Effect of Hic-5 gene knockout on NF-κB/p65 expression and CCl4-induced liver fibrosis degree in mice
-
摘要:
目的探讨Hic-5基因敲除对NF-κB/p65表达及肝纤维化的影响。方法野生型C57BL/6雄性小鼠10只,随机分为2组,野生型对照组(WT-Control,n=5)、野生型实验组(WT-CCl4,n=5); Hic-5基因敲除C57BL/6雄性小鼠10只,随机分为2组,敲除对照组(Hic-5 KO-Control,n=5)、敲除实验组(Hic-5 KO-CCl4,n=5)。检测血清ALT和AST;天狼猩红染色观察肝组织胶原沉积;免疫组化检测α平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)、p65蛋白表达;定量PCR检测肝组织中α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA表达。分离小鼠原代肝星状细胞,在予以不同浓度TGFβ1刺激后定量PCR检测肝星状细胞中α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA的表达。多组间计量资料比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。结果天狼猩红染色显示,与WT-CCl4组相比较Hic-5 KO-CCl4组肝组织胶原纤维减少(P值<0. 001)。血清ALT和AST检测结果提示WT-Control组、WT-CCl4组、Hic-5 KO-Control组、Hic-5 KO-CCl4组间ALT、AST比较差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为22.85、25.15,P值均<0.001),Hic-5 KO-CCl4组血清ALT和AST水平均低于WT-CCl4组(P值均<0.05);免疫组化显示WT-Control组、WT-CCl4组、Hic-5 KO-Control组、Hic-5 KO-CCl4组4组间肝组织α-SMA、p65蛋白表达水平比较差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为207.10、9816,P值均<0.001),Hic-5 KO-CCl4组肝组织α-SMA、p65蛋白表达量低于WT-CCl4组(P值均<0.01);定量PCR结果示WT-Control组、WT-CCl4组、Hic-5 KO-Control组、Hic-5 KO-CCl4组4组间肝组织α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA相对表达量比较差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为41.62、13.93、98.16,P值均<0.001),Hic-5 KO-CCl4组肝组织α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA相对表达量低于WT-CCl4组(P值均<0.05);0 ng/ml、5 ng/ml、10 ng/ml TGFβ1刺激原代肝星状细胞,WT(0 ng/ml、5 ng/ml、10 ng/ml)组及KO(0 ng/ml、5 ng/ml、10 ng/ml)组间α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA相对表达量比较差异均有统计学意义(F值分别为53.90、75.82、52.41,P值均<0.001),不同浓度TGFβ1刺激原代肝星状细胞Hic-5 KO组α-SMA、Collagen1、p65 mRNA相对表达量均低于WT组(P值均<0.01)。结论Hic-5基因敲除抑制NF-κB/p65表达,抑制肝星状细胞活化,缓解CCl4诱导的肝纤维化。
-
关键词:
- 肝硬化 /
- 肝星状细胞 /
- 小鼠,基因敲除 /
- 小鼠,近交C57BL
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Hic-5 gene knockout on NF-κB/p65 expression and liver fibrosis. Methods Ten wild-type male C57 BL/6 mice were randomly divided into wild-type control group( WT-Control group with 5 mice) and wild-type experimental group( WT-CCl4 group with 5 mice),and ten male C57 BL/6 mice with Hic-5 gene knockout were randomly divided into Hic-5 knockout control group( Hic-5 KO-Control group with 5 mice) and Hic-5 knockout experimental group( Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group with5 mice). The serum levels of alanine aminotransferase( ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase( AST) were measured. Picrosirius red staining was used to observe collagen deposition in liver tissue. Immunohistochemistry was used to measure the expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin( α-SMA) and p65 protein,and real-time quantitative PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of α-SMA,collagen1,and p65 in liver tissue. The primary hepatic stellate cells of mice were isolated and stimulated with different concentrations of TGF-β1,and then real-time quantitative PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of α-SMA,collagen 1,and p65 in primary hepatic stellate cells. A one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison of continuous data between multiple groups,and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. Results Picrosirius red staining showed that compared with the WT-CCl4 group,the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group had a significant reduction in collagen fibers in liver tissue( P < 0. 001). Measurement of serum ALT and AST showed that there were significant differences in ALT and AST between the WT-Control group,the WT-CCl4 group,the Hic-5 KO-Control group,and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group( F = 22. 85 and 25. 15,both P < 0. 001),and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group had significantly lower serum levels of ALT and AST than the WT-CCl4 group( both P < 0. 05). Immunohistochemistry showed that there were significant differences in the expression levels of α-SMA and p65 protein in liver tissue between the WT-Control group,the WT-CCl4 group,the Hic-5 KO-Control group,and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group( F = 207. 10 and 98. 16,both P < 0. 001),and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group had significantly lower expression of α-SMA and p65 protein in liver tissue than the WT-CCl4 group( both P < 0. 01).The results of real-time quantitative PCR showed that there were significant differences in the relative mR NA expression of α-SMA,collagen 1,and p65 in liver tissue between the WT-Control group,the WT-CCl4 group,the Hic-5 KO-Control group,and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group( F = 41. 62,13. 93,and 98. 16,all P < 0. 001),and the Hic-5 KO-CCl4 group had significantly lower relative mR NA expression of α-SMA,collagen 1,and p65 in liver tissue than the WT-CCl4 group( all P < 0. 05). After the primary hepatic stellate cells were stimulated by TGF-β1 at concentrations of 0,5,and 10 ng/ml,there were significant differences in the relative mR NA expression ofα-SMA,collagen 1,and p65 between the WT 0 ng/ml group,the WT 5 ng/ml group,the WT 10 ng/ml group,the KO 0 ng/ml group,the KO 5 ng/ml group,and the KO 10 ng/ml group( F = 53. 9,75. 82,and 52. 41,all P < 0. 001),and the Hic-5 KO group had significantly lower relative mR NA expression of α-SMA,collagen 1,and p65 than the WT group( all P < 0. 01). Conclusion Hic-5 knockout inhibits NF-κB/p65 expression and hepatic stellate cell activation and alleviates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis.
-
Key words:
- liver cirrhosis /
- hepatic stellate cells /
- mice,knockout /
- mice,inbred C57BL
-
慢性HBV感染的自然史划分为4个期,即免疫耐受期、免疫清除期、免疫控制期和再活动期[1]。目前,对于处于免疫清除期以及再活动期的慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者,各大指南均推荐抗病毒治疗,对于免疫耐受期则不推荐抗病毒治疗,建议长期随访[1-4]。然而,有研究[5-11]表明,10%~49%免疫耐受期CHB (Immune-tolerant CHB,IT-CHB) 患者经肝组织病理学检查证实存在明显的肝脏炎症和/或纤维化,若不积极治疗,发展至肝硬化及肝癌的风险增加。IT-CHB患者是否抗病毒治疗尚存在争议[12-18],而评估肝组织学显著肝脏炎症及纤维化对于抗病毒治疗具有重要意义,肝活检仍然是金标准,但其有创性及不易重复等缺点限制了临床应用。本研究通过分析IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)的高危因素,构建无创的个体化列线图预测模型,旨在为指导IT-CHB抗病毒治疗提供参考依据。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性选取2002年8月—2017年12月在解放军总医院第五医学中心住院的IT-CHB患者。免疫耐受期的诊断标准符合2018年版美国肝病学会CHB指南[2]中的定义。纳入标准:(1)年龄>18岁;(2)HBsAg阳性及HBeAg阳性>1年;(3)ALT水平持续正常(男性35 U/L,女性25 U/L)>1年;(4)HBV DNA>1×106 IU/ml;(5)接受肝活检。排除标准:(1)合并其他病毒感染;(2)其他类型肝脏疾病;(3)失代偿期肝硬化;(4)肝癌或其他恶性肿瘤病史;(5)严重的心脏、肾脏或者其他脏器的原发疾病或精神系统疾病。
1.2 肝组织学检查
采用16G活检针进行超声引导下经皮肝活检,要求肝组织长度≥15 mm,至少包括11个汇管区[19]。由2名经验丰富的病理医师进行双盲法阅片,肝组织炎症分级和纤维化分期标准参照《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年版)》[20]。显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)定义为肝组织学存在明显的肝脏炎症(≥G2)或纤维化(≥S2)。
1.3 血清学检测
采用贝克曼库尔特AU5421全自动生化仪检测血清ALT、AST、TBil、PLT等。乙型肝炎血清学标志物采用罗氏E170电化学发光法检测。计算APRI指数和FIB-4指数,APRI = (AST/正常值上限×100)/PLT,FIB-4=(年龄×AST)/(PLT×ALT1/2)[21]。
1.4 伦理学审查
本研究通过解放军总医院第五医学中心伦理委员会审批,批号:2020056D。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0进行统计分析。正态分布的计量数据以x±s表示,2组间比较采用独立样本t检验;非正态分布数据以M(P25~P75)表示,2组间比较采用Mann- Whitney U检验; 多组比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验;计数资料2组间比较采用χ2检验。相关性分析采用Spearman秩相关。通过多因素logistic回归模型进入法筛选显著肝损伤的相关因素,采用R语言(3.6.1)的RMS(Regression Modeling Strategies)程序包构建列线图模型,通过Bootstrap重抽样法对模型进行内部验证,用一致性指数(C-指数)、ROC曲线、校准曲线来评价列线图的区分度及校准度。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入382例IT-CHB患者,其中82例(21.5%)存在显著肝损伤。肝组织炎症活动度分级: G0 29例(7.6%)、G1 301例(78.8%)、G2 50例(13.1%)、G3 2例(0.5%);肝组织纤维化分期: S0 57例(14.9%)、S1 251例(65.7%)、S2 39例(10.2%)、S3 23例(6.0%)、S4 12例(3.1%)。按照是否存在显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)分为2组,2组年龄、HBV DNA载量、ALT、AST、PLT比较差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)(表 1)。
表 1 患者基线的一般资料指标 总体(n=382) 非显著肝损伤组(n=300) 显著肝损伤组(n=82) 统计值 P值 男性[例(%)] 261(68.3) 201(67.0) 60(73.2) χ2=1.133 0.287 年龄(岁) 33.3±10.2 31.5±9.1 39.9±11.2 t=-7.071 <0.001 年龄段[例(%)] χ2=56.472 <0.001 <30岁 161(42.1) 147(49.0) 14(17.1) 30~39岁 130(34.0) 106(35.3) 24(29.3) 40~49岁 64(16.8) 35(11.7) 29(35.4) ≥50岁 27(7.1) 12(4.0) 15(18.3) 乙型肝炎家族史[例(%)] 221(57.9) 173(57.7) 48(58.5) χ2=0.020 0.888 BMI(kg/m2) 23.2±3.53 23.0±3.4 23.7±3.9 t=-1.021 0.308 HBV DNA(log10IU/ml) 8.4(7.8~8.8) 8.4(8.0~8.8) 7.9(6.9~8.5) Z=-4.924 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 25.5(21.0~32.0) Z=-3.693 <0.001 AST(U/L) 23.0(19.0~27.0) 21.0(19.0~26.0) 28.0(23.0~34.0) Z=-6.945 <0.001 TBil(μmol/L) 11.1(8.3~15.3) 10.9(8.3~15.3) 11.5(8.6~15.4) Z=-0.585 0.559 PLT(×109/L) 202(164~234) 208(176~239) 161(137~209) Z=-5.723 <0.001 2.2 年龄与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
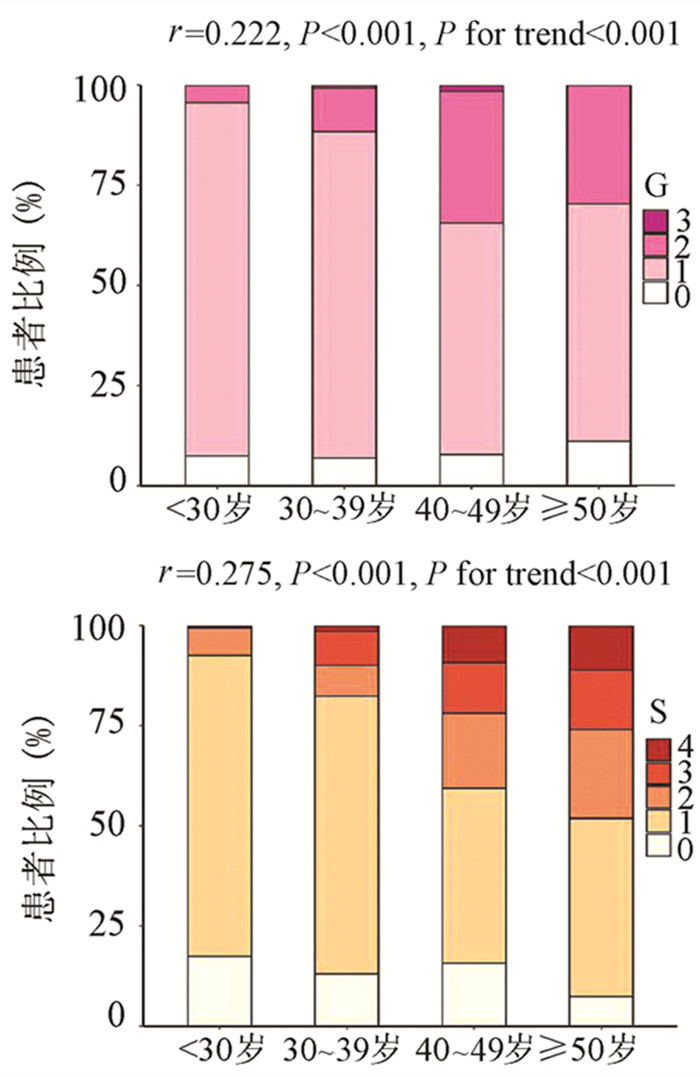
为了评估年龄对IT-CHB显著肝损伤的影响,将患者分为4个年龄段,即<30岁、30~39岁、40~49岁和≥50岁。随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高,趋势性检验结果表明差异均具有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)。Spearman等级相关分析显示,两者呈正相关(r值分别为0.222、0.275,P值均<0.001)(图 1)。Logistic单因素分析结果显示,较年龄<30岁组,30~39岁组、40~49岁组、年龄≥50岁组出现显著肝损伤的可能性分别为2.4倍(95%CI: 1.175~4.811)、8.7倍(95%CI: 4.165~18.175)、13.1倍(95%CI: 5.146~33.477)(P值均<0.05)。
2.3 HBV DNA与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
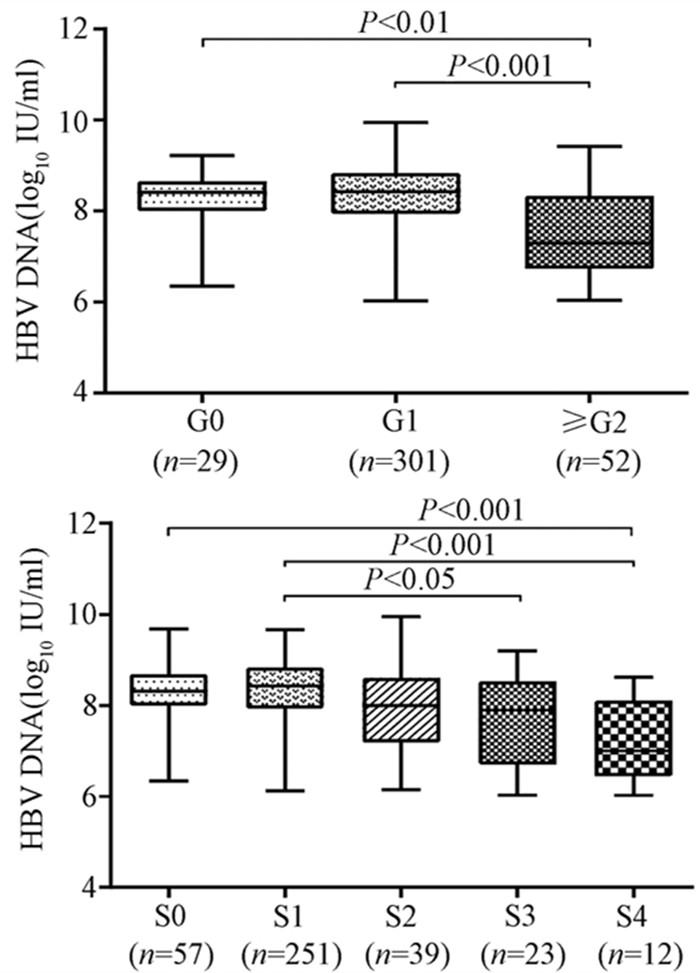
随着肝脏坏死性炎症的加剧,HBV DNA水平呈下降趋势(H=34.161,P<0.001),组间两两比较结果显示:G0组、G1组与≥G2组之间差异有统计学意义(H值分别为80.688、96.903,P值均<0.05),而GO组与G1组无差异(图 2)。伴随肝纤维化的进展,HBV DNA同样表现出下降的趋势(H=26.627,P<0.001),组间两两比较显示,S0与S4、S1与S4、S1与S3之间差异均有统计学意义(H值分别为112.287、125.953、74.354,P值均<0.05)(图 2)。
2.4 显著肝损伤的单因素及多因素分析
为进一步构建无创预测模型,基于无创参数中单因素分析P<0.05的变量作为自变量,以显著肝损伤作为因变量进行logistic回归分析。结果显示,年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT是显著肝损伤的独立影响因素(P值均<0.01)(表 2)。
表 2 显著肝损伤的logistic回归分析因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 年龄 1.084 (1.057~1.113) <0.001 1.074(1.043~1.107) <0.001 HBV DNA 0.437 (0.324~0.589) <0.001 0.442(0.314~0.624) <0.001 ALT 1.076(1.036~1.119) <0.001 1.009(0.959~1.060) 0.736 AST 1.132 (1.089~1.177) <0.001 1.096(1.051~1.142) <0.001 PLT 0.985 (0.98~0.991) <0.001 0.992(0.986~0.998) 0.006 2.5 列线图的制作与检验
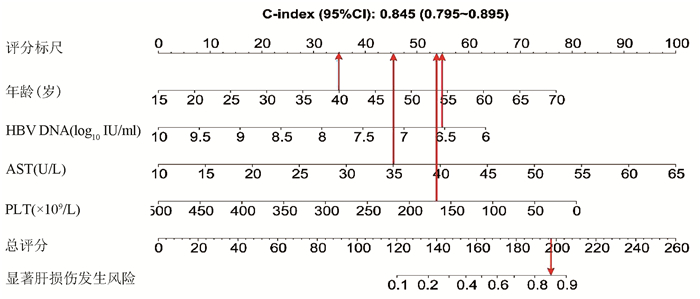
基于logistic回归分析结果,将独立影响因素引入R软件建立预测显著肝损伤的个体化列线图预测模型,并绘制校准曲线和ROC曲线。结果显示,列线图模型预测IT-CHB发生显著肝损伤的C-指数的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.845(95%CI: 0.795~0.895), 明显优于单独使用APRI(AUC=0.781, 95%CI: 0.723~0.840)以及FIB-4(AUC=0.802, 95%CI: 0.746~0.859),差异有统计学意义。校正曲线贴近于理想曲线(对角线),斜率为1.017,Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验χ2=8.224,P=0.412,提示模型预测值与实际观测值之间的差异无统计学意义,预测模型有良好的校准度。ROC曲线分析显示,列线图的AUC高于APRI、FIB-4,预测IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤的最佳界值为141.4,其敏感度、特异度分别为74.4%、84.7%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 3, 图 3)。
表 3 列线图、APRI、FIB-4诊断显著肝损伤的效能比较诊断参数 AUC 95%CI 界值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) Youden指数 列线图 0.845 0.795 ~ 0.895 141.4 74.4 84.7 57.0 92.4 0.59 APRI 0.781 0.723 ~ 0.840 0.338 70.7 77.7 46.4 90.7 0.48 FIB-4 0.802 0.746 ~ 0.859 0.882 78.1 72.3 43.5 92.3 0.50 3. 讨论
全球慢性HBV感染者约2.92亿人,其中约5940万处于免疫耐受期,我国的IT-CHB患者约有1584万例[22]。目前国内外指南对于免疫耐受期的定义尚存在争议[1-4, 23-25],ALT正常上限的标准亦不同, 按照美国肝病学会的标准意味我国IT-CHB患者并非全部处于免疫耐受阶段。单纯用病毒学、ALT水平评估免疫耐受可能存在临床误判,“真正”的免疫耐受需在肝活检基础上进一步确诊,目前多项研究[5-9]表明,10%~49% IT-CHB患者存在明显的肝细胞炎症坏死和肝纤维化病理学改变, 此类患者是否应抗病毒治疗逐渐成为热点问题。
本研究发现IT-CHB患者中21.5%(82/382)存在显著肝损伤,19.4%(74/382)呈显著肝纤维化,其中12例患者(3.1%)处于S4期,提示并不是全部IT-CHB患者均不需要治疗,如何筛选出需要治疗的患者尤为重要。本研究筛选出4个显著肝损伤的高危因素,包括年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT,其中AST、PLT作为APRI、FIB-4的参数之一,已被充分证实与肝纤维化程度有关[21, 26]。既往研究[27-28]表明,年龄是CHB患者疾病进展的独立危险因素,尤其年龄>30岁时,HBV相关性肝纤维化、肝硬化、肝癌患者的比例显著增加。Xing等[6]发现年龄是影响肝组织炎症及纤维化的独立预测因子,这一点与本研究结果一致,将IT-CHB患者的年龄分为4个年龄亚组,结果表明,随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高。关于HBV DNA,我国台湾的大样本研究[29]发现高HBV DNA水平CHB患者进展至肝硬化的风险增加,但其中81.6%(2923/3582) 为HBeAg阴性患者,不属于IT-CHB患者,因此该研究无法准确反映高HBV DNA水平与IT-CHB患者肝纤维化的关系。而本研究发现,IT-CHB患者随着肝脏炎症及纤维化程度的加重,HBV DNA呈下降趋势;并且轻度肝损伤(<G2/S2)的IT- CHB患者中位HBV DNA水平更高(8.4 log10 IU/ml),因此单纯HBV DNA水平并不能准确反映出IT-CHB患者纤维化程度。基于上述分析,本研究建立了无创的列线图模型用于预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,该模型具有无创的优势,并将多因素分析结果可视化、量化、个体化,具有可重复性,可作为肝活检的有效替代方式。根据该列线图模型,假设某40岁的IT-CHB患者,HBV DNA水平为6.56 log10 IU/ml,AST 35 U/L,PLT 166×109/L,则该患者总得分为188.6分,发生显著肝损伤的概率高达85%,需积极抗病毒治疗。
综上所述,免疫耐受期具有显著肝损伤的患者比例并不少见,基于年龄、HBV DNA、AST、PLT 4个因素构建的列线图模型具有良好的预测准确性,可用于个体化预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,减少肝活检,为抗病毒的精准治疗提供参考。
-
[1] YANG JJ,TAO H,LI J. Hedgehog signaling pathway as key player in liver fibrosis:New insights and perspectives[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets,2014,18(9):1-11. [2] ISMAIL MH,PINZANI M. Reversal of hepatic fibrosis:pathophysiological basis of antifibrotic therapies[J]. Hepat Med,2011,3:69-80. [3] HIGASHI T,FRIENDMAN SL,HOSHIDA Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2017,121:27-42. [4] LI H,LAN J,HAN C,et al. Brg1 promotes liver fibrosis via activation of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Exp Cell Res,2018,364(2):191-197. [5] WANG Y,WANG R,PENG R,et al. Ginkgo biloba extract mitigates liver fibrosis and apoptosis by regulating p38 MAPK,NF-κB/IκBα,and Bcl-2/Bax signaling[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther,2015,9:6303-6317. [6] SU FF,JIN HY,QING S,et al. Downregulation of UBC9 promotes apoptosis of activated human LX-2 hepatic stellate cells by suppressing the canonical NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. PLo S One,2017,12(3):e0174374. [7] LEI XF,FU W,KIM-KANEYAMA JR,et al. Hic-5 deficiency attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through upregulation of Smad7 in mice[J]. J Hepatol,2015,64(1):110-117. [8] MASCHMEYER P,FLACH M,WINAU F. Seven steps to stellate cells[J]. J Vis Exp,2011,51:2710. [9] ASSELAH T,MARCELLIN P,BEDOSSA P. Improving performance of liver biopsy in fibrosis assessment[J]. J Hepatol,2014,61(2):193-195. [10] ALMPANIS Z,DEMONAKOU M,TINIAKOS D. Evaluation of liver fibrosis:“Something old,something new…”[J]. Ann Gastroenterol,2016,29(4):445-453. [11] GBD 2013 Risk Factors Collaborators,FOROUZANFAR MH,ALEXANDER L,et al. Global,regional,and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural,environmental and occupational,and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188countries,1990-2013:A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10010):2287-2323. [12] TSOCHATZIS EA,BOSCH J,BURROUGHS AK. Liver cirrhosis[J]. Lancet,2014,383(9930):1749-1761. [13] CAMPANA L,IREDALE JP. Regression of liver fibrosis[J].Semin Liver Dis,2017,37(1):1-10. [14] JUNG YK,YIM HJ. Reversal of liver cirrhosis:Current evidence and expectations[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2017,32(2):213-228. [15] LIU W,YU SY,YAN HZ,et al. Therapeutic effect of MSCs transplantation on rats with hepatic fibrosis[J]. Chin J Med Offic,2017,45(9):903-907.(in Chinese)刘卫,余森源,严和中,等.骨髓间质干细胞移植对肝纤维化模型大鼠治疗效果[J].临床军医杂志,2017,45(9):903-907. [16] CHEN W,ZHANG Z,YAO Z,et al. Activation of autophagy is required for Oroxylin A to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Int Immunopharmacol,2018,56:148-155. [17] GANDHI,CHANDRASHEKHAR R. Hepatic stellate cell activation and pro-fibrogenic signals[J]. J Hepatol,2017,67(5):1104-1105. [18] CHRISTIAN T,FRIEDMAN SL,DETLEF S,et al. Hepatic fibrosis:Concept to treatment[J]. J Hepatol,2015,62(1):s15-s24. [19] ANDREA O,SANKAR G,The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol,2009,1(4):a000034. [20] LIU JM,LIU CC,LIU XM,et al. Long term toxicity of chelerythrine on lung tissue of rats and its effect on expression of NF-κB in lung tissue[J]. J Jilin Univ:Med Edit,2019,45(3):518-523.(in Chinese)刘建明,刘宸辰,刘新民,等.白屈菜赤碱对大鼠肺组织的长期毒性作用及其对肺组织中NF-κB表达的影响[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2019,45(3):518-523. [21] WANG R,WANG J,SONG F,et al. Tanshinol ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats through the regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB/IκBαsignaling pathway[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther,2018,12:1281-1292. [22] GHOSH G,WANG VY,HUANG DB,et al. NF-κB regulation:Lessons from structures[J]. Immunol Rev,2012,246(1):36-58. [23] SEKI E,de MINICIS S,CHRISTOPH H,et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-βsignaling and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Nat Med,2007,13(11):1324-1332. [24] XING H,GUANG BIN P,RUI T,et al. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B in the hepatic stellate cells of mice with schistosomiasis japonica[J]. PLo S One,2014,9(8):e104323. [25] WANG F,LIU S,DU T,et al. NF-κB inhibition alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis via suppression of activated hepatic stellate cells[J]. Exp Ther Med,2014,8(1):95-99. [26] MCFARLAND BC,HONG SW,RAJBHANDARI R,et al. NF-κB-induced IL-6 ensures STAT3 activation and tumor aggressiveness in glioblastoma[J]. PLo S One, 2013, 8(11):e78728. [27] POLINA K,MAYA S,IRINA T,et al. Both MAPK and STAT3signal transduction pathways are necessary for IL-6-dependent hepatic stellate cells activation[J]. PLo S One,2017,12(5):e0176173. [28] FLETCHER NF,CLARK AR,BALFE P,et al. TNF superfamily members promote hepatitis C virus entry via an NF-κB and myosin light chain kinase dependent pathway[J]. J Gen Virol,2017,98(3):405-412. [29] CHEN G,WANG Y,LI M,et al. Curcumol induces HSC-T6 cell death through suppression of Bcl-2:Involvement of PI3K and NF-κB pathways[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci,2014,65:21-28. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 李晓蓉,姚家喜,施志斌. SAA、GRP78、miR-21-3p与老年急性胰腺炎Ranson和APACHEⅡ评分的关联性. 中国老年学杂志. 2025(05): 1092-1095 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 赵永红,陈爱荣,胡梦茹,王燚鑫,衣桂荣. 急性胰腺炎伴代谢综合征的临床特点和危险因素分析. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2024(06): 664-669 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 宋小利,陈璐. 大剂量维生素C联合乌司他丁、生长抑素治疗急性胰腺炎的效果及对肝肾功能的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2024(28): 39-42 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 卢景涛,彭琼. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊断联合BISAP评分对急性胰腺炎严重程度的预测价值. 医学信息. 2023(04): 118-122 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 黄雯雪,陈春洁,孙艳. 急性胰腺炎相关危险因素、严重程度评估及临床护理研究进展. 中国基层医药. 2022(03): 473-476 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 刘国雄,匡桥贵,喻欣荷,刘访,王宇,俞洋,陈杨. 加味大承气汤治疗湿热蕴结型高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的疗效及作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2021(05): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 王婷婷,何家俊,杨楚婷,李圆浩,陈炜炜,刘军. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病与急性胰腺炎的关系. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2021(03): 729-732 .  本站查看
本站查看8. 赵冬雨,成丽娅,邵伟,马程,沈宏. 胰胆舒胶囊联合乌司他丁治疗急性胰腺炎的临床研究. 现代药物与临床. 2021(04): 712-716 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 黄莹,苗雨,林晚,刘昊,张飞雄,阮继刚. 急性复发性胰腺炎合并代谢综合征的临床特点及预后分析. 宁夏医学杂志. 2021(11): 968-971 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(7)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2590 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2590 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: