中国肝癌多学科综合治疗专家共识
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.008
文天夫 任正刚 刘连新 刘秀峰 孙惠川 沈 锋 单 鸿 郭荣平 黄志勇 程树群
执笔专家(以姓氏笔画为序):
名誉主任委员(以姓氏笔画为序):
李 强 陈孝平 周 俭 樊 嘉
委员(以姓氏笔画为序):
主任委员:陈敏山
丁国善 丁晓毅 马宽生 王 征 王 葵 王文涛 王立明 王兆海 王志明 王顺祥 元云飞 韦 玮 毛一雷 仇毓东 方世明 方壮伟 尹 涛 尹震宇 左朝晖 石 明 石 洁 卢 倩 代 智 白雪莉 匡 铭 毕新宇 吕国悦 华向东 刘景丰 汤朝晖 孙世杰 孙倍成 李 汛 李 涛 李 滨 李斌奎 杨连粤 吴 泓 应敏刚 宋天强 张 峰 张 倜 张 磊 张一心 张水军 张必翔 张耀军 陈拥军 陈建国 邵江华 周 东 周存才 周伟平 庞 春 赵 明 郝纯毅 荚卫东 钟 林 饶荣生 姚登福 贾长库 贾昌俊 夏 锋 徐 立 郭文治 陶 锋 黄 涛 梁 萍 梁廷波 彭 涛 韩国宏 蔡建强 樊海宁 黎乐群 戴朝六 瞿旭东
《中国肝癌多学科综合治疗专家共识》编写专家委员会
副主任委员(以姓氏笔画为序):
丁晓毅 王 征 石 洁 匡 铭 毕新宇 刘秀峰 孙惠川 张 倜 张耀军 赵 明 荚卫东 贾昌俊 徐 立 郭文治 郭荣平 黄 涛 程树群
Chinese expert consensus on multidisciplinary treatment of liver cancer
-
-
Key words:
- Liver Neoplasms /
- Therapeutics /
- Consensus
-
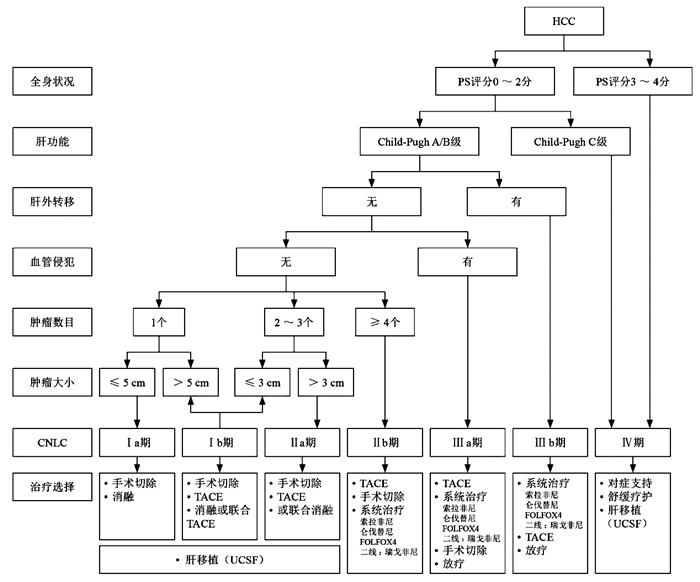
图 1 中国肝癌临床分期及治疗路线图[5]
注:HCC为肝细胞癌;PS为体力活动状态;CNLC为中国肝癌分期;TACE为经肝动脉化疗栓塞;FOLFOX4为氟尿嘧啶、奥沙利铂、亚叶酸钙;UCSF为美国加州大学旧金山分校。
-
[1] ZHENG RS, SUN KX, ZHANG SW, et al. Report of cancer epidemiology in China, 2015[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2019, 41(1): 19-28. (in Chinese)郑荣寿, 孙可欣, 张思维, 等. 2015年中国恶性肿瘤流行情况分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2019, 41(1): 19-28. [2] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492 [3] FENG RM, ZONG YN, CAO SM, et al. Current cancer situation in China: Good or bad news from the 2018 Global Cancer Statistics?[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2019, 39(1): 22. DOI: 10.1186/s40880-019-0368-6 [4] ZENG H, CHEN W, ZHENG R, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2018, 6(5): e555-e567. DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30127-X [5] Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition)[J/CD]. J Multidiscip Cancer Manage (Electronic Version), 2020, 6(2): 55-85. (in Chinese)中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会医政医管局. 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[J/CD]. 肿瘤综合治疗电子杂志, 2020, 6(2): 55-85. [6] Society of Liver Cancer, Guangdong Provincial Anti-cancer Association. Establishment of multi-disciplinary team for comprehensive treatment of liver cancer-consensus of experts in Guangdong, China(1)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2014, 24(8): 732-734. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD201411005.htm广东省抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会, 中山大学肿瘤防治中心肝胆科. 肝癌多学科综合治疗团队建立——广东专家共识(1)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 24(18): 732-734. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCGD201411005.htm [7] Society of Liver Cancer, Guangdong Provincial Anti-cancer Association. Strategyandmethodofmulti-disciplinarycomprehensivetreatmentoflivercancer-consensus of experts in Guangdong, China(2)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2014, 24(11): 735-738. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201408021.htm广东省抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会, 中山大学肿瘤防治中心肝胆科. 肝癌多学科联合治疗策略与方法——广东专家共识(2)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2014, 24(11): 735-738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201408021.htm [8] Guidelines Working Committee of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) diagnosis and treatment guidelines for primary liver cancer 2020[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2020. (in Chinese)中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)原发性肝癌诊疗指南2020[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2020. [9] JIA WD. Multidisciplinary treatments for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precise liver surgery[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2015, 18(2): 120-123. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2015.02.004荚卫东. 精准肝脏外科时代肝癌多学科治疗[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2015, 18(2): 120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2015.02.004 [10] Section of Hepatic Surgery, Branch of Surgery, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on selection of surgical treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma (2016 3rd edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2017, 16(2): 113-115. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2017.02.001中华医学会外科学分会肝脏外科学组. 肝细胞癌外科治疗方法的选择专家共识(2016年第3次修订)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2017, 16(2): 113-115. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2017.02.001 [11] OMATA M, CHENG AL, KOKUDO N, et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2017, 11(4): 317-370. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-017-9799-9 [12] CHEN MS, LI JQ, ZHENG Y, et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing percutaneous local ablative therapy and partial hepatectomy for small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2006, 243(3): 321-328. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000201480.65519.b8 [13] FENG K, YAN J, LI X, et al. A randomized controlled trial of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection in the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 57(4): 794-802. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.05.007 [14] XU Q, KOBAYASHI S, YE X, et al. Comparison of hepatic resection and radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis of 16, 103 patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2014, 4: 7252. [15] PENG ZW, LIN XJ, ZHANG YJ, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for the treatment of hepato-cellular carcinomas 2 cm or smaller: A retrospective comp-arative study[J]. Radiology, 2012, 262(3):1022-1033. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.11110817 [16] LIVRAGHI T, MELONI F, DI STASI M, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Is resection still the treatment of choice?[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 47(1): 82-89. [17] PENG ZW, ZHANG YJ, CHEN MS, et al. Radiofrequency ablation with or without transcatheter arterial chemoembo-lization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prosp-ective randomized trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31(4):426-432. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.9936 [18] PAN YX, XI M, FU YZ, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy as a salvage therapy after incomplete radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective propensity score matching study[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2019, 11(8): 1116. DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081116 [19] ZHAO M, WANG JP, WU PH, et al. Comparative analysis of TACE alone or plus RFA in the treatment of 167 cases of intermediate and advanced staged primary hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Natl Med J China, 2010, 90(41): 2916-2921. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2010.41.009赵明, 王健鹏, 吴沛宏, 等. TACE与TACE联合RFA治疗中晚期原发性肝癌167例临床对比分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2010, 90(41): 2916-2921. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2010.41.009 [20] CHEN QF, JIA ZY, YANG ZQ, et al. TACE combined with MWA versus simple TACE for the treatment of large hepatic cancers: A meta-analysis of curative effect[J]. J Intervent Radiol, 2017, 26(3): 225-231. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2017.03.009陈奇峰, 贾振宇, 杨正强, 等. 肝动脉化疗栓塞联合微波消融与单独肝动脉化疗栓塞治疗大肝癌疗效meta分析[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2017, 26(3): 225-231. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2017.03.009 [21] WEI W, JIAN PE, LI SH, et al. Adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with solitary tumor and microvascular invasion: A randomized clinical trial of efficacy and safety[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2018, 38(1): 61. DOI: 10.1186/s40880-018-0331-y [22] LI S, MEI J, WANG Q, et al. Postoperative adjuvant transarterial infusion chemotherapy with FOLFOX could improve outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion: A preliminary report of a phase Ⅲ, randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2020, 27(13): 5183-5190. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-020-08601-8 [23] WANG Z, PENG Y, HU J, et al. Associating liver partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy for unresectable hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A single center study of 45 patients[J]. Ann Surg, 2020, 271(3): 534-541. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002942 [24] LU L, ZENG J, WEN Z, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation followed by three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy versus transcatheter arterial chemoembolisation alone for primary hepatocellular carcinoma in adults[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 2: CD012244. [25] YIN L, LI H, LI AJ, et al. Partial hepatectomy vs. transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable multiple hepato-cellular carcinoma beyond Milan Criteria: A RCT[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 61(1): 82-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.03.012 [26] ZHONG JH, KE Y, GONG WF, et al. Hepatic resection associated with good survival for selected patients with intermediate and advanced-stage hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Surg, 2014, 260(2): 329-340. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000236 [27] CHEN W, MA T, ZHANG J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization after curative resection for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2020, 22(6): 795-808. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.12.013 [28] WANG Z, REN Z, CHEN Y, et al. Adjuvant transarterial chemoembolization for HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma after resection: A randomized controlled study[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(9): 2074-2081. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2899 [29] ZHOU C, PENG Y, ZHOU K, et al. Surgical resection plus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2019, 8(1): 19-28. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.11.19 [30] ZHANG Y, HUANG G, WANG Y, et al. Is salvage liver resection necessary for initially unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients downstaged by transarterial chemoembolization? Ten years of experience[J]. Oncologist, 2016, 21(12): 1442-1449. DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0094 [31] Chinese College of Interventionalists, Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese Clinical Practice Guidelines for transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Intervent Radiol, 2018, 27(12): 1117-1126. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2018.12.001中国医师协会介入医师分会. 中国肝细胞癌经动脉化疗栓塞治疗(TACE)临床实践指南[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2018, 27(12): 1117-1126. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2018.12.001 [32] CHEN QW, YING HF, GAO S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation plus chemoembolization versus radiofrequency ablation alone for hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2016, 40(3): 309-314. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2015.07.008 [33] KUDO M. A New Treatment option for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with high tumor burden: Initial lenvatinib therapy with subsequent selective TACE[J]. Liver Cancer, 2019, 8(5): 299-311. DOI: 10.1159/000502905 [34] SHUQUN C, MENGCHAO W, HAN C, et al. Tumor thrombus types influence the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma with the tumor thrombi in the portal vein[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2007, 54(74): 499-502. [35] XUE TC, XIE XY, ZHANG L, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A meta-analysis[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2013, 13: 60. DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-60 [36] HE M, LI Q, ZOU R, et al. Sorafenib plus hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin vs sorafenib alone for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: A randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5(7): 953-960. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.0250 [37] CHOI JH, CHUNG WJ, BAE SH, et al. Randomized, prospective, comparative study on the effects and safety of sorafenib vs. hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombosis[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2018, 82(3): 469-478. DOI: 10.1007/s00280-018-3638-0 [38] PENG ZW, GUO RP, ZHANG YJ, et al. Hepatic resection versus transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus[J]. Cancer, 2012, 118(19): 4725-4736. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.26561 [39] SHI J, LAI EC, LI N, et al. Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus[J]. Ann Surg Oncol, 2010, 17(8): 2073-2080. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-010-0940-4 [40] Radiation Oncology Branch of the Chinese Medical Association, Expert Committee on Liver Cancer and Digestive System of China Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Liver Cancer Research Group of Radiation Oncology Branch of China Research Hospital. Consensus on radiation therapy for primary liver cancer in 2016[J]. Chin J Radiat Oncol, 2016, 25(11): 1141-1150. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.11.001中华医学会放射肿瘤学分会, 中国生物医学工程学会精确放疗分会肝癌学组与消化系统肿瘤专家委员会, 中国研究型医院学会放射肿瘤学分会肝癌学组. 2016年原发性肝癌放疗共识[J]. 中华放射肿瘤学杂志, 2016, 25(11): 1141-1150. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1004-4221.2016.11.001 [41] SUN J, YANG L, SHI J, et al. Postoperative adjuvant IMRT for patients with HCC and portal vein tumor thrombus: An open-label randomized controlled trial[J]. Radiother Oncol, 2019, 140: 20-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.05.006 [42] CHENG S, CHEN M, CAI J, et al. Chinese expert consensus on multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus (2018 Edition)[J]. Liver Cancer, 2020, 9(1): 28-40. DOI: 10.1159/000503685 [43] The Society of Liver Cancer of Guangdong Anti-Cancer Association, The Society of Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary Surgery of Guangdong Medical Association. Cantonese expert consensus on multidisciplinary team treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus (2015 edition)[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2015, 14(9): 694-701. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2015.09.002广东省抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会, 广东省医学会肝胆胰外科学分会. 肝细胞肝癌合并门静脉癌栓多学科团队综合治疗广东专家共识(2015版)[J]. 中华消化外科杂志, 2015, 14(9): 694-701. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2015.09.002 [44] ZHU K, CHEN J, LAI L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: Treatment with transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib--a retrospective controlled study[J]. Radiology, 2014, 272(1): 284-293. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.14131946 [45] WEI X, JIANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Neoadjuvant three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A randomized, open-label, multicenter controlled study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2019, 37(24): 2141-2151. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.18.02184 [46] PENG BG, HE Q, LI JP, et al. Adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization improves efficacy of hepatectomy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and portal vein tumor thrombus[J]. Am J Surg, 2009, 198(3): 313-318. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.09.026 [47] ZHANG YF, GUO RP, ZOU RH, et al. Efficacy and safety of preoperative chemoembolization for resectable hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein invasion: A prospective comparative study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2016, 26(7): 2078-2088. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-015-4021-8 [48] LYU N, KONG Y, PAN T, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin in hepatocellular cancer with extrahepatic spread[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2019, 30(3): 349-357. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2018.09.004 [49] ZHANG H, CHEN Y, HU Y, et al. Image-guided intensity-modulated radiotherapy improves short-term survival for abdominal lymph node metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2019, 8(5): 717-727. DOI: 10.21037/apm.2019.11.17 [50] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2017, 25(9): 664 -677. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.09.006中华医学会肝病学分会. 肝硬化腹水及相关并发症的诊疗指南[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2017, 25(9): 664-677. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2017.09.006 [51] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Clinical guidelines on nutrition in end-stage liver disease[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2019, 27(5): 330-342. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.05.003中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会. 终末期肝病临床营养指南[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(5): 330-342. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.05.003 [52] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer pain (2018 edition)[J]. Chin Clin Oncol, 2018, 23(10): 937-944. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCZL201810016.htm中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 癌症疼痛诊疗规范(2018年版)[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2018, 23(10): 937-944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCZL201810016.htm [53] YAO FY, FERRELL L, BASS NM, et al. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of the proposed UCSF criteria with the Milan criteria and the Pittsburgh modified TNM criteria[J]. Liver Transpl, 2002, 8(9): 765-774. DOI: 10.1053/jlts.2002.34892 [54] Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B (version 2019)[J/CD]. Chin J Front Med Sci(Electronic Version), 2019, 11(12): 51-77. (in Chinese)中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2019年版)[J/CD]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2019, 11(12): 51-77. -



 PDF下载 ( 2013 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2013 KB)

 下载:
下载:


