NLRP3炎症小体激活促进肝星状细胞活化的机制
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.035
-
摘要: 肝纤维化是慢性肝脏损伤的共同结果,可进展为肝硬化甚至是肝癌,目前尚无有效逆转肝纤维化的手段。在窦周隙中被激活的肝星状细胞转变为肌成纤维细胞并分泌胶原,是肝纤维化进程中的中心事件。NLRP3炎症小体可被各种损伤刺激激活,介导炎症反应和细胞焦亡。近年研究发现NLRP3炎症小体与肝星状细胞活化密切相关。介绍了在各种病理因素刺激下,NLRP3炎症小体在肝星状细胞内不同通路的激活,以及促进胞外炎症微环境的形成,从而介导肝星状细胞活化,在促肝纤维化中发挥重要作用。Abstract: Liver fibrosis is the common result of various chronic liver injuries and can progress to liver cirrhosis and even liver cancer, and at present, there is still no effective means to reverse liver fibrosis. The transformation of activated hepatic stellate cells (HSC) in perisinusoidal space into myofibroblasts and the secretion of collagen are a central event in the process of liver fibrosis. NLRP3 inflammasome can be activated by various injury stimuli and mediate inflammatory response and pyroptosis. Recent studies have found that the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome is closely associated with HSC activation. This article introduces the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in different pathways in HSC under various pathological factors and role of NLRP3 inflammasome in the formation of extracellular inflammatory microenvironment, thereby mediating HSC activation and playing an important role in promoting liver fibrosis.
-
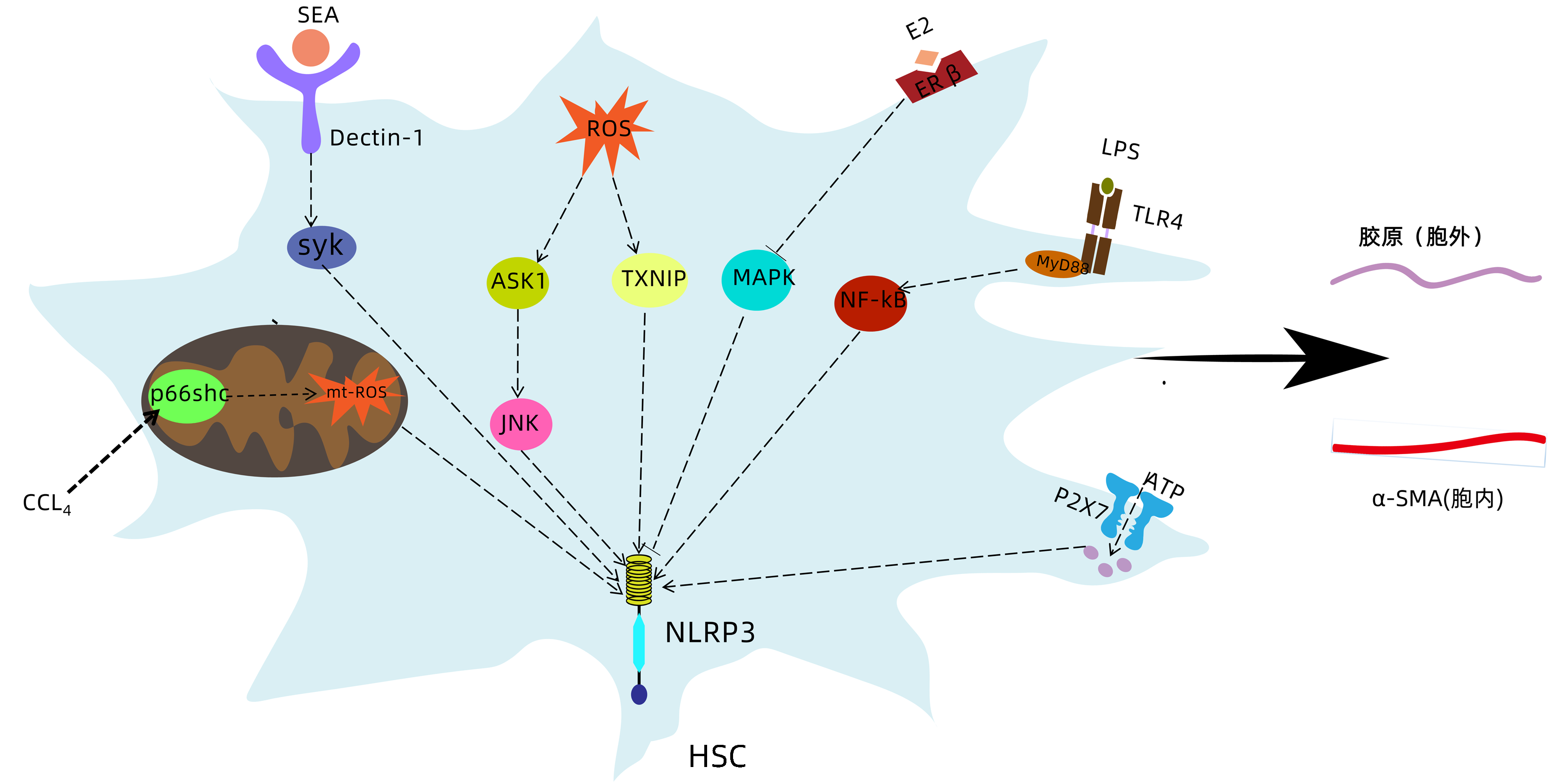
图 1 NLRP3炎症小体的两步激活模型
注:微生物组成部分和内源性损伤因子提供启动信号,导致关键转录因子NF-κB激活,随后上调NLRP3和pro-IL-1β表达。细胞外ATP、K+外流、Ca2+内流、ROS的产生、溶酶体损伤、颗粒物质等激活NLRP3炎症小体。dsRNA,双链RNA;TLR4,Toll样受体4;ROS,活性氧;Ox-mtDNA,氧化线粒体DNA;TXNIP,硫氧还蛋白互作蛋白;TWIK2,弱内向整流二孔K+通道2;TRPM2,瞬时受体电位M2通道;P2X7R,嘌呤能离子通道型受体7;MAVS,线粒体抗病毒信号蛋白;CLIC,胞内氯离子通道。
Figure 1. Two steps activation model of NLRP3 inflammasome
-
[1] DHAR D, BAGLIERI J, KISSELEVA T, et al. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer[J]. Exp Biol Med (Maywood), 2020, 245(2): 96-108. DOI: 10.1177/1535370219898141. [2] KHOMICH O, IVANOV AV, BARTOSCH B. Metabolic hallmarks of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis[J]. Cells, 2019, 9(1): 24. DOI: 10.3390/cells9010024. [3] NATARAJAN V, HARRIS EN, KIDAMBI S. SECs (sinusoidal endothelial cells), liver microenvironment, and fibrosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 4097205. DOI: 10.1155/2017/4097205. [4] GAUL S, LESZCZYNSKA A, ALEGRE F, et al. Hepatocyte pyroptosis and release of inflammasome particles induce stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74(1): 156-167. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.07.041. [5] INZAUGARAT ME, JOHNSON CD, HOLTMANN TM, et al. NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 inflammasome activation in hepatic stellate cells induces liver fibrosis in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 69(2): 845-859. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30252. [6] BAEZA-RAJA B, GOODYEAR A, LIU X, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of P2RX7 ameliorates liver injury by reducing inflammation and fibrosis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(6): e0234038. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234038. [7] SWANSON KV, DENG M, TING JP. The NLRP3 inflammasome: molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(8): 477-489. DOI: 10.1038/s41577-019-0165-0. [8] KELLEY N, JELTEMA D, DUAN Y, et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(13): 3328. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20133328. [9] ZHANG Y, LI Y, MU T, et al. Hepatic stellate cells specific liposomes with the Toll-like receptor 4 shRNA attenuates liver fibrosis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(2): 1299-1313. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16209. [10] DONG Z, ZHUANG Q, NING M, et al. Palmitic acid stimulates NLRP3 inflammasome activation through TLR4-NF-κB signal pathway in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(5): 168. DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.21. [11] CAI SM, YANG RQ, LI Y, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) improves liver fibrosis by regulating the NLRP3 inflammasome via redox balance modulation[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2016, 24(14): 795-812. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2015.6498. [12] JIANG S, ZHANG Y, ZHENG JH, et al. Potentiation of hepatic stellate cell activation by extracellular ATP is dependent on P2X7R-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2017, 117: 82-93. DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.040. [13] JIANG M, CUI BW, WU YL, et al. P2X7R orchestrates the progression of murine hepatic fibrosis by making a feedback loop from macrophage to hepatic stellate cells[J]. Toxicol Lett, 2020, 333: 22-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.07.023. [14] GASBARRINI A, BORLE AB, CARACENI P, et al. Effect of ethanol on adenosine triphosphate, cytosolic free calcium, and cell injury in rat hepatocytes. Time course and effect of nutritional status[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1996, 41(11): 2204-2212. DOI: 10.1007/BF02071401. [15] SHAN L, JIANG T, CI L, et al. Purine signaling regulating HSCs inflammatory cytokines secretion, activation, and proliferation plays a critical role in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2020, 466(1-2): 91-102. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-020-03691-0. [16] LU L, LU Q, CHEN W, et al. Vitamin D(3) protects against diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting high-glucose-induced activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2018, 2018: 8193523. DOI: 10.1155/2018/8193523. [17] SHIMIZU H, TSUBOTA T, KANKI K, et al. All-trans retinoic acid ameliorates hepatic stellate cell activation via suppression of thioredoxin interacting protein expression[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 233(1): 607-616. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25921. [18] LIU X, ZHANG YR, CAI C, et al. Taurine alleviates schistosoma-induced liver injury by inhibiting the TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signal pathway and pyroptosis[J]. Infect Immun, 2019, 87(12): e00732-19. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00732-19. [19] WANG Z, ZHAO Y, SUN R, et al. circ-CBFB upregulates p66Shc to perturb mitochondrial dynamics in APAP-induced liver injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(11): 953. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-03160-y. [20] ZHAO Y, WANG Z, FENG D, et al. p66Shc contributes to liver fibrosis through the regulation of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(5): 1510-1522. DOI: 10.7150/thno.29620. [21] ZHANG B, ZHANG CG, JI LH, et al. Estrogen receptor β selective agonist ameliorates liver cirrhosis in rats by inhibiting the activation and proliferation of hepatic stellate cells[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(3): 747-755. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13976. [22] LIN L, ZHOU M, QUE R, et al. Saikosaponin-d protects against liver fibrosis by regulating the estrogen receptor-β/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2021, 99(5): 666-674. DOI: 10.1139/bcb-2020-0561. [23] QUE R, SHEN Y, REN J, et al. Estrogen receptor-β-dependent effects of saikosaponin-d on the suppression of oxidative stress-induced rat hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2018, 41(3): 1357-1364. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3349. [24] XIONG M, LI J, YANG S, et al. Influence of gender and reproductive factors on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2019, 10(10): e00085. DOI: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000085. [25] LIMA-JUNIOR DS, MINEO T, CALICH V, et al. Dectin-1 activation during leishmania amazonensis phagocytosis prompts Syk-dependent reactive oxygen species production to trigger inflammasome assembly and restriction of parasite replication[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(6): 2055-2068. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700258. [26] LU YQ, ZHONG S, MENG N, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in liver inflammation and fibrosis in mice infected with Schistosoma japonicum in a Syk-dependent manner[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 8120. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-08689-1 [27] LIN YC, HUANG DY, WANG JS, et al. Syk is involved in NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activation through adaptor ASC phosphorylation and enhanced oligomerization[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2015, 97(5): 825-835. DOI: 10.1189/jlb.3HI0814-371RR. [28] YOON YC, FANG Z, LEE JE, et al. Selonsertib inhibits liver fibrosis via downregulation of ASK1/MAPK pathway of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Biomol Ther (Seoul), 2020, 28(6): 527-536. DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.016. [29] SANDALL CF, MACDONALD JA. Effects of phosphorylation on the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2019, 670: 43-57. DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.020. [30] SCHUSTER-GAUL S, GEISLER LJ, MCGEOUGH MD, et al. ASK1 inhibition reduces cell death and hepatic fibrosis in an Nlrp3 mutant liver injury model[J]. JCI Insight, 2020, 5(2). DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.123294. [31] LOOMBA R, LAWITZ E, MANTRY PS, et al. The ASK1 inhibitor selonsertib in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, phase 2 trial[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(2): 549-559. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29514. [32] MCQUITTY CE, WILLIAMS R, CHOKSHI S, et al. Immunomodulatory role of the extracellular matrix within the liver disease microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 574276. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574276. [33] QIN CC, LIU YN, HU Y, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 as mediator of inflammation in acute liver injury[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(17): 3043-3052. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i17.3043. [34] HOLTMANN TM, INZAUGARAT ME, KNORR J, et al. Bile acids activate NLRP3 inflammasome, promoting murine liver inflammation or fibrosis in a cell type-specific manner[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2618. DOI: 10.3390/cells10102618. [35] YAN W, SHEN Y, HUANG J, et al. MCC950 ameliorates acute liver injury through modulating macrophage polarization and myeloid-derived suppressor cells function[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2021, 8: 752223. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.752223. [36] BERINGER A, MIOSSEC P. IL-17 and TNF-α co-operation contributes to the proinflammatory response of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2019, 198(1): 111-120. DOI: 10.1111/cei.13316. [37] KAGAN P, SULTAN M, TACHLYTSKI I, et al. Both MAPK and STAT3 signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(5): e0176173. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176173. [38] GE S, YANG W, CHEN H, et al. MyD88 in macrophages enhances liver fibrosis by activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in HSCs[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 12413. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222212413. [39] WREE A, MCGEOUGH MD, INZAUGARAT ME, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome driven liver injury and fibrosis: Roles of IL-17 and TNF in mice[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(2): 736-749. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29523. [40] ZHOU Z, XU MJ, CAI Y, et al. Neutrophil-hepatic stellate cell interactions promote fibrosis in experimental steatohepatitis[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 5(3): 399-413. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.01.003. [41] KANG H, SEO E, OH YS, et al. TGF-β activates NLRP3 inflammasome by an autocrine production of TGF-β in LX-2 human hepatic stellate cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2022, 477(5): 1329-1338. DOI: 10.1007/s11010-022-04369-5. [42] WANG H, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activation by Escherichia coli RNA induces transforming growth factor beta 1 secretion in hepatic stellate cells[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2016, 16(2): 126-131. DOI: 10.17305/bjbms.2016.699. [43] LEE KY, ITO K, HAYASHI R, et al. NF-kappaB and activator protein 1 response elements and the role of histone modifications in IL-1beta-induced TGF-beta1 gene transcription[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 176(1): 603-615. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.1.603. [44] REITER FP, WIMMER R, WOTTKE L, et al. Role of interleukin-1 and its antagonism of hepatic stellate cell proliferation and liver fibrosis in the Abcb4(-/-) mouse model[J]. World J Hepatol, 2016, 8(8): 401-410. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i8.401. [45] YAPING Z, YING W, LUQIN D, et al. Mechanism of interleukin-1β-induced proliferation in rat hepatic stellate cells from different levels of signal transduction[J]. APMIS, 2014, 122(5): 392-398. DOI: 10.1111/apm.12155. [46] FRISSEN M, LIAO L, SCHNEIDER KM, et al. Bidirectional role of NLRP3 during acute and chronic cholestaticliver injury[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(5): 1836-1854. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31494. [47] SCHWAID AG, SPENCER KB. Strategies for targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in the clinical and preclinical space[J]. J Med Chem, 2021, 64(1): 101-122. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01307. [48] KENNEDY CR, GOYA GROCIN A, KOVAČIČ T, et al. A probe for NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 identifies carbonic anhydrase 2 as a novel target[J]. ACS Chem Biol, 2021, 16(6): 982-990. DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00218. [49] MASSARO MG, POMPILI M, SICIGNANO LL, et al. Improvement of liver involvement in familial mediterranean fever after the introduction of canakinumab: A case report[J]. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis, 2020, 12(1): e2020059. DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2020.059. -



 PDF下载 ( 2985 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2985 KB)


 下载:
下载: