20例糖原累积症Ⅸa型患者的临床和基因特点分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.026
利益冲突声明:本研究不存在研究者、伦理委员会成员、受试者监护人以及与公开研究成果有关的利益冲突,特此声明。
作者贡献声明:李玉川负责收集数据,资料分析,撰写论文;冯佳燕负责病理报告解读,提供病理图片;王建设参与课题设计;陆怡参与课题设计,拟定写作思路,指导撰写文章并最后定稿。
Clinical and genetic features of patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa: An analysis of 20 cases
-
摘要:
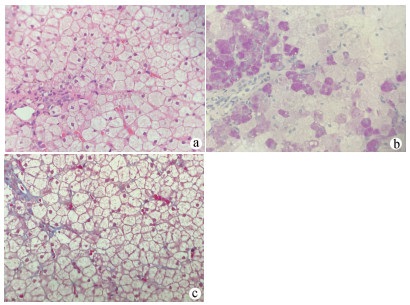
目的 总结糖原累积症Ⅸa型(GSD Ⅸa)患者的临床和基因特点,加强对该病的认识。 方法 回顾性分析2015年1月—2018年12月在复旦大学附属儿科医院住院并经基因确诊的20例GSD Ⅸa型患者的临床资料,总结其临床和基因特点。 结果 20例GSD Ⅸa型患者均为男性,确诊中位年龄为2.5岁。所有患者均有肝肿大,转氨酶水平升高;生长发育迟缓5例(25.0%),空腹低血糖19例(95.0%),高乳酸血症14例(70.0%),高甘油三酯血症9例(45.0%),高胆固醇血症5例(25.0%)。8例患者进行了空腹血酮检查,结果显示均升高;所有患者尿酸均正常,5例(25.0%)患者尿酮体阳性。18例患者进行了肝穿刺检查,其中15例存在轻至中度肝纤维化。共检测到16种PHKA2基因突变,5种为已知致病突变,11种为新突变,其中c.3614位点是高发突变位点。所有患者均使用生玉米淀粉治疗,大多数患者的临床表现均为好转。 结论 GSD Ⅸa型以男性为主。肝肿大,转氨酶升高,生长发育迟缓,空腹低血糖,空腹血酮升高,尿酸正常需考虑该病可能。可通过肝穿刺协助诊断,临床生化指标和基因检测可明确诊断及分型。该病多数临床表现较轻,但也可导致肝纤维化,使用生玉米淀粉治疗能够改善病情。 -
关键词:
- 糖原贮积病 /
- 病理状态, 体征和症状 /
- 突变
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical and genetic features of patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa (GSD Ⅸa), and to improve the clinical understanding of the disease. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 20 patients who were hospitalized and genetically diagnosed with GSD Ⅸa in Children's Hospital of Fudan University from January 2015 to December 2018, and their clinical and genetic features were summarized. Results All 20 patients with GSD Ⅸa were male, with a median age of 2.5 years at the time of confirmed diagnosis. All patients had hepatomegaly and elevated aminotransferases; of all patients, there were 5 patients (25.0%) with growth retardation, 19 (95.0%) with fasting hypoglycemia, 14 (70.0%) with hyperlactatemia, 9 (45.0%) with hypertriglyceridemia, and 5 (25.0%) with hypercholesterolemia. Fasting blood ketone was measured for 8 patients and all of these patients had an increase in blood ketone; all patients had normal uric acid, and 5 patients (25.0%) had positive urine ketone. Liver biopsy was performed for 18 patients, among whom 15 had mild to moderate liver fibrosis. A total of 16 mutations were detected in the PHKA2 gene, among which 5 were known pathogenic mutations and 11 were novel mutations, and most of the mutations were detected in the c.3614 locus. All patients were treated with uncooked cornstarch, and most patients achieved an improvement in clinical manifestations. Conclusion GSD Ⅸa is more common in male patients. This disease should be considered for patients with hepatomegaly, elevated aminotransferases, growth retardation, fasting hypoglycemia, elevated fasting blood ketone, and normal uric acid. Liver biopsy may help with the diagnosis of this disease, and clinical biochemical parameters and gene detection can be used to confirm diagnosis and classification. Most patients have mild clinical manifestations, while some patients may have liver fibrosis, and treatment with uncooked cornstarch can improve the condition of this disease. -
表 1 20例GSD Ⅸa型患者的临床及病理资料
病例 确诊年龄(岁) 确诊时身高(cm)/百分位 2020年9月随访时身高(cm)/百分位 确诊时体质量(kg)/百分位 2020年9月随访时体质量(kg)/百分位 ALT (U/L) AST (U/L) 1 2.33 85/10th 118/50th 14.5/75th 31.0/97th 170 172 2 1.50 86/90th 118/25th 11.0/50th 21.0/25th 153 212 3 2.00 87/25th 123/25th 14.0/75th 24.0/50th 67 114 4 2.08 85/10th 105/10th 13.5/75th 17.0/25th 1530 3061 5 2.00 84/10th 104/10th 13.0/50th 18.0/50th 513 554 6 1.92 86/50th 119/75th 12.0/50th 26.0/97th 156 132 7 3.67 85/3rd 113/25th 14.0/10th 24.0/75th 205 548 8 8.00 127/25th 139/25th 29.0/50th 37.0/50th 61 69 9 3.83 92/3rd 125/25th 13.0/3rd 24.0/25th 186 192 10 5.33 100/3rd 135/25th 20.0/50th 33.0/50th 176 233 11 3.00 104/50th 140/75th 18.0/75th 45.0/97th 69 108 12 1.75 80/10th 103/25th 11.0/25th 17.0/50th 190 170 13 2.50 90/10th 135/75th 13.0/50th 39.0/97th 308 164 14 7.00 115/3rd 137/50th 18.5/3rd 28.0/25th 231 265 15 1.25 78/25th 98/25th 12.0/90th 15.0/50th 106 109 16 1.83 83/10th 130/75th 12.0/50th 29.0/75th 232 425 17 2.58 91/25th 124/75th 14.5/75th 29.0/97th 108 133 18 4.00 106/75th 136/75th 18.0/75th 31.0/75th 122 108 19 4.92 103/3rd 135/25th 18.0/50th 32.0/50th 223 170 20 3.75 100/25th 114/25th 16.0/50th 19.0/25th 93 101 病例 空腹血糖(mmol/L) 空腹血酮(mmol/L) 甘油三酯(mmol/L) 总胆固醇(mmol/L) 乳酸(mmol/L) 肝纤维化分期 1 3.4 1.4 2.61 4.67 2.5 S0 2 2.9 0.5 1.85 2.20 1.4 S0 3 2.8 0.84 4.49 2.8 S0 4 3.0 0.5 2.20 6.01 8.0 S1~2 5 3.6 1.16 4.19 3.9 S1~2 6 2.0 2.6 0.84 2.73 2.7 S1~2 7 3.5 1.3 1.66 4.46 7.5 S1~2 8 3.2 1.25 5.73 3.2 S1~2 9 3.4 1.71 6.78 4.2 S1~2 10 2.9 1.34 4.41 1.8 S1~2 11 3.4 1.23 4.26 1.9 S1~2 12 4.5 0.8 1.49 4.06 3.6 S1~2 13 2.8 1.73 3.55 2.8 S1~2 14 2.9 1.2 2.51 5.74 2.6 S1~2 15 3.6 1.6 2.19 4.31 1.7 S1~2 16 3.0 1.63 4.26 1.5 S1~2 17 2.8 1.74 5.70 3.4 S3 18 3.4 0.71 4.89 1.5 S3 19 2.0 1.07 3.40 2.3 20 3.2 2.70 4.26 2.9 注:ALT正常值9~50 U/L;AST正常值15~40 U/L;空腹血糖正常值3.9~6.1 mmol/L;空腹血酮正常值0~0.3 mmol/L;甘油三酯正常值0~1.7 mmol/L;总胆固醇正常值0~5.18 mmol/L;乳酸正常值0.5~2.2 mmol/L。 表 2 20例GSD Ⅸa型患者PHKA2基因检测结果
病例 碱基改变 氨基酸改变 突变类型 备注 1 c.3331C>T p.R1111X 无义突变 新突变 2 c.883C>T p.R295C 错义突变 已报道 3 c.347A>G p.Y116C 错义突变 新突变 4 c.883C>T p.R295C 错义突变 已报道 5 c.3614C>T p.P1205L 错义突变 已报道 6 c.3614C>T p.P1205L 错义突变 已报道 7 c.773G>A p.G258E 错义突变 新突变 8 c.3614C>T p.P1205L 错义突变 已报道 9 c.3614C>T p.P1205L 错义突变 已报道 10 c.884G>A p.R295H 错义突变 已报道 11 c.3614C>G p.P1205R 错义突变 新突变 12 c.2597+1G>C Splicing 剪接突变 新突变 13 c.919-2A>G Splicing 剪接突变 新突变 14 c.395A>G p.H132R 错义突变 新突变 15 c.285G>C p.Q95H 错义突变 新突变 16 c.898G>A p.G300S 错义突变 新突变 17 c.338A>G p.H113R 错义突变 已报道 18 c.3210_3212delGAG p.R1070del 缺失突变 已报道 19 c.524_537+1del15 FS+Splicing 小片段缺失 新突变 20 c.3336+2T>C Splicing 剪接突变 新突变 -
[1] ACHOUITAR S, GOLDSTEIN JL, MOHAMED M, et al. Common mutation in the PHKA2 gene with variable phenotype Ⅰn patients with liver phosphorylase b kinase deficiency[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2011, 104(4): 691-694. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.08.021 [2] MAICHELE AJ, BURWINKEL B, MAIRE I, et al. Mutations in the testis/liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase gamma subunit (PHKG2) cause autosomal liver glycogenosis in the gsd rat and in humans[J]. Nat Genet, 1996, 14(3): 337-340. DOI: 10.1038/ng1196-337 [3] BRUSHIA RJ, WALSH DA. Phosphorylase kinase: The complexity of its regulation is reflected in the complexity of its structure[J]. Front Biosci, 1999, 4: d618-d641. [4] DAVIDSON JJ, OZÇELIK T, HAMACHER C, et al. cDNA cloning of a liver isoform of the phosphorylase kinase alpha subunit and mapping of the gene to Xp22.2-p22.1, the region of human X-linked liver glycogenosis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1992, 89(6): 2096-2100. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2096 [5] FU J, WANG T, XIAO X. A novel PHKA2 mutation in a Chinese child with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa: A case report and literature review[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2019, 20(1): 56. DOI: 10.1186/s12881-019-0789-8 [6] LIU J, ZHANG MH, GONG JY, et al. Report of 7 cases of glycogen storage disease type Ⅵ and type Ⅸa[J]. Chin J Evid Based Pediatr, 2017, 12(4): 284-288. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2017.04.009刘杰, 张梅红, 龚敬宇, 等.糖原累积病Ⅵ型和Ⅹa型7例病例报告并文献复习[J].中国循证儿科杂志, 2017, 12(4): 284-288. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5501.2017.04.009 [7] KISHNANI PS, GOLDSTEIN J, AUSTIN SL, et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage diseases type Ⅵ and Ⅸ: A clinical practice resource of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)[J]. Genet Med, 2019, 21(4): 772-789. DOI: 10.1038/s41436-018-0364-2 [8] FERNANDES J, PIKAAR NA. Ketosis in hepatic glycogenosis[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1972, 47(251): 41-46. DOI: 10.1136/adc.47.251.41 [9] ZHANG J, YUAN Y, MA M, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of 17 Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸa[J]. Gene, 2017, 627: 149-156. DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.026 [10] BEAUCHAMP NJ, DALTON A, RAMASWAMI U, et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ: High variability in clinical phenotype[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2007, 92(1-2): 88-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.06.007 [11] HIRONO H, SHOJI Y, TAKAHASHI T, et al. Mutational analyses in four Japanese families with X-linked liver phosphorylase kinase deficiency type 1[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 1998, 21(8): 846-852. DOI: 10.1023/A:1005422819207 [12] ROSCHER A, PATEL J, HEWSON S, et al. The natural history of glycogen storage disease types Ⅵ and Ⅸ: Long-term outcome from the largest metabolic center in Canada[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2014, 113(3): 171-176. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.09.005 [13] BURWINKEL B, AMAT L, GRAY RG, et al. Variability of biochemical and clinical phenotype Ⅰn X-linked liver glycogenosis with mutations in the phosphorylase kinase PHKA2 gene[J]. Hum Genet, 1998, 102(4): 423-429. DOI: 10.1007/s004390050715 [14] KISHNANI PS, AUSTIN SL, ABDENUR JE, et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type Ⅰ: A practice guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics[J]. Genet Med, 2014, 16(11): e1. DOI: 10.1038/gim.2014.128 [15] HONG FX, QIU HR, XUE ZJ, et al. Management of fluid and metabolic/electrolytic disorders in living donor with liver transplantation in children with glycogen storage disease[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2020, 19(1): 91-95. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLC202001026.htm洪方晓, 仇焕容, 薛照静, 等.糖原贮积病患儿行肝移植手术术中液体及内环境的管理[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2020, 19(1): 91-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLC202001026.htm [16] TSILIANIDIS LA, FISKE LM, SIEGEL S, et al. Aggressive therapy improves cirrhosis in glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2013, 109(2): 179-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.03.009 [17] JOHNSON AO, GOLDSTEIN JL, BALI D. Glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ: Novel PHKA2 missense mutation and cirrhosis[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2012, 55(1): 90-92. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31823276ea [18] LAU CK, HUI J, FONG FN, et al. Novel mutations in PHKA2 gene in glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ patients from Hong Kong, China[J]. Mol Genet Metab, 2011, 102(2): 222-225. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.11.004 [19] CHEN ST, CHEN HL, NI YH, et al. X-linked liver glycogenosis in a Taiwanese family: Transmission from undiagnosed males[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2009, 50(5): 230-233. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-9572(09)60068-1 [20] WANG P, DONG Y, XU ZQ, et al. Clinical and pathological features and gene mutation analysis in 12 Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2018, 23(9): 764-768. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUAN201809007.htm王璞, 董漪, 徐志强, 等.糖原累积症Ⅸ型12例临床、病理特点及基因突变位点分析[J].肝脏, 2018, 23(9): 764-768. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUAN201809007.htm [21] YANG F, XU Y, FANG C, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of three Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸα[J]. Pediatr Neonatol, 2019, 60(4): 463-466. DOI: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2019.05.007 [22] CHOI R, PARK HD, KANG B, et al. PHKA2 mutation spectrum in Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type Ⅸ: Prevalence of deletion mutations[J]. BMC Med Genet, 2016, 17: 33. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4839068/ [23] CHO SY, LAM CW, TONG SF, et al. X-linked glycogen storage disease IXa manifested in a female carrier due to skewed X chromosome inactivation[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2013, 426: 75-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.08.026 [24] van den BERG IE, van BEURDEN EA, MALINGRÉ HE, et al. X-linked liver phosphorylase kinase deficiency is associated with mutations in the human liver phosphorylase kinase alpha subunit[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 1995, 56(2): 381-387. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1801119/ [25] HENDRICKX J, LEE P, KEATING JP, et al. Complete genomic structure and mutational spectrum of PHKA2 in patients with x-linked liver glycogenosis type Ⅰ and Ⅱ[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 1999, 64(6): 1541-1549. DOI: 10.1086/302399 [26] BURWINKEL B, MOSES SW, KILIMANN MW. Phosphorylase-kinase-deficient liver glycogenosis with an unusual biochemical phenotype Ⅰn blood cells associated with a missense mutation in the beta subunit gene (PHKB)[J]. Hum Genet, 1997, 101(2): 170-174. DOI: 10.1007/s004390050608 [27] WILLEMS PJ, GERVER WJ, BERGER R, et al. The natural history of liver glycogenosis due to phosphorylase kinase deficiency: A longitudinal study of 41 patients[J]. Eur J Pediatr, 1990, 149(4): 268-271. DOI: 10.1007/BF02106291 -



 PDF下载 ( 2251 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2251 KB)

 下载:
下载:


