系统免疫炎症指数与肝泡型包虫病患者预后的相关性分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.025
Correlation between systemic immune-inflammation index and prognosis in patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis
-
摘要:
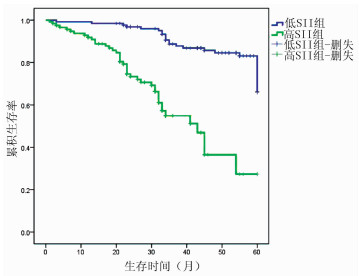
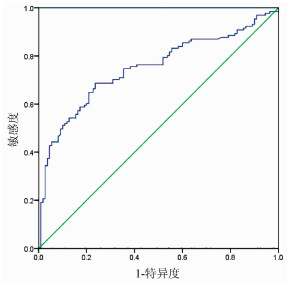
目的 探讨分析系统免疫炎症指数(SⅡ)与肝泡型包虫病患者预后的相关性分析。 方法 回顾性分析2015年1月-2018年12月青海大学附属医院肝胆胰外科收治的242例行肝泡型包虫病手术患者的临床资料,计算SⅡ数值。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。相关性分析采用Spearman相关分析。应用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)确定SⅡ的最佳临界值,Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,对两组患者的总生存时间进行分析,并用log-rank比较两组生存率差异;采用单因素和多因素Cox回归模型分析肝泡型包虫病患者预后的影响因素。 结果 SⅡ与肝泡型包虫病患者术后病死率呈正相关(r=0.267,P < 0.001)。应用ROC曲线确定术前SⅡ的最佳临界值为758.92,将242例患者分为低SⅡ组(SⅡ≤758.92,126例)和高SⅡ组(SⅡ>758.92,n=116例)。低SⅡ组与高SⅡ组肝泡型包虫患者术后1、3、5年生存率分别为98.20%、88.47%、66.10%和90.80%、53.05%、27.40%,低SⅡ组累积生存率>50%,平均生存时间为55.584个月(95%CI:53.550~57.617);高SⅡ组累积生存率 < 50%,平均生存时间为39.384个月(95%CI:35.070~43.698),中位生存时间为43个月(95%CI:34.694~51.306),低SⅡ组肝泡型包虫病患者生存率明显优于高SⅡ组,两组总体生存率差异有统计学意义(χ2=46.979,P < 0.05)。单因素分析结果显示SⅡ>758.92是肝泡型包虫病患者总体生存时间的影响因素(HR=5.907,95% CI:3.386~10.306,P=0.001);Cox多因素分析显示术前外周血SⅡ是肝泡型包虫病患者总体生存率的独立危险因素(HR=3.507,95% CI:1.911~6.435,P=0.001)。 结论 术前SⅡ水平与肝泡型包虫病患者预后有明确的相关性,可作为临床评估患者预后的指标,术前外周血SⅡ越高,患者预后越差。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation between systemic immune-inflammation index (SⅡ) and prognosis in patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 242 patients who were admitted to Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Qinghai University Affiliated Hospital, from January 2015 to December 2018 and underwent surgery for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis, and SⅡ was calculated. The chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups, and a Spearman correlation analysis was performed. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to determine the optimal cut-off value of SⅡ; the Kaplan-Meier method was used to plot survival curves and analyze overall survival time in the two groups, and the log-rank test was used for comparison of survival rates between the two groups; univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses were used to identify the influencing factors for the prognosis of patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Results The Spearman correlation analysis showed that SⅡ was positively correlated with the postoperative fatality rate of patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (r=0.267, P < 0.001). The ROC curve showed that the optimal cut-off value of SⅡ before surgery was 758.92, and based on this, 242 patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis were divided into low SⅡ (SⅡ ≤758.92) group with 126 patients and high SⅡ (SⅡ >758.92) group with 116 patients. The low SⅡ group had 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates of 98.20%, 88.47%, and 66.10%, respectively, and the high SⅡ group had 1-, 3-, and 5-year survival rates of 90.80%, 53.05%, and 27.40%, respectively. The low SⅡ group had a cumulative survival rate of >50% and a mean survival time of 55.584 months (95% confidence interval[CI]: 53.550-57.617), while the high SⅡ group had a cumulative survival rate of < 50%, a mean survival time of 39.384 months (95% CI: 35.070-43.698), and a median survival time of 43 months (95% CI: 34.694-51.306). The low SⅡ group had a significantly better survival rate than the high SⅡ group, and there was a significant difference in overall survival rate between the two groups (χ2=46.979, P < 0.05). The univariate analysis showed that SⅡ >758.92 (hazard ratio [HR]=5.907, 95% CI: 3.386-10.306, P=0.001) was an influencing factor for the overall survival time of patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis, and the multivariate Cox regression analysis showed that preoperative peripheral blood SⅡ (HR=3.507, 95% CI: 1.911-6.435, P=0.001) was an independent risk factor for the overall survival rate of patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Conclusion Preoperative SⅡ level is clearly correlated with the prognosis of patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis and can thus be used as a clinical indicator to evaluate the prognosis of patients. The higher the peripheral blood SⅡ before surgery, the worse the prognosis of patients. -
Key words:
- Echinococcosis, Hepatic /
- Systemic Immune Inflammatory /
- Prognosis /
- Risk Factors
-
表 1 SⅡ与肝泡型包虫病患者临床病理因素的关系
指标 高SⅡ组(n=116) 低SⅡ组(n=126) χ2值 P值 年龄[例(%)] 2.385 0.130 ≤30岁 42(36.2) 34(27.0) >30岁 74(63.8) 92(73.0) 性别[例(%)] 0.517 0.511 男 43(37.1) 53(42.1) 女 73(62.9) 73(57.9) 手术方式[例(%)] 20.197 < 0.001 根治性治疗 75(64.7) 112(88.9) 姑息治疗 41(35.3) 14(11.1) 术中出血量[例(%)] 22.278 < 0.001 < 1000 ml 50(43.1) 92(73.0) ≥1000 ml 66(56.9) 34(27.0) 包虫分期[例(%)] 0.942 0.040 早、中期 47(40.5) 68(54.0) 晚期 69(59.5) 58(46.0) 病灶数[例(%)] 0.223 0.693 单发 68(58.6) 77(61.1) 多发 48(41.4) 49(38.9) Child-Pugh分级[例(%)] 9.489 0.003 A级 38(32.8) 66(52.4) B级 78(67.2) 60(47.6) 并发症[例(%)] 48.624 < 0.001 有 90(77.6) 41(32.5) 无 26(22.4) 85(67.5) ALT[例(%)] 6.947 0.010 ≤40 U/L 43(37.1) 68(54.0) >40 U/L 73(62.9) 58(46.0) AST[例(%)] 5.415 0.021 ≤40 U/L 48(41.4) 71(56.3) >40 U/L 68(58.6) 55(44.7) TBil[例(%)] 9.238 0.002 ≤32.4 μmol/L 52(44.8) 81(64.3) >32.4 μmol/L 64(55.2) 45(35.7) Alb[例(%)] 4.990 0.031 ≤35 g/L 84(72.4) 74(58.7) >35 g/L 32(27.6) 52(41.3) ALP[例(%)] 5.973 0.020 ≤150 U/L 18(15.5) 36(28.6) >150 U/L 98(84.5) 90(71.4) PT[例(%)] 6.947 0.010 ≤16 s 43(37.1) 68(54.0) >16 s 73(62.9) 58(46.0) 中性粒细胞[例(%)] 1.865 0.232 ≤6.3×109/L 104(89.7) 119(94.4) >6.3×109/L 12(10.3) 7(5.6) 血小板[例(%)] 21.158 < 0.001 ≤300×109/L 44(37.9) 85(67.5) >300×109/L 72(62.1) 41(32.5) 白细胞[例(%)] 5.543 0.06 ≤10×109 /L 93(80.2) 112(88.9) >10×109/L 23(19.8) 14(11.1) 表 2 影响肝泡型包虫病患者生存的单因素及多因素Cox回归分析
指标 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR(95% CI) P值 HR(95% CI) P值 年龄(≤30岁vs >30岁) 1.272(0.744~2.175) 0.324 性别(男vs女) 1.268(0.791~2.033) 0.379 手术方式(根治性治疗vs姑息治疗) 3.195(1.973~5.176) 0.001 2.053(1.138~3.704) 0.019 术中出血量(< 1000 ml vs ≥1000 ml) 6.832(3.893~11.990) 0.001 4.615(2.545~8.369) 0.001 包虫分期(早期vs中、晚期) 3.841(2.017~7.318) 0.009 病灶数(单发vs多发) 1.104(0.688~1.773) 0.681 SⅡ(>758.92 vs ≤758.92) 5.907(3.386~10.306) 0.001 3.507(1.911~6.435) 0.001 Child-Pugh分级(A级vs B级) 3.066(2.716~6.449) 0.028 1.973(1.084~3.588) 0.041 并发症(有vs无) 2.278(1.398~3.711) 0.001 ALT(≤40 U/L vs >40 U/L) 1.201(0.748~1.931) 0.448 AST(≤40 U/L vs >40 U/L) 1.436(0.894~2.307) 0.134 ALP(≤150 U/L vs >150 U/L) 2.237(1.180~4.790) 0.015 PT(≤16 s vs >16 s) 1.824(1.113~2.991) 0.017 -
[1] WANG WT, YANG C, YAN LN. New concept and strategy of surgical radical treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Natl Med J China, 2018, 98(38): 3049-3051. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.38.001王文涛, 杨闯, 严律南.肝泡型包虫病外科根治性治疗的新理念与策略[J].中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(38): 3049-3051. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.38.001 [2] GERAMIZADEH B, BAGHERNEZHAD M. Hepatic alveolar hydatid cyst: A brief review of published cases from Iran in the last 20 years[J]. Hepat Mon, 2016, 16(10): e38920. DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.38920 [3] FANG D, CHEN ZY. Diagnosis and treatment of hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(5): 990-993. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.05.042方丹, 陈哲宇.肝泡状棘球蚴病的诊断和治疗[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(5): 990-993. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.05.042 [4] LIU R, HE J, WANG H, et al. Accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus contrast-enhanced computed tomography in measuring hepatic alveolar echinococcosis lesions: A comparative study[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2019, 47(7): 750-751. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGZ201907037.htm刘荣, 赫娟, 王辉, 等.超声造影及增强CT测量肝泡型包虫病病灶对比研究[J].临床军医杂志, 2019, 47(7): 750-751. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYGZ201907037.htm [5] SHAO J, WANG ZX, WANG H, et al. Antibody microarray analysis of the serum inflammatory cytokines in patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 26(5): 566-569. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX201705024.htm邵军, 王志鑫, 王虎, 等.泡型肝包虫病患者血清炎症因子的抗体芯片检测及分析[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2017, 26(5): 566-569. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX201705024.htm [6] LI YF, SHAO J, WANG ZX, et al. Effects of hydatid cyst fluid on the expression of TGF-β1, IL-6 and TNF-α in rat hepatic stellate cells[J]. Chin J Bases Clin Gen Surg, 2016, 23(12): 1500-1502. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.7507/1007-9424.20160378李衍飞, 邵军, 王志鑫, 等.泡球蚴囊液对大鼠肝星状细胞TGF-β1、IL-6及TNF-α表达的影响[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2016, 23(12): 1500-1502. DOI: 10.7507/1007-9424.20160378 [7] TURGUN TS, SHAN JY, LI T, et al. Effect of Th17 cells and Treg cells on immune evasion in patients with hepatic hydatid disease[J]. Chin J Dig Surg, 2010, 9(4): 283-286. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2010.04.015吐尔洪江·吐逊, 单骄宇, 李涛, 等. Th17细胞和调节性T细胞在肝包虫病免疫逃避中的作用[J].中华消化外科杂志, 2010, 9(4): 283-286. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-9752.2010.04.015 [8] LABELLE M, BEGUM S, HYNES RO. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2011, 20(5): 576-590. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.09.009 [9] GAO Y, GUO W, CAI S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(14): 3188-3196. DOI: 10.7150/jca.30281 [10] WANG P, YUE W, LI W, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index and ultrasonographic classification of breast imaging-reporting and data system predict outcomes of triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2019, 11: 813-819. DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S185890 [11] HU B, YANG XR, XU Y, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(23): 6212-6222. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442 [12] AZIZ MH, SIDERAS K, AZIZ NA, et al. The systemic-immune-inflammation index independently predicts survival and recurrence in resectable pancreatic cancer and its prognostic value depends on bilirubin levels: A retrospective multicenter cohort study[J]. Ann Surg, 2019, 270(1): 139-146. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002660 [13] BEAL EW, WEI L, ETHUN CG, et al. Elevated NLR in gallbladder cancer and cholangiocarcinoma - making bad cancers even worse: Results from the US extrahepatic biliary malignancy consortium[J]. HPB (Oxford), 2016, 18(11): 950-957. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2016.08.006 [14] PINATO DJ, NORTH BV, SHARMA R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: The prognostic nutritional index (PNI)[J]. Br J Cancer, 2012, 106(8): 1439-1445. DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2012.92 [15] LI C, TIAN W, ZHAO F, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index, SII, for prognosis of elderly patients with newly diagnosed tumors[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(82): 35293-35299. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.24293 [16] YANG R, CHANG Q, MENG X, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. J Cancer, 2018, 9(18): 3295-3302. DOI: 10.7150/jca.25691 [17] WANG K, DIAO F, YE Z, et al. Prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with gastric cancer[J]. Chin J Cancer, 2017, 36(1): 75. DOI: 10.1186/s40880-017-0243-2 [18] ZHANG GJ. Parasitic infection and neutrophils[J]. Foreign Med Sci (Parasitosis), 1999, 26(1): 1-5. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWJC199901000.htm张桂筠.寄生虫感染与中性粒细胞[J].国外医学(寄生虫病分册), 1999, 26(1): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWJC199901000.htm [19] ZHOU WL, ZHAO WX, WU GL, et al. Immune function of red blood cells and platelets and parasitic infection[J]. Chin J Parasitic Dis, 1992, 5(2): 140-142. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZISC199202034.htm周维立, 赵慰先, 吴观陵, 等.红细胞、血小板免疫功能与寄生虫感染[J].中国寄生虫病防治杂志, 1992, 5(2): 140-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZISC199202034.htm [20] YIN SH. The preliminary study of TGF-β inhibiting the natural killer cells functions in the immune escape of Echinococcus granulosus[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2014. (in Chinese)印双红. TGF-β抑制自然杀伤细胞在细粒棘球蚴免疫逃逸作用中的初步探讨[D].石河子: 石河子大学, 2014. [21] ZHANG F, PANG N, ZHU Y, et al. CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5(+) CD4(+) T cells are positively correlated with levels of IL-21 in active and transitional cystic echinococcosis patients[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2015, 15: 457. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-015-1156-9 -



 PDF下载 ( 2281 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2281 KB)

 下载:
下载: