大网膜包裹胰肠吻合口预防胰十二指肠切除术后并发症有效性和安全性的Meta分析
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240122
Efficacy and safety of omental wrapping technique for pancreaticojejunal anastomosis in preventing complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
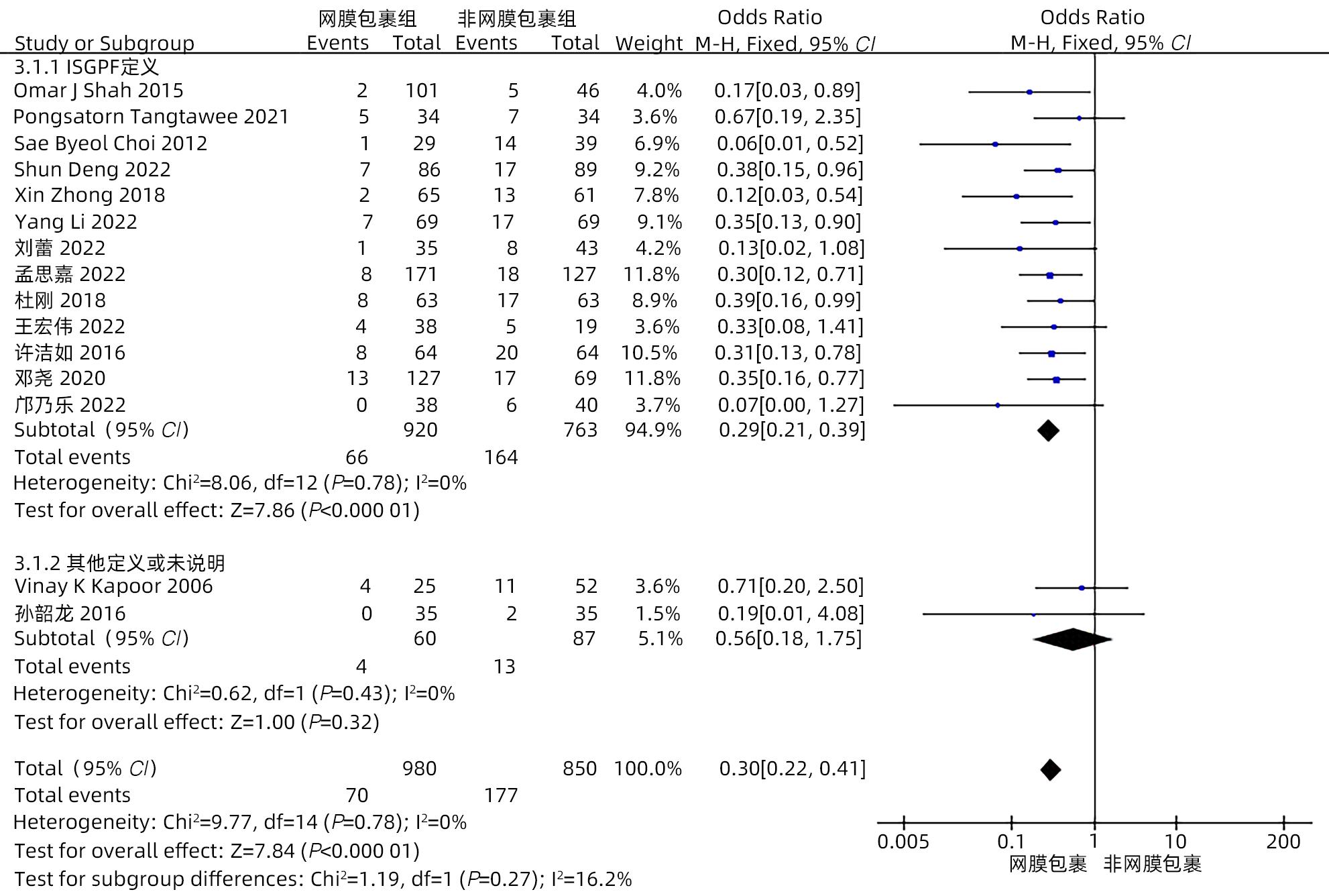
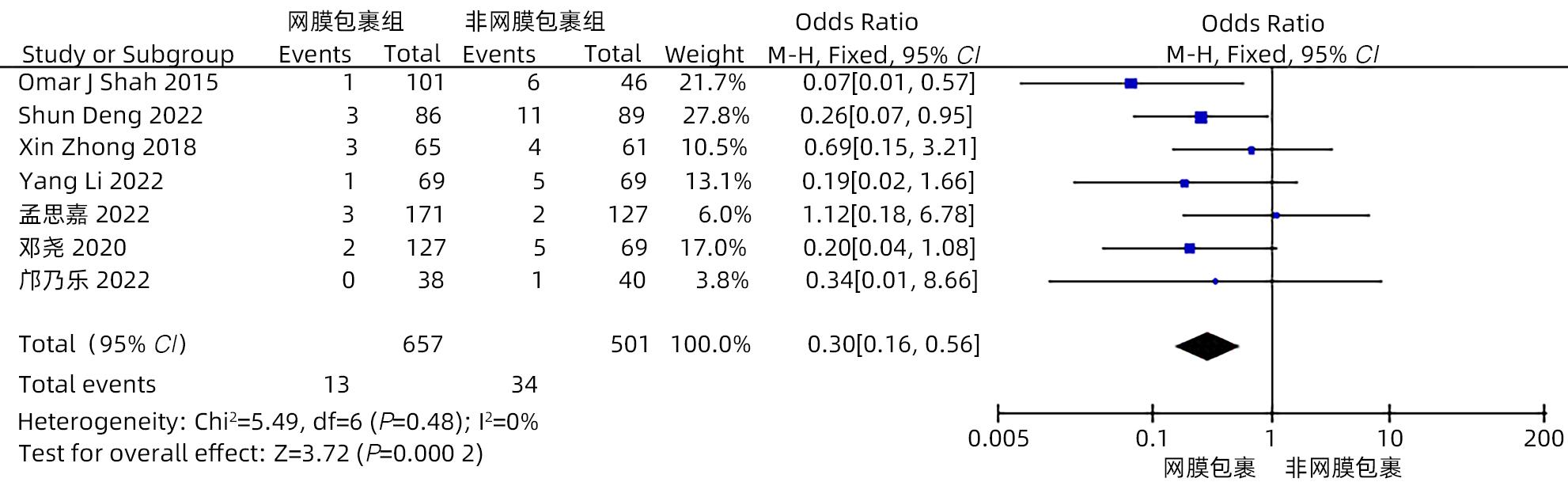
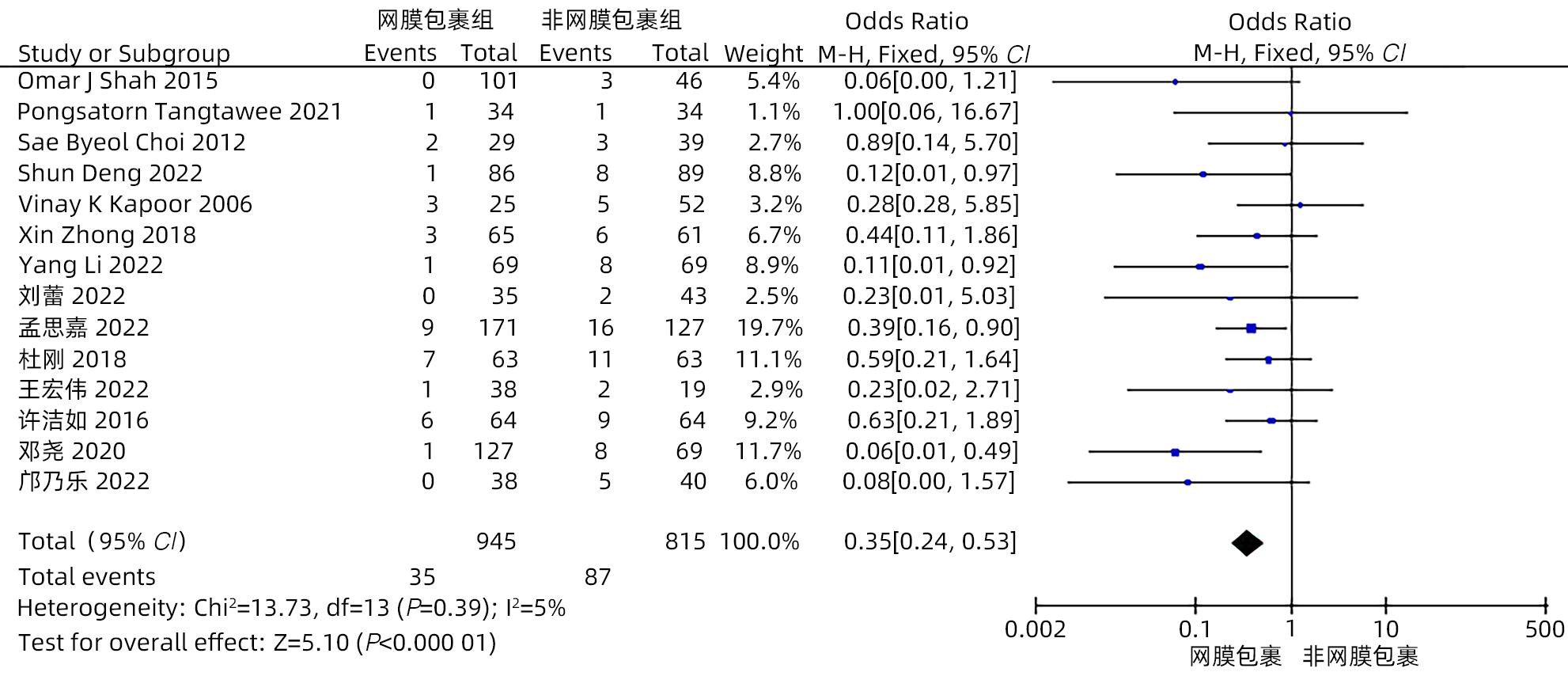
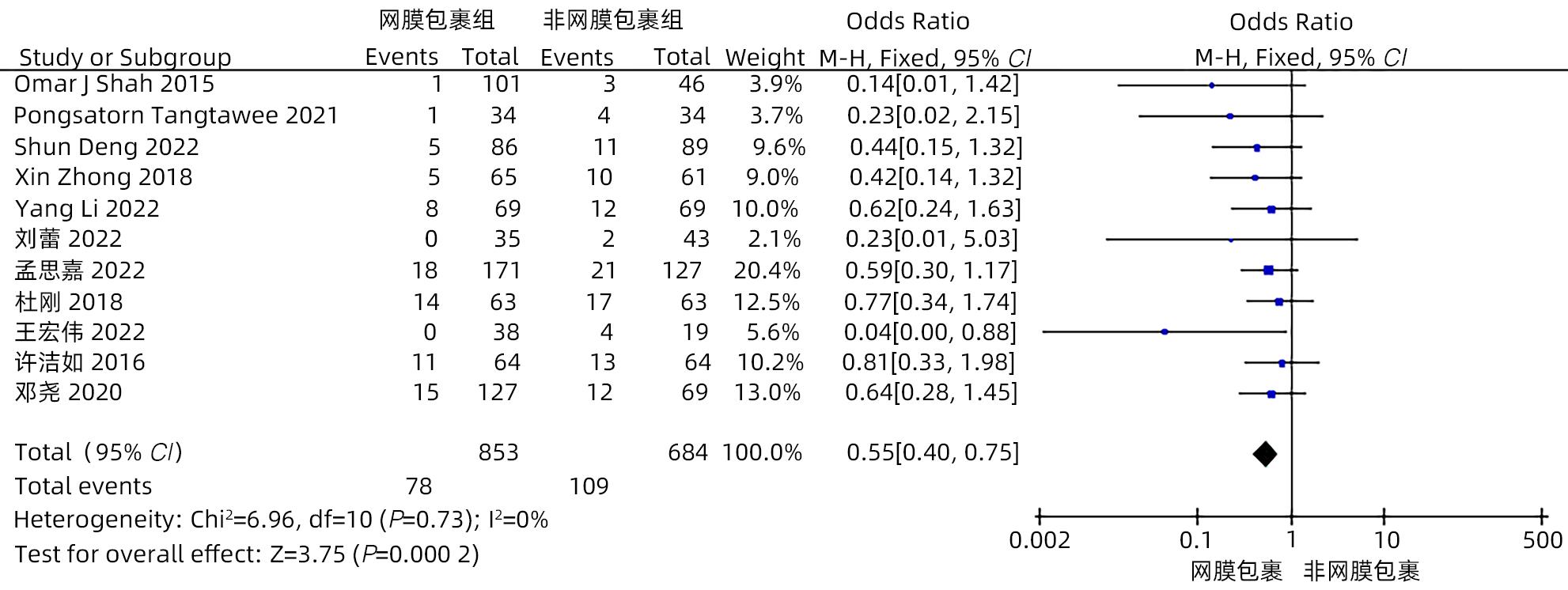
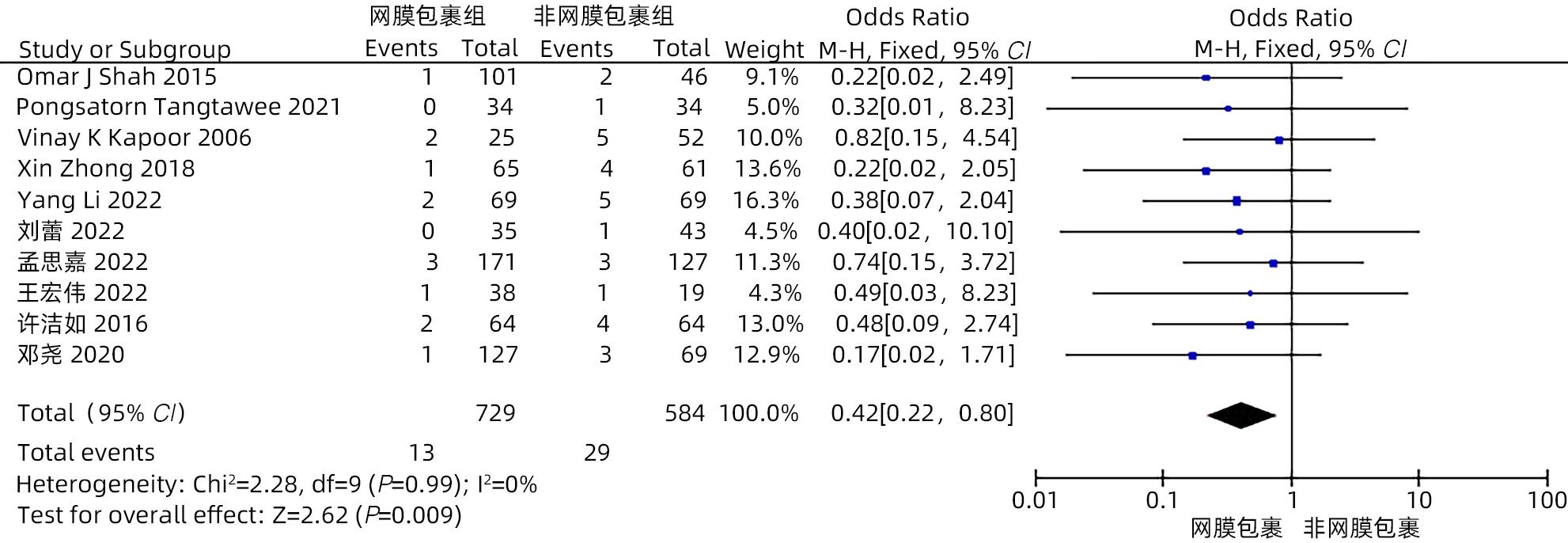
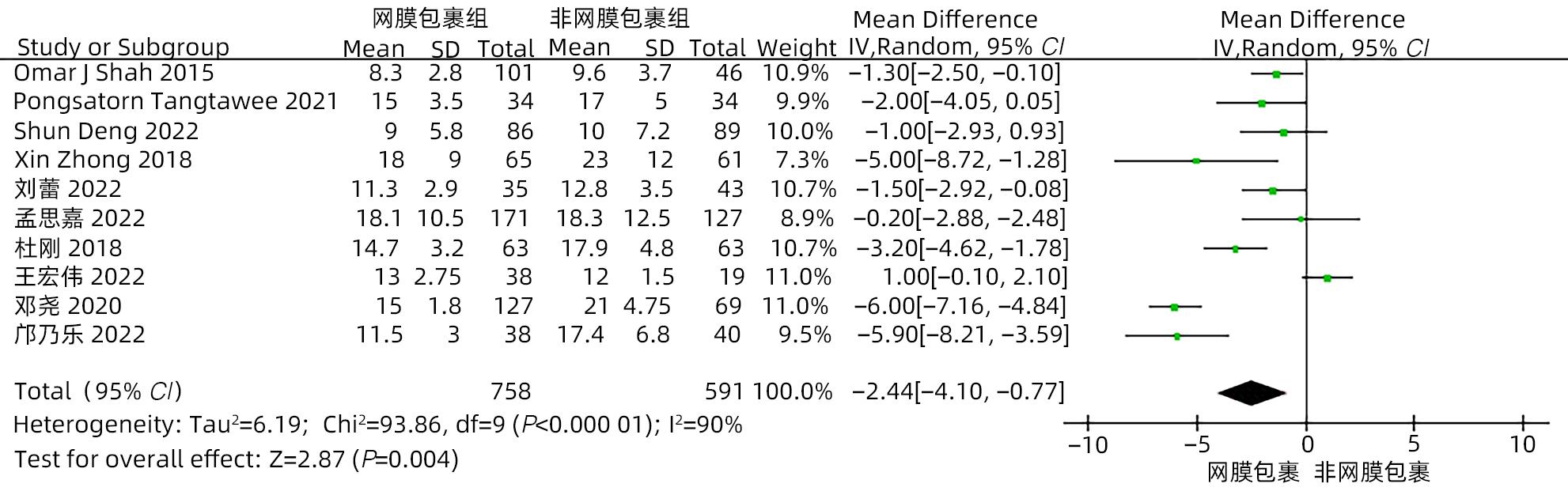
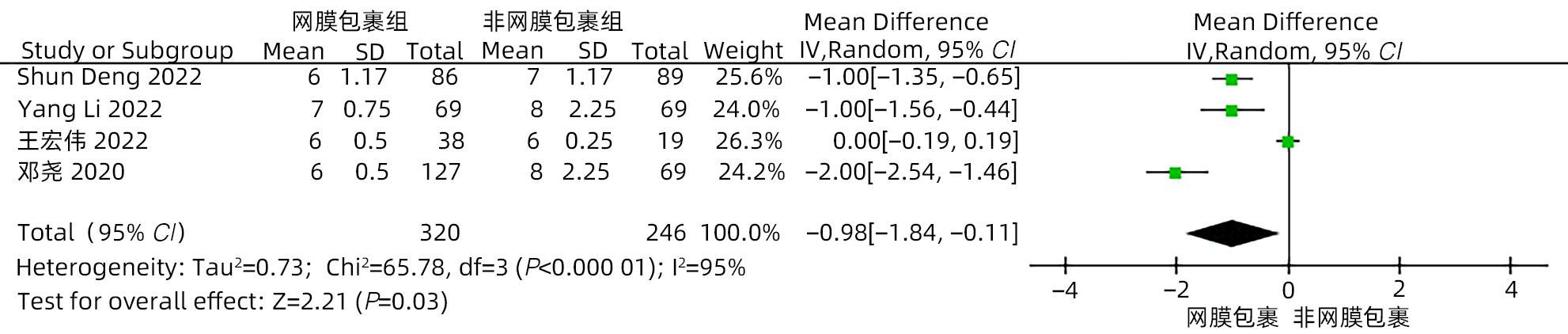
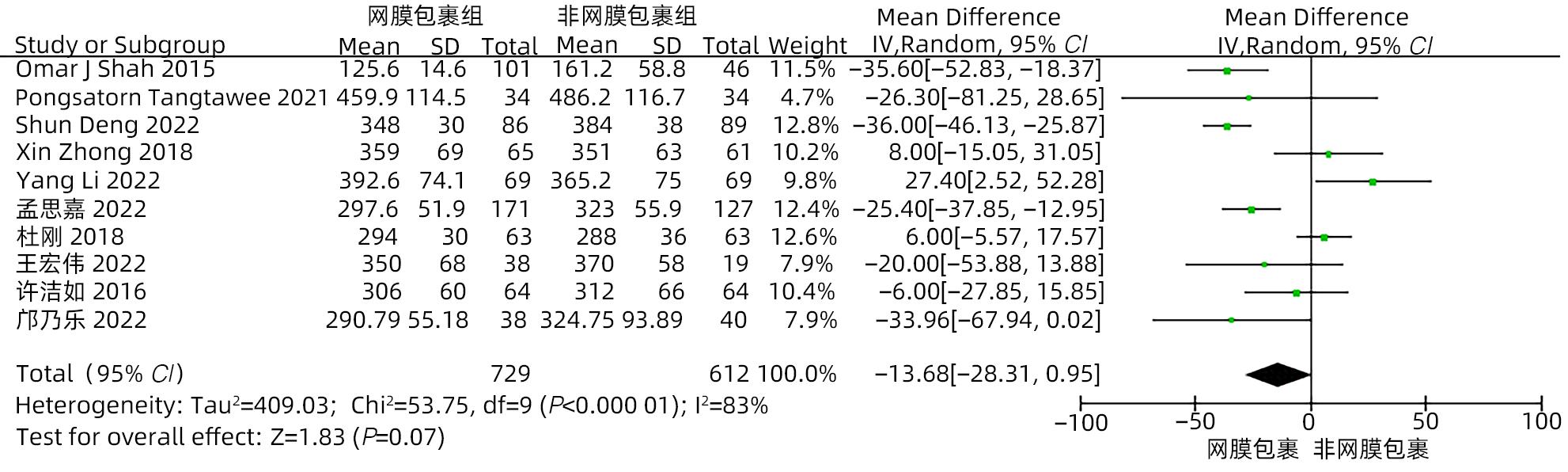
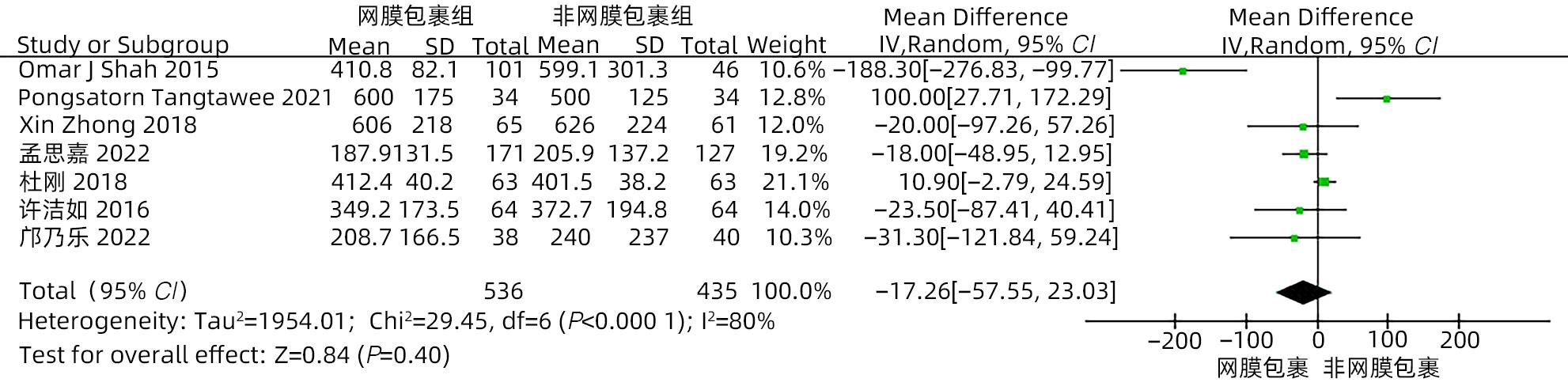
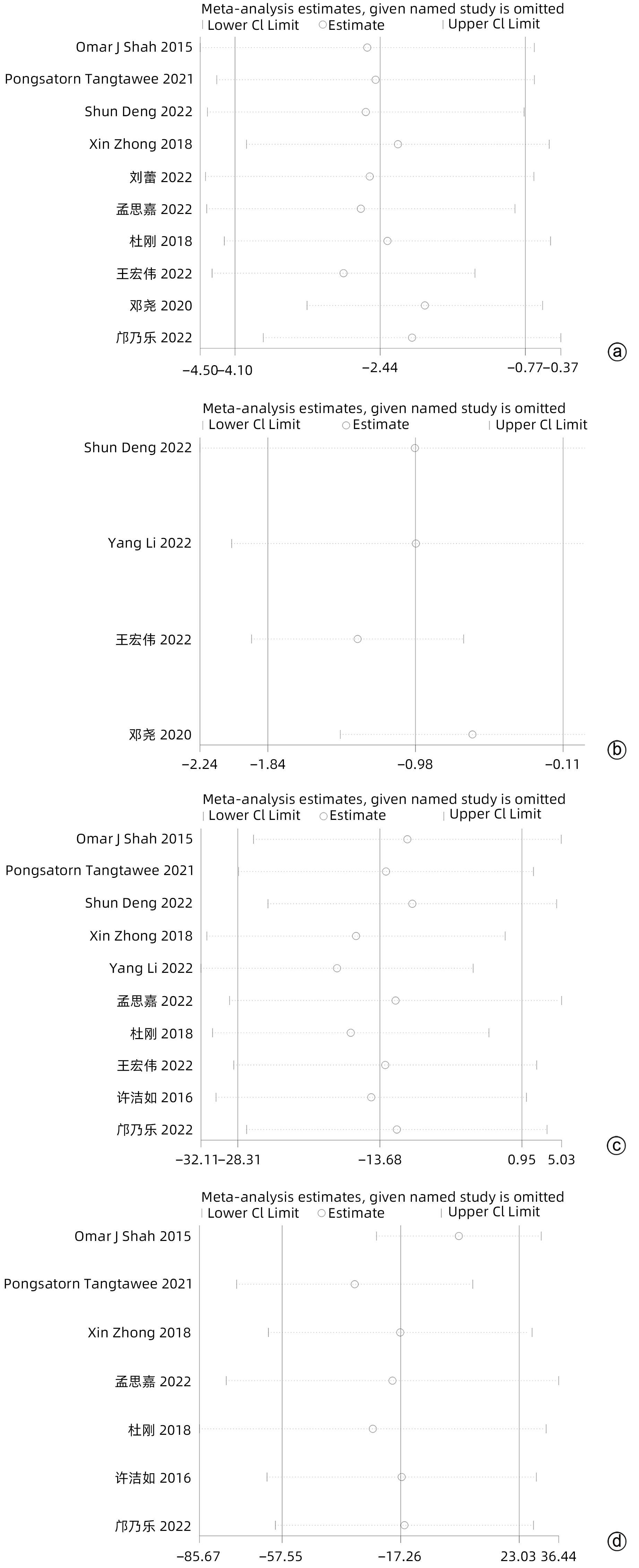
目的 系统评价大网膜包裹胰肠吻合口预防胰十二指肠切除术后并发症的有效性和安全性。 方法 本研究根据PRISMA指南完成。计算机检索中国知网、万方、维普、中国生物医学文献数据库、Cochrane Library、PubMed、Embase和Web of Science等中英文数据库,从数据库建立至2022年11月有关大网膜包裹胰肠吻合口预防胰十二指肠切除术后并发症的临床研究,采用Stata 16和Review Manager 5.4进行Meta分析。 结果 纳入15项研究,共1 830例患者。Meta分析结果显示:网膜包裹组术后胰瘘总体发生率较非网膜包裹组更低(OR=0.30,95%CI:0.22~0.41,P<0.001),亚组分析提示网膜包裹组B/C级术后胰瘘发生率较非网膜包裹组更低(OR=0.29,95%CI:0.21~0.39,P<0.001)。网膜包裹组相较于非网膜包裹组,术后胆漏(OR=0.30,95%CI:0.16~0.56,P<0.001)、术后出血(OR=0.35,95%CI:0.24~0.53,P<0.001)、胃排空障碍(OR=0.45,95%CI:0.31~0.64,P<0.001)、腹腔感染(OR=0.55,95%CI:0.40~0.75,P<0.001)、再次手术(OR=0.31,95%CI:0.18~0.54,P<0.001)、术后30天死亡(OR=0.42,95%CI:0.22~0.80,P=0.009)的发生率更低,开放饮食时间更早(MD=-0.98,95%CI:-1.84~-0.11,P=0.03)、术后住院时间更短(MD=-2.44,95%CI:-4.10~-0.77,P=0.004),两组手术方式在手术时间(MD=-13.68,95%CI:-28.31~0.95,P=0.07)及术中出血量(MD=-17.26,95%CI:-57.55~23.03,P=0.40)方面差异无统计学意义。 结论 网膜包裹可降低术后胰瘘、胆漏、出血、腹腔感染、胃排空障碍等术后并发症的发生率,改善患者预后,缩短住院时间,且不增加手术难度及手术时间。 Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the efficacy and safety of omental wrapping technique for pancreaticojejunal anastomosis in preventing complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy. Methods This study was conducted according to the PRISMA guideline. English and Chinese databases including CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP, CBM, the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science were searched for clinical studies on omental wrapping technique for pancreaticojejunal anastomosis in preventing complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy published up to November 2022, and Stata 16 and Review Manager 5.4 were used to perform the meta-analysis. Results A total of 15 studies with 1 830 patients were included in this study. The meta-analysis showed that the omental wrapping group had a significantly lower overall incidence rate of postoperative pancreatic fistula (POPF) than the non-omental wrapping group (odds ratio [OR]=0.30, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.22 — 0.41, P<0.001), and the subgroup analysis showed that the omental wrapping group had a significantly lower incidence rate of grade B/C POPF than the non-omental wrapping group (OR=0.29, 95%CI: 0.21 — 0.39, P<0.001). Compared with the non-omental wrapping group, the omental wrapping group had significantly lower incidence rates of postoperative bile leakage (OR=0.30, 95%CI: 0.16 — 0.56, P<0.001), postoperative hemorrhage (OR=0.35, 95%CI: 0.24 — 0.53, P<0.001), delayed gastric emptying (OR=0.45, 95%CI: 0.31 — 0.64, P<0.001), abdominal infection (OR=0.55, 95%CI: 0.40 — 0.75, P<0.001), reoperation (OR=0.31, 95%CI: 0.18 — 0.54, P<0.001), and death within 30 days after surgery (OR=0.42, 95%CI: 0.22 — 0.80, P=0.009), a significantly earlier time to diet (mean difference [MD]=-0.98, 95%CI: -1.84 to -0.11, P=0.03), and a significantly shorter length of postoperative hospital stay (MD=-2.44, 95%CI: -4.10 to -0.77, P=0.004). There were no significant differences between the two groups in the time of operation (MD=-13.68, 95%CI: -28.31 to -0.95, P=0.07) and intraoperative blood loss (MD=-17.26, 95%CI: -57.55 to -23.03, P=0.40). Conclusion Omental wrapping can reduce the incidence rates of postoperative complications such as pancreatic fistula, bile leakage, postoperative hemorrhage, abdominal infection, and delayed gastric emptying, improve the prognosis of patients, and shorten the length of hospital stay, without increasing surgical difficulty or time of operation. -
Key words:
- Pancreaticoduodenectomy /
- Omentum /
- Surgical Stomas /
- Postoperative Complications /
- Meta-Analysis
-
表 1 纳入研究的基线资料
Table 1. Baseline data included in the study
作者 发表时间 研究类型 国家 研究周期 组别 年龄(岁) 男/女(例) 例数 BMI (kg/m2) 结局指标 Shah[11] 2015 RCS 印度 2006—2012 T C 61.5 60.2 59/42 27/19 101 46 21.5 20.6 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑩⑪ Tangtawee[12] 2021 RCT 泰国 2017—2019 T C 62.0 58.2 17/17 16/18 34 34 22.7 23.2 ①③④⑤⑦⑧⑩⑪ Choi[13] 2012 RCS 韩国 2009—2011 T C 63.9 63.9 19/10 25/14 29 39 23.6 23.6 ①③ Deng[14] 2022 RCS 中国 2015—2020 T C 60.6 57.6 49/37 60/29 86 89 23.0 23.1 ①②③④⑤⑥⑧⑨⑩ Kapoor[15] 2006 RCS 印度 2002—2006 T C NA NA NA/NA NA/NA 25 52 NA NA ①③⑦ Zhong[16] 2018 RCS 中国 2005—2016 T C 59.8 57.8 31/34 31/30 65 61 22.6 22.1 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑩⑪ Li[17] 2022 RCS 中国 2015—2019 T C 64.2 62.1 46/23 44/25 69 69 21.9 22.0 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑨⑩ 刘蕾[18] 2022 RCS 中国 2017—2020 T C 64.3 59.1 17/18 20/23 35 43 NA NA ①③④⑤⑥⑦⑧ 孙韶龙[19] 2016 RCT 中国 2013—2015 T C 65 63 13/5 11/7 35 35 NA NA ① 孟思嘉[20] 2022 RCS 中国 2015—2021 T C 61.0 61.3 102/69 71/56 171 127 NA NA ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑩⑪ 杜刚[21] 2018 RCS 中国 2012—2017 T C 53.3 52.8 33/30 34/29 63 63 NA NA ①③④⑤⑥⑩⑪ 王宏伟[22] 2022 RCS 中国 2018—2021 T C 64.6 62.8 22/16 11/8 38 19 21.8 20.8 ①③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑩ 许洁如[23] 2016 RCS 中国 2009—2015 T C 56.3 56.8 38/26 41/43 64 64 NA NA ①③④⑤⑥⑦⑩⑪ 邓尧[24] 2020 RCS 中国 2015—2018 T C 64.8 62.1 79/48 44/25 127 69 21.9 22.0 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨ 邝乃乐[25] 2022 RCS 中国 2018—2020 T C 59.6 62.6 22/16 19/21 38 40 NA NA ①②③④⑥⑧⑩⑪ 注:T,网膜包裹组;C,非网膜包裹组。结局指标:①POPF;②胆漏;③PPH;④DGE;⑤腹腔感染;⑥再手术;⑦术后30天内病死率;⑧术后住院时间;⑨开放饮食时间;⑩手术时间;⑪术中出血量;NA,未提供。 表 2 纳入RCS的质量评价
Table 2. Quality evaluation of the included RCS
表 3 纳入RCT的质量评价
Table 3. Quality evaluation of the included RCT
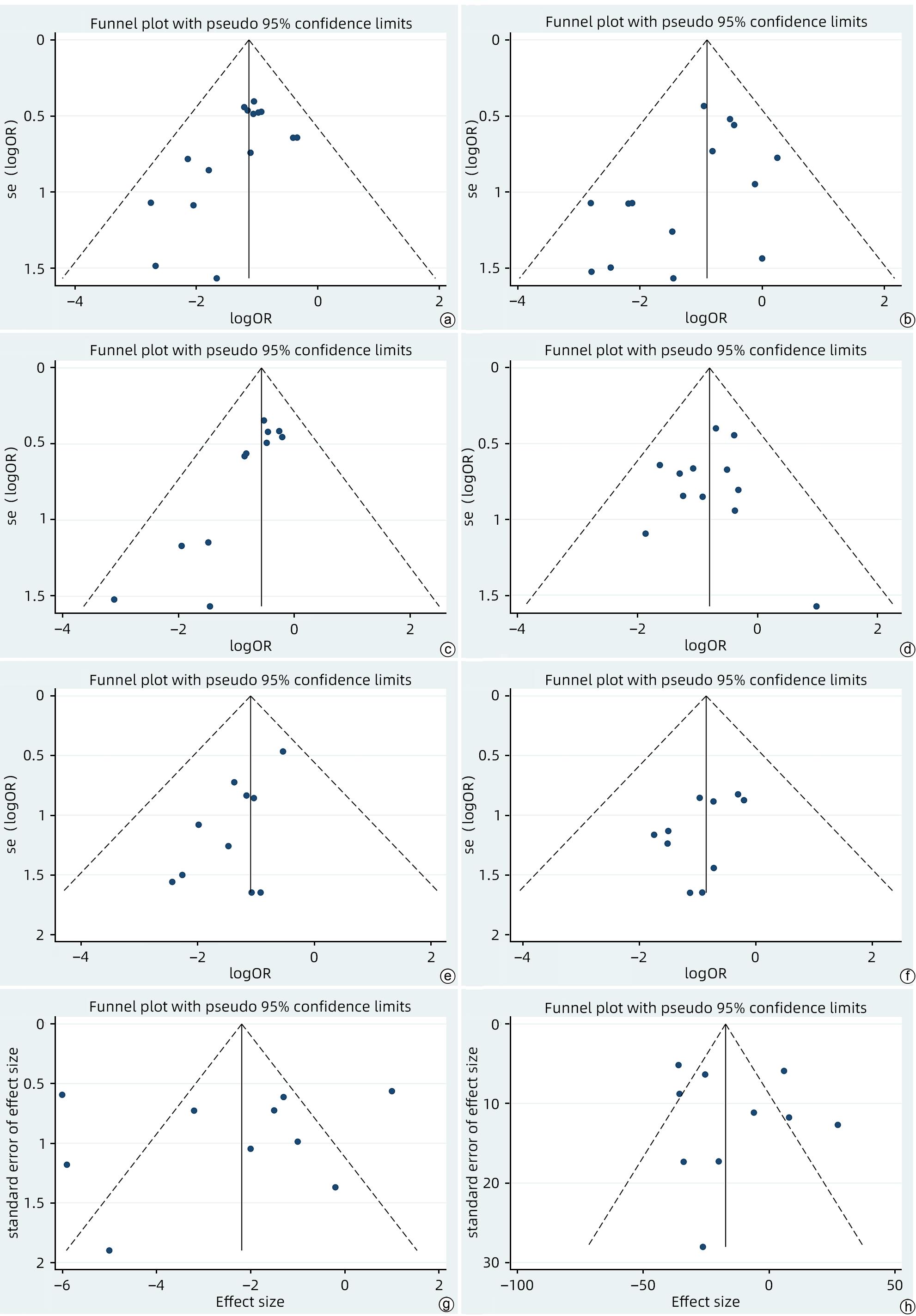
表 4 发表偏倚结果
Table 4. Publication bias results
结局指标 例数 Begg’s检验 Egger’s检验 Z值 Pr>|Z| t值 P值 POPF 15 1.88 0.060 -2.58 0.023 PPH 14 1.53 0.125 -1.97 0.072 术后腹腔感染 11 2.80 0.005 -5.04 0.001 术后DGE 12 0.34 0.732 -0.27 0.796 再次手术 10 0.36 0.721 -3.10 0.015 术后30天病死率 11 1.67 0.283 -1.65 0.137 术后住院时间 10 0.89 0.371 -0.44 0.671 手术时间 10 0.36 0.721 0.62 0.551 -
[1] ZHU L, YANG XL, LIU L, et al. Efficacy and safety of enhanced recovery after surgery in the perioperative period of pancreaticoduodenectomy: A systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1356- 1363. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.026.朱琳, 杨小李, 刘莉, 等. 加速康复外科在胰十二指肠切除术围手术期应用有效性和安全性的系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2022, 38( 6): 1356- 1363. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.026. [2] STROBEL O, NEOPTOLEMOS J, JÄGER D, et al. Optimizing the outcomes of pancreatic cancer surgery[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2019, 16( 1): 11- 26. DOI: 10.1038/s41571-018-0112-1. [3] OLAKOWSKI M, GRUDZIŃSKA E. Pancreatic head cancer-Current surgery techniques[J]. Asian J Surg, 2023, 46( 1): 73- 81. DOI: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.05.117. [4] YAN Y, HUA YG, CHANG C, et al. Laparoscopic versus open pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic and periampullary tumor: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and non-randomized comparative studies[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1093395. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1093395. [5] HARTWIG W, WERNER J, JÄGER D, et al. Improvement of surgical results for pancreatic cancer[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2013, 14( 11): e476- e485. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70172-4. [6] MCMILLAN MT, VOLLMER CM Jr. Predictive factors for pancreatic fistula following pancreatectomy[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2014, 399( 7): 811- 824. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-014-1220-8. [7] WELSCH T, EISELE H, ZSCHÄBITZ S, et al. Critical appraisal of the International Study Group of Pancreatic Surgery(ISGPS) consensus definition of postoperative hemorrhage after pancreatoduodenectomy[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2011, 396( 6): 783- 791. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-011-0811-x. [8] ANDREASI V, PARTELLI S, CRIPPA S, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on the role of omental or falciform ligament wrapping during pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. HPB, 2020, 22( 9): 1227- 1239. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2020.05.003. [9] TANI M, KAWAI M, HIRONO S, et al. Use of omentum or falciform ligament does not decrease complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy: Nationwide survey of the Japanese Society of Pancreatic Surgery[J]. Surgery, 2012, 151( 2): 183- 191. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.07.023. [10] HOZO SP, DJULBEGOVIC B, HOZO I. Estimating the mean and variance from the Median, range, and the size of a sample[J]. BMC Med Res Methodol, 2005, 5: 13. DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13. [11] SHAH OJ, BANGRI SA, SINGH M, et al. Omental flaps reduces complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2015, 14( 3): 313- 319. DOI: 10.1016/S1499-3872(15)60372-1. [12] TANGTAWEE P, MINGPHRUEDHI S, RUNGSAKULKIJ N, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of omental roll-up technique on pancreatojejunostomy anastomosis for reducing perioperative complication in patients undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2021, 28( 5): 450- 456. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.948. [13] CHOI SB, LEE JS, KIM WB, et al. Efficacy of the omental roll-up technique in pancreaticojejunostomy as a strategy to prevent pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Arch Surg, 2012, 147( 2): 145- 150. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.2011.865. [14] DENG S, LUO JH, OUYANG YZ, et al. Application analysis of omental flap isolation and modified pancreaticojejunostomy in pancreaticoduodenectomy(175 cases)[J]. BMC Surg, 2022, 22( 1): 127. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-022-01552-9. [15] KAPOOR VK, SHARMA A, BEHARI A, et al. Omental flaps in pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. JOP, 2006, 7( 6): 608- 615. [16] ZHONG X, WANG XF, PAN JH, et al. Mesh-reinforced pancreaticojejunostomy versus conventional pancreaticojejunostomy after pancreaticoduodenectomy: A retrospective study of 126 patients[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2018, 16( 1): 68. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-018-1365-y. [17] LI Y, LIANG Y, DENG Y, et al. Application of omental interposition to reduce pancreatic fistula and related complications in pancreaticoduodenectomy: A propensity score-matched study[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2022, 14( 5): 482- 493. DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v14.i5.482. [18] LIU L, MA RR, WANG Y, et al. Application of pedicled omentum wrapping pancreaticojejunostomy in pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Chin J Pancreatol, 2022( 2): 123- 126.刘蕾, 马睿锐, 汪洋, 等. 带蒂大网膜包裹胰肠吻合在胰十二指肠切除术中的应用[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2022( 2): 123- 126. [19] SUN SL, YANG HW, GU SL, et al. Omental roll-up technique in pancreaticojejunostomy as a strategy to prevent postoperative pancreatic fistula[J]. J Clin Surg, 2016, 24( 1): 39- 41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2016.01.013.孙韶龙, 杨华威, 顾帅林, 等. 采用胰肠吻合口大网膜缠绕方法预防术后胰瘘[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2016, 24( 1): 39- 41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6483.2016.01.013. [20] MENG SJ, LI SD, MOU YP, et al. Application of omental flap technique in laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2022, 42( 5): 580- 584. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2022.05.20.孟思嘉, 李少栋, 牟一平, 等. 应用网膜垫技术行腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除术临床研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2022, 42( 5): 580- 584. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2022.05.20. [21] DU G, JIN FT, YUAN T, et al. Effect of pancreatic-intestinal anastomosis with greater omentum wrapping in pancreaticoduodenectomy and its influence on pancreatic fistula[J]. Chin J Clin Res, 2018, 31( 7): 918- 921. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2018.07.013.杜刚, 靳福廷, 袁涛, 等. 胰肠吻合口大网膜包裹技术在胰十二指肠切除术中的应用效果及其对胰瘘的影响[J]. 中国临床研究, 2018, 31( 7): 918- 921. DOI: 10.13429/j.cnki.cjcr.2018.07.013. [22] WANG HW, LI Y, DENG Y, et al. Application of an omental pad to reduce pancreatic fistula and related complications in laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: A propensity score-matched study[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2022, 42( 8): 900- 905. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2022.08.11.王宏伟, 李杨, 邓尧, 等. 应用大网膜衬垫技术预防腹腔镜胰十二指肠切除术后胰瘘及相关并发症研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2022, 42( 8): 900- 905. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2022.08.11. [23] XU JR, CHEN C, SHEN NJ, et al. A comparative study of omentum wrapping in pancreaticojejunostomy for reducing postoperative pancreatic fistula[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2016, 36( 11): 1200- 1204.许洁如, 陈超, 沈宁佳, 等. 胰肠吻合口网膜包裹技术临床疗效研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2016, 36( 11): 1200- 1204. [24] DENG Y, JIANG CY, LIANG Y, et al. Application of omental-pad in reducing postoperative pancreatic fistula and associated severe complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2020, 40( 2): 218- 223. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.02.18.邓尧, 姜翀弋, 梁赟, 等. 大网膜衬垫技术在胰十二指肠切除术中应用研究[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40( 2): 218- 223. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.02.18. [25] KUANG NL, XU JN, CHEN YY, et al. Experience in the application of greater omentum wrapping pancreaticoenteric anastomotic sto? ma in preventing pancreatic leakage in pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Lingnan Mod Clin Surg, 2022, 22( 3): 232- 235, 244. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2022.03.004.邝乃乐, 许洁娜, 陈云扬, 等. 大网膜包裹胰肠吻合口在胰十二指肠切除术中的应用体会[J]. 岭南现代临床外科, 2022, 22( 3): 232- 235, 244. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-976X.2022.03.004. [26] BASSI C, DERVENIS C, BUTTURINI G, et al. Postoperative pancreatic fistula: An international study group(ISGPF) definition[J]. Surgery, 2005, 138( 1): 8- 13. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.05.001. [27] BASSI C, MARCHEGIANI G, DERVENIS C, et al. The 2016 update of the International Study Group(ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 Years After[J]. Surgery, 2017, 161( 3): 584- 591. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.11.014. [28] HIRASHITA T, IWASHITA Y, FUJINAGA A, et al. Short internal pancreatic stent reduces pancreatic fistula in pancreatoduodenectomy[J]. Langenbecks Arch Surg, 2021, 406( 3): 721- 728. DOI: 10.1007/s00423-020-02036-1. [29] KAWAIDA H, KONO H, HOSOMURA N, et al. Surgical techniques and postoperative management to prevent postoperative pancreatic fistula after pancreatic surgery[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25( 28): 3722- 3737. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i28.3722. [30] YE P, CAO JL, LI QY, et al. Mediastinal transposition of the omentum reduces infection severity and pharmacy cost for patients undergoing esophagectomy[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2016, 8( 7): 1653- 1660. DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2016.05.92. [31] MORIURA S, IKEDA S, IKEZAWA T, et al. The inclusion of an omental flap in pancreatoduodenectomy[J]. Surg Today, 1994, 24( 10): 940- 941. DOI: 10.1007/BF01651016. [32] ANDRIANELLO S, MARCHEGIANI G, MALLEO G, et al. Biliary fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy: Data from 1618 consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies[J]. HPB, 2017, 19( 3): 264- 269. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2016.11.011. [33] NA Z, ZHANG XW, DONG KG, et al. Experimental study on the effect of omental adipose on bile duct stricture scar[J]. J Kunming Med Univ, 2015, 36( 5): 25- 29.纳钊, 张小文, 董克刚, 等. 大网膜脂肪对胆管瘢痕狭窄作用的实验研究[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2015, 36( 5): 25- 29. [34] GOEV AA, BERELAVICHUS SV, KARCHAKOV SS, et al. Postpancreatectomy hemorrhage[J]. Khir Z Im NI Pirogova, 2021( 1): 77. DOI: 10.17116/hirurgia202101177. [35] MENG LW, GAO P, PENG B. The pedicled teres hepatis ligament flap wrap around the gastroduodenal artery stump to prevent postoperative hemorrhage after laparoscopic pancreatoduodenectomy(with video)[J]. J Sichuan Univ Med Sci Ed, 2020, 51( 4): 453- 456. DOI: 10.12182/20200760602.孟令威, 高攀, 彭兵. 带蒂肝圆韧带包裹胃十二指肠动脉残端预防LPD术后出血(附手术视频)[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2020, 51( 4): 453- 456. DOI: 10.12182/20200760602. [36] MENG LW, CAI H, CAI YQ, et al. Wrapping the stump of the gastroduodenal artery using the ligamentum teres hepatis during laparoscopic pancreaticoduodenectomy: A center’s preliminary experience[J]. BMC Surg, 2021, 21( 1): 70. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-021-01076-8. [37] ELLIS RJ, GUPTA AR, HEWITT DB, et al. Risk factors for post-pancreaticoduodenectomy delayed gastric emptying in the absence of pancreatic fistula or intra-abdominal infection[J]. J Surg Oncol, 2019, 119( 7): 925- 931. DOI: 10.1002/jso.25398. [38] LIU QY, LI L, XIA HT, et al. Risk factors of delayed gastric emptying following pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2016, 86( 1-2): 69- 73. DOI: 10.1111/ans.12850. [39] ZHANG JZ, LI S, ZHU WH, et al. Subtotal gastrectomy pancreaticoduodenectomy versus conventional pancreaticoduodenectomy in the incidence of delayed gastric emptying: Single-center retrospective cohort study[J]. BMC Surg, 2022, 22( 1): 376. DOI: 10.1186/s12893-022-01824-4. [40] MIRRIELEES JA, WEBER SM, ABBOTT DE, et al. Pancreatic fistula and delayed gastric emptying are the highest-impact complications after Whipple[J]. J Surg Res, 2020, 250: 80- 87. DOI: 10.1016/j.jss.2019.12.041. -



 PDF下载 ( 2134 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2134 KB)

 下载:
下载: