A clinical study of chronic hepatitis B patients with Epstein-Barr virus infection
-
摘要: 目的探讨重叠EB病毒(EBV)感染对慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者肝功能及HBV复制的影响。方法选取徐州医科大学附属医院2015年1月-2017年8月收治的CHB患者119例,依据CHB临床分度标准,分为轻度(60例)、中度(38例)和重度(21例)。其中60例为CHB重叠EBV感染患者(重叠感染组),59例为单纯CHB患者(单纯CHB组)。收集2组患者性别、年龄、住院天数、肝功能指标、HBV DNA载量、血常规、凝血功能等临床资料进行对比分析。计量资料2组间比较采用t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验,计数资料组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验。结果 CHB重度患者EBV DNA检出率(76.19%,16例)较轻度(43.33%,26例)和中度(47.37%,18例)患者均明显升高(χ2值分别为6.727、4.601,P值均<0.05);与单纯CHB组比较,重叠感染组患者住院天数、ALT、AST、TBil、DBil、GGT水平均显著升高(t值分别为3.523、4.085、3.755、10.976、8.380;Z=-3.474,...
-
关键词:
- 肝炎,乙型,慢性 /
- 爱泼斯坦巴尔病毒感染 /
- 重叠感染
Abstract: Objective To investigate the influence of Epstein-Barr virus ( EBV) infection on liver function and hepatitis B virus ( HBV) replication in chronic hepatitis B ( CHB) patients. Methods A total of 119 CHB patients who were admitted to The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University from January 2015 to August 2017 were enrolled, and according to the criteria for clinical grading of CHB, they were divided into mild group with 60 patients, moderate group with 38 patients, and severe group with 21 patients. Of all patients, 60 had CHB and EBV superinfection ( superinfection group) and 59 had CHB alone ( CHB group) . The two groups were compared in terms of the clinical data including sex, age, length of hospital stay, liver function parameters, HBV DNA quantification, routine blood test results, and coagulation function. The t-test and the Mann-Whitney U test were used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test and the Fisher's exact test were used for comparison of categorical data between groups. Results The severe group had a significantly higher EBV DNA detection rate than the mild and moderate groups [76. 19% ( 16/21) vs 43. 33% ( 26/60) and 47. 37% ( 18/38) , χ2= 6. 727 and 4. 601, both P < 0. 05]. Compared with the CHB group, the superinfection group had significant increases in the length of hospital stay and the levels of alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase ( t = 3. 523, 4. 085, 3. 755, 10. 976, and 8. 380, Z =-3. 474, all P < 0. 05) and significant reductions in prothrombin time activity and HBV DNA quantification ( t =-2. 501 and-6. 140, both P < 0. 05) . The superinfection group had significantly lower positive rates of HBeAg and HBV DNA than the CHB group ( both P < 0. 05) , and there were no significant differences between these two groups in lymphocyte percentage, albumin, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, and platelet count ( all P > 0. 05) . Conclusion In CHB patients, the risk of EBV superinfection or reactivation of latent EBV in the body increases with the severity of disease condition. EBV infection can aggravate patients' conditions and prolong the course of the disease, but it can reduce the serum level of HBV DNA, possibly by inhibiting the replication of HBV.-
Key words:
- hepatitis B, chronic /
- Epstein-Barr virus infections /
- superinfection
-
目前我国慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者主要使用核苷(酸)类似物(NUC)抗病毒治疗[1],作为目前最重要的抗HBV治疗手段,NUC主要以抑制HBV的逆转录来降低循环血中的HBV DNA水平。目前的NUC药物并不能完全清除肝细胞内的HBV共价闭合环状DNA(cccDNA)[2-3],cccDNA的存在是CHB患者HBV持续感染的关键因素,因此肝内HBV cccDNA的消失是目前国内公认的CHB患者最可能达到病毒学治愈的状态。HBV cccDNA存在于肝细胞内,其检测具有创伤性,在临床难以广泛开展[4]。目前HBV相关的血清学标志物包括HBV DNA、HBeAg、HBsAg,经NUC治疗后HBV DNA阴转并不代表HBV cccDNA的清除,即使HBV cccDNA转录沉默,整合HBV S基因区也可转录翻译成HBsAg[5],在前C区以及基本cp区变异后可导致HBeAg载量下调甚至消失,但检测HBV cccDNA仍存在一定的转录活性。因此,目前常用的血清学标志物反映肝内HBV cccDNA的转录水平存在一定的局限性。
新型生物学标志物HBV前基因组RNA(pgRNA)、乙型肝炎核心相关抗原(HBcrAg)已引起广泛关注,HBV pgRNA作为cccDNA的直接转录产物,HBcAg作为HBV衣壳的主要结构蛋白,表达于完整的HBV Dane颗粒中[6],其水平与cccDNA的转录活性和水平具有良好的相关性[7-8]。本团队在研究了经NUC治疗CHB患者各时间段的HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平之后,收集到治疗至少5年到达完全应答并满足2017年版欧洲肝病学会(EASL)指南[9]停药标准的CHB患者,研究其停药后各时间段HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平,分析pgRNA、HBcrAg水平变化与复发的相关性,探索其在临床的应用价值。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
研究对象来自2019年12月—2022年7月川北医学院附属医院门诊中抗HBV治疗至少5年到达完全应答并满足2017年版EASL指南停药标准的随访队列。所有研究对象年龄均满18周岁且具有民事行为能力。排除标准:合并其他嗜肝/非嗜肝病毒感染及其他原因所致肝组织炎症;合并肝硬化、肝癌等其他疾病。完全应答标准:满足生化学、血清学以及病毒学联合应答,生化指标ALT、AST正常,e抗原阴转,HBV DNA检测不到。复发标准:病毒学复发指的是获得病毒学应答的患者停药后,间隔1个月2次检测HBV DNA均>2×103 IU/mL;临床复发指的是病毒学复发且ALT>2倍正常值上限,但排除其他因素引起的ALT增高。
1.2 标本的采集与处理
收集CHB患者停药时、停药4周、12周以及24周时的空腹静脉血样本3 mL于肝素抗凝管内,在6 h内以1000 r/min离心15 min并获取上清液,置于-80 ℃冰箱保存。
1.3 检测方法
1.3.1 HBV pgRNA检测
采用湖南圣湘公司HBV pgRNA定量测定试剂盒检测血清中HBV RNA含量。
1.3.2 HBcrAg检测
采用ELISA酶联免疫分析试剂盒,运用CObase601全自动免疫分析系统检测。
1.3.3 HBV DNA水平检测
运用实时荧光定量法高精度检测样品中HBV DNA载量,标准值>20 IU/mL,如低于检测值下限按20 IU/mL进行统计学计算,严格按照说明书专人操作。
1.4 统计学方法
数据运用SPSS 21.0统计软件进行分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,两组间比较采用t检验;多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。采用Pearson相关检验分析循环血中各指标间的相关性。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 CHB患者停药后随访24周内病毒学复发人数及累积复发率
本研究收集CHB患者108例,其中失访者26例,82例随访者在4周、12周、24周的复发情况见表 1,累积复发率达到29.3%(24/82)。复发者均为病毒学复发,无临床复发者,病毒学复发的患者从复发时结束随访观察。
表 1 CHB患者停药后随访24周内病毒学复发人数及累积复发率Table 1. The number of viral recurrences and cumulative recurrence rate of CHB patients within 24 weeks of follow-up after drug withdrawal组别 复发率(%) 停药4周 0 停药12周 17.1(14/82) HBV DNA复阳 64.3(9/14) HBeAg复阳 28.6(4/14) HBV DNA、HBeAg同时复阳 7.1(1/14) 停药24周 14.7(10/68) HBV DNA复阳 60.0(6/10) HBeAg复阳 20.0(2/10) HBV DNA、HBeAg同时复阳 20.0(2/10) 2.2 CHB患者停药后各时段循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA的表达水平
停药24周时,CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平较停药时及停药4周表达明显升高(P值均<0.05);停药后各时段组间CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)(表 2)。
表 2 CHB患者停药后各时段循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平比较Table 2. Comparison of HBV pgRNA, HBcrAg and HBV DNA expression levels in circulating serum of CHB patients at different periods after drug withdrawal组别 例数 HBV pgRNA (log10拷贝/mL) HBcrAg (log10 U/L) HBV DNA (log10 IU/mL) 停药时 82 1.36±0.12 1.31±0.16 1.30±0.18 停药4周 82 1.37±0.10 1.31±0.17 1.61±0.20 停药12周 82 1.39±0.12 1.40±0.13 2.38±0.26 停药24周 68 1.42±0.141)2) 1.51±0.161)2) 2.50±0.351)2) F值 10.276 14.359 21.473 P值 0.022 0.013 < 0.001 注:与停药时相比,1)P<0.05;与停药4周相比,2)P<0.05。 2.3 CHB患者停药后复发组与未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA水平比较
对CHB患者停药后复发组选择复发当时循环血清中各指标水平状态,未复发组选择随访24周后循环血清中各指标的水平状态,复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA水平较未复发组显著高表达(P值均<0.05)(表 3)。对复发组进一步分析发现,在12~24周时复发患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA[(1.59±0.16)log10拷贝/mL vs (1.42±0.14)log10拷贝/mL,t=2.903,P<0.05]、HBcrAg[(2.43±0.12)log10 U/L vs (1.73±0.06)log10 U/L,t=18.163,P<0.05]以及HBV DNA[(3.97±0.44)log10 IU/mL vs (3.57±0.31)log10 IU/mL,t=2.640,P<0.05]水平较4~12周时高表达。
表 3 CHB患者停药后复发组与未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA、HBsAg水平比较Table 3. Comparison of HBV pgRNA, HBcrAg, HBV DNA and HBsAg levels in circulating serum between relapse group and non relapse group of CHB patients after drug withdrawal组别 例数 HBV pgRNA (log10拷贝/mL) HBcrAg (log10 U/L) HBV DNA (log10 IU/mL) 复发组 24 1.49±0.15 2.02±0.11 3.74±0.39 未复发组 58 1.39±0.13 1.35±0.17 2.24±0.15 t值 2.549 8.654 25.680 P值 0.015 < 0.001 < 0.001 2.4 CHB患者停药后复发组与未复发组在停药时循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg表达水平比较
复发组时循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的表达水平较未复发组显著升高(P值均<0.05)(表 4)。
表 4 停药时复发组与未复发组CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg表达水平比较Table 4. Comparison of HBV pgRNA, HBcrAg expression levels in circulating serum of CHB patients in relapse and non relapse groups at the time of drug withdrawal组别 例数 HBV pgRNA (log10拷贝/mL) HBcrAg (log10 U/L) 复发组 24 1.42±0.11 1.55±0.20 未复发组 58 1.34±0.07 1.21±0.11 t值 18.561 6.152 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 2.5 CHB患者复发组和未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA的相关性分析
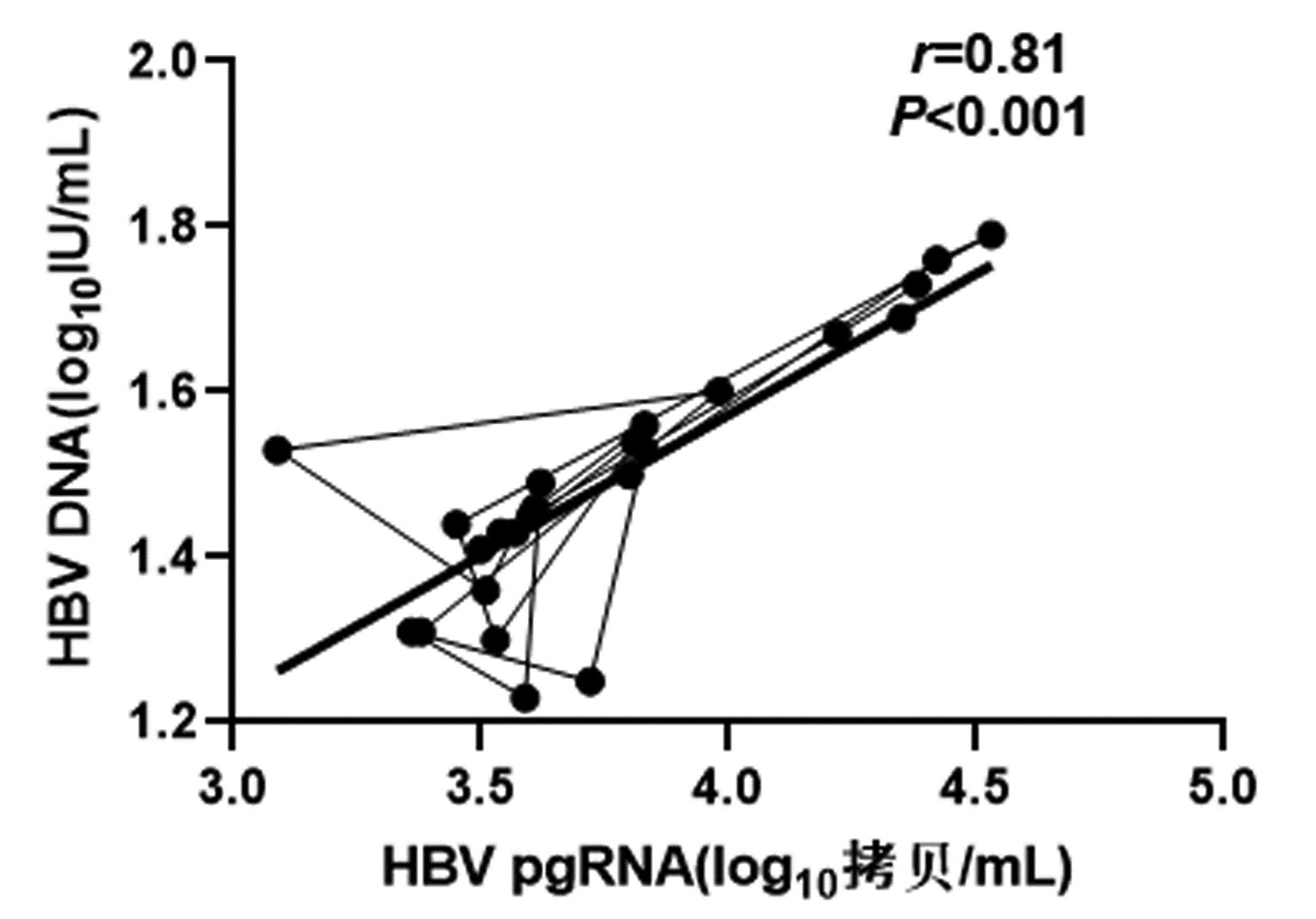
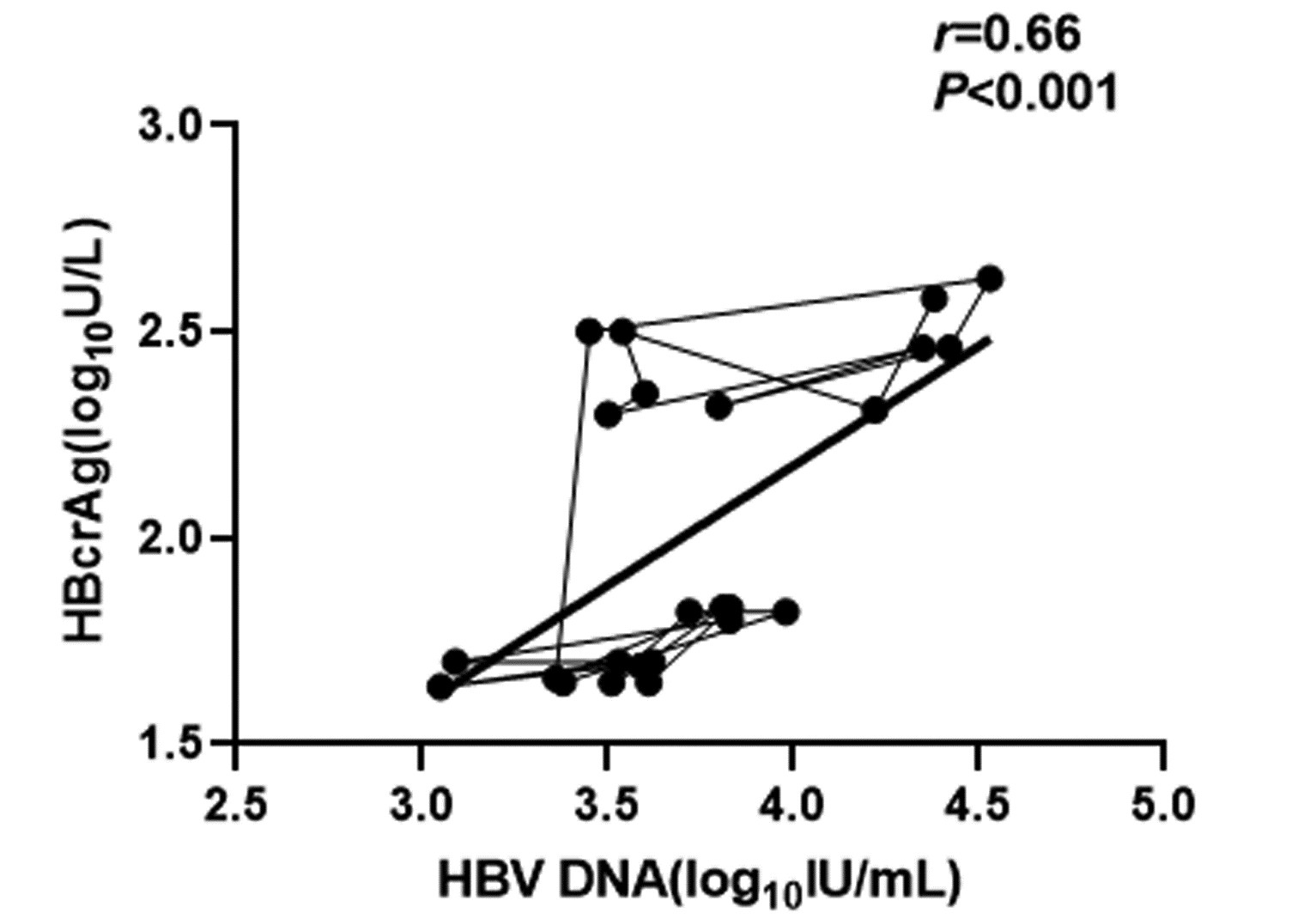
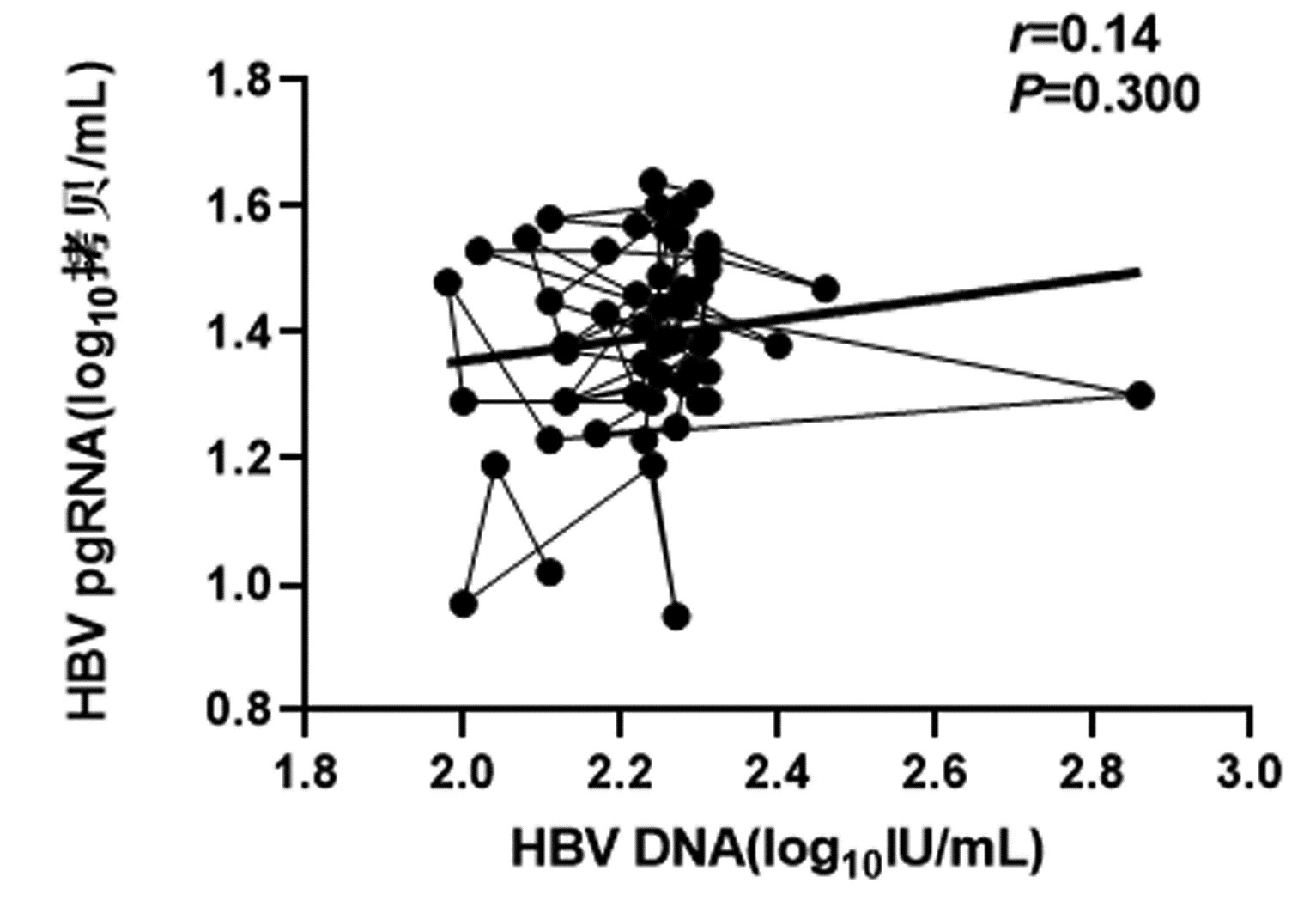
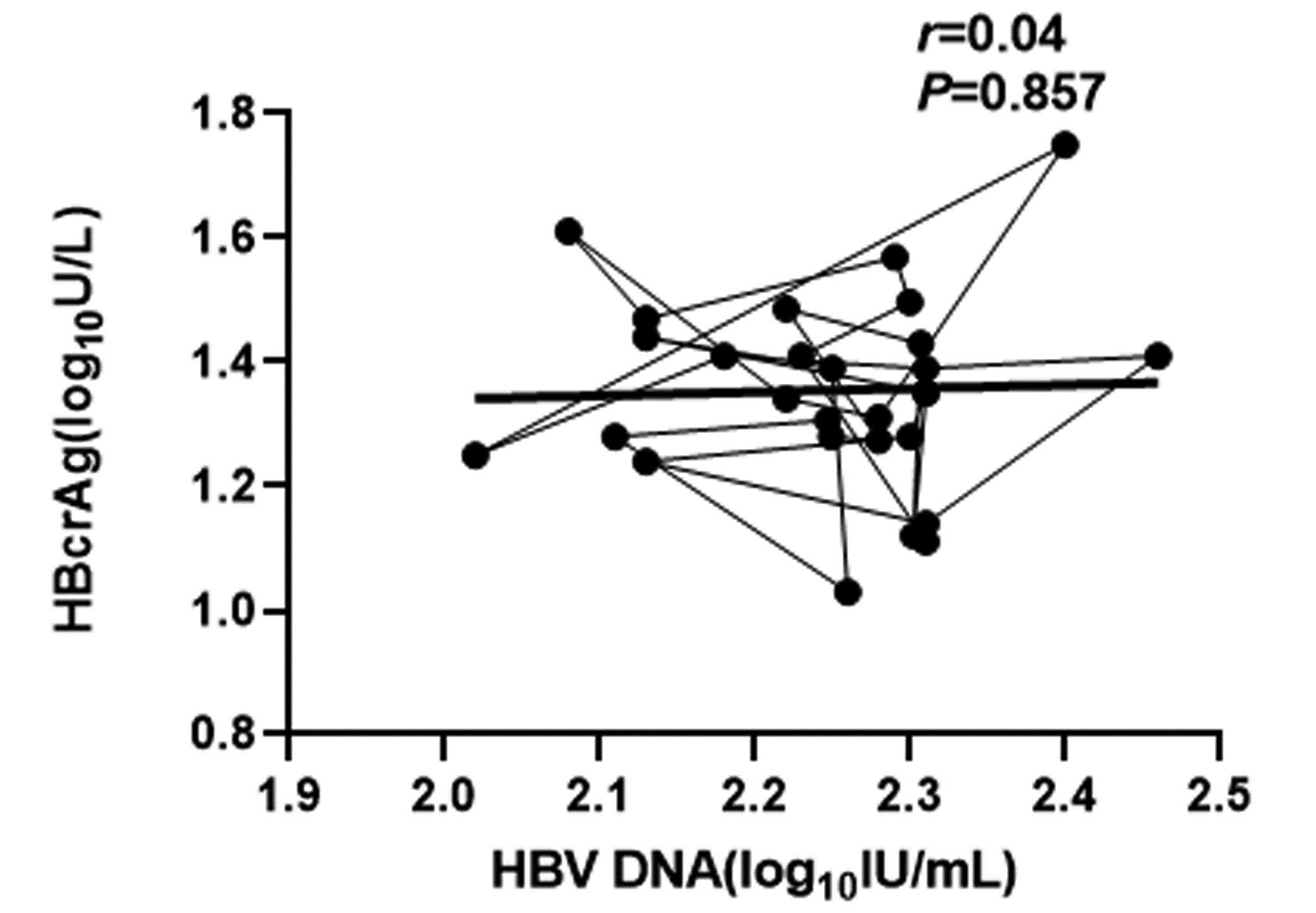
CHB患者停药后复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA均呈正相关(r值分别为0.81、0.66,P值均<0.001);未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA均无相关性(r值分别为0.14、0.04,P值均>0.05)(图 1~4)。
3. 讨论
CHB患者经NUC药物治疗后可以达到HBV DNA阴转,但CHB患者体内仍存在一定量的HBV cccDNA,HBV cccDNA的持续低表达是HBV不断复制的根源,目前只有HBV cccDNA彻底清除才是CHB等肝病患者根治的核心指标[5]。已有研究[10]表明,CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA水平检测可以反映肝细胞内cccDNA水平;也有研究[11-12]发现,HBcrAg表达水平与HBV cccDNA水平呈正相关。因此,本研究通过检测CHB患者停药后各时段循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的表达水平以及复发组与未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的表达差异,分析HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg停药时水平与复发的相关性以及其水平能否作为停药的参考临界值指标,HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的检测可能为后续选择停药时机、评估药物疗效等提供临床价值基础。
本研究显示,CHB患者停药后随访4~12周时复发率17.1%,随访24周时累积复发率达到29.3%。其中单独HBV DNA复阳者各占64.3%、60.0%,所有复发者均为病毒学复发,未发现临床复发患者。目前CHB患者抗病毒治疗主要依赖于NUC药物。NUC药物主要是抑制HBV逆转录酶来抑制HBV DNA的转录,降低CHB患者循环血清中HBV DNA的表达水平,对肝细胞内的HBV cccDNA清除能力较低,HBV pgRNA作为HBV cccDNA的直接转录产物即可长期以低水平存在于CHB患者体内。本研究的CHB患者经过至少5年的NUC抗病毒治疗,满足2017年版EASL指南停药标准后停药,由结果可见,尽管CHB患者经治疗后HBV DNA阴转,e抗原发生转换,在停药后随访中发现,仍有一部分患者发生HBV DNA和/或HBeAg复阳,其中HBV DNA单独复阳者占多数,这可能是由于CHB患者循环血清中的HBV DNA来源于HBV pgRNA,pgRNA再经过逆转录形成HBV rcDNA,被病毒蛋白包裹后释放到肝细胞外成为新的HBV DNA,HBV DNA形成与HBV pgRNA关系密切,在后续研究结果中发现低水平的HBV pgRNA是HBV DNA复阳的关键,既往也有研究[13]证实,停止NUC治疗后,血清pgRNA水平与病毒复发风险有密切关系。
本研究在CHB患者停药24周内的随访中发现,随着停药时间的延长,CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平成上升趋势,差异具有统计学意义;进一步对复发组进行分析,复发组CHB患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平较未复发组高表达,且12~14周复发组患者循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA表达水平较4~12周复发组高表达;停药24周后未复发组患者循环血中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg、HBV DNA的表达水平相比较于最初停药时有所上升,但未达到复发组患者水平。由于本研究观察时间较短,在后续的停药过程中,未复发组患者循环血中各指标水平是否会进一步上升甚至达到复发组患者水平还需要进一步观察;根据未复发组患者24周时循环血中各指标的表达水平能否预测其未来复发的可能性还需要进一步研究证明。本研究的CHB患者停药时HBV DNA阴转,但检测结果提示其循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg仍微量存在,在停药后CHB患者循环血清中各指标水平逐渐升高,以HBV DNA水平上升为著,这可能是由于CHB患者体内HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的持续存在,在失去NUC药物的抑制后,HBV pgRNA经过逆转录酶重新生成HBV DNA,导致循环血清中HBV DNA表达水平上升明显。也有研究[14]显示,在CHB患者达到2017年版EASL指南停药标准后,仍有约半数的患者循环血清中pgRNA未阴转,这表明肝细胞内HBV cccDNA仍有一定的转录活性,在停药后其复制活跃程度增高,导致患者发生病毒学复发。
进一步分析复发组和未复发组在停药时其循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg的水平差异,研究结果提示复发组在停药时其循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg表达水平较未复发组高表达。这表明,相比较于未复发患者,复发患者在停药时,其循环血清中存在较高水平的HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg,这可能是导致复发组患者体内HBV再活跃的关键指标,因本研究停药后观察时间较短,未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg停药时水平是否能作为停药的临界指标尚需进一步观察研究。免疫系统的激活与应答对乙型肝炎的进展和临床结局起着关键作用,清除CHB患者体内HBV需要固有免疫以及获得性免疫的协同作用。在大多数CHB患者体内免疫细胞处于“无应答”状态,经NUC治疗后,部分免疫细胞激活,免疫系统重新构建。近期研究[15-16]表明,经长期NUC治疗后停药复发与患者体内各种细胞因子激活等也有一定关系。
复发组以及未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA之间的相关性分析发现,复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA呈正相关,未复发组循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg与HBV DNA无相关性,这与部分学者[17-18]研究结果一致。作者认为在CHB患者经NUC药物治疗至HBV DNA阴转后,其HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平下降滞后于HBV DNA,此时CHB患者体内HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平不能反映HBV DNA活性,而更能准确反映HBV cccDNA的转录活性与药物治疗疗效;在复发组患者循环血清中存在较高水平的HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg,HBV cccDNA的转录活性更强,经逆转录酶生成HBV DNA能力提高,HBV DNA载量越高,HBV cccDNA活性越强,因此HBV DNA与HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg呈正相关。
综上所述,目前CHB患者治疗主要依赖NUC药物,根据2017年版EASL指南停药标准,即使HBV DNA阴转,循环血清中仍存在一定量的HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg,本研究发现复发组与未复发组停药时循环血清中HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平存在差异,但由于随访时间较短,未复发组患者在停药时HBV pgRNA、HBcrAg水平是否能代表安全停药的临界值指标尚需进一步观察研究。本研究仅纳入了HBV DNA阴转检测HBV pgRNA仍呈阳性的患者,未检测出HBV pgRNA阴性的患者,两者未予以比较,对于停药时HBV pgRNA阴性的患者停药后其水平是否会进一步升高、是否发生病毒学复发、其水平是否更能代表安全停药的临界值指标等诸多问题需要进一步扩大样本,延长随访时间进行研究观察。
-
[1]LU FM, ZHUANG H.Management of hepatitis B in China[J].Chin Med J (Engl) , 2009, 122 (1) :3-4. [2]WANG FS, FAN JG, ZHANG Z, et al.The global burden of liver disease:The major impact of China[J].Hepatology, 2014, 60 (6) :2099-2108. [3]LIU Y, ZHANG SQ, LI XH, et al.Investigation and clinical characteristics of EBV infection in patients with hepatitis[J].Chin J Exp Clin Virol, 2005, 19 (2) :109. (in Chinese) 刘雅, 张树琴, 李杏红, 等.肝炎患者EBV感染调查及临床特点分析[J].中华实验和临床病毒学杂志, 2005, 19 (2) :109. [4]YANG YQ, ZHANG H, LI X, et al.A cross-sectional survey of relationship between hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus co-infected with epstein-barr virus infection and liver cirrhosis[J/CD].Chin J Liver Dis:Electronic Edition, 2015, 7 (4) :90-93. (in Chinese) 杨玉奇, 张慧, 李昕, 等.乙型肝炎、丙型肝炎合并EB病毒感染与肝硬化发生的横断面研究[J/CD].中国肝脏病杂志:电子版, 2015, 7 (4) :90-93. [5]Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infection Diseases, Chinese Medical Association.The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B:A 2015 update[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31 (12) :1941-1960. (in Chinese) 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会.慢性乙型肝炎防治指南 (2015年更新版) [J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31 (12) :1941-1960. [6]JIANG ZF, SHEN KL, SHEN Y.Zhu Futang practice of pediatrics[M].8th ed.Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House, 2015:916-921. (in Chinese) 江载芳, 申昆玲, 沈颖.诸福棠实用儿科学[M].8版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2015:916-921. [7]TIAN QH, ZHU SX.Research progress of Epstein-Barr virus-related diseases in infants[J].Int J Virol, 2017, 24 (1) :69-72. (in Chinese) 田巧焕, 朱淑霞.儿童EB病毒感染及其相关常见疾病研究进展[J].国际病毒学杂志, 2017, 24 (1) :69-72. [8]YOUNG LS, YAP LF, MURRAY PG.Epstein-Barr virus:More than 50 years old and still providing surprises[J].Nature Reviews Cancer, 2016, 16 (12) :789-802. [9]LI M, GAO RP.Investigation and characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus infection among patients with different liver diseases[D].Changchun:Jilin Univ, 2016. (in Chinese) 李敏, 高润平.不同肝病Epstein-Barr virus感染的调查及临床特点分析[D].长春:吉林大学, 2016. [10]PETROVA M, KAMBUROV V, NIKOLOVSKA D, et al.EpsteinBarr virus:Is there any contribution to chronic hepatitis B and C?[J].Liver Int, 2010, 30 (3) :488-489. [11]HOSOI H, SONOKI T, MURATA S, et al.Successful immunosuppressive therapy for severe infectious mononucleosis in a patient with clonal proliferation of EBV-infected CD8-positive cells[J].Intern Med, 2015, 54 (12) :1537-1541. [12]YANG YY, WANG XH, WAN G, et al.Clinical features of liver injury associated with acute Epstein-Barr virus infection inadults:An analysis of 115 cases[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33 (6) :1141-1144. (in Chinese) 杨玉英, 王欣慧, 万钢, 等.115例成人急性EB病毒感染相关肝损伤临床特征分析[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33 (6) :1141-1144. [13]AN H, ZHOU XJ, MIAO CM.Clinical study on the relationship between EBV infection and liver disease infected by HBV[J].Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2005, 15 (3) :144-145. (in Chinese) 安辉, 周小军, 缪灿铭.EB病毒感染与乙肝病毒相关性肝病关系的临床研究[J].中西医结合肝病杂志, 2005, 15 (3) :144-145. [14]RAO SC, ASHRAF I, MIR F, et al.Dual infection with hepatitis B and epstein-barr virus presenting with severe jaundice, coagulopathy, and hepatitis B virus chronicity outcome[J].Am J Case Rep, 2017, 18:170-172. [15]BAKIR OZBEY S, MISTIK R, GURCUOGLU E, et al.Polyclonal activation due to Epstein-Barr virus superinfection in a case with chronic hepatitis B[J].Mikrobiyol Bul, 2007, 41 (4) :607-612. [16]YANG YD, LIN Q.Analysis on the virus markers and liver function of patients with EBV-Ig M positive[J/CD].Chin J Exp Clin Infect Dis:Electronic Edition, 2014, 8 (6) :36-39. (in Chinese) 杨友道, 林青.EB病毒抗-VCA Ig M阳性患者病毒标志物及肝功能检查结果分析[J].中华实验和临床感染病杂志:电子版, 2014, 8 (6) :36-39. [17]KOFTERIDIS DP, KOULENTAKI M, VALACHIS A, et al.Epstein Barr virus hepatitis[J].Eur J Intern Med, 2011, 22 (1) :73-76. [18]GRU AA, HAVERKOS BH, FREUD AG, et al.The EpsteinBarr virus (EBV) in T cell and NK cell lymphomas:Time for a reassessment[J].Curr Hematol Malig Rep, 2015, 10 (4) :456-467. [19]WANG HS, WEI Q, LEI MM, et al.Acute hepatitis B complicated by EB virus infection:A case report[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33 (4) :725-727. (in Chinese) 王洪莎, 魏祺, 雷嫚嫚, 等.急性乙型肝炎合并EB病毒感染1例报告[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33 (4) :725-727. 期刊类型引用(14)
1. 刘波,陈昌兰. 研究ELISA联合荧光定量PCR检测丙型肝炎病毒的效果. 系统医学. 2024(02): 79-82 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 王学英. HBV pgRNA联合cccDNA对慢性乙型肝炎患者抗病毒疗效的预测价值. 罕少疾病杂志. 2024(04): 54-56 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 陈春燕,樊子勉. 慢性乙型肝炎者外周血SAA/CRP、NLR水平与HBV-DNA载量、病情程度的相关性分析. 昆明医科大学学报. 2024(05): 144-150 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 隋娟,钟芳芳,郑秀霞. 乙肝患者HBV-DNA载量与血清标志物水平的相关性及其对抗病毒疗效的预测价值. 中国民康医学. 2024(10): 148-150+154 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 周芳,王永平,欧阳宇. HBV pgRNA联合HBcrAg对慢性乙型肝炎患者停药后复发的预测价值. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版). 2024(02): 42-47 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 朱启泰,黄帆,宋华峰,陈慧,周芬,胥萍. 苏州地区HBV感染患者血清中乙型肝炎核心相关抗原表达特点分析. 标记免疫分析与临床. 2024(09): 1648-1652+1764 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 蒋贤静,潘小平,周颖,潘强,池林峰,饶芳. 慢性乙型肝炎中西医双重诊疗体系的实践与应用进展. 中西医结合肝病杂志. 2024(11): 1041-1044 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 王丽莉. 不同抗病毒方案对慢性乙型肝炎患者的影响. 实用中西医结合临床. 2024(22): 42-44 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 巫翟,祝达. TDF与TAF交替使用治疗慢性乙型肝炎的临床效果观察. 现代养生. 2024(24): 1849-1853 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 田晓晓,张娟,李琳彬,赵小芬,刘力瑜,余焰. Th1/Th2细胞因子表达水平对慢性乙型肝炎患者停用核苷(酸)类似物后复发的预测价值. 中国药物经济学. 2024(12): 59-63+67 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 陈柏伶. 动态护理模式对门诊慢性乙型肝炎患者疾病认知及遵医行为的影响. 现代养生. 2023(18): 1410-1413 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 刘虹,王鹏雁,刘友德. 监测血清HBV RNA水平变化对于NAs治疗CHB停药复发的预测价值. 国际医药卫生导报. 2023(19): 2762-2766 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 陈长红. 肝爽颗粒联合恩替卡韦对乙型肝炎肝硬化患者HBV-DNA水平及肝功能的影响. 黑龙江医药. 2023(06): 1349-1351 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 戎云清,徐敬轩. 加味补肾生髓成肝方联合聚乙二醇干扰素α对慢性乙型肝炎患者肝纤维化的影响. 世界复合医学. 2023(12): 98-102 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1821 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1821 KB)

 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: