[16-17]报道,仍有少数患者组织获取质量欠佳。一方面,实施TJLB的患者部分为肝衰竭患者,肝组织炎症水肿明显,获取肝组织过程中容易破碎; 另一方面,部分为肝硬化患者,肝组织纤维化严重,获取肝组织时受纤维组织的牵拉,组织容易断裂,获取的肝组织有时难以达到病理检测的要求,影响病理医师的判定,因此术中应注意观察获取的组织质量,必要时需反复穿刺。
TJLB为肝硬化合并腹水、肝衰竭及凝血机制障碍的肝病患者提供了肝组织获取的方法,同时可进行HVPG测定,对协助疑难重症肝病诊断及评估预后发挥重要作用,但尚有一定局限性,临床上应注意筛选适宜患者实施。
-
[1] ZHENG X, HE WH, LYU NH. International reseach progress on acute pancreatitis in 2018[J]. Chin J Pancreatol, 2019, 19(4): 241-244. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.04.001.郑西, 何文华, 吕农华. 2018年国际急性胰腺炎研究进展[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2019, 19(4): 241-244. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2019.04.001. [2] Pancreas Study Group, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Pancreatology, Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Digestion. Chinese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis (Shenyang, 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.013.中华医学会消化病学分会胰腺疾病学组, 《中华胰腺病杂志》编委会, 《中华消化杂志》编委会. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2019年, 沈阳)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2706-2711. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.013. [3] ESCOBAR-ARELLANO R, GURAIEB-BARRAGÁN E, MANSANARES-HERNÁNDEZ A, et al. Sensitivity, specificity and reliability of the POP score vs. APACHE Ⅱ score as predictors of severe acute biliary pancreatitis[J]. Cir Cir, 2019, 87(4): 402-409. DOI: 10.24875/CIRU.18000662. [4] NASSAR TI, QUNIBI WY. AKI associated with acute pancreatitis[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 14(7): 1106-1115. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.13191118. [5] ZHENG CM, WANG ZJ, DOU HH. The influence of Shenfu injection on the expression of P38 MAPK protein and inflammatory factors in rats with severe acute pancreatitis complicated with acute renal injury[J]. J Qiqihar Med Coll, 2019, 40(14): 1721-1724. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1256.2019.14.002.郑传明, 王振杰, 窦贺贺. 参附注射液对重症急性胰腺炎大鼠合并急性肾损伤p38 MAPK蛋白表达及其炎性因子的影响[J]. 齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2019, 40(14): 1721-1724. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1256.2019.14.002. [6] SHAO GJ, WANG L, LIU Q, et al. The diagnostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte rate (NLR) in acute pancreatitis related acute kidney injury patients[J]. Chin J Pancreatol, 2016, 16(3): 181-184. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2016.03.009.邵国建, 王雷, 刘琦, 等. 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值在急性胰腺炎并发急性肾损伤患者病情诊断中的价值[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2016, 16(3): 181-184. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2016.03.009. [7] ZHANG ZQ, WEI MB, WANG BY, et al. The predictive value of NLR, RDW and C-reactive protein for acute pancreatitis with severe acute kidney injury[J]. J Clin Nephrol, 2020, 20(11): 891-896. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2020.11.008.张治琴, 魏茂碧, 王白莹, 等. 中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞比值、红细胞分布宽度联合C反应蛋白对急性胰腺炎并发严重急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2020, 20(11): 891-896. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2020.11.008. [8] WU LL, TANG EY, SHI L. The prognostic value of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Modern Practical Medicine, 2018, 30(9): 1149-1150, 1239. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.09.014.伍利利, 唐恩燕, 石亮. 中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值预测急性胰腺炎患者发生急性肾损伤的价值分析[J]. 现代实用医学, 2018, 30(9): 1149-1150, 1239. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2018.09.014. [9] WEI MB, ZHANG ZQ, MA Z, et al. Ratios of neutrophil, lymphocyte and monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in acute pan-creatitis complicated with acute kidney injury[J]. J Clin Nephrol, 2021, 21(1): 1-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.m20-147.魏茂碧, 张治琴, 马洲, 等. 全血细胞计数和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇之比与急性胰腺炎相关急性肾损伤的临床研究[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2021, 21(1): 1-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.m20-147. [10] LIEW FY, GIRARD JP, TURNQUIST HR. Interleukin-33 in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2016, 16(11): 676-689. DOI: 10.1038/nri.2016.95. [11] WANG X, LIANG L, YAO BH. Variations of serum IL-33 and sST2 levels in patients with acute pancreatitis and its clinical significance[J]. J Dalian Med Univ, 2015, 37(6): 537-540. DOI: 10.11724/jdmu.2015.06.05.王欣, 梁鲁, 姚碧辉. 急性胰腺炎患者血清IL-33及sST2水平变化及临床意义[J]. 大连医科大学学报, 2015, 37(6): 537-540. DOI: 10.11724/jdmu.2015.06.05. [12] CHEN WL, DUAN JF, BAI LL, et al. Role of NF-κB, IL-33 and sST2 in acute renal injury following acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Curr Adv Gen Surg, 2018, 21(10): 778-782. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2018.10.005.陈文亮, 段俊芳, 白露露, 等. NF-κB、IL-33及sST2在急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤中的价值研究[J]. 中国现代普通外科进展, 2018, 21(10): 778-782. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9905.2018.10.005. [13] HUANG X, ZHANG LJ, WANG P. Predictive value of serum miR-10a and IL-33 levels in patients with se-vere acute pancreatitis complicated with acute kidney injury[J]. China Med Herald, 2021, 18(4): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202104008.htm黄鲜, 张丽涓, 王平. 血清miR-10a、IL-33水平对重症急性胰腺炎患者并发急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 中国医药导报, 2021, 18(4): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY202104008.htm [14] ZHANG XH, LI ML, WANG B, et al. Caspase-1 inhibition alleviates acute renal injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(30): 10457-10463. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10457. [15] WANG H, CAI ZF, AO DS, et al. Urinary IL-18 and NGAL as early biomarkers of acute kidney injury following adult severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Immunol, 2012, 28(7): 642-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MYXZ201207022.htm王虹, 蔡治方, 敖弟书, 等. 尿IL-18及NGAL在重症急性胰腺炎患者并发急性肾损伤的早期诊断价值[J]. 免疫学杂志, 2012, 28(7): 642-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MYXZ201207022.htm [16] MALMSTRØM ML, HANSEN MB, ANDERSEN AM, et al. Cytokines and organ failure in acute pancreatitis: Inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(2): 271-277. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182240552. [17] PRASADA R, MUKTESH G, SAMANTA J, et al. Natural history and profile of selective cytokines in patients of acute pancreatitis with acute kidney injury[J]. Cytokine, 2020, 133: 155177. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155177. [18] FU CP, HUANG LY, YANG L. Expression of CX3CR1 in acute kidney injury associated with acute pancreatitis in rats[J]. World Chin J Digestol, 2015, 23(10): 1553-1559. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v23.i10.1553.付春萍, 黄李雅, 杨力. CX3CR1在大鼠重症急性胰腺炎继发急性肾损伤中的表达及作用[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2015, 23(10): 1553-1559. DOI: 10.11569/wcjd.v23.i10.1553. [19] TONG Q, HOU YY, TIAN Y, et al. Clinical significance of urinary NGAL, Scr and Cys C in the diagnosis of sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury[J]. Chin J Lab Diag, 201, 25(3): 398-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD202103028.htm佟庆, 侯燕燕, 田颖, 等. 尿NGAL、Scr、Cys C在脓毒血症并发急性肾损伤诊断中的价值研究[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2021, 25(3): 398-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD202103028.htm [20] CHEN YQ, JIANG X, XU H, et al. Value of serum cystatin C in predicting acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(11): 2505-2508. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.021.陈雨晴, 蒋鑫, 徐欢, 等. 血清胱抑素C对急性胰腺炎并发急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(11): 2505-2508. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.021. [21] CHAI X, HUANG HB, FENG G, et al. Baseline serum cystatin C is a potential predictor for acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Dis Markers, 2018, 2018: 8431219. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8431219. [22] HUANG Y, DON-WAUCHOPE AC. The clinical utility of kidney injury molecule 1 in the prediction, diagnosis and prognosis of acute kidney injury: A systematic review[J]. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets, 2011, 10(4): 260-271. DOI: 10.2174/187152811796117735. [23] KARAGÖZ F, SIT D, KIRANKAYA A, et al. The predictive role of new markers in early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Open J Nephrol, 2020, 10, 254-263. DOI: 10.4236/ojneph.2020.103025. [24] SHAO X, TIAN L, XU W, et al. Diagnostic value of urinary kidney injury molecule 1 for acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(1): e84131. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084131. [25] CHENG XY, WANG L. Predictive value of APACHEⅡ score combined with urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated apolipoprotein in sepsis combined with acute kidney injury[J]. Clin Misdiagn Misther, 2020, 33(6): 57-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2020.06.014.程晓迎, 王磊. APACHEⅡ评分联合尿中性粒细胞明胶酶相关载脂蛋白检测对脓毒症合并急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2020, 33(6): 57-62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2020.06.014. [26] ZHOU HL, FU Y, HUANG YQ. Correlation of plasma lipocalin-2 with inflammation and predictive value of lipocalin-2 for detecting acute kidney injury in acute pancreatitis[J]. West China Med J, 2020, 35(11): 1350-1356. DOI: 10.7507/1002-0179.201910043.周皓岚, 付英, 黄元庆. 血清脂质运载蛋白-2与炎症反应的关系及其对急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 华西医学, 2020, 35(11): 1350-1356. DOI: 10.7507/1002-0179.201910043. [27] CHEN YH, WU YH, YU HM, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin in prediction of acute kidney injury following severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Nephrol, 2018, 18(5): 281-284. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2018.05.006.陈艳红, 吴艳红, 于海明, 等. 中性粒细胞明胶酶相关载脂蛋白在重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤中的意义[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2018, 18(5): 281-284. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2390.2018.05.006. [28] WU S, ZHOU YL, LI ZJ. Predictive value of serum LCN2 and Cys C levels in acute pancreatitis complicated with acute kidney injury[J]. Shandong Med J, 2021, 61(25): 6-9, 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2021.25.002.吴松, 周依林, 李治君. 血清LCN2、Cys C水平对急性胰腺炎并发急性肾损伤的预测价值[J]. 山东医药, 2021, 61(25): 6-9, 22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2021.25.002. [29] ORENES-PIÑERO E, MANZANO-FERNÁNDEZ S, LÑPEZ-CUENCA Á, et al. β-Trace protein: from GFR marker to cardiovascular risk predictor[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2013, 8(5): 873-881. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08870812. [30] WAJDA J, DUMNICKA P, SPOREK M, et al. Does Beta-Trace Protein (BTP) outperform cystatin C as a diagnostic marker of acute kidney injury complicating the early phase of acute pancreatitis?[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(1): 205. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9010205. [31] BLEYER AJ, KMOCH S. Tamm horsfall glycoprotein and uromodulin: It is all about the Tubules![J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 11(1): 6-8. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.12201115. [32] RISCH L, LHOTTA K, MEIER D, et al. The serum uromodulin level is associated with kidney function[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2014, 52(12): 1755-1761. DOI: 10.1515/cclm-2014-0505. [33] WANG YH, WU GK, ZHENG RJ, et al. Clinical significance of serum UMOD on prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Crit Care Med, 2019, 39(10): 958-962. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2019.10.008.王宇涵, 吴贵恺, 郑荣娟, 等. 血清尿调节素在急性胰腺炎早期急性肾损伤患者外周血中的表达及临床意义[J]. 中国急救医学, 2019, 39(10): 958-962. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2019.10.008. [34] Pancreatic Surgery Group, Surgical Society of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis in China (2021)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2021, 20(7): 730-739. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210622-00297.中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2021)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2021, 20(7): 730-739. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20210622-00297. [35] HAITSMA MULIER J, ROZEMEIJER S, RÖTTGERING JG, et al. Renal resistive index as an early predictor and discriminator of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients; A prospective observational cohort study[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(6): e0197967. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197967. [36] WU J, XU ZW, ZHANG H, et al. Clinical study on the early predictive value of renal resistive index in acute kidney injury associated with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin Critical Care Med, 2019, 31(8): 998-1003. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.08.017.武钧, 许志伟, 张泓, 等. 肾血管阻力指数对重症急性胰腺炎相关性急性肾损伤早期预测价值的临床研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2019, 31(8): 998-1003. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.08.017. [37] LV Y, YAO Y, LIU Q, et al. Accuracy of angiopoietin-2 for predicting organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(2): 300060520986708. DOI: 10.1177/0300060520986708. [38] SPOREK M, DUMNICKA P, GALA-BLADZINSKA A, et al. Angiopoietin-2 is an early indicator of acute pancreatic-renal syndrome in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2016, 2016: 5780903. DOI: 10.1155/2016/5780903. [39] ZHOU HY, NING GH, NIE SL. Early predicting value of procalcitonin levels in severe acute pancreatitis combined with acute kidney injury[J]. J Clin Emerg Call, 2015, 16(2): 106-108. DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2015.02.008.周海洋, 宁果豪, 聂绍良. 降钙素原对重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤早期预测作用的研究[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2015, 16(2): 106-108. DOI: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2015.02.008. [40] HUANG HL, NIE X, CAI B, et al. Procalcitonin levels predict acute kidney injury and prognosis in acute pancreatitis: A prospective study[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e82250. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082250. [41] GUO QH, LI ZZ, ZHOU W, et al. Renal vascular resistance index combined with procalcitonin in predicting acute renal injury in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. J Hepatobil Surg, 2020, 28(1): 56-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2020.01.016.郭庆宏, 李志州, 周威, 等. 肾血管阻力指数联合降钙素原对急性胰腺炎患者发生急性肾损伤预测价值[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2020, 28(1): 56-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4761.2020.01.016. [42] MUNSHI R, JOHNSON A, SIEW ED, et al. MCP-1 gene activation marks acute kidney injury[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 22(1): 165-175. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010060641. [43] YANG YZ, XIANG Y, CHEN M, et al. Clinical significance of dynamic detection for serum levels of MCP-1, TNF-α and IL-8 in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2016, 9(11): 1111-1114. DOI: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2016.09.001. [44] KE GB, LIU Z, XU YY, et al. The diagnostic value of L-FABP and NAG in adult severe acute pancreatitis with acute kidney injury[J]. J Modern Clin Med, 2015, 41(4): 263-264, 267. DOI: 10.11851/j.issn.1673-1557.2015.04.008.柯贵宝, 刘哲, 徐云滢, 等. L-FABP和NAG在重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤中的早期诊断价值[J]. 现代临床医学, 2015, 41(4): 263-264, 267. DOI: 10.11851/j.issn.1673-1557.2015.04.008. [45] YUE YL, CHEN SS, HAN B. The value of ALR and β2-MG combined with Scr in early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis and acute kidney injury[J]. J Guangxi Med Univ, 2019, 36(8): 1309-1313. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2019.08.021.岳英丽, 陈珊珊, 韩斌. ALR、β2-MG联合Scr对重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤的早期预测价值[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2019, 36(8): 1309-1313. DOI: 10.16190/j.cnki.45-1211/r.2019.08.021. [46] ZHANG W, ZHANG L, CHEN YX, et al. Identification of nestin as a urinary biomarker for acute kidney injury[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2014, 39(2): 110-121. DOI: 10.1159/000358260. [47] MORALES-BUENROSTRO LE, SALAS-NOLASCO OI, BARRERA-CHIMAL J, et al. Hsp72 is a novel biomarker to predict acute kidney injury in critically ill patients[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e109407. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109407. [48] WANG B, JIANG Q, WU X. Association of D-dimers with acute kidney injury in pregnant women: A retrospective study[J]. J Int Med Res, 2020, 48(11): 300060520966899. DOI: 10.1177/0300060520966899. [49] ZHOU X, ZHAO KL, YANG B, et al. The study in the level of 1α-hydroxylase in kidney tissue and the variation of serum calcium in rats with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Chin J Emerg Med, 2014, 23(10): 1088-1092. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2014.10.005.周星, 赵凯亮, 杨波, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎大鼠肾脏1α-羟化酶表达与血钙变化的研究[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2014, 23(10): 1088-1092. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2014.10.005. [50] MOHAMED W, ASIMAKOPOULOS G. Preoperative C-reactive protein as a predictor of postoperative acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting[J]. Perfusion, 2021, 36(4): 330-337. DOI: 10.1177/0267659120947684. [51] LYU YC, YAO YH, LEI JJ, et al. Value of soluble fms-like tyrosine 1 in early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2020, 28(14): 594-604. DOI: 10.11569/WCJDv28.I14.594.吕永才, 姚燕华, 雷静静, 等. 可溶性fms样酪氨酸激酶-1与急性胰腺炎早期严重程度预测价值的系统评价和meta分析[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2020, 28(14): 594-604. DOI: 10.11569/WCJDv28.I14.594. [52] LI H, LIU J, WANG W, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 and vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein related to acute kidney injury in severe acute pancreatitis rats[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2015, 60(12): 3647-3655. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-015-3820-8. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 刘继云. 医学防治对HBV携带者子女HBV感染状况的影响研究. 中国实用医药. 2025(04): 107-109 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 周志强,孙星星,李世勇,万里,罗爱林,韩东吉. 新型冠状病毒肺炎流行期间剖宫产术的麻醉管理. 中华麻醉学杂志. 2020(03): 291-295 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1924 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1924 KB)

 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: