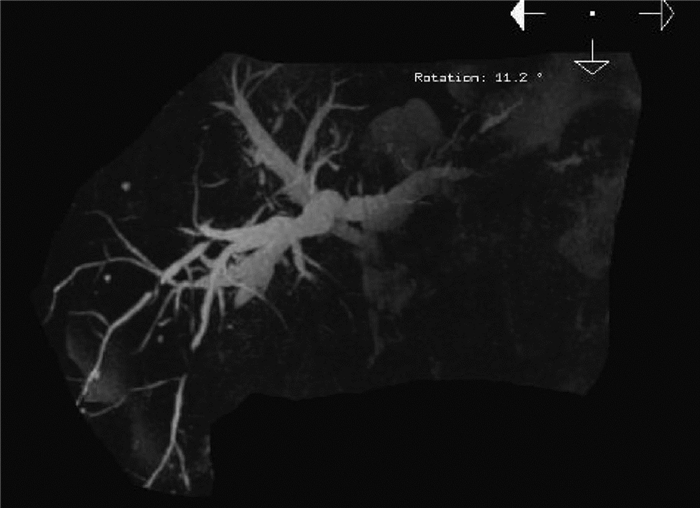
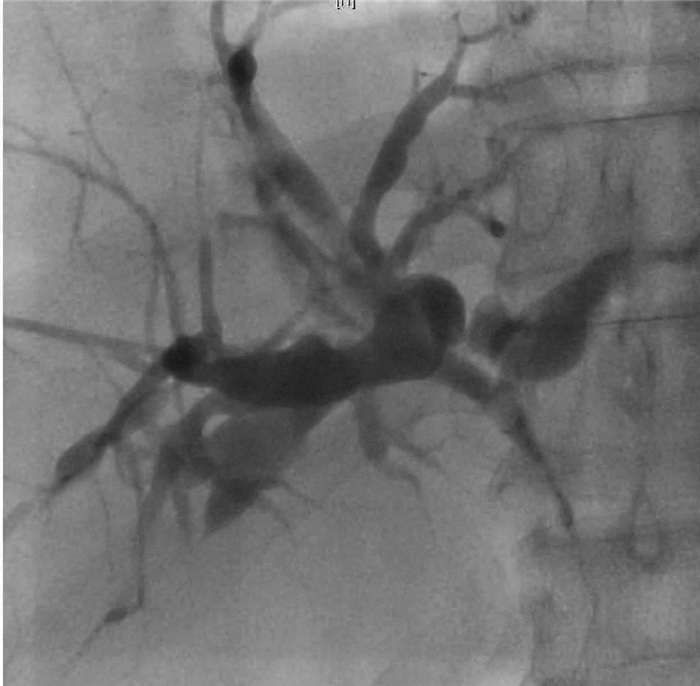
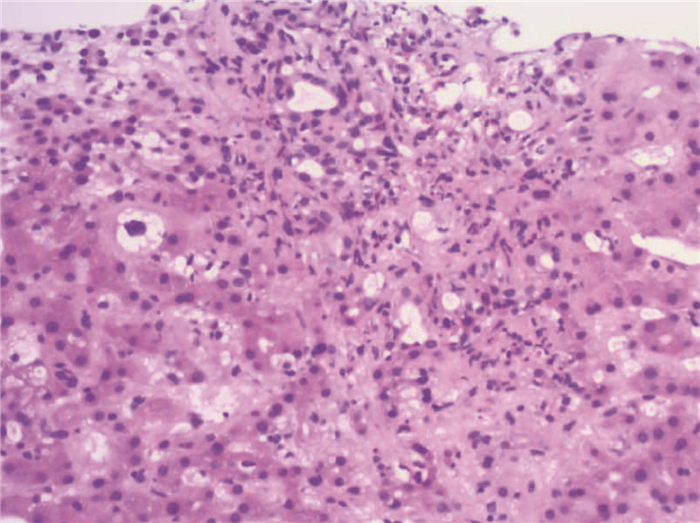
晚期原发性肝癌综合治疗后黄疸的诊治及鉴别1例报告
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.030
作者贡献声明:谢思采集数据,分析及解释数据,起草文章;杨明对文章的知识性内容作批阅性审阅,材料支持和指导;黄缘负责指导,支持性贡献;魏来对文章的知识性内容作批阅性审阅、指导和支持性贡献。
Differential diagnosis and treatment of jaundice after comprehensive treatment of advanced primary liver cancer: A case report
-
-
Key words:
- Liver Neoplasms /
- Jaundice /
- Diagnosis, Differential /
- Combined Modality Therapy
-
表 1 肝功能及肿瘤标志物变化
时间 ALT(U/L) AST(U/L) ALP(U/L) GGT(U/L) TBil(μmol/L) DBil(μmol/L) Alb(g/L) AFP(ng/ml) CA19-9(U/ml) 2019年8月20日 56.2 71.4 390 192 281.2 228.9 26.2 1362.16 10 968.75 2019年8月23日 45.2 73.7 449 321 427.5 364.0 30.0 - - 2019年8月27日 47.3 50.3 486 673 548.5 450.7 33.4 - - 2019年8月30日 49.5 63.1 257 312 429.6 349.4 32.6 - - 2019年9月2日 38.2 36.2 236 371 669.9 533.8 35.3 3471.43 28 106.72 2019年9月5日 29.6 53.9 151 222 566.0 473.0 29.0 - - 注:“-”表示未检查。 -
[1] Bureau of Medical Administration, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in China (2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(2): 277-292. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会医政医管局. 原发性肝癌诊疗规范(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(2): 277-292. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.02.007 [2] MINAMI Y, KUDO M. Hepatocellular carcinoma with obstructive jaundice: Endoscopic and percutaneous biliary drainage[J]. Dig Dis, 2012, 30(6): 592-597. DOI: 10.1159/000343087 [3] YU H, GUO Z, XING W, et al. Bile culture and susceptibility testing of malignant biliary obstruction via PTBD[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2012, 35(5): 1136-1144. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-011-0263-2 [4] KUDO M, FINN RS, QIN S, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10126): 1163-1173. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30207-1 [5] Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Guidance Working Committee. Guidelines of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) management of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related toxicity[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2019: 33-36. (in Chinese)中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)免疫检查点抑制剂相关的毒性管理指南2019[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2019: 33-36. [6] PAN C, WANG QL, ZHENG YF, et al. Progress in monitoring and treatment strategies for adverse reactions of tumor immunological checkpoint inhibitors[J]. China Med Herald, 2019, 16(7): 41-44. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201907011.htm潘岑, 王庆兰, 郑永法, 等. 肿瘤免疫检查点抑制剂不良反应的监测与处理策略研究进展[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(7): 41-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYCY201907011.htm [7] ZHANG QY, CHEN LL, GAO F, et al. Pathological features of immune-mediated hepatitis due to immune checkpoint inhibitors and anti-angiogenesis targeted therapy[J]. Chin J Pathol, 2020, 49(4): 329-335. (in Chinese) http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zhblx202004005章琼燕, 陈伶俐, 高峰, 等. 免疫检查点抑制剂治疗后肝功能异常的组织病理学分析[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2020, 49(4): 329-335. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/zhblx202004005 [8] TROTTI A, BYHARDT R, STETZ J, et al. Common toxicity criteria: Version 2.0. an improved reference for grading the acute effects of cancer treatment: Impact on radiotherapy[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2000, 47(1): 13-47. DOI: 10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00559-3 [9] REED GB Jr, COX AJ Jr. The human liver after radiation injury. A form of veno-occlusive disease[J]. Am J Pathol, 1966, 48(4): 597-611. [10] WU DC. Radioactive medicine[M]. Beijing: Military Medical Science Press, 2001: 104-105. (in Chinese)吴德昌. 放射医学[M]. 北京:军事医学科学出版社, 2001: 104-105. -



 PDF下载 ( 2088 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2088 KB)

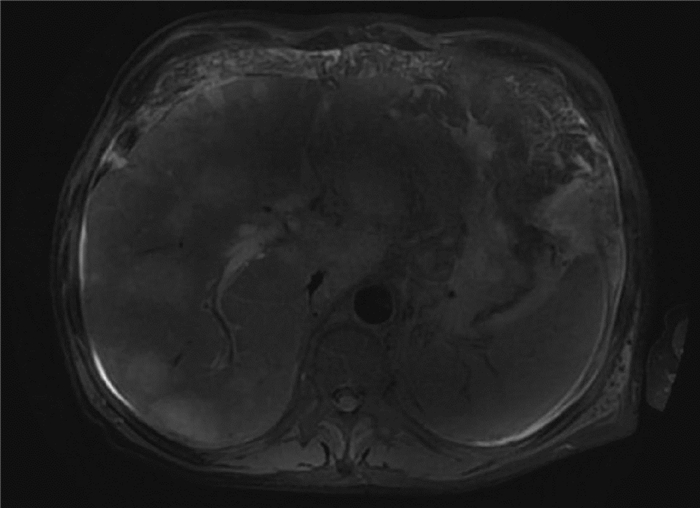
 下载:
下载: