驱动蛋白家族成员15(KIF15)对肝细胞癌增殖能力的影响及其作用机制
DOI: 10.12449/JCH240217
Effect of kinesin family member 15 on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism of action
-
摘要:
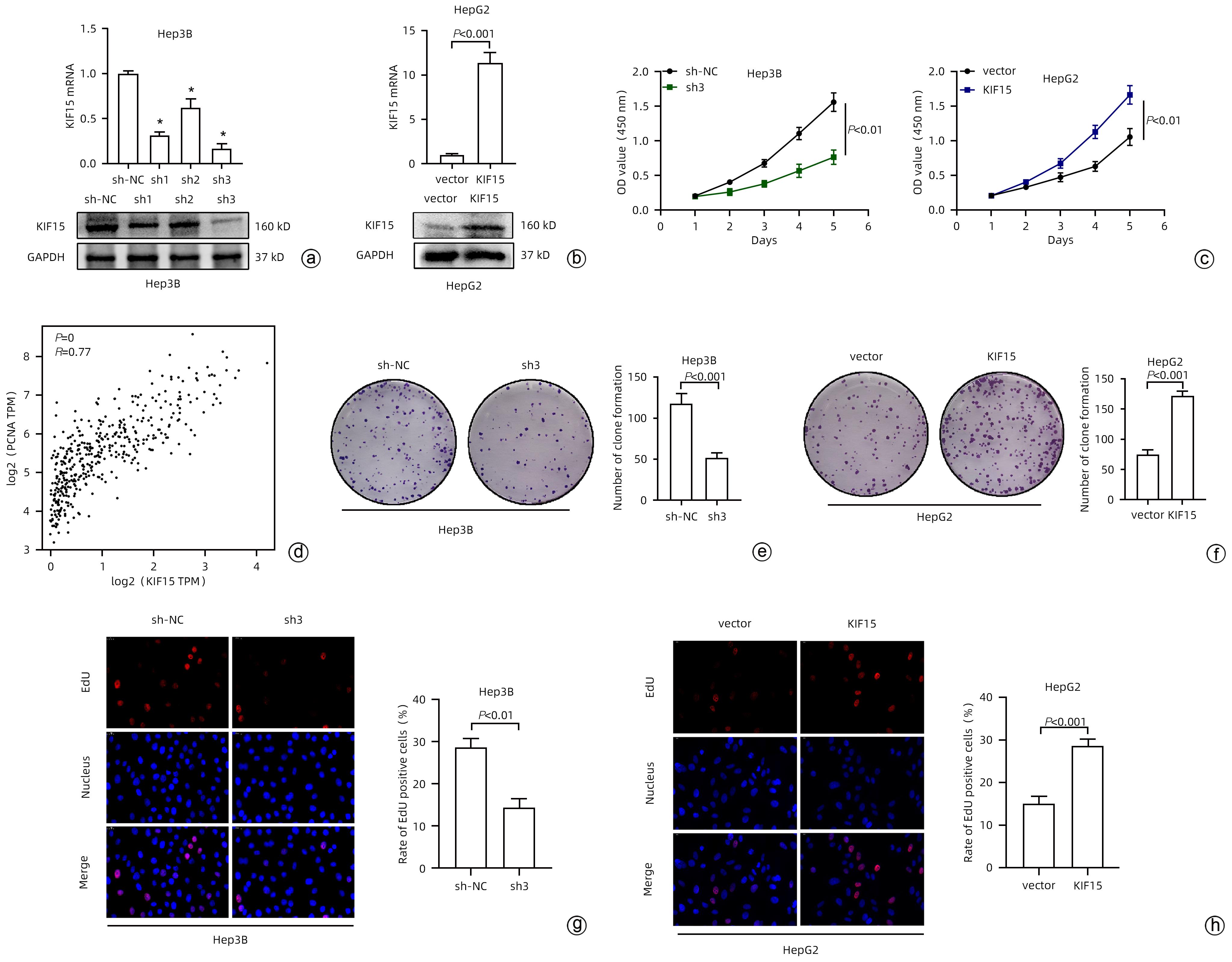
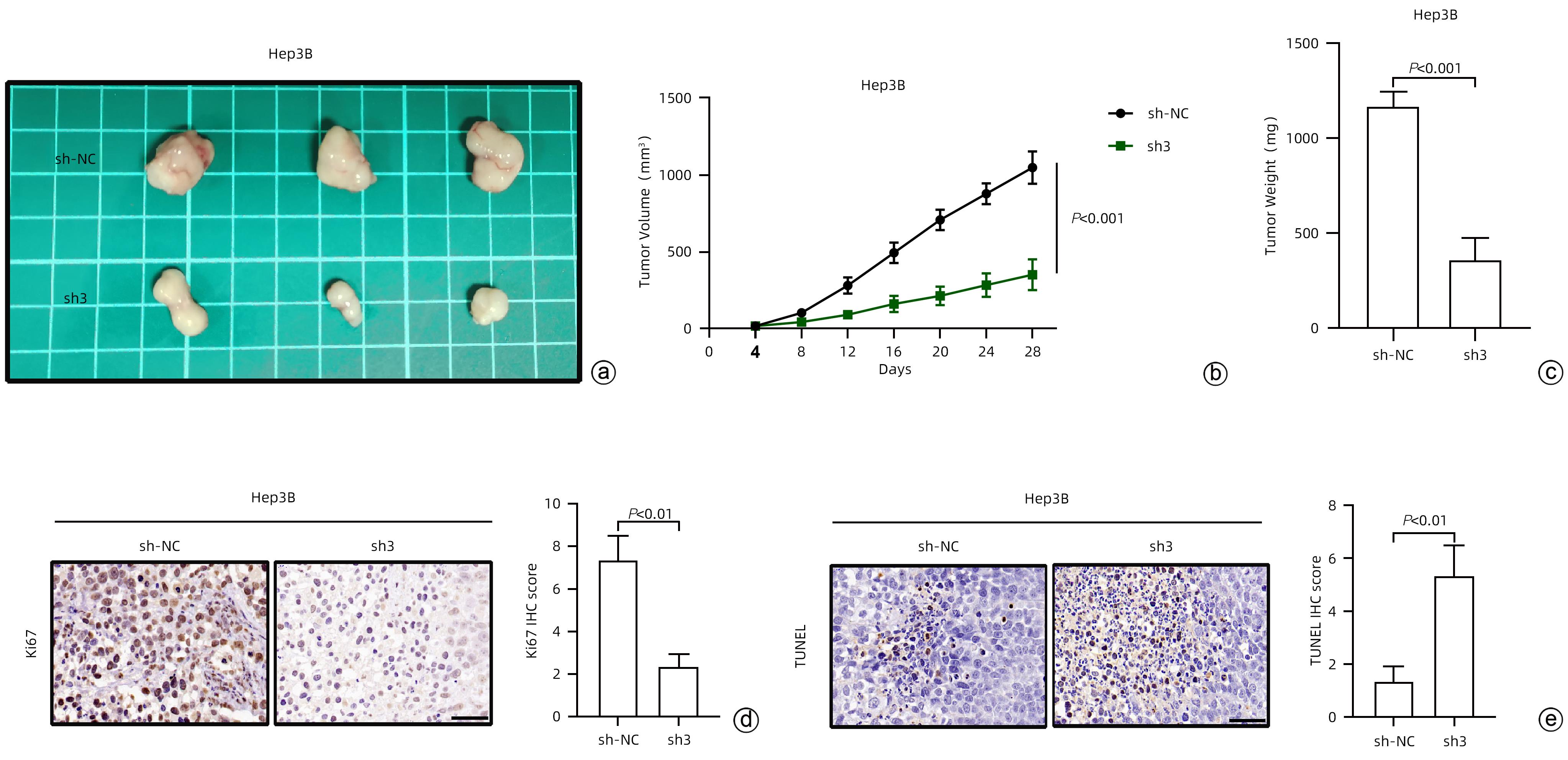
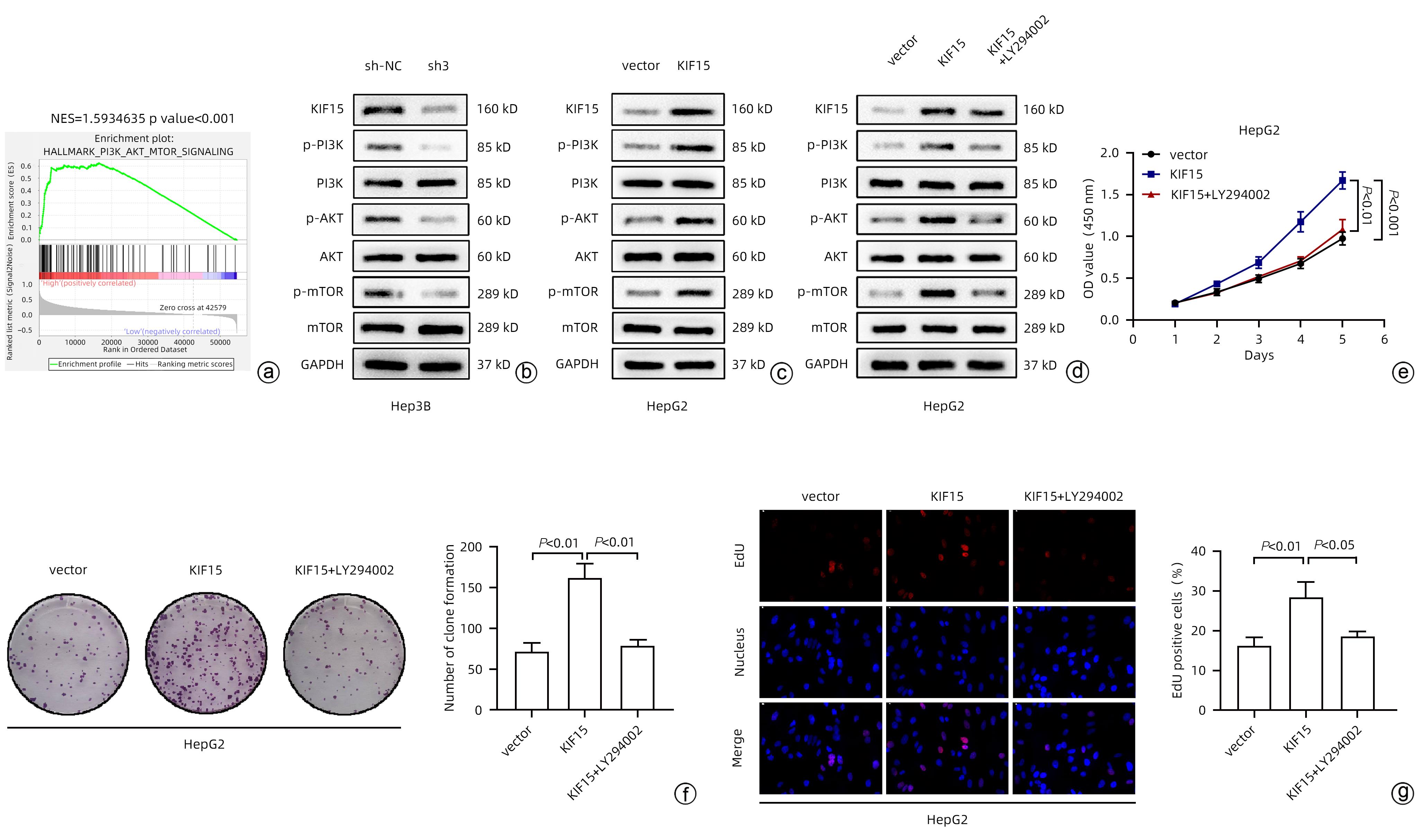
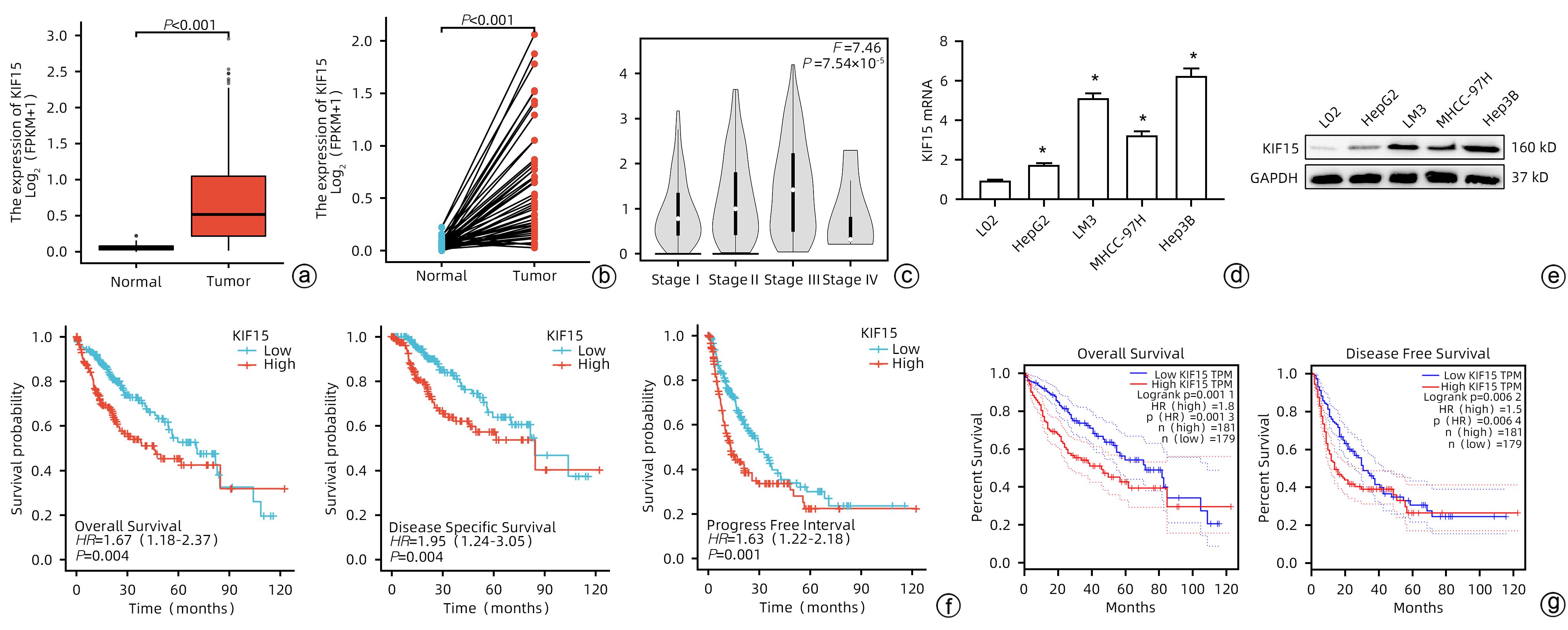
目的 探究驱动蛋白家族成员15(KIF15)对肝细胞癌(HCC)增殖能力的影响及其作用机制。 方法 通过分析TCGA和GEPIA数据集确定KIF15在HCC中的表达情况以及对肿瘤分期、生存的影响。采用qRT-PCR和Western Blot检测体外培养的人源HCC细胞系(HepG2、Hep3B、MHCC-97H和LM3)与人正常肝细胞系L02细胞的KIF15表达水平,并选择Hep3B和HepG2进行后续研究。通过对Hep3B慢病毒转染sh-NC/sh-KIF15和对HepG2慢病毒转染LV-vector/LV-KIF15进行CCK-8、平板克隆和EdU染色实验评估细胞的活力和增殖能力。GSEA分析KIF15与HCC相关的作用信号通路并通过Western Blot进行检测。计量资料两组间比较采用成组t检验;多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。 结果 TCGA和GEPIA数据集分析结果显示KIF15在HCC患者癌组织中的表达明显高于正常组织,并且KIF15与HCC分期成正比,KIF15高表达的HCC患者的生存更差。与sh-NC-Hep3B相比,sh3-Hep3B的KIF15 mRNA水平和蛋白水平均下降(P值均<0.05);与sh-NC-Hep3B相比,sh3-Hep3B的细胞活力、克隆形成数和EdU阳性率均显著降低(P值均<0.05)。与vector-HepG2相比,LV-KIF15-HepG2的KIF15 mRNA水平和蛋白水平均升高(P值均<0.05);与vector-HepG2相比,LV-KIF15-HepG2的细胞活力、克隆形成数和EdU阳性率均提高(P值均<0.05)。皮下瘤实验结果显示:与sh-NC-Hep3B相比,sh3-Hep3B的瘤体积和瘤重量降低;Ki67的组化评分降低,而TUNEL的组化评分提高(P值均<0.05)。GSEA分析显示在HCC中PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路与KIF15呈正相关(NES=1.59,P<0.001),Western Blot检测发现LY294002能够抑制LV-KIF15-HepG2中上调的PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路,与LV-KIF15-HepG2相比,LY294002+LV-KIF15-HepG2的细胞活力、克隆形成数和EdU阳性率降低(P值均<0.05)。 结论 KIF15通过上调PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路增强HCC的活力和增殖能力。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of kinesin family member 15 (KIF15) on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells and its mechanism of action. Methods TCGA and GEPIA datasets were analyzed to determine the expression of KIF15 in HCC and its effect on tumor stage and survival. Quantitative real-time PCR and Western blot were used to measure the expression level of KIF15 in human-derived HCC cell lines (HepG2, Hep3B, MHCC-97H, and LM3) and human normal liver cell line L02 cultured in vitro, and Hep3B and HepG2 were selected for subsequent studies. CCK-8 assay, plate colony formation assay, and EdU staining were performed for Hep3B cells transfected with shRNA-NC or shRNA-KIF15 and HepG2 cells transfected with LV-vector or LV-KIF15 to evaluate the viability and proliferative capacity of these cells. GSEA was used to analyze the potential signaling pathways associated with KIF15 in HCC, and Western blot was used for detection. The independent-samples t test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups; a one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between multiple groups, and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results The analysis of TCGA and GEPIA datasets showed that in HCC patients, the expression of KIF15 in HCC tissue was significantly higher than that in normal tissue, and the HCC patients with high KIF15 expression tended to have a poorer prognosis. Compared with sh-NC-Hep3B, sh3-Hep3B showed significant reductions in the mRNA and protein levels of KIF15 (P<0.05), cell viability, clone formation number, and EdU positive rate (all P<0.05). Compared with vector-HepG2, LV-KIF15-HepG2 showed significant increases in the mRNA and protein levels of KIF15 (P<0.05), cell viability, clone formation number, and EdU positive rate (all P<0.05). Subcutaneous tumor assay showed that compared with sh-NC-Hep3B, sh3-Hep3B showed reductions in tumor volume and tumor weight, as well as a significant reduction in the immunohistochemical score of Ki67 and a significant increase in the immunohistochemical score of TUNEL (P<0.05). GSEA analysis showed that the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway was positively correlated with KIF15 in HCC (NES=1.59, P<0.001). Western blot showed that LY294002 could inhibit the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway upregulated in LV-KIF15-HepG2, and compared with LV-KIF15-HepG2, LY294002+LV-KIF15-HepG2 showed significant reductions in cell viability, clone formation number, and EdU positive rate (all P<0.05). Conclusion KIF15 enhances the viability and proliferative capacity of HCC cells by upregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- Kinesin /
- Signal Transduction /
- Cell Proliferation
-
注: a,GSEA分析KIF15在HCC中潜在的作用通路;b,Western Blot验证Hep3B细胞中PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路表达情况;c、d,Western Blot验证HepG2细胞中PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路表达情况;e,CCK-8实验分析HepG2细胞增殖活力;f,克隆形成实验分析HepG2细胞克隆数;g,EdU实验分析HepG2细胞增殖活力。
图 4 KIF15对HCC增殖能力影响的机制探究
Figure 4. The mechanism of the effect of KIF15 on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma
表 1 Western Blot 检测KIF15蛋白在HCC细胞株中的表达水平
Table 1. The protein expression level of KIF15 in HCC cell lines by Western Blot
组别 KIF15 L02 1.00±0.02 HepG2 1.45±0.101) LM3 5.22±0.391) MHCC-97H 3.49±0.251) Hep3B 7.69±0.611) F值 192.40 P值 <0.001 注:与L02组比较,1)P<0.05。 表 2 Western Blot 检测KIF15蛋白在Hep3B中的表达水平
Table 2. The protein expression level of KIF15 in Hep3B by Western Blot
分组 KIF15 sh-NC 1.00±0.08 sh1 0.54±0.141) sh2 0.66±0.081) sh3 0.15±0.051) F值 41.63 P值 <0.001 注:与sh-NC组比较,1)P<0.05。 表 3 Western Blot 检测Hep3B细胞中相关蛋白表达结果
Table 3. Western Blot analysis was performed to determine the expression levels of related proteins in Hep3B cells
分组 KIF15 p-PI3K/PI3K p-AKT/AKT p-mTOR/mTOR sh-NC 1.05±0.10 0.99±0.06 0.99±0.06 0.98±0.07 sh3 0.19±0.03 0.14±0.04 0.24±0.05 0.22±0.02 t值 13.88 19.66 16.71 17.48 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 4 Western Blot 检测HepG2细胞中相关蛋白表达结果
Table 4. Western Blot analysis was performed to determine the expression levels of related proteins in HepG2 cells
分组 KIF15 p-PI3K/PI3K p-AKT/AKT p-mTOR/mTOR vector 1.00±0.06 1.04±0.10 1.02±0.06 0.96±0.04 KIF15 6.12±0.20 5.11±0.22 4.56±0.49 4.56±0.55 t值 41.97 29.29 12.46 11.24 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 表 5 LY294002抑制剂干预对HepG2细胞中相关蛋白表达的影响
Table 5. The effect of inhibitor LY294002 intervention on the expression of related proteins in HepG2 cells
分组 KIF15 p-PI3K/PI3K p-AKT/AKT p-mTOR/mTOR vector 1.06±0.13 1.01±0.09 0.96±0.08 0.97±0.05 KIF15 5.68±0.35 4.64±0.57 4.70±0.51 4.82±0.37 KIF15+LY294002 5.42±0.251) 1.17±0.091) 1.07±0.121) 1.22±0.101) F值 301.05 111.64 145.32 284.41 P值 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 注:与KIF15组比较,1)P<0.05。 -
[1] YU SJ. Immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advances and future targets[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 244: 108387. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108387. [2] BROWN ZJ, TSILIMIGRAS DI, RUFF SM, et al. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review[J]. JAMA Surg, 2023, 158( 4): 410- 420. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2022.7989. [3] ALMEIDA AC, MAIATO H. Chromokinesins[J]. Curr Biol, 2018, 28( 19): R1131- R1135. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2018.07.017. [4] BEGLEY MA, SOLON AL, DAVIS EM, et al. K-fiber bundles in the mitotic spindle are mechanically reinforced by Kif15[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2021, 32( 22): br11. DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E20-06-0426. [5] LUO Y, ZHANG B, XU L, et al. Downregulation of KIF15 inhibits the tumorigenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer via inactivating Raf/MEK/ERK signaling[J]. Histol Histopathol, 2022, 37( 3): 269- 285. DOI: 10.14670/HH-18-408. [6] GE W, CHEN Y, GUO Y, et al. KIF15 upregulation promotes leiomyosarcoma cell growth via promoting USP15-mediated DEK deubiquitylation[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2021, 570: 117- 124. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.042. [7] TAO J, SUN G, LI Q, et al. KIF15 promotes the evolution of gastric cancer cells through inhibition of reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235( 12): 9388- 9398. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.29743. [8] RUMGAY H, ARNOLD M, FERLAY J, et al. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 77( 6): 1598- 1606. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.08.021. [9] SUN Y, ZHANG W, BI X, et al. Systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Chinese consensus-based interdisciplinary expert statements[J]. Liver Cancer, 2022, 11( 3): 192- 208. DOI: 10.1159/000521596. [10] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2022[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2022, 72( 1): 7- 33. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21708. [11] Chinese Association of Liver Cancer of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese expert consensus on the whole‐course management of hepatocellular carcinoma(2023 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2023, 22( 7): 824- 842. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20230605-00261.中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会. 肝细胞癌全程管理中国专家共识(2023版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2023, 22( 7): 824- 842. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115610-20230605-00261. [12] ZHANG S, TU Q, QIAN X, et al. Deficiency of Kif15 gene inhibits tumor growth due to host CD8+T lymphocytes increase[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2023, 655: 110- 117. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.03.006. [13] VANNESTE D, FERREIRA V, VERNOS I. Chromokinesins: localization-dependent functions and regulation during cell division[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2011, 39( 5): 1154- 1160. DOI: 10.1042/BST0391154. [14] HE Z, WANG J, XU J, et al. Dynamic regulation of KIF15 phosphorylation and acetylation promotes focal adhesions disassembly in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13( 10): 896. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-022-05338-y. [15] SUN RF, HE N, ZHANG GY, et al. Combined inhibition of KIF11 and KIF15 as an effective therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer[J]. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 2023, 23( 4): 293- 306. DOI: 10.2174/1568009622666220616122846. [16] QUAN G, XU J, WANG J, et al. KIF15 is essential for USP10-mediated PGK1 deubiquitination during the glycolysis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14( 2): 137. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-05679-2. [17] WANG L, ZHANG X, LIU J, et al. Kinesin family member 15 can promote the proliferation of glioblastoma[J]. Math Biosci Eng, 2022, 19( 8): 8259- 8272. DOI: 10.3934/mbe.2022384. [18] MI J, MA S, CHEN W, et al. Integrative pan-cancer analysis of KIF15 reveals its diagnosis and prognosis value in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 772816. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.772816. [19] GAO L, ZHANG W, ZHANG J, et al. KIF15-mediated stabilization of AR and AR-V7 contributes to enzalutamide resistance in prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81( 4): 1026- 1039. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1965. [20] CHAN YT, LIN RJ, WANG YH, et al. The interplay between IGF-1R signaling and Hippo-YAP in breast cancer stem cells[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21( 1): 81. DOI: 10.1186/s12964-023-01088-2. [21] TIAN LY, SMIT DJ, JÜCKER M. The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24( 3): 2652. DOI: 10.3390/ijms24032652. [22] LIU M, HUANG XD, HAN Z, et al. Effect of cadherin-17 on proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells and its PI3K/AKT/m TOR signaling pathway regulatory mechanism[J]. J Jilin Univ(Med Edit), 2023, 49( 4): 1008- 1017. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230423.刘蒙, 黄晓东, 韩峥, 等. 钙黏蛋白17对结直肠癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路调节机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023, 49( 4): 1008- 1017. DOI: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230423. [23] JIANG Q, GUAN Y, ZHENG J, et al. TBK1 promotes thyroid cancer progress by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11( 3): e796. DOI: 10.1002/iid3.796. [24] LI Y, WANG S, JIN K, et al. UHMK1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma oncogenesis by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2023, 14( 12): 1077- 1088. DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.14850. [25] CHEN J, LIU F, WU J, et al. Effect of STK3 on proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Cell Signal, 2023, 106: 110642. DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110642. -



 PDF下载 ( 1773 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1773 KB)

 下载:
下载: