小儿巨大肝脏局灶性结节性增生1例报告
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.029
伦理学声明:本例报告已获得患者知情同意。
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:陈诚负责课题设计,资料分析,撰写论文;王俊杰参与收集数据,修改论文;吴涯昆负责拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
-
-
Key words:
- Focal Nodular Hyperplasia /
- Liver Diseases /
- Child
-
-
[1] MAILLETTE de BUY WENNIGER L, TERPSTRA V, BEUERS U. Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatic adenoma: Epidemiology and pathology[J]. Dig Surg, 2010, 27(1): 24-31. DOI: 10.1159/000268404. [2] MARRERO JA, AHN J, RAJENDER REDDY K, et al. ACG clinical guideline: The diagnosis and management of focal liver lesions[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2014, 109(9): 1328-1347; quiz 1348. DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2014.213. [3] MYERS L, AHN J. Focal Nodular hyperplasia and hepatic adenoma: evaluation and management[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2020, 24(3): 389-403. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2020.04.013. [4] CRISTIANO A, DIETRICH A, SPINA JC, et al. Focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatic adenoma: Current diagnosis and management[J]. Updates Surg, 2014, 66(1): 9-21. DOI: 10.1007/s13304-013-0222-3. [5] ZHANG G, WANG M, DUAN F, et al. Transarterial embolization with bleomycin for symptomatic hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2017, 23(1): 66-70. DOI: 10.5152/dir.2016.16061. [6] GE L, ZHAN JH. Progress in etiology, diagnosis and treatment of focal nodular hyperplasia of liver in children[J]. J China Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2018, 23(1): 49-52. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5323.2018.01.012.葛亮, 詹江华. 儿童肝脏局灶性结节性增生的病因机制及诊治进展[J]. 中国小儿血液与肿瘤杂志, 2018, 23(1): 49-52. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5323.2018.01.012. [7] CHEN Y, ZHOU B, SHEN YL, et al. Multi-slice spiral CT and MRI findings and pathological basis of hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia[J]. J Chin Pract Diagn Ther, 2017, 31(12): 1217-1219. DOI: 10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2017.12.021.陈燕, 周碧, 申玉兰, 等. 肝脏局灶性结节增生的多层螺旋CT和MRI表现及病理基础[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2017, 31(12): 1217-1219. DOI: 10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2017.12.021. [8] ZHANG Y, DING H. Lmaging study and clinical progress of focal nodular hyperplasia of liver[J/CD]. Chin J Med Ultrasound(Electronic Edition), 2016, 13(4): 245-248. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2016.04.002.张悦, 丁红. 肝脏局灶性结节性增生的影像学研究及临床新进展[J/CD]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2016, 13(4): 245-248. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1672-6448.2016.04.002. [9] GIAMBELLUCA D, TAIBBI A, MIDIRI M, et al. The "spoke wheel" sign in hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia[J]. Abdom Radiol (NY), 2019, 44(3): 1183-1184. DOI: 10.1007/s00261-018-1852-1. [10] WANG W, QIE YY, FU CW. Clinical analysis of liver cancer misdiagnosed as focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver[J]. Clin Misdiagn Misther, 2020, 33(4): 18-20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2020.04.005.王伟, 郄言言, 付彩文. 肝癌误诊为肝脏局灶结节性增生临床分析[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2020, 33(4): 18-20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3429.2020.04.005. [11] WANG W, CHEN LD, LU MD, et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound features of histologically proven focal nodular hyperplasia: Diagnostic performance compared with contrast-enhanced CT[J]. Eur Radiol, 2013, 23(9): 2546-2554. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-013-2849-3. [12] YANG XW. Differential value of 64 slice spiral CT in liver carcinoma and focal nodular hyperplasia[J]. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2016, 25(12): 1344-1345, 1350. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.12.033.杨秀文. 64层螺旋CT对肝癌及肝脏局灶性结节增生的鉴别价值[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2016, 25(12): 1344-1345, 1350. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2016.12.033. [13] WU J, JING ZL. Research advances in MRI features and diagnosis of hepatocellular adenomas[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(10): 2012-2015. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.10.045.吴杰, 敬宗林. 各类肝腺瘤磁共振成像特征及诊断的研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(10): 2012-2015. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.10.045. [14] KHANNA M, RAMANATHAN S, FASIH N, et al. Current updates on the molecular genetics and magnetic resonance imaging of focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma[J]. Insights Imaging, 2015, 6(3): 347-362. DOI: 10.1007/s13244-015-0399-8. [15] NAULT JC, BLANC JF, MOGA L, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis and follow-up of benign liver tumours[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2022, 46(1): 101765. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101765. [16] ROWAN DJ, ALLENDE DS, BELLIZZI AM, et al. Diagnostic challenges of focal nodular hyperplasia: interobserver variability, accuracy, and the utility of glutamine synthetase immunohistochemistry[J]. Histopathology, 2021, 79(5): 791-800. DOI: 10.1111/his.14424. [17] SUN J, WANG J. Diagnosis and standardized management of hepatic focal nodular hyperplasia[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2013, 33(9): 742-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201309009.htm孙健, 王捷. 肝脏局灶性结节性增生诊断及规范化治疗[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2013, 33(9): 742-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201309009.htm [18] RAMAI D, OFOSU A, LAI JK, et al. Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma: A population-based observational study[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(1): 308-314. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06135-3. [19] YAO Z, ZENG Q, YU X, et al. Case report: Ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of focal nodular hyperplasia in a 9-year-old girl[J]. Front Pediatr, 2021, 9: 710779. DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.710779. [20] PERRAKIS A, DEMIR R, MVLLER V, et al. Management of the focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver: Evaluation of the surgical treatment comparing with observation only[J]. Am J Surg, 2012, 204(5): 689-696. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2012.02.006. -



 PDF下载 ( 3134 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3134 KB)

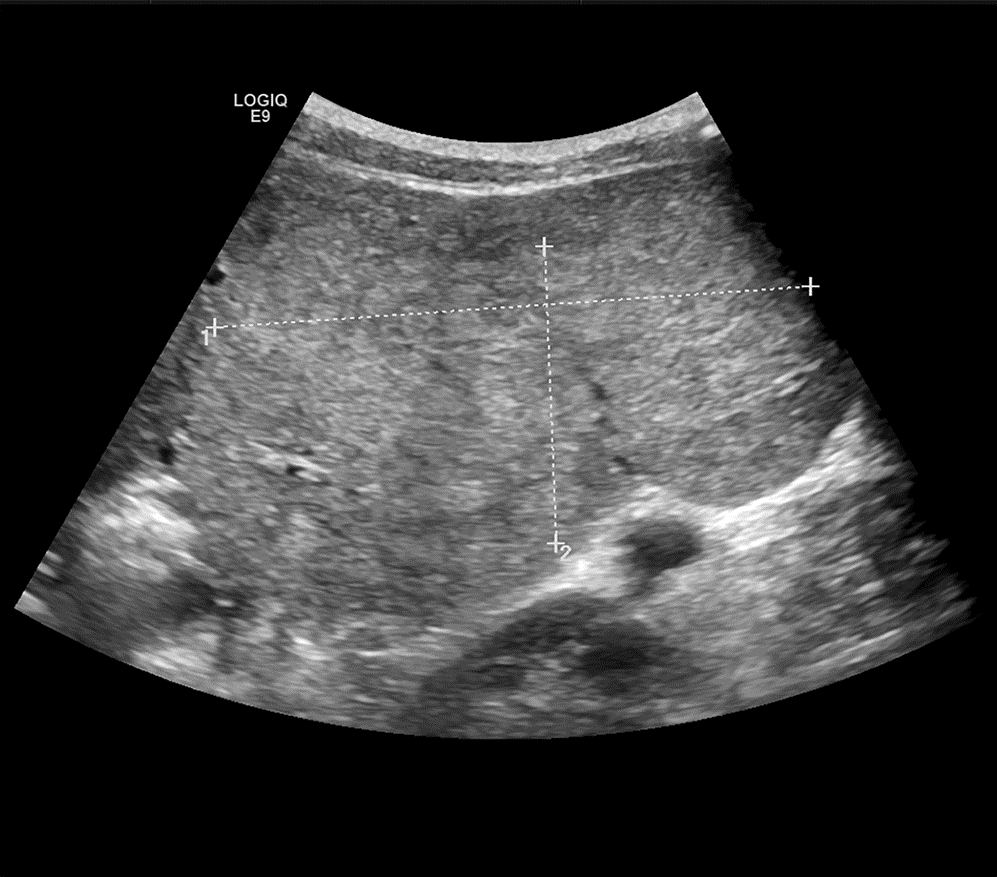
 下载:
下载:







