胰高血糖素样肽1系统与非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治的关系
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.039
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:鲁彤收集文献,撰写初稿;崔泓亮收集文献,撰写并修改论文;徐立负责课题设计,资料分析,拟定写作思路,指导撰写和修改文章并最后定稿。
Association of glucagon-like peptide-1 system with the prevention and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
-
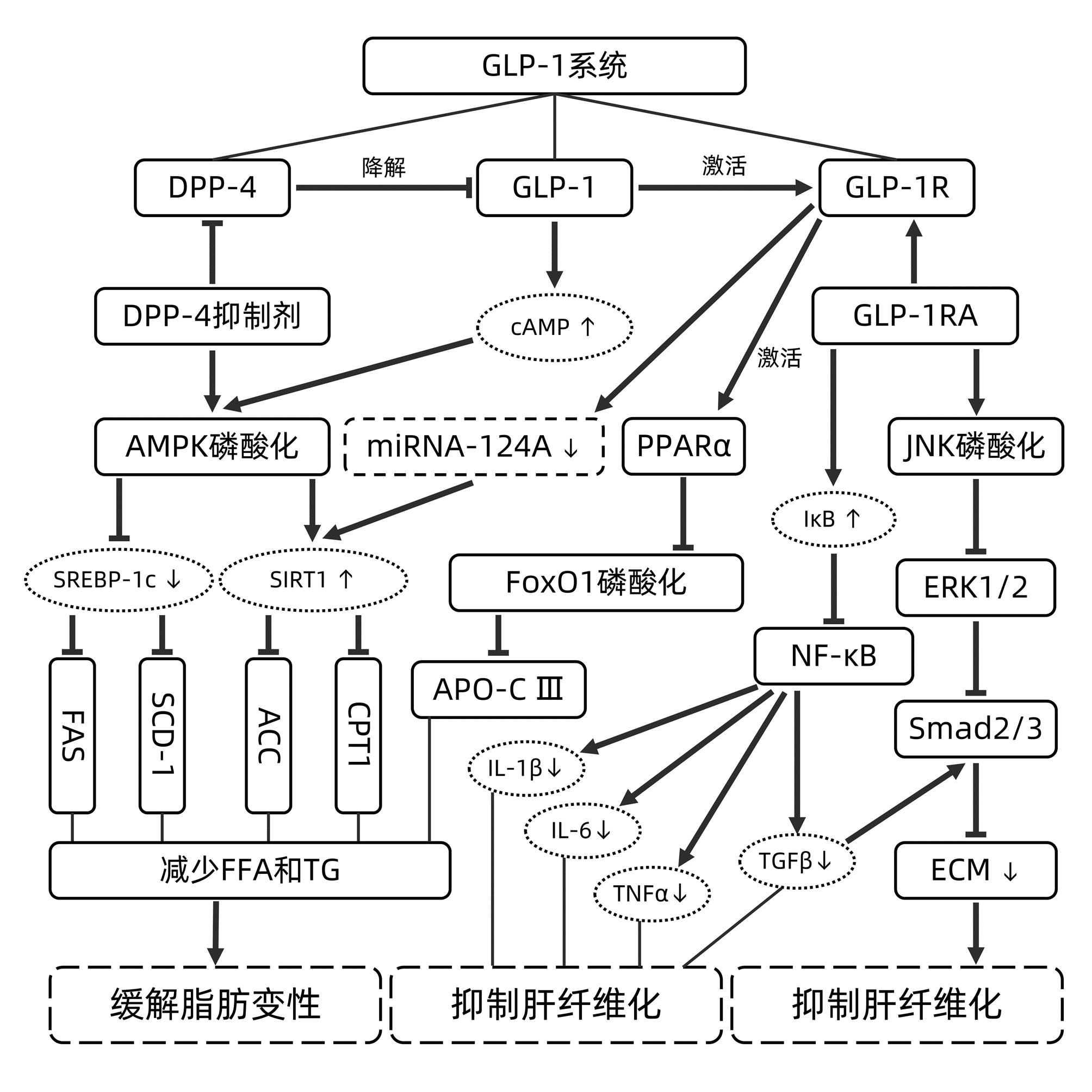
摘要: 非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)的发病人数众多,现已成为严重危害世界人民建康的主要慢性肝病之一。本文介绍了胰高血糖素样肽1(GLP-1)系统中与GLP-1的产生、分解和受体效应相关的主要因素,总结了GLP-1系统对NAFLD的调控机理,提出利用GLP-1系统治疗NAFLD的主要问题,为NAFLD的研究和临床治疗提供参考。Abstract: With a large number of patients, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become one of the major chronic liver diseases that jeopardize the health of people worldwide. This article introduces the major factors in glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) system that are associated with the production, decomposition, and receptor effect of GLP-1, summarizes the regulatory mechanism of GLP-1 system on NAFLD, and proposes the main problems of GLP-1 system in the treatment of NAFLD, so as to provide a reference for the research and clinical treatment of NAFLD.
-
[1] NAKATSUKA T, TATEISHI R, KOIKE K. Changing clinical management of NAFLD in Asia[J]. Liver Int, 2021. DOI: 10.1111/liv.15046.[Online ahead of print] [2] ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702. [3] BESSONE F, RAZORI MV, ROMA MG. Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(1): 99-128. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-018-2947-0. [4] EL-AGROUDY NN, KURZBACH A, RODIONOV RN, et al. Are lifestyle therapies effective for NAFLD treatment?[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 30(10): 701-709. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.07.013. [5] ARMSTRONG MJ, HULL D, GUO K, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(2): 399-408. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.038. [6] ANDERSEN A, LUND A, KNOP FK, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(7): 390-403. DOI: 10.1038/s41574-018-0016-2. [7] FUJIWARA Y, EGUCHI S, MURAYAMA H, et al. Relationship between diet/exercise and pharmacotherapy to enhance the GLP-1 levels in type 2 diabetes[J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, 2019, 2(3): e00068. DOI: 10.1002/edm2.68. [8] SMITH NK, HACKETT TA, GALLI A, et al. GLP-1: Molecular mechanisms and outcomes of a complex signaling system[J]. Neurochem Int, 2019, 128: 94-105. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.010. [9] DEACON CF. Physiology and pharmacology of DPP-4 in glucose homeostasis and the treatment of type 2 diabetes[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2019, 10: 80. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00080. [10] KAMAKURA R, RAZA GS, PRASANNAN A, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and GLP-1 interplay in STC-1 and GLUTag cell lines[J]. Peptides, 2020, 134: 170419. DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170419. [11] VARIN EM, MULVIHILL EE, BAGGIO LL, et al. Distinct neural sites of GLP-1R expression mediate physiological versus pharmacological control of incretin action[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(11): 3371-3384.e3. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.055. [12] MA H, HUANG W, WANG X, et al. Structural insights into the activation of GLP-1R by a small molecule agonist[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(12): 1140-1142. DOI: 10.1038/s41422-020-0384-8. [13] MVLLER TD, FINAN B, BLOOM SR, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1)[J]. Mol Metab, 2019, 30: 72-130. DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2019.09.010. [14] LI S, WANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Exenatide ameliorates hepatic steatosis and attenuates fat mass and FTO gene expression through PI3K signaling pathway in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2018, 51(8): e7299. DOI: 10.1590/1414-431x20187299. [15] LEE J, HONG SW, RHEE EJ, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonist and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Diabetes Metab J, 2012, 36(4): 262-267. DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2012.36.4.262. [16] YU X, HAO M, LIU Y, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis activation via mitophagy[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2019, 864: 172715. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172715. [17] GILBERT MP, PRATLEY RE. GLP-1 analogs and DPP-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes therapy: Review of head-to-head clinical trials[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2020, 11: 178. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00178. [18] TOBITA H, YAZAKI T, KATAOKA M, et al. Comparison of dapagliflozin and teneligliptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients without type 2 diabetes mellitus: A prospective randomized study[J]. J Clin Biochem Nutr, 2021, 68(2): 173-180. DOI: 10.3164/jcbn.20-129. [19] SHIRAKAWA J, FUJII H, OHNUMA K, et al. Diet-induced adipose tissue inflammation and liver steatosis are prevented by DPP-4 inhibition in diabetic mice[J]. Diabetes, 2011, 60(4): 1246-1257. DOI: 10.2337/db10-1338. [20] SHEN T, XU B, LEI T, et al. Sitagliptin reduces insulin resistance and improves rat liver steatosis via the SIRT1/AMPKα pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(4): 3121-3128. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2018.6554. [21] SANTOS FO, CORREIA B, MARINHO TS, et al. Anti-steatotic linagliptin pleiotropic effects encompasses suppression of de novo lipogenesis and ER stress in high-fat-fed mice[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2020, 509: 110804. DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110804. [22] OKUYAMA T, SHIRAKAWA J, TAJIMA K, et al. Linagliptin ameliorates hepatic steatosis via non-canonical mechanisms in mice treated with a dual inhibitor of insulin receptor and IGF-1 receptor[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(21): 7815. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21217815. [23] KAWAGUCHI T, NAKANO D, KOGA H, et al. Effects of a DPP4 inhibitor on progression of NASH-related HCC and the p62/ Keap1/Nrf2-pentose phosphate pathway in a mouse model[J]. Liver Cancer, 2019, 8(5): 359-372. DOI: 10.1159/000491763. [24] RANJBAR G, MIKHAILIDIS DP, SAHEBKAR A. Effects of newer antidiabetic drugs on nonalcoholic fatty liver and steatohepatitis: Think out of the box![J]. Metabolism, 2019, 101: 154001. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154001. [25] LEE M, SHIN E, BAE J, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor protects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice by targeting TRAIL receptor-mediated lipoapoptosis via modulating hepatic dipeptidyl peptidase-4 expression[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 19429. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-75288-y. [26] ZHENG W, ZHOU J, SONG S, et al. Dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitor sitagliptin ameliorates hepatic insulin resistance by modulating inflammation and autophagy in ob/ob mice[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2018, 2018: 8309723. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8309723. [27] WU C, CHEN W, DING H, et al. Salvianolic acid B exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects via inhibition of MAPK-mediated phospho-Smad2/3 at linker regions in vivo and in vitro[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 239: 116881. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116881. [28] KHALIL R, SHATA A, ABD EL-KADER EM, et al. Vildagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by targeting ERK1/2, p38α, and NF-κB signaling[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2020, 407: 115246. DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.115246. [29] PATEL CHAVEZ C, CUSI K, KADIYALA S. The emerging role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of NAFLD[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2022, 107(1): 29-38. DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab578. [30] JIANPING W, XUELIAN Z, ANJIANG W, et al. Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of metabolic associated fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2021, 55(7): 586-593. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001556. [31] LV X, DONG Y, HU L, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review[J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab, 2020, 3(3): e00163. DOI: 10.1002/edm2.163. [32] WANG XC, GUSDON AM, LIU H, et al. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(40): 14821-14830. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14821. [33] VENDRELL J, EL BEKAY R, PERAL B, et al. Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Endocrinology, 2011, 152(11): 4072-4079. DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-1070. [34] FANG QH, SHEN QL, LI JJ, et al. Inhibition of microRNA-124a attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through upregulation of adipose triglyceride lipase and the effect of liraglutide intervention[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49(7): 743-757. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13330. [35] FANG Y, JI L, ZHU C, et al. Liraglutide alleviates hepatic steatosis by activating the TFEB-regulated autophagy-lysosomal pathway[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2020, 8: 602574. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.602574. [36] YANG M, MA X, XUAN X, et al. Liraglutide attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by regulating the local renin-angiotensin system[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 432. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00432. [37] KUCHAY MS, KRISHAN S, MISHRA SK, et al. Effect of dulaglutide on liver fat in patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD: Randomised controlled trial (D-LIFT trial)[J]. Diabetologia, 2020, 63(11): 2434-2445. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-020-05265-7. [38] FENG WH, BI Y, LI P, et al. Effects of liraglutide, metformin and gliclazide on body composition in patients with both type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized trial[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2019, 10(2): 399-407. DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12888. [39] CHRISTOU GA, KATSIKI N, BLUNDELL J, et al. Semaglutide as a promising antiobesity drug[J]. Obes Rev, 2019, 20(6): 805-815. DOI: 10.1111/obr.12839. [40] NEWSOME P, FRANCQUE S, HARRISON S, et al. Effect of semaglutide on liver enzymes and markers of inflammation in subjects with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 50(2): 193-203. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15316. [41] SAAD ZA, KHODEER DM, ZAITONE SA, et al. Exenatide ameliorates experimental non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats via suppression of toll-like receptor 4/NFκB signaling: Comparison to metformin[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 253: 117725. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117725. [42] LUO Y, YANG P, LI Z, et al. Liraglutide improves non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic mice by modulating inflammatory signaling pathways[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 4065-4074. DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S224688. [43] SHAO N, YU XY, MA XF, et al. Exenatide delays the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in C57BL/6 mice, which may involve inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome through the mitophagy pathway[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2018, 2018: 1864307. DOI: 10.1155/2018/1864307. [44] TESHOME G, AMBACHEW S, FASIL A, et al. Efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review[J]. Hepat Med, 2020, 12: 139-151. DOI: 10.2147/HMER.S265631. [45] WU L, LIU Y, SHI L, et al. Promotion of apoptosis in high glucose-activated hepatic stellate cells by GLP-1 receptor agonist and its potential mechanism[J]. Gene Mol Res, 2017, 16(4): gmr16039818. DOI: 10.4238/gmr16039818. [46] HAN X, DING C, ZHANG G, et al. Liraglutide ameliorates obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating Sestrin2-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 525(4): 895-901. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.032. [47] GHADIEH HE, MUTURI HT, NAJJAR SM. Exenatide prevents diet-induced hepatocellular injury in a CEACAM1-dependent mechanism[J]. J Diabetes Treat, 2017, 2017(4): 10.29011/2574.7568.000033. DOI: 10.29011/2574.7568.000033. [48] REED J, KANAMARLAPUDI V. GLP-1. [M]//CHOI S. Encyclopedia of Signaling Molecules. Cham; Springer International Publishing. 2018: 2098-2106. [49] DHIR G, CUSI K. Glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A novel therapeutic option[J]. J Investig Med, 2018, 66(1): 7-10. DOI: 10.1136/jim-2017-000554. [50] RICHARDS P, PARKER HE, ADRIAENSSENS AE, et al. Identification and characterization of GLP-1 receptor-expressing cells using a new transgenic mouse model[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(4): 1224-1233. DOI: 10.2337/db13-1440. [51] CANTINI G, MANNUCCI E, LUCONI M. Perspectives in GLP-1 research: New targets, new receptors[J]. Trends Endocrinol Metab, 2016, 27(6): 427-438. DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2016.03.017. [52] SOFOGIANNI A, FILIPPIDIS A, CHRYSAVGIS L, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An update[J]. World J Hepatol, 2020, 12(8): 493-505. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i8.493. -



 PDF下载 ( 2126 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2126 KB)

 下载:
下载:


