IL-10对非酒精性脂肪性肝病发病的保护机制及其治疗前景
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.029
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:李瑞风确定文章的框架,查阅文献,撰写论文;宗廷妮参与修改论文;戴光荣负责拟定写作思路,修稿并最后定稿。
Protective mechanism of interleukin-10 against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its prospect in treatment
-
摘要: 随着肥胖和代谢综合征的流行,非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)已成为我国第一大慢性肝病。然而NAFLD的发病机制尚未完全阐明,近年来研究发现IL-10不仅在自身免疫性疾病、炎症性疾病、恶性肿瘤的发病中起重要作用,而且在NAFLD的发病中起到关键的调节作用。本文就IL-10对NAFLD发病的保护机制及其治疗前景进行综述,以便进一步发掘IL-10在NAFLD诊断以及治疗中的临床价值。Abstract: With the prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become the largest chronic liver disease in China. However, the pathogenesis of NAFLD remains unclear, and recent studies have found that interleukin-10 (IL-10) not only plays an important role in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory diseases, and malignant tumors, but also plays a key regulatory role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. This article reviews the protective mechanism of IL-10 against NAFLD and its prospect in treatment, so as to further explore the clinical value of IL-10 in the diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD.
-
Key words:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease /
- Interleukin-10 /
- Therapeutics
-
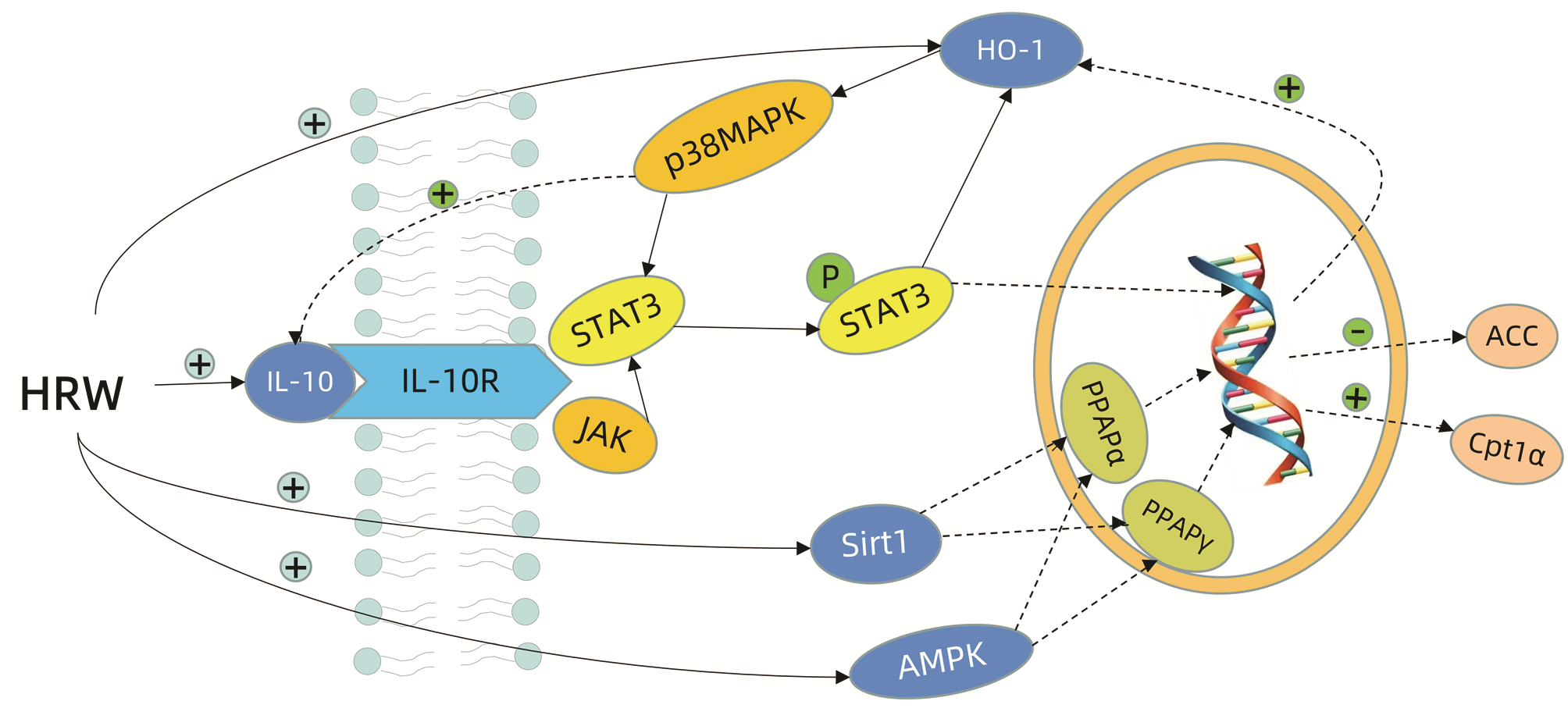
[1] FIORENTINO DF, BOND MW, MOSMANN TR. Two types of mouse T helper cell. Ⅳ. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones[J]. J Exp Med, 1989, 170(6): 2081-2095. DOI: 10.1084/jem.170.6.2081. [2] RUTZ S, OUYANG W. Regulation of interleukin-10 expression[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2016, 941: 89-116. DOI: 10.1007/978-94-024-0921-5_5. [3] BEDKE T, MUSCATE F, SOUKOU S, et al. IL-10-producing T cells and their dual functions[J]. Semin Immunol, 2019, 44: 101335. DOI: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.101335. [4] SARAIVA M, O'GARRA A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2010, 10(3): 170-181. DOI: 10.1038/nri2711. [5] National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(5): 947-957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007.中华医学会肝病学分会脂肪肝和酒精性肝病学组, 中国医师协会脂肪性肝病专家委员会. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病防治指南(2018年更新版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(5): 947-957. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.007. [6] ZHOU F, ZHOU J, WANG W, et al. Unexpected rapid increase in the burden of NAFLD in China from 2008 to 2018: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70(4): 1119-1133. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30702. [7] PERUMPAIL BJ, KHAN MA, YOO ER, et al. Clinical epidemiology and disease burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(47): 8263-8276. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i47.8263. [8] NOUREDDIN M, SANYAL AJ. Pathogenesis of NASH: the impact of multiple pathways[J]. Curr Hepatol Rep, 2018, 17(4): 350-360. DOI: 10.1007/s11901-018-0425-7. [9] XIAO WS, LE YY, ZENG SL, et al. Research advances in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(8): 1874-1879. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.043.肖伟松, 乐滢玉, 曾胜澜, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的发病机制研究进展[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(8): 1874-1879. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.043. [10] ABU-SHANAB A, QUIGLEY EM. The role of the gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 7(12): 691-701. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.172. [11] BUZZETTI E, PINZANI M, TSOCHATZIS EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)[J]. Metabolism, 2016, 65(8): 1038-1048. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.12.012. [12] YU J, MARSH S, HU J, et al. The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and genetic background[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2016, 2016: 2862173. DOI: 10.1155/2016/2862173. [13] QIN YH. Expression of IL-10 mRNA in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Univ, 2004: 1-43.秦月花. IL-10mRNA在大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病中的表达[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2004: 1-43. [14] QIN Q, ZHOU DS, LIANG ZQ, et al. Change of plasma interleukin-18, interleukin-10 and interleukin-18/interleukin-10 ratio in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Anhui Med Univ, 2013, 48(9): 1041-1043. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2013.09.011.秦青, 周冬生, 梁志清, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病大鼠血清白介素18、白介素10及其比值的变化和意义[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2013, 48(9): 1041-1043. DOI: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2013.09.011. [15] CHEN HD. Study on the relationship between CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells and their related cytokines (IL-10, TGF β 1) and insulin resistance in rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Med Univ, 2014: 1-48.陈惠弟. 大鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节性T细胞及其相关细胞因子(IL-10、TGF-β1)与胰岛素抵抗的相关性研究[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2014: 1-48. [16] DAI G, TAN Y, LIU J, et al. The significance of IL-28B and CK-18 M30 levels in the diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in SD rats[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2020, 216(4): 152901. DOI: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152901. [17] HAMMERICH L, TACKE F. Interleukins in chronic liver disease: lessons learned from experimental mouse models[J]. Clin Exp Gastroenterol, 2014, 7: 297-306. DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S43737. [18] WANG Q, XU QY, WU HM, et al. Effect of lipid-induced macrophage M1/M2 polarization on lipid metabolism in hepatocytes[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2018, 26(4): 276-281. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.009.王祺, 许钦瑜, 吴惠敏, 等. 脂质诱导的巨噬细胞M1/M2型极化对肝细胞脂质代谢的影响[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2018, 26(4): 276-281. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.04.009. [19] CHAN IH, van HOOF D, ABRAMOVA M, et al. PEGylated IL-10 activates kupffer cells to control hypercholesterolemia[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(6): e0156229. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156229. [20] CINTRA DE, PAULI JR, ARAÚJO EP, et al. Interleukin-10 is a protective factor against diet-induced insulin resistance in liver[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(4): 628-637. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.12.017. [21] BARRY JC, SHAKIBAKHO S, DURRER C, et al. Hyporesponsiveness to the anti-inflammatory action of interleukin-10 in type 2 diabetes[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 21244. DOI: 10.1038/srep21244. [22] BREUER DA, PACHECO MC, WASHINGTON MK, et al. CD8+ T cells regulate liver injury in obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2020, 318(2): G211-G224. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00040.2019. [23] PAREDES-TURRUBIARTE G, GONZÁLEZ-CHÁVEZ A, PÉREZ-TAMAYO R, et al. Severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with high systemic levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and low serum interleukin 10 in morbidly obese patients[J]. Clin Exp Med, 2016, 16(2): 193-202. DOI: 10.1007/s10238-015-0347-4. [24] CHU PL. Study on the relationship between Serum MCP-1, IL-17A, IL-10 levels and NAFLD[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Med Univ, 2019: 1-45.储佩玲. 血清MCP-1、IL-17A、IL-10水平与NAFLD的相关性研究[D]. 太原: 山西医科大学, 2019: 1-45. [25] FONTES-CAL T, MATTOS RT, MEDEIROS NI, et al. Crosstalk between plasma cytokines, inflammation, and liver damage as a new strategy to monitoring NAFLD progression[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 708959. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.708959. [26] ZHANG GD. Analysis of serum hs-CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10 and irigenin levels in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clin Res Pract, 2021, 6(32): 24-26, 30. DOI: 10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202132008.张国栋. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病合并2型糖尿病患者血清hs-CRP、TNF-α、IL-6、IL-10与鸢尾素水平及相关性分析[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2021, 6(32): 24-26, 30. DOI: 10.19347/j.cnki.2096-1413.202132008. [27] SHI JQ, SHEN WX, WANG XZ, et al. Relationship between immune parameters and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children[J]. Indian Pediatr, 2017, 54(10): 825-829. DOI: 10.1007/s13312-017-1143-x. [28] VONGHIA L, MAGRONE T, VERRIJKEN A, et al. Peripheral and hepatic vein cytokine levels in correlation with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-related metabolic, histological, and haemodynamic features[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(11): e0143380. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143380. [29] ALI AL, NAILWAL NP, DOSHI GM. Emerging role of interleukins for the assessment and treatment of liver diseases[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, 2022, 22(4): 371-382. DOI: 10.2174/1871530321666211124102837. [30] SHEN JX, LIU Y, ZHANG YY. Changes and significance of serum inflammatory factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Shandong Med J, 2015, 55(37): 34-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.37.011.沈静雪, 刘宇, 张盈妍. 2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪性肝病患者血清炎性因子水平的变化及意义[J]. 山东医药, 2015, 55(37): 34-36. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2015.37.011. [31] CHAUVEAU C, RÉMY S, ROYER PJ, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 expression inhibits dendritic cell maturation and proinflammatory function but conserves IL-10 expression[J]. Blood, 2005, 106(5): 1694-1702. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0494. [32] LI SW, TAKAHARA T, QUE W, et al. Hydrogen-rich water protects against liver injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis through HO-1 enhancement via IL-10 and Sirt 1 signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2021, 320(4): G450-G463. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00158.2020. [33] MANDAL P, PRITCHARD MT, NAGY LE. Anti-inflammatory pathways and alcoholic liver disease: role of an adiponectin/interleukin-10/heme oxygenase-1 pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2010, 16(11): 1330-1336. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1330. [34] WAN X, ZHU X, WANG H, et al. PGC1α protects against hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance via enhancing IL10-mediated anti-inflammatory response[J]. FASEB J, 2020, 34(8): 10751-10761. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201902476R. [35] ZHONG X, LIU H. Honokiol attenuates diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating macrophage polarization through activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(2): 524-532. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13853. [36] XU Q, FAN Y, LOOR JJ, et al. Aloin protects mice from diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(2): 696-705. DOI: 10.1039/d0fo02684k. [37] QI SY, HUANG H, LI YK, et al. Effects of curcumol on liver function and fibrosis in rats of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its mechanism[J]. Chin J Appl Physiol, 2021, 37(6): 611-615, 672. DOI: 10.12047/j.cjap.6058.2021.082.齐书妍, 黄华, 李永坤, 等. 莪术醇对非酒精性脂肪性肝大鼠肝功能和肝纤维化的影响及机制[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2021, 37(6): 611-615, 672. DOI: 10.12047/j.cjap.6058.2021.082. [38] TRUSHINA EN, RIGER NA, MUSTAFINA OK, et al. Effect of carnosine and α-lipoic acid on hepatocyte apoptosis and the cytokine profile in induced fatty liver disease in Wistar rats[J]. Vopr Pitan, 2020, 89(5): 6-16. DOI: 10.24411/0042-8833-2020-10061. [39] JORDÃO CANDIDO C, SILVA FIGUEIREDO P, DEL CIAMPO SILVA R, et al. Protective effect of α-linolenic acid on non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and interleukin-6 and -10 in Wistar rats[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 12(1): 9. DOI: 10.3390/nu12010009. [40] WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Advances in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Med Offic, 2022, 50(9): 897-899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06.王彩娥, 许文涛, 宫建, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病治疗研究进展[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50(9): 897-899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. [41] MILLER SJ, TIWARI AK, OHM JT, et al. Towards understanding the mechanisms of how exercise improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: role of skeletal muscle secreted IL-10 and IL-15[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 152(5): S823. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5085(17)32843-3. [42] DINIZ TA, de LIMA JUNIOR EA, TEIXEIRA AA, et al. Aerobic training improves NAFLD markers and insulin resistance through AMPK-PPAR-α signaling in obese mice[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 266: 118868. DOI: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118868. [43] SHEN T, LEI T, CHEN L, et al. Effect of sitagliptin on the expression of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with NAFLD[J]. Shanxi Med J, 2021, 50(12): 1907-1911. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2021.12.003.申甜, 雷涛, 陈琳, 等. 西格列汀对2型糖尿病合并非酒精性脂肪肝病患者外周血单个核细胞肿瘤坏死因子-α白细胞介素-6及白细胞介素-10 mRNA表达的影响[J]. 山西医药杂志, 2021, 50(12): 1907-1911. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2021.12.003. [44] TUTUNCHI H, OSTADRAHIMI A, SAGHAFI-ASL M, et al. Expression of NF-κB, IL-6, and IL-10 genes, bodycomposition, and hepatic fibrosis in obese patients with NAFLD—Combined effects of oleoylethanolamidesupplementation and calorie restriction: A triple-blindrandomized controlled clinical trial[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(1): 417-426. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29870. [45] GÓMEZ-HURTADO I, ZAPATER P, BELLOT P, et al. Interleukin-10-mediated heme oxygenase 1-induced underlying mechanism in inflammatory down-regulation by norfloxacin in cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 53(3): 935-944. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24102. -



 PDF下载 ( 2118 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2118 KB)

 下载:
下载:


