Association of vitamin D-related gene polymorphisms with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
-
摘要:
目的探究维生素D相关基因单核苷酸多态性(SNP)在HBV相关慢加急性肝衰竭(ACLF)患者中的表达情况及其与HBV-ACLF短期预后的关系。方法纳入福建医科大学附属第一医院肝病中心于2012年7月-2018年3月收治的慢性乙型肝炎患者400例,根据其病程中是否发生ACLF,分为HBV-ACLF组(n=122)和Non-ACLF组(n=278)。分别收集两组患者的临床资料及实验室检查结果,同时采集外周血标本,应用imLDRTM多重SNP分型试剂盒检测维生素D受体(VDR)基因rs1544410、rs2228570及维生素D结合蛋白(VDBP)基因rs2282679共3个位点的SNP表达分型;并对HBV-ACLF组患者进行随访观察,追踪其3个月的生存情况。对比分析维生素D相关基因SNP与HBV-ACLF易感性及预后的关系。采用Hardy-Weinberg平衡检验评估各组基因样本的群体代表性。对于满足正态分布的计量资料,2组间比较采用t检验;对于不满足正态分布的计量资料,2组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。SNP与HBV-ACLF发生的相对风险度采用多元logistic回归分析。...
Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) of vitamin D-related genes in patients with hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) and its association with short-term prognosis of HBV-ACLF. Methods The patients with chronic hepatitis B who were admitted to Liver Diseases Research Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, from July 2012 to March 2018 were enrolled, and according to the presence or absence of acute-on-chronic liver failure during the course of the disease (n = 400) , they were divided into HBV-ACLF group (n = 122) and non-ACLF group (n = 278) . The clinical data and laboratory examination results were collected; peripheral blood samples were collected, and imLDRTM multiple SNP typing kit was used to determine the genotypes of the SNPs of vitamin D receptor (VDR) rs1544410 and rs2228570 and vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP) rs2282679. The patients in the HBV-ACLF group were followed up for 3 months to observe their survival. The association of vitamin D-related gene SNP with HBV-ACLF susceptibility and prognosis was analyzed. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was used to evaluate the representativeness of gene samples. The t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between two groups, and the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between two groups. A logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the odds ratio of SNP in the development of HBV-ACLF. Results There were no significant differences in the genotype and allele frequencies of VDR rs1544410 and rs2228570 and VDBP rs2282679 between the HBV-ACLF group and the non-ACLF group (all P > 0. 05) . In addition, there were also no significant differences in the genotype and allele frequencies of VDR rs1544410 and rs2228570 and VDBP rs2282679 between the HBV-ACLF patients who survived and those who died (all P > 0. 05) . Conclusion SNPs of VDR rs1544410 and rs2228570 and VDBP rs2282679 are not associated with the development and short-term prognosis of HBV-ACLF.
-
慢性HBV感染的自然史划分为4个期,即免疫耐受期、免疫清除期、免疫控制期和再活动期[1]。目前,对于处于免疫清除期以及再活动期的慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者,各大指南均推荐抗病毒治疗,对于免疫耐受期则不推荐抗病毒治疗,建议长期随访[1-4]。然而,有研究[5-11]表明,10%~49%免疫耐受期CHB (Immune-tolerant CHB,IT-CHB) 患者经肝组织病理学检查证实存在明显的肝脏炎症和/或纤维化,若不积极治疗,发展至肝硬化及肝癌的风险增加。IT-CHB患者是否抗病毒治疗尚存在争议[12-18],而评估肝组织学显著肝脏炎症及纤维化对于抗病毒治疗具有重要意义,肝活检仍然是金标准,但其有创性及不易重复等缺点限制了临床应用。本研究通过分析IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)的高危因素,构建无创的个体化列线图预测模型,旨在为指导IT-CHB抗病毒治疗提供参考依据。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性选取2002年8月—2017年12月在解放军总医院第五医学中心住院的IT-CHB患者。免疫耐受期的诊断标准符合2018年版美国肝病学会CHB指南[2]中的定义。纳入标准:(1)年龄>18岁;(2)HBsAg阳性及HBeAg阳性>1年;(3)ALT水平持续正常(男性35 U/L,女性25 U/L)>1年;(4)HBV DNA>1×106 IU/ml;(5)接受肝活检。排除标准:(1)合并其他病毒感染;(2)其他类型肝脏疾病;(3)失代偿期肝硬化;(4)肝癌或其他恶性肿瘤病史;(5)严重的心脏、肾脏或者其他脏器的原发疾病或精神系统疾病。
1.2 肝组织学检查
采用16G活检针进行超声引导下经皮肝活检,要求肝组织长度≥15 mm,至少包括11个汇管区[19]。由2名经验丰富的病理医师进行双盲法阅片,肝组织炎症分级和纤维化分期标准参照《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年版)》[20]。显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)定义为肝组织学存在明显的肝脏炎症(≥G2)或纤维化(≥S2)。
1.3 血清学检测
采用贝克曼库尔特AU5421全自动生化仪检测血清ALT、AST、TBil、PLT等。乙型肝炎血清学标志物采用罗氏E170电化学发光法检测。计算APRI指数和FIB-4指数,APRI = (AST/正常值上限×100)/PLT,FIB-4=(年龄×AST)/(PLT×ALT1/2)[21]。
1.4 伦理学审查
本研究通过解放军总医院第五医学中心伦理委员会审批,批号:2020056D。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0进行统计分析。正态分布的计量数据以x±s表示,2组间比较采用独立样本t检验;非正态分布数据以M(P25~P75)表示,2组间比较采用Mann- Whitney U检验; 多组比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验;计数资料2组间比较采用χ2检验。相关性分析采用Spearman秩相关。通过多因素logistic回归模型进入法筛选显著肝损伤的相关因素,采用R语言(3.6.1)的RMS(Regression Modeling Strategies)程序包构建列线图模型,通过Bootstrap重抽样法对模型进行内部验证,用一致性指数(C-指数)、ROC曲线、校准曲线来评价列线图的区分度及校准度。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入382例IT-CHB患者,其中82例(21.5%)存在显著肝损伤。肝组织炎症活动度分级: G0 29例(7.6%)、G1 301例(78.8%)、G2 50例(13.1%)、G3 2例(0.5%);肝组织纤维化分期: S0 57例(14.9%)、S1 251例(65.7%)、S2 39例(10.2%)、S3 23例(6.0%)、S4 12例(3.1%)。按照是否存在显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)分为2组,2组年龄、HBV DNA载量、ALT、AST、PLT比较差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)(表 1)。
表 1 患者基线的一般资料指标 总体(n=382) 非显著肝损伤组(n=300) 显著肝损伤组(n=82) 统计值 P值 男性[例(%)] 261(68.3) 201(67.0) 60(73.2) χ2=1.133 0.287 年龄(岁) 33.3±10.2 31.5±9.1 39.9±11.2 t=-7.071 <0.001 年龄段[例(%)] χ2=56.472 <0.001 <30岁 161(42.1) 147(49.0) 14(17.1) 30~39岁 130(34.0) 106(35.3) 24(29.3) 40~49岁 64(16.8) 35(11.7) 29(35.4) ≥50岁 27(7.1) 12(4.0) 15(18.3) 乙型肝炎家族史[例(%)] 221(57.9) 173(57.7) 48(58.5) χ2=0.020 0.888 BMI(kg/m2) 23.2±3.53 23.0±3.4 23.7±3.9 t=-1.021 0.308 HBV DNA(log10IU/ml) 8.4(7.8~8.8) 8.4(8.0~8.8) 7.9(6.9~8.5) Z=-4.924 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 25.5(21.0~32.0) Z=-3.693 <0.001 AST(U/L) 23.0(19.0~27.0) 21.0(19.0~26.0) 28.0(23.0~34.0) Z=-6.945 <0.001 TBil(μmol/L) 11.1(8.3~15.3) 10.9(8.3~15.3) 11.5(8.6~15.4) Z=-0.585 0.559 PLT(×109/L) 202(164~234) 208(176~239) 161(137~209) Z=-5.723 <0.001 2.2 年龄与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
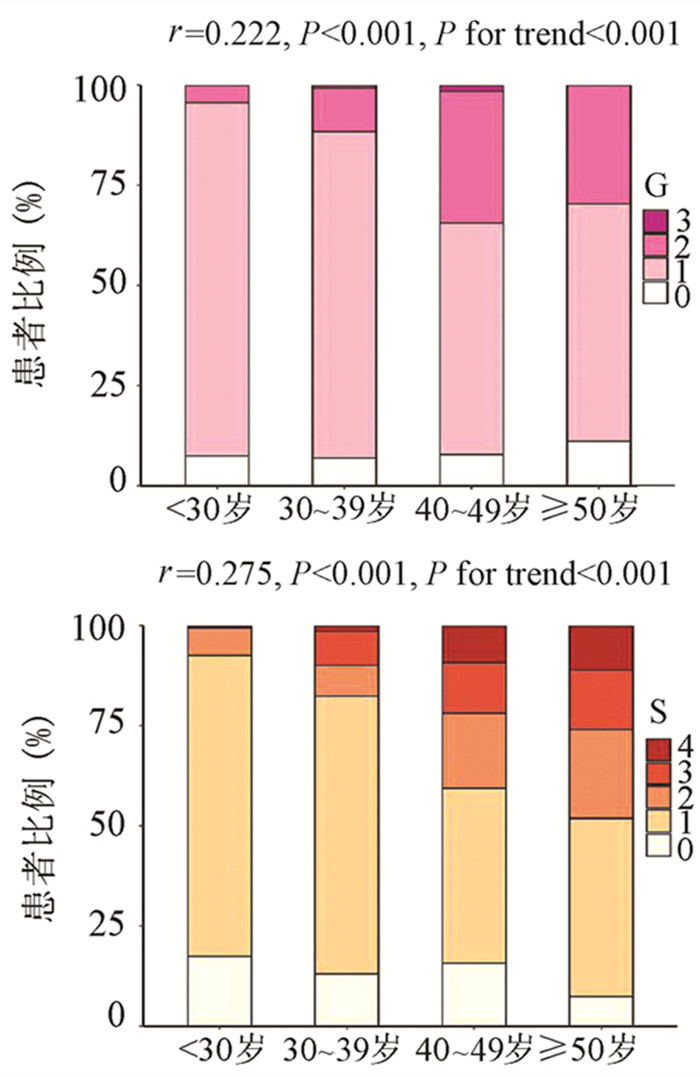
为了评估年龄对IT-CHB显著肝损伤的影响,将患者分为4个年龄段,即<30岁、30~39岁、40~49岁和≥50岁。随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高,趋势性检验结果表明差异均具有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)。Spearman等级相关分析显示,两者呈正相关(r值分别为0.222、0.275,P值均<0.001)(图 1)。Logistic单因素分析结果显示,较年龄<30岁组,30~39岁组、40~49岁组、年龄≥50岁组出现显著肝损伤的可能性分别为2.4倍(95%CI: 1.175~4.811)、8.7倍(95%CI: 4.165~18.175)、13.1倍(95%CI: 5.146~33.477)(P值均<0.05)。
2.3 HBV DNA与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
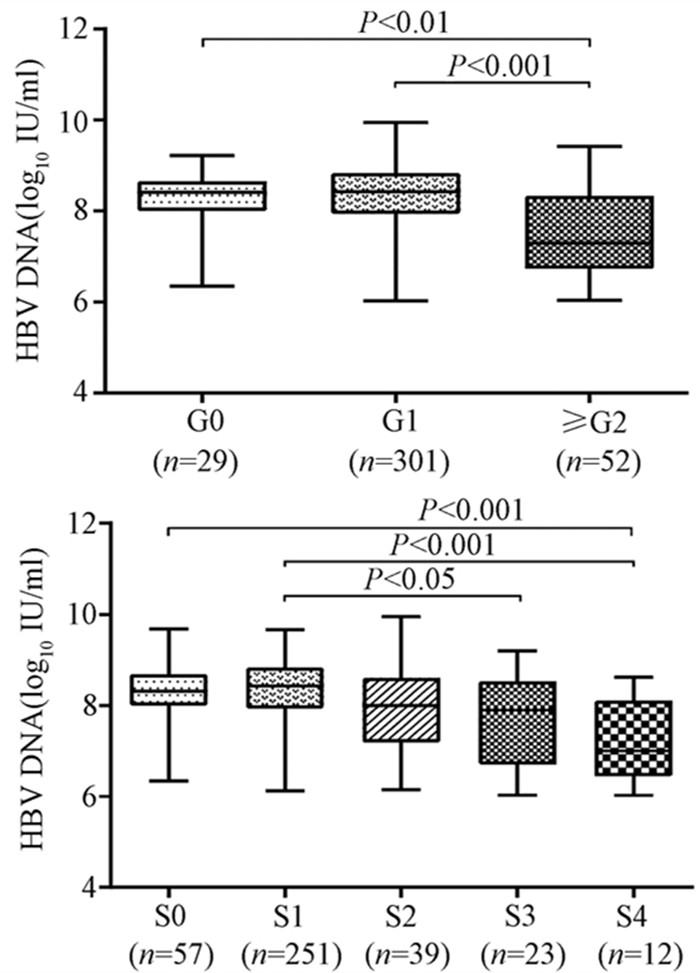
随着肝脏坏死性炎症的加剧,HBV DNA水平呈下降趋势(H=34.161,P<0.001),组间两两比较结果显示:G0组、G1组与≥G2组之间差异有统计学意义(H值分别为80.688、96.903,P值均<0.05),而GO组与G1组无差异(图 2)。伴随肝纤维化的进展,HBV DNA同样表现出下降的趋势(H=26.627,P<0.001),组间两两比较显示,S0与S4、S1与S4、S1与S3之间差异均有统计学意义(H值分别为112.287、125.953、74.354,P值均<0.05)(图 2)。
2.4 显著肝损伤的单因素及多因素分析
为进一步构建无创预测模型,基于无创参数中单因素分析P<0.05的变量作为自变量,以显著肝损伤作为因变量进行logistic回归分析。结果显示,年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT是显著肝损伤的独立影响因素(P值均<0.01)(表 2)。
表 2 显著肝损伤的logistic回归分析因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 年龄 1.084 (1.057~1.113) <0.001 1.074(1.043~1.107) <0.001 HBV DNA 0.437 (0.324~0.589) <0.001 0.442(0.314~0.624) <0.001 ALT 1.076(1.036~1.119) <0.001 1.009(0.959~1.060) 0.736 AST 1.132 (1.089~1.177) <0.001 1.096(1.051~1.142) <0.001 PLT 0.985 (0.98~0.991) <0.001 0.992(0.986~0.998) 0.006 2.5 列线图的制作与检验
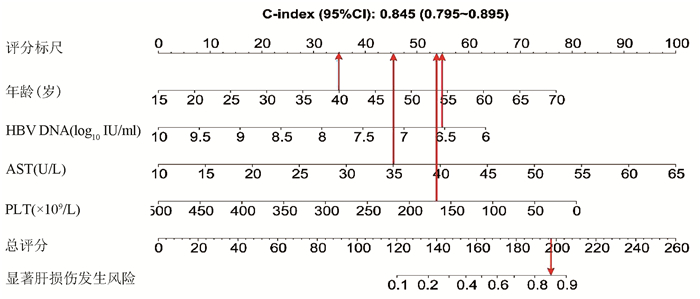
基于logistic回归分析结果,将独立影响因素引入R软件建立预测显著肝损伤的个体化列线图预测模型,并绘制校准曲线和ROC曲线。结果显示,列线图模型预测IT-CHB发生显著肝损伤的C-指数的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.845(95%CI: 0.795~0.895), 明显优于单独使用APRI(AUC=0.781, 95%CI: 0.723~0.840)以及FIB-4(AUC=0.802, 95%CI: 0.746~0.859),差异有统计学意义。校正曲线贴近于理想曲线(对角线),斜率为1.017,Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验χ2=8.224,P=0.412,提示模型预测值与实际观测值之间的差异无统计学意义,预测模型有良好的校准度。ROC曲线分析显示,列线图的AUC高于APRI、FIB-4,预测IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤的最佳界值为141.4,其敏感度、特异度分别为74.4%、84.7%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 3, 图 3)。
表 3 列线图、APRI、FIB-4诊断显著肝损伤的效能比较诊断参数 AUC 95%CI 界值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) Youden指数 列线图 0.845 0.795 ~ 0.895 141.4 74.4 84.7 57.0 92.4 0.59 APRI 0.781 0.723 ~ 0.840 0.338 70.7 77.7 46.4 90.7 0.48 FIB-4 0.802 0.746 ~ 0.859 0.882 78.1 72.3 43.5 92.3 0.50 3. 讨论
全球慢性HBV感染者约2.92亿人,其中约5940万处于免疫耐受期,我国的IT-CHB患者约有1584万例[22]。目前国内外指南对于免疫耐受期的定义尚存在争议[1-4, 23-25],ALT正常上限的标准亦不同, 按照美国肝病学会的标准意味我国IT-CHB患者并非全部处于免疫耐受阶段。单纯用病毒学、ALT水平评估免疫耐受可能存在临床误判,“真正”的免疫耐受需在肝活检基础上进一步确诊,目前多项研究[5-9]表明,10%~49% IT-CHB患者存在明显的肝细胞炎症坏死和肝纤维化病理学改变, 此类患者是否应抗病毒治疗逐渐成为热点问题。
本研究发现IT-CHB患者中21.5%(82/382)存在显著肝损伤,19.4%(74/382)呈显著肝纤维化,其中12例患者(3.1%)处于S4期,提示并不是全部IT-CHB患者均不需要治疗,如何筛选出需要治疗的患者尤为重要。本研究筛选出4个显著肝损伤的高危因素,包括年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT,其中AST、PLT作为APRI、FIB-4的参数之一,已被充分证实与肝纤维化程度有关[21, 26]。既往研究[27-28]表明,年龄是CHB患者疾病进展的独立危险因素,尤其年龄>30岁时,HBV相关性肝纤维化、肝硬化、肝癌患者的比例显著增加。Xing等[6]发现年龄是影响肝组织炎症及纤维化的独立预测因子,这一点与本研究结果一致,将IT-CHB患者的年龄分为4个年龄亚组,结果表明,随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高。关于HBV DNA,我国台湾的大样本研究[29]发现高HBV DNA水平CHB患者进展至肝硬化的风险增加,但其中81.6%(2923/3582) 为HBeAg阴性患者,不属于IT-CHB患者,因此该研究无法准确反映高HBV DNA水平与IT-CHB患者肝纤维化的关系。而本研究发现,IT-CHB患者随着肝脏炎症及纤维化程度的加重,HBV DNA呈下降趋势;并且轻度肝损伤(<G2/S2)的IT- CHB患者中位HBV DNA水平更高(8.4 log10 IU/ml),因此单纯HBV DNA水平并不能准确反映出IT-CHB患者纤维化程度。基于上述分析,本研究建立了无创的列线图模型用于预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,该模型具有无创的优势,并将多因素分析结果可视化、量化、个体化,具有可重复性,可作为肝活检的有效替代方式。根据该列线图模型,假设某40岁的IT-CHB患者,HBV DNA水平为6.56 log10 IU/ml,AST 35 U/L,PLT 166×109/L,则该患者总得分为188.6分,发生显著肝损伤的概率高达85%,需积极抗病毒治疗。
综上所述,免疫耐受期具有显著肝损伤的患者比例并不少见,基于年龄、HBV DNA、AST、PLT 4个因素构建的列线图模型具有良好的预测准确性,可用于个体化预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,减少肝活检,为抗病毒的精准治疗提供参考。
-
[1]SARIN SK, KUMAR A, ALMEIDA JA, et al.Acute-on-chronic liver failure:Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the study of the liver (APASL) [J].Hepatol Int, 2009, 3 (1) :269-282. [2]ZHANG DJ, ZHOU B, HOU JL.Research progress in prognostic models of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34 (6) :1351-1356. (in Chinese) 张东敬, 周彬, 侯金林.慢加急性肝衰竭预后模型的研究进展[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34 (6) :1351-1356. [3]ZHAO RH, SHI Y, ZHAO H, et al.Acute-on-chronic liver failure in chronic hepatitis B:An update[J].Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 12 (4) :341-350. [4]BASIT S.Vitamin D in health and disease:A literature review[J].Br J Biomed Sci, 2013, 70 (4) :161-172 [5]WANG YL, LIU CY, WANG J, et al.Correlation of peripheral blood 25 (OH) D with T lymphocyte subsets and interferon-αin patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Clin J Med Offic, 2017, 45 (11) :1199-1201, 1210. (in Chinese) 王医林, 刘英纯, 王健, 等.系统性红斑狼疮患者外周血25 (OH) D与T淋巴细胞亚群及IFN-α关系研究[J].临床军医杂志, 2017, 45 (11) :1199-1201, 1210. [6]KEANE JT, ELANGOVAN H, STOKES RA, et al.Vitamin Dand the liver-correlation or cause?[J].Nutrients, 2018, 10 (4) :496. [7]ARTEH J, NARRA S, NAIR S.Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in chronic liver disease[J].Dig Dis Sci, 2010, 55 (9) :2624-2628. [8]FARNIK H, BOJUNGA J, BERGER A, et al.Low vitamin D serum concentration is associated with high levels of hepatitis Bvirus replication in chronically infected patients[J].Hepatology, 2013, 58 (4) :1270-1276. [9]HOAN NX, KHUYEN N, BINH MT, et al.Association of vitamin D deficiency with hepatitis B virus-related liver diseases[J].BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16 (1) :507. [10]WANG TJ, ZHANG F, RICHARDS JB, et al.Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency:A genome-wide association study[J].Lancet, 2010, 376 (9736) :180-188. [11]HE Q, HUANG Y, ZHANG L, et al.Association between vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and hepatitis B virus infection susceptibility:A meta-analysis study[J].Gene, 2018, 645:105-112. [12]BOGLIONE L, CUSATO J, DE NICOLO A, et al.Role of CYP27B1+2838 promoter polymorphism in the treatment of chronic hepatitis BHBe Ag negative with PEG-interferon[J].J Viral Hepat, 2015, 22 (3) :318-327. [13]HUANG YW, LIAO YT, CHEN W, et al.Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and distinct clinical phenotypes of hepatitis B carriers in Taiwan[J].Genes Immun, 2010, 11 (1) :87-93. [14]PENG Q, YANG S, LAO X, et al.Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in VDR and DBP genes with HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a Chinese population[J].PLo S One, 2014, 9 (12) :e116026. [15]LI YJ, TANG YW, SHI YQ, et al.Polymorphisms in the vitamin Dreceptor gene and risk of primary biliary cirrhosis:A meta-analysis[J].J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2014, 29 (4) :706-715. [16]BAUR K, MERTENS JC, SCHMITT J, et al.Combined effect of 25-OH vitamin D plasma levels and genetic vitamin D receptor (NR 1I1) variants on fibrosis progression rate in HCVpatients[J].Liver Int, 2012, 32 (4) :635-643. [17]LIMOTHAI U, CHUAYPEN N, KHLAIPHUENGSIN A, et al.Association of vitamin-D-related genetic variations and treatment response to pegylated interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Antivir Ther, 2017, 22 (8) :681-688. [18]SHAKER O, NASSAR Y, AYOUB S, et al.Impact of Fok I (rs10735810) and Bsm I (rs1544410) on treatment of chronic HCV patients with genotype 4[J].J Clin Lab Anal, 2016, 30 (6) :1021-1027. [19]GIBSON PS, QUAGLIA A, DHAWAN A, et al.Vitamin D status and associated genetic polymorphisms in a cohort of UKchildren with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J].Pediatr Obes, 2018, 13 (7) :433-441. [20]KEMPINSKA-PODHORODECKA A, MILKIEWICZ M, JABLONSKID, et al.ApaI polymorphism of vitamin D receptor affects health-related quality of life in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis[J].PLo S One, 2017, 12 (4) :e0176264. [21]KARATAYLI SC, ULGER ZE, ERGUL AA, et al.Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-10, interferon-gamma and vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in patients with chronic hepatitis delta[J].J Viral Hepat, 2014, 21 (4) :297-304. [22]MATEOS-MUNOZ B, GARCIA-MARTIN E, TORREJON MJ, et al.GC gene polymorphism and unbound serum retinolbinding protein 4 are related to the risk of insulin resistance in patients with chronic hepatitis C:A prospective cross-sectional study[J].Medicine, 2016, 95 (10) :e3019. [23]YU R, TAN D, NING Q, et al.Association of baseline vitamin D level with genetic determinants and virologic response in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J].Hepatol Res, 2018, 48 (3) :e213-e221. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 李晓蓉,姚家喜,施志斌. SAA、GRP78、miR-21-3p与老年急性胰腺炎Ranson和APACHEⅡ评分的关联性. 中国老年学杂志. 2025(05): 1092-1095 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 赵永红,陈爱荣,胡梦茹,王燚鑫,衣桂荣. 急性胰腺炎伴代谢综合征的临床特点和危险因素分析. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2024(06): 664-669 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 宋小利,陈璐. 大剂量维生素C联合乌司他丁、生长抑素治疗急性胰腺炎的效果及对肝肾功能的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2024(28): 39-42 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 卢景涛,彭琼. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊断联合BISAP评分对急性胰腺炎严重程度的预测价值. 医学信息. 2023(04): 118-122 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 黄雯雪,陈春洁,孙艳. 急性胰腺炎相关危险因素、严重程度评估及临床护理研究进展. 中国基层医药. 2022(03): 473-476 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 刘国雄,匡桥贵,喻欣荷,刘访,王宇,俞洋,陈杨. 加味大承气汤治疗湿热蕴结型高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的疗效及作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2021(05): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 王婷婷,何家俊,杨楚婷,李圆浩,陈炜炜,刘军. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病与急性胰腺炎的关系. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2021(03): 729-732 .  本站查看
本站查看8. 赵冬雨,成丽娅,邵伟,马程,沈宏. 胰胆舒胶囊联合乌司他丁治疗急性胰腺炎的临床研究. 现代药物与临床. 2021(04): 712-716 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 黄莹,苗雨,林晚,刘昊,张飞雄,阮继刚. 急性复发性胰腺炎合并代谢综合征的临床特点及预后分析. 宁夏医学杂志. 2021(11): 968-971 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(7)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2013 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2013 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: