吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶——多种肝病中发挥双刃剑作用的重要介质
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.046
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王宏宾对研究的思路、设计有关键贡献;叶森负责研究内容的获取、分析和解释;付永负责审阅修改文章关键内容。
Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase: An important medium with the role of a double-edged sword in various liver diseases
-
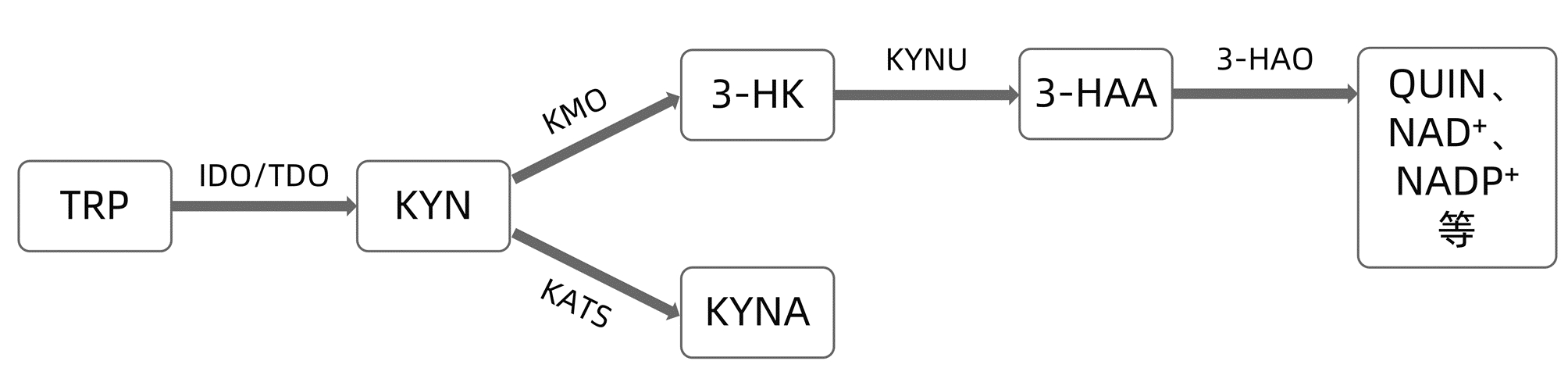
摘要: 吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶(IDO)是一种重要的免疫调节酶,可降解哺乳动物必需氨基酸色氨酸水平,通过犬尿氨酸途径催化起始和限速步骤并产生多种代谢产物参与免疫应答。IDO一方面对微环境发挥免疫抑制作用,导致感染、肿瘤细胞免疫逃逸等;另一方面,对细菌、寄生虫等病原体同样发挥抑制作用,一定程度上保护机体免受病原体的侵害。因此,IDO被认为是在多种肝脏疾病发生发展中具有双刃剑作用的重要介质。本文就IDO在病毒性肝炎、肝纤维化、肝硬化、肝癌、肝棘球蚴病中的最新研究进展作一综述。
-
关键词:
- 肝疾病 /
- 吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶 /
- 免疫系统现象
Abstract: Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) is an important immunoregulatory enzyme, which can degrade the level of the mammalian essential amino acid tryptophan (TRP), catalyze the initiation and rate-limiting steps through the kynurenine pathway, and produce a variety of metabolites to participate in the immune response. On the one hand, IDO plays an immunosuppressive role in microenvironment and thus leads to infection and immune escape of tumor cells; on the other hand, IDO also exerts an inhibitory effect on the pathogens such as bacteria and parasites and thus protects the body from the harm of pathogens to a certain extent. Therefore, IDO is considered an important medium with the role of a double-edged sword in the development and progression of various liver diseases. This article reviews the latest research advances in IDO in viral hepatitis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatic echinococcosis.-
Key words:
- Liver Diseases /
- Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase /
- Immune System Phenomena
-
[1] WANG LJ, MA PY, LIU H, et al. Progress of researches on the involvement of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in regulation of parasite-host immune interactions[J]. Chin J Schisto Control, 2021, 33(2): 209-212, 224. DOI: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020069.王莉君, 马培玉, 刘晖, 等. 吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶参与调控寄生虫与宿主免疫互作关系的研究进展[J]. 中国血吸虫病防治杂志, 2021, 33(2): 209-212, 224. DOI: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2020069. [2] NI XL, HU RH, HE C, et al. Research progress of canine urinary ammonia pathway metabolic enzymes and tumors[J]. J Chongqing Med Univ, 2017, 42(11): 1363-1365. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.001251.倪晓琳, 胡润晖, 贺晨, 等. 犬尿氨酸途径代谢酶与肿瘤的研究进展[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2017, 42(11): 1363-1365. DOI: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.001251. [3] WU H, GONG J, LIU Y. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase regulation of immune response (Review)[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 17(4): 4867-4873. DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8537 [4] WIRTHGEN E, TUCHSCHERER M, OTTEN W, et al. Activation of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase by LPS in a porcine model[J]. Innate Immun, 2014, 20(1): 30-39. DOI: 10.1177/1753425913481252. [5] ITO H, HOSHI M, OHTAKI H, et al. Ability of IDO to attenuate liver injury in alpha-galactosylceramide-induced hepatitis model[J]. J Immunol, 2010, 185(8): 4554-4560. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904173. [6] CERVENKA I, AGUDELO LZ, RUAS JL. Kynurenines: Tryptophan's metabolites in exercise, inflammation, and mental health[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6349): eaaf9794. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf9794. [7] KWON OS, CHOI SH, KIM JH. Inflammation and hepatic fibrosis, then hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2015, 66(6): 320-324. DOI: 10.4166/kjg.2015.66.6.320. [8] CUI FQ. Global elimination of viral hepatitis as a public health threat: Promoting diagnosis and treatment is the key to reducing mortality[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(7): 1522-1524. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.006.崔富强. 全球消除病毒性肝炎的公共卫生威胁: 促进诊断和治疗是降低死亡率的关键[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(7): 1522-1524. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.006. [9] ZHOU Q, SHI Y, CHEN C, et al. A narrative review of the roles of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and tryptophan-2, 3-dioxygenase in liver diseases[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(2): 174. DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-3594. [10] MAO R, ZHANG J, JIANG D, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase mediates the antiviral effect of gamma interferon against hepatitis B virus in human hepatocyte-derived cells[J]. J Virol, 2011, 85(2): 1048-1057. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01998-10. [11] YOSHIO S, SUGIYAMA M, SHOJI H, et al. Indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase as an effector and an indicator of protective immune responses in patients with acute hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63(1): 83-94. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28282. [12] YOSHIO S, KANTO T. Host-virus interactions in hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2016, 51(5): 409-420. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-016-1183-3. [13] MEHRAJ V, ROUTY JP. Tryptophan catabolism in chronic viral infections: Handling uninvited guests[J]. Int J Tryptophan Res, 2015, 8: 41-48. DOI: 10.4137/IJTR.S26862. [14] LEPILLER Q, SOULIER E, LI Q, et al. Antiviral and immunoregulatory effects of indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase in hepatitis C virus infection[J]. J Innate Immun, 2015, 7(5): 530-544. DOI: 10.1159/000375161. [15] HIGASHITANI K, KANTO T, KURODA S, et al. Association of enhanced activity of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in dendritic cells with the induction of regulatory T cells in chronic hepatitis C infection[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2013, 48(5): 660-670. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-012-0667-z. [16] ASGHAR K, ASHIQ MT, ZULFIQAR B, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression and activity in patients with hepatitis C virus- induced liver cirrhosis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 9(3): 901-904. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2014.2146. [17] JALLON JM, RISLER Y, IWATSUBO M. Beef liver L-Glutamate dehydrogenase mechanism: presteady state study of the catalytic reduction of 2. oxoglutarate by NADPH[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1975, 67(4): 1527-1536. DOI: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90200-4. [18] ZHONG W, GAO L, ZHOU Z, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 deficiency attenuates CCl4-induced fibrosis through Th17 cells down-regulation and tryptophan 2, 3-dioxygenase compensation[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(25): 40486-40500. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17119. [19] OGISO H, ITO H, ANDO T, et al. The deficiency of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase aggravates the CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(9): e0162183. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162183. [20] OH JE, SHIM KY, LEE JI, et al. 1-Methyl-L-tryptophan promotes the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells arrested by interferon-γ by increasing the expression of IFN-γRβ, IRF-1 and FAS[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2017, 40(2): 576-582. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3043. [21] MILOSAVLJEVIC N, GAZDIC M, SIMOVIC MARKOVIC B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells attenuate liver fibrosis by suppressing Th17 cells-an experimental study[J]. Transpl Int, 2018, 31(1): 102-115. DOI: 10.1111/tri.13023. [22] LABADIE BW, BAO R, LUKE JJ. Reimagining IDO pathway inhibition in cancer immunotherapy via downstream focus on the tryptophan-kynurenine-aryl hydrocarbon axis[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(5): 1462-1471. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2882. [23] KIM M, TOMEK P. Tryptophan: A rheostat of cancer immune escape mediated by immunosuppressive enzymes IDO1 and TDO[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 636081. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.636081. [24] Chinese Journal of Hepatology, Liver Cancer Study Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of precancerous lesions of hepatocellular carcinoma (2020 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(3): 514-518. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.03.007.《中华肝脏病杂志》编辑委员会, 中华医学会肝病学分会肝癌学组. 肝细胞癌癌前病变的诊断和治疗多学科专家共识(2020版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(3): 514-518. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.03.007. [25] LIN L, YANG DH, HUANG Y, et al. Relationship between the expressions of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in hepatocellular carcinoma and clinicopathological parameters[J]. Natl Med J China, 2013, 93(28): 2186-2190. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2013.28.004.林梁, 杨定华, 黄毓, 等. 吲哚胺2, 3双加氧酶在HCC中的表达与临床病理参数之间的关系[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013, 93(28): 2186-2190. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2013.28.004. [26] YE LY, CHEN W, BAI XL, et al. Hypoxia-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma induces an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment to promote metastasis[J]. Cancer Res, 2016, 76(4): 818-830. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0977. [27] HAN Y, CHEN Z, YANG Y, et al. Human CD14+ CTLA-4+ regulatory dendritic cells suppress T-cell response by cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4-dependent IL-10 and indoleamine-2, 3-dioxygenase production in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 59(2): 567-579. DOI: 10.1002/hep.26694. [28] WANG Y, YAO R, ZHANG L, et al. IDO and intra-tumoral neutrophils were independent prognostic factors for overall survival for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2019, 33(5): e22872. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22872. [29] SHIBATA Y, HARA T, NAGANO J, et al. The role of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in diethylnitrosamine-induced liver carcinogenesis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0146279. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0146279. [30] BROWN ZJ, YU SJ, HEINRICH B, et al. Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase provides adaptive resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 2018, 67(8): 1305-1315. DOI: 10.1007/s00262-018-2190-4. [31] LABADIE BW, BAO R, LUKE JJ. Reimagining IDO pathway inhibition in cancer immunotherapy via downstream focus on the tryptophan-kynurenine- aryl hydrocarbon axis[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 25(5): 1462-1471. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2882. [32] Chinese Doctor Association, Chinese College of Surgeons (CCS). Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of hepatic cystic and alveolar echinococcosis (2019 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2019, 18(8): 711-721. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2019.08.002.中国医师协会外科医师分会包虫病外科专业委员会. 肝两型包虫病诊断与治疗专家共识(2019版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2019, 18(8): 711-721. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2019.08.002. [33] MA JX, DUAN S, TUERGANAILI AJ, et al. Application value of 3D laparoscopy in the treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J/CD]. Chin J Hepat Surg(Electronic Edition), 2020, 9(6): 567-570. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2020.06.015.马建雄, 段帅, 吐尔干艾力·阿吉, 等. 3D腹腔镜在肝泡型包虫病治疗中的应用价值[J/CD]. 中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2020, 9(6): 567-570. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.2095-3232.2020.06.015. [34] SHAN JY, LI HT, LI CY, et al. Experimental study on indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression in dendritic cells induced by different Echinococcus antigens[J]. Chin J Parasitol Parasitic Dis, 2013, 31(3): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSB201303008.htm单骄宇, 李海涛, 李春燕, 等. 不同棘球蚴抗原诱导树突状细胞表达吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶的实验研究[J]. 中国寄生虫学与寄生虫病杂志, 2013, 31(3): 188-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSB201303008.htm [35] SHAN JY, LI HT, XIAO J, et al. Dynamic observation of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase expression in dendritic cells induced by Echinococcus granulosus antigen[J]. J Pathog Biol, 2012, 7(9): 688-692. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.2012.09.014.单骄宇, 李海涛, 肖晋, 等. 细粒棘球蚴抗原诱导树突状细胞表达吲哚胺2, 3-双加氧酶的动态观察[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2012, 7(9): 688-692. DOI: 10.13350/j.cjpb.2012.09.014. [36] FU Y, MENG R, JIANG T, et al. Effect of mouse vesicular hydatid cyst fluid on the expression of IDO in mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells[J]. Chin J Zoonosis, 2018, 34(11): 1001-1005. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2018.00.171.付永, 孟茹, 姜涛, 等. 小鼠泡型包虫囊液对小鼠骨髓来源树突状细胞表达IDO的影响[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2018, 34(11): 1001-1005. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2018.00.171. [37] WANG Y, LV S, WANG Q, et al. Mechanisms underlying immune tolerance caused by recombinant Echinococcus granulosus antigens Eg mMDH and Eg10 in dendritic cells[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(9): e0204868. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204868. -



 PDF下载 ( 1905 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1905 KB)

 下载:
下载:


