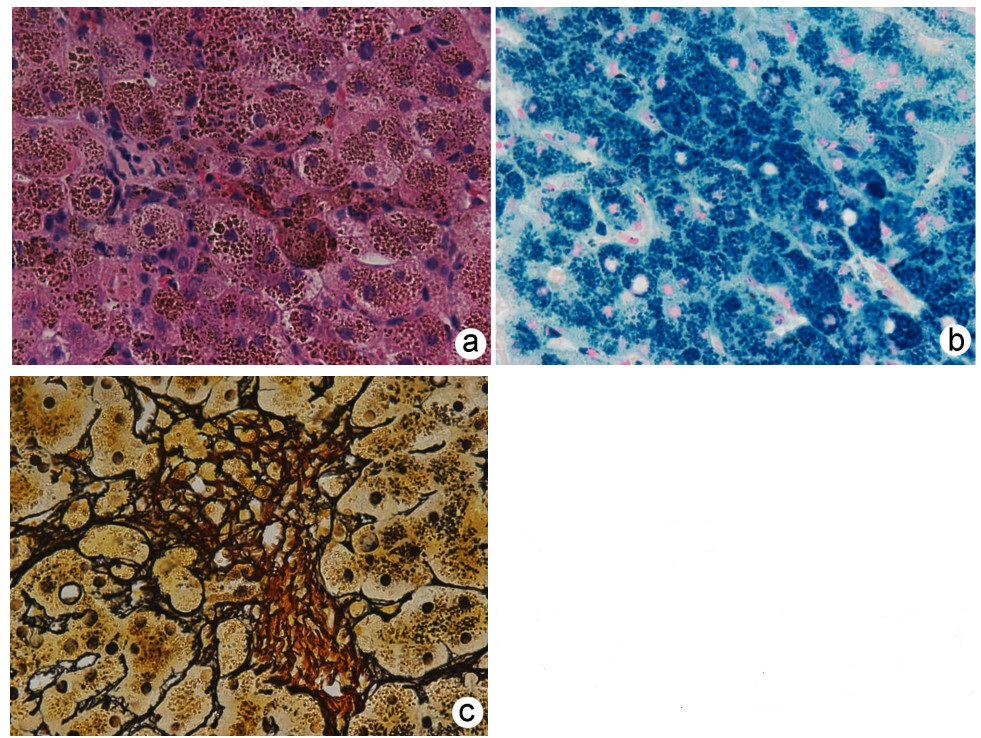
HJV基因突变致多器官损伤的成人遗传性血色病1例报告
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.026
Hereditary hemochromatosis with multiple organ damage caused by HJV gene mutation in adults: A case report
-
-
Key words:
- Hemochromatosis /
- Iron Metabolism Disorders /
- Mutation /
- HJV gene
-
表 1 治疗过程中铁代谢及肝功能指标的变化情况
Table 1. The changes of iron metabolism and liver function indexes during treatment
指标 静脉放血前 静脉放血(50 mL/3 d, 维持1个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持2个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持4个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持5个月) 血清铁(μmol/L) 28.4 31.9 35.7 59.1 63.6 铁蛋白(ng/mL) >2 000.0 >2 000.0 >1 650.0 2 262.0 2 332.0 转铁蛋白饱和度 92.5% 96.7% 89.7% 80.0% 80.0% 血红蛋白(g/L) 125 119 159 118 135 ALT(U/L) 26 23 49 60 51 AST(U/L) 46 70 50 56 48 指标 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持6个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持7个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持8个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持9个月) 静脉放血(500 mL/周, 维持10个月) 血清铁(μmol/L) 49.0 41.6 51.1 43.4 31.9 铁蛋白(ng/mL) 1 401.0 1 238.4 828.7 630.7 276.3 转铁蛋白饱和度 66.0% 95.0% 95.0% 95.0% 69.3% 血红蛋白(g/L) 119 125 146 130 124 ALT(U/L) 46 35 46 32 31 AST(U/L) 44 30 44 27 24 -
[1] GOLFEYZ S, LEWIS S, WEISBERG IS. Hemochromatosis: pathophysiology, evaluation, and management of hepatic iron overload with a focus on MRI[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 12(8): 767-778. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2018.1496016. [2] KOWDLEY KV, BROWN KE, AHN J, et al. ACG clinical guideline: Hereditary hemochromatosis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2019, 114(8): 1202-1218. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000315. [3] GUO RM, TANG WJ, ZHU YQ, et al. Diagnostic value of MRI IDEAL-IQ sequence to hepatic steatosis and hepatic iron-overloaded[J]. J SUN Yat-sen Univ(Med Sci), 2015, 36(5): 689-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSYK201505008.htm郭若汨, 唐文杰, 朱叶青, 等. 磁共振IDEAL-IQ序列对肝脏脂肪变性和铁过载的诊断价值[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2015, 36(5): 689-692. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSYK201505008.htm [4] WANG XL. CT and MRI manifestations of hemochromatosis[J]. J Imag Res Med Appl, 2019, 3(15): 57-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYY201915030.htm王秀兰. 血色病的CT及MRI表现[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2019, 3(15): 57-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXYY201915030.htm [5] MILMAN NT. Managing genetic hemochromatosis: An overview of dietary measures, which may reduce intestinal iron absorption in persons with iron overload[J]. Gastroenterology Res, 2021, 14(2): 66-80. DOI: 10.14740/gr1366. [6] LIMA TG, BENEVIDES F, ESMERALDO FILHO FL, et al. Treatment of iron overload syndrome: a general review[J]. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992), 2019, 65(9): 1216-1222. DOI: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.9.1216. [7] NIEDERAU C, FISCHER R, SONNENBERG A, et al. Survival and causes of death in cirrhotic and in noncirrhotic patients with primary hemochromatosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 1985, 313(20): 1256-1262. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM198511143132004. [8] ADAMS P, ALTES A, BRISSOT P, et al. Therapeutic recommendations in HFE hemochromatosis for p. Cys282Tyr (C282Y/C282Y) homozygous genotype[J]. Hepatol Int, 2018, 12(2): 83-86. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-018-9855-0. [9] HAN Y, ZHANG XX. Genetic diagnosis of hereditary hemochromatosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(8): 1673 -1679. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.004.韩悦, 张欣欣. 遗传性血色病的基因诊断[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(8): 1673-1679. DOl: 10.3969/j. issn. 1001-5256.2019.08.004. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.08.004 -



 PDF下载 ( 3477 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3477 KB)


 下载:
下载: