The role of traditional Chinese medicine in blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis:current status, hope, and challenge
-
摘要:
中医药辨证论治具有阻断逆转肝纤维化的整体治疗优势,是未来治疗肝纤维化候选药物的源泉。概述了中医药治疗肝纤维化的渊源和现状,重点论述了如何按照循证医学和国际认同的临床试验标准再评价中医药阻断逆转肝纤维化的临床疗效和安全性,介绍了最新临床研究成果。强调了发掘和认同中医药阻断逆转肝纤维化所面临的挑战与重要意义。
Abstract:Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome differentiation-based treatment has certain advantages in blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis and is the source of candidate drugs for hepatic fibrosis in future.This article overviews the origin and current status of TCM treatment of hepatic fibrosis, discusses how to reevaluate the clinical effect and safety of TCM in blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis in accordance with evidence-based medicine and internationally acknowledged standards for clinical trials, and introduces the latest clinical research findings.It also emphasizes the challenge and significance of the exploration and recognition of TCM in blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis.
-
Key words:
- liver cirrhosis /
- TCM science /
- drugs, Chinese herbal /
- therapy
-
临床上,胰腺恶性肿瘤大部分为原发肿瘤,胰腺转移癌少见[1]。胰腺转移癌与胰腺原发肿瘤鉴别困难,极易造成误诊,延误治疗。目前,胰腺转移癌国内外尚无统一治疗标准,原发肿瘤的生物学特性和针对原发肿瘤的综合治疗是决定其预后的主要因素,个体化差异较大。近期,笔者接诊1例宫颈鳞癌胰腺转移患者,现将病例资料及经验总结报告如下。
1. 病例资料
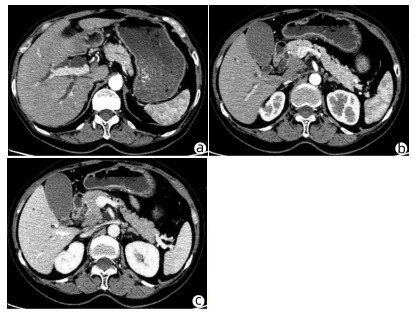
患者女性,63岁,因“皮肤、巩膜黄染20余天”于2021年3月27日入本院。起初黄染程度不重,后进行性加重,无腹痛腹胀,无阴道流血等其他不适。曾于2013年9月6日因阴道异常流血于外院行宫颈活检,病理学诊断为宫颈中分化鳞癌ⅢB期,予局部放疗联合TP方案(多西他赛+奥沙利铂)化疗,于2015年结束治疗后复查腹盆腔脏器、腹腔、盆腔均未见肿瘤转移。出院后患者再未复查,亦无特殊不适。入院查体:皮肤巩膜明显黄染,腹平坦,腹部无压痛,腹部未触及肿块。辅助检查:TBil 282.99 μmol/L,DBil 203.80 μmol/L,CA19-9正常;妇科彩超示:老年性子宫;全腹盆腔增强CT示:肝内外胆管扩张,主胰管可见(图 1a),胆囊明显增大,胆总管下段狭窄,动脉期见胰腺钩突区低密度肿块(图 1b),静脉期肿块轻度强化(图 1c),子宫显示不明显,腹膜后可见多发淋巴结肿大;磁共振胰胆管造影示:胰头区异常信号肿块,肝内外胆管扩张,胆汁淤积;超声内镜示:胰头钩突区占位,直径约3 cm。入院后予以护肝利胆治疗,患者黄疸进行性加重,建议患者行穿刺活检、PET-CT检查,患方拒绝。2021年4月4日行剖腹探查:术中探查发现肿瘤位于胰头钩突区,质地硬,侵犯十二指肠壁和胆总管,腹膜后见多发淋巴结肿大,行胰头十二指肠切除术。术后病理学检查结果:胰腺钩突肿块大小3.0 cm×2.0 cm×1.5 cm,癌组织侵犯十二指肠及胆总管,胰腺切缘未见癌。癌组织呈团块状或条索状癌巢(图 2a),癌细胞及核大小、形态不一,分布不规则,核分裂像多见,癌组织侵犯淋巴管及血管,脉管内见癌栓(图 2b),周围淋巴结可见癌转移(2/2)。免疫组化:P16(弥漫性+),P63(+),P40(+),CK7(+),CK8(+),CK19(+),ER(+)(图 2c、d)。诊断考虑胰腺钩突区中分化鳞状细胞癌,结合临床病史及免疫组化结果,考虑宫颈鳞癌转移。目前,该患者于本院进一步针对原发肿瘤行化疗等综合治疗,日常生活行为已恢复正常。
2. 讨论
据统计,宫颈癌的患病/病死率在女性恶性肿瘤中居第4位,鳞状细胞癌是最常见的病理类型,占比约80%,P16、P40等表达阳性对宫颈鳞癌诊断有重要意义。宫颈鳞癌早期往往无特殊表现,晚期可出现异常阴道流血、腰痛、盆腔痛、性交痛、贫血等表现,诊断时大多发生转移,多转移至直肠、膀胱、盆腔、肺、骨、肝等。临床上,胰腺癌多为原发肿瘤,胰腺转移癌罕见,仅占胰腺恶性肿瘤总数的2%~3%[2]。在一项纳入973例胰腺肿瘤手术标本病理资料的研究[3]中,共38例为胰腺转移瘤,主要包括淋巴瘤11例,胃癌7例,肾癌6例,肺癌2例,肝癌、前列腺癌、卵巢癌、子宫癌各1例,默克尔细胞癌1例,另有3例胃肠道恶性间质瘤和1例腹膜后平滑肌肉瘤;81例转移性胰腺肿瘤尸检报告显示,主要来源肺癌34例,胃肠道20例,肾脏4例,乳腺3例,肝脏2例,卵巢和膀胱各1例,另有6例来自造血系统,黑色素瘤、肉瘤和间皮瘤各2例。来源于宫颈的胰腺转移癌并不多见,笔者在国内外文献检索系统中,共检出各类型宫颈癌胰腺转移病例报告10例[4-7],其中鳞癌3例,神经内分泌癌5例,腺癌2例;转移灶位于胰头3例,位于颈部1例,位于胰腺体部3例,位于尾部、体尾部和胰头及体尾部各1例。转移灶位于胰头的3例患者中,1例为鳞癌,2例为神经内分泌癌,胰腺转移部位与宫颈癌病理类型无明显关联。本例患者在宫颈鳞癌同步放化疗后再未复查,6年后转移至胰腺钩突,临床表现为梗阻性黄疸,行胰头十二指肠切除术,术后病理学检查考虑鳞癌,结合免疫组化考虑为宫颈癌来源。目前,国内尚未见类似报道,国外也鲜有相关报道。
原发性胰腺癌与胰腺转移癌鉴别需依赖血清CA19-9水平、CT、MRI、磁共振胰胆管造影、内镜逆行胰胆管造影、超声内镜等检查手段。本例患者CT和MRI特点较原发性胰腺癌无特异表现,鉴别困难。血清CA19-9水平升高常见于胆道、胰腺恶性肿瘤,对诊断原发性胰腺癌有较高的敏感度和特异度[8]。鉴别困难时,可采用通过超声、CT及内镜引导下穿刺活检获取胰腺组织学、细胞学标本进行确诊,但需要评估穿刺活检的出血风险[9]。一般认为,超声内镜经十二指肠细针穿刺抽吸活检可提高胰腺疾病诊断的准确性,且相对安全[10-11]。本例患者术前影像学检查提示胰头钩突区占位,CA19-9水平不高,且有宫颈鳞癌病史,建议进一步行穿刺活检、PET-CT检查。但患者存在梗阻性黄疸,肝功能持续恶化,有手术指征,且患者家属不同意术前行穿刺活检、PET-CT等进一步检查,因此术前未能获得病理学诊断。
转移性胰腺癌临床表现因胰腺转移部位不同而异。在笔者检出的10例报告中,仅有1例(鳞癌)出现梗阻性黄疸,提示宫颈癌胰腺转移鲜有梗阻性黄疸症状,部分病例可因肿瘤压迫出现胆胰管扩张。转移性胰腺癌出现胰胆管梗阻较少见,可能与原发肿瘤主要经过淋巴及血行途径转移侵犯胰腺,不侵犯胆胰管有关[12]。本例患者胰腺转移性肿瘤致梗阻性黄疸,目前国内尚未见类似报道,国外仅有1例类似报道,但未分析相关转移机制。本例患者影像学检查示肝、胃、肠道等器官均未见肿瘤,但有腹膜后淋巴结肿大,病理学检查阳性;在既往10例报告中,3例胰腺转移性宫颈鳞癌有2例伴腹膜后淋巴结肿大,因此笔者推测宫颈鳞癌胰腺转移可能与腹膜后淋巴结侵犯相关。
关于转移性胰腺癌是否需要手术,意见尚未统一。以急腹症、进行性黄疸、出血为临床表现患者,应行急诊手术治疗,解除症状同时,切除病灶送检,根据病理学检查结果制订综合治疗方案。研究[13-14]表明,转移性胰腺癌行手术切除相较于保守治疗可延长生存期,且根治性手术相较于姑息性手术,预后更好。术后根据原发病灶辅以化疗等综合治疗,可提高治疗效果。对无法接受手术的转移性胰腺癌患者,应根据原发肿瘤的生物学特性制订以放疗为主的个体化综合治疗方案[15]。本例患者影像学检查提示存在胆道梗阻,并见胰头钩突区占位;胆红素水平持续升高,手术指征明确,手术切除胰腺钩突病灶、解除胆道梗阻后,胆红素水平明显下降,目前患者恢复良好,进一步接受化疗等综合治疗,延长生存期。
笔者经验总结:(1)对于诊断不明确的胰腺肿瘤,术前条件允许情况下需行穿刺活检明确性质,以指导下一步治疗方案;(2)胰腺转移癌在具备手术条件情况下,应积极采取以根治性手术为主的治疗方案,姑息性切除方案亦可行。胰腺转移癌为晚期癌症,术后需早期予以放化疗、靶向、免疫治疗等综合治疗;(3)对于不具备手术条件的患者,需根据原发肿瘤予以抗肿瘤综合治疗,包括放疗、化疗以及免疫治疗、靶向治疗等[16-17]。
-
[1]SCHUPPAN D, KIM YO.Evolving therapies for liver fibrosis[J].J Clin Invest, 2013, 123 (5) :1887-1901. [2]FRIEDMAN SL, SHEPPARD D, DUFFIELD JS, et al.Therapy for fibrotic diseases:nearing the starting line[J].Sci Transl Med, 2013, 5 (167) :167-161. [3]SCHUPPAN D, JIA JD, BRINKHAUS B, et al.Herbal products for liver diseases:a therapeutic challenge for the new millennium[J].Hepatology, 1999, 30 (4) :1099-1104 [4]XU LM.An exploration of therapeutic evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of hepatic fibrosis[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33 (5) :825-828. (in Chinese) 徐列明.中医药抗肝纤维化疗效评价的探索[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33 (5) :825-828. [5]World Health Organization.WHO traditional medicine strategy 2014-2023[EB/OL].http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/traditional/trm_strategy14_23/en. [6]ZHANG L, SCHUPPAN D.Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for fibrotic liver disease:hope and hype[J].J Hepatol, 2014, 61 (1) :166-168. [7]LIU CH, LIU P, HU YY, et al.Progress of clinical and basic research on liver fibrosis with traditional Chinese medicine[J].World Sci Technol Modern Tradit Chin Med, 2007, 9 (2) :112-119. (in Chinese) 刘成海, 刘平, 胡义扬, 等.中医药抗肝纤维化临床与基础研究进展[J].世界科学技术:中医药现代化, 2007, 9 (2) :112-119. [8]LUK JM, WANG X, LIU P, et al.Traditional Chinese herbal medicines for treatmentof liver fibrosis and cancer:from laboratory discovery to clinical evaluation[J].Liver Int, 2007, 27 (7) :879-890. [9]Hepatobiliary Disease Group, Internal Medicine of Traditional Chinese, China Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine;Expert Consensus of Hepatology, World Federation of Chinese Medicine Societies;Hepatology Group, Chinese Association of the Integration of Traditional and Western Medicine.Guideline for traditional Chinese medical diagnosis of chronic heoatitis B[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2012, 28 (3) :164-168. (in Chinese) 中华中医药学会内科肝胆病学组, 世界中医药联合学会肝病专业委员会, 中国中西医结合学会肝病分组.慢性乙型肝炎中医诊疗专家共识 (2012年1月) [J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2012, 28 (3) :164-168. [10]YIN SS, WANG BE, WANG TL, et al.The effect of Cpd 861 on chronic hepatitis B related fibrosis and early cirrhosis:a randomized, double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2004, 12 (8) :467-470. (in Chinese) 尹珊珊, 王宝恩, 王泰龄, 等.复方861治疗慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化与早期肝硬化的临床研究[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2004, 12 (8) :467-470. [11]GAO GF, YANG X.Effects of Fufang Biejia Ruangan pills on hepatic fibrosis in patients with HBV-relate cirrhosis[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2005, 21 (6) :375-376. (in Chinese) 高广甫, 杨宣.复方鳖甲软肝片临床研究[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2005, 21 (6) :375-376. [12]LIU P, LIU C, XU LM, et al.Effects of Fuzheng Huayu 319 recipe on liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B[J].World J Gastroenterol, 1998, 4 (4) :348-353. [13]WANG ZW.Effects of Qianggan Ruanjian Tang for 38 patients with hepatitis cirrhosis[J].J Military Surg Southwest China, 2009, 11 (4) :805. (in Chinese) 王兆伟.强肝软坚汤化裁治疗肝炎肝硬化38例[J].西南军医, 2009, 11 (4) :805. [14]WANG XS, LI Y.The effects of Qianggan Ruangan Formulas on liver function, portal vein flow and fibrotic markers in patients with cirrhosis[J].Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2003, 37 (4) :26-27. (in Chinese) 王晓素, 李勇.强肝软坚方对肝硬化患者肝功能、门脉血流及纤维化标志物的影响[J].上海中医药杂志, 2003, 37 (4) :26-27. [15]SHI HL, ZHANG JY, TIAN FL, et al.Clinical observation of 70cases of liver cirrhosis after hepatitis by Qianggan Ruanjian Capsule[J].Jilin J Tradit Chin Med, 2006, 26 (1) :16-17. (in Chinese) 史海立, 张继元, 田锋亮, 等.强肝软坚丸治疗肝炎后肝硬化脾大70例临床观察[J].吉林中医药, 2006, 26 (1) :16-17. [16]LI L, ZHANG XJ, LAN Y, et al.Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by Qianggan Capsule[J].Chin J Integr Med, 2010, 16 (1) :23-27. [17]WANG H, YANG LM, HUANG L, et al.Clinical effects of qianggan capsule on the liver tissue pathology and PDGF-BB, TGFbeta1, TIMP-1, and MMP-1 factors in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Chin J Integr Trad West Med, 2011, 31 (10) :1337-1340. (in Chinese) 王华, 杨柳明, 黄玲, 等.强肝胶囊对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝组织病理及PDGF-BB, TGF-β1, TIMP-1, MMP-1的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2011, 31 (10) :1337-1340. [18]ZHANG W, XING LJ, WANG Y, et al.Clinical obsevation of“Qianggan Capsule”in treating 60 cases of non-alcohol-fatty liver disese of damp-heat retention[J].Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2007, 41 (4) :26-27. (in Chinese) 张玮, 邢练军, 王奕, 等.强肝胶囊治疗非酒精性脂肪肝湿热蕴结证的临床观察[J].上海中医药杂志, 2007, 41 (4) :26-27. [19]XUE GQ, JI FF.Treantment of 80 patients with chronic hepatitis B-related hepatic fibrosis by Qianggan capsule[J].Shandong J Tradit Chin Med, 2004, 23 (7) :404-405. (in Chinese) 薛桂芹, 季风帆.强肝胶囊治疗慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化80例[J].山东中医杂志, 2004, 23 (7) :404-405. [20]YAO HS, YAO XX, YAO DM, et al.Treantment of 365 patients with chronic hepatitis B-related hepatic fibrosis by Yigan Kang[J].Clin Focus, 2009, 24 (8) :690-693. (in Chinese) 姚洪森, 姚希贤, 姚冬梅, 等.益肝康治疗慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化365例疗效观察[J].临床荟萃, 2009, 24 (8) :690-693. [21]CUI SY, JIA M.Preparation and clinical observation of yihekang oral liquid[J].Chin Remed Clin, 2007, 7 (10) :802-803. (in Chinese) 崔淑云, 贾曼.益肝康口服液的制备及临床疗效观察[J].中国药物与临床, 2007, 7 (10) :802-803. [22]HUANG QW.Effects of anluohuaxian capsule on hepatic fibrosis indexes in patients of chronic hepatitis[J].Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2004, 14 (4) :206-208. (in Chinese) 黄其文.安络化纤丸对慢性肝炎患者肝纤维化指标的影响[J].中西医结合肝病杂志, 2004, 14 (4) :206-208. [23]ZHANG YH, GUO WQ, GUO PJ.The effect of adefovir dioxin combined with Anluo Huaqian pills on hepatic fibrosis indexes in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Chin Hepatol, 2013, 18 (9) :620. (in Chinese) 张义红, 郭伟琪, 郭平静.阿德福韦酯联合安络化纤丸对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化指标的影响[J].肝脏, 2013, 18 (9) :620. [24]HE J, DU L, LIU G, et al.Quality assessment of reporting of randomization, allocation concealment, and blinding in traditional Chinese medicine RCTs:a review of 3159 RCTs identified from 260 systematic reviews[J].Trials, 2011, 12:122-131. [25]CHENG CW, WU TX, SHANG HC, et al.CONSORT Extension for Chinese herbal medicine formulas 2017:recommendations, explanation, and elaboration[J].Ann Intern Med, 2017, 167 (2) :112-121. [26]CHEN JM, YANG YP, CHEN DY, et al.Efficacy and safety of Fufang Biejia Ruangan tablet in patients with chronic hepatitis B complicated with hepatic fibrosis[J].Chin J Exp Clin Virol, 2007, 21 (4) :358-360. (in Chinese) 陈菊梅, 杨永平, 陈德永, 等.复方鳖甲软肝片治疗慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化的临床研究[J].中华实验和临床病毒学杂志, 2007, 21 (4) :358-360. [27]DONG Q, QIU LL, ZHANG CE, et al.Identification of compounds in an anti-fibrosis Chinese medicine (Fufang Biejia Ruangan Pill) and its absorbed components in rat biofluids and liver by UPLCMS[J].J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2016, 1026:145-151. [28]ZHOU J, CHEN XM, LIU SW, et al.Effects of Biejia Ruangan Tablet-containing serum on matrix metalloproteinase-9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 expression in cultured renal interstitial fibroblasts[J].Chin J Integr Med, 2015, 21 (2) :152-156. [29]YANG FR, FANG BW, LOU JS.Effects of Fufang Biejia Ruangan pills on hepatic fibrosis in vivo and in vitro[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19 (32) :5326-5333. [30]GUO SG, ZHANG W, JIANG T, et al.Influence of serum collected from rat perfused with compound Biejiaruangan drug on hepatic stellate cells[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2004, 10 (10) :1487-1494. [31]QU J, YU Z, LI Q, et al.Blocking and reversing hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated by traditional Chinese medicine (tablets of biejia ruangan or RGT) :study protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J].Trials, 2014, 15 (1) :438. [32]CHANG TT, LIAW YF, WU SS, et al.Long-term entecavir therapy results in the reversal of fibrosis/cirrhosis and continued histological improvement in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatology, 2010, 52 (3) :886-893. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李帅,王娟,夏仕雪,顾鹏. 子宫颈混合性腺神经内分泌癌胰腺转移1例. 中国医学影像学杂志. 2022(12): 1283-1284 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1710 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1710 KB)


 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: