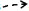microRNA-335在慢性肝病中的作用
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.02.047
Role of microRNA-335 in chronic liver diseases
-
摘要: 近年来,microRNA(miRNA)在肝脏病理过程中的调控作用备受关注。在病毒性及脂肪性肝炎中, miRNA-335通过Y盒上的性别决定区(SOX)4转录因子调控肝炎进展;在进展性肝纤维化及肝癌发生发展过程中,miRNA-335通过缺氧诱导因子1α、磷酸酶和紧张素同系物、靶向Rho蛋白激酶1、纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1、碱性螺旋-环-螺旋转录因子家族1及间质-上皮细胞转化因子等靶基因调控肝脏中胶原的产生、沉积和降解,从而调控肝星状细胞或肝癌细胞的迁移和侵袭等生物学行为。主要归纳了近几年报道的miRNA-335在肝炎、肝纤维化和肝癌中作用的研究进展,同时,结合现有研究,提出miRNA-335/巯基氧化酶1调控轴可能通过抑制肝星状细胞活化介导青蒿琥酯抗血吸虫性肝纤维化的猜想,以期为抗肝纤维化及其他肝病治疗提供新思路。Abstract: In recent years, the regulatory role of microRNAs in liver pathological process has attracted more and more attention. In viral hepatitis and steatohepatitis, microRNA-335 (miRNA-335) regulates the progression of hepatitis via the transcription factor sex-determining region Y-box 4; in the development and progression of progressive liver fibrosis and liver cancer, miRNA-335 affects collagen production, deposition, and degradation in the liver via the target genes including hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, phosphatase and tensin homologue, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing protein kinase 1, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, twist family bHLH transcription factor 1, and mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor and thus regulates the migration and invasion of hepatic stellate cells and hepatoma cells. This article summarizes the research advances in the role of miRNA-335 in hepatitis, liver fibrosis, and liver cancer in recent years, and based on existing data, it is pointed out that the miRNA-335/QSOX1 regulatory axis may mediate artesunate against schistosomal liver fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation, so as to provide new ideas for the treatment of liver fibrosis and other liver diseases.
-
Key words:
- Hepatitis /
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Carcinoma, Hepatocellular /
- MicroRNAs
-
肝病在全球尤其是亚太地区是一个严重的公共卫生问题[1-2]。全球每年有100多万人死于HBV、HCV感染引起的肝硬化和肝癌,预计2040年全球慢性肝炎死亡人数约达220万,将超过HIV感染、结核病和疟疾相关的总死亡人数(约190万)[1]。近年来,随着肥胖和2型糖尿病在全球的流行,非酒精性脂肪性肝病(NAFLD)和非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)的发病率相应增加。据估计,从2016年—2030年,NAFLD发展为晚期肝病的人数以及导致的死亡率将会增加1倍以上[3]。肝纤维化是乙型肝炎、NAFLD、肝癌等各种慢性肝病共同的病理学基础,也是肝病治疗的关键阶段[4]。肝纤维化的有效干预能够提高肝病患者的生存率,对于肝病防治具有重大意义。
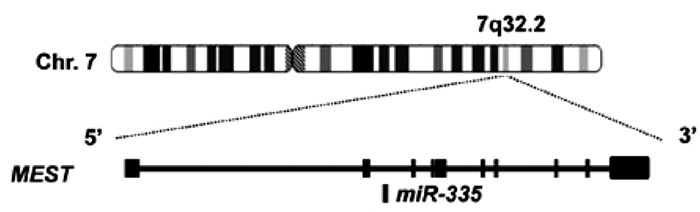
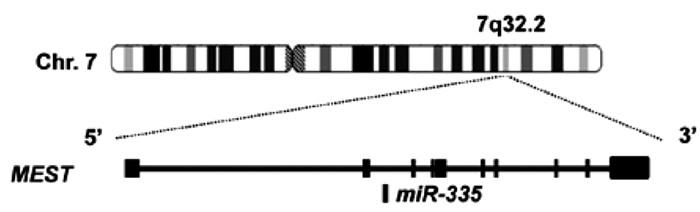
microRNA(miRNA)是一类生物体内广泛存在的长21~26 nt的非编码微小核糖核酸,通过与靶mRNA 3′UTR结合抑制其翻译而调控细胞的生物学功能。研究[5]发现miRNA在肝病的发生、发展与干预中具有重要调控作用。miRNA-335位于染色体7q32.2,由MEST的内含子编码(图 1),在细胞增殖、凋亡、迁移、侵袭以及衰老过程中发挥重要调控作用。研究[6-9]显示,miRNA-335在HBV感染、华支睾吸虫感染的肝组织,肝纤维化组织,以及肝癌细胞中表达水平均下调,并通过靶向Rho蛋白激酶1(Rho associated protein kinase 1, ROCK1)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1(mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK1)等基因参与调控肝病的发生发展。本文将综述miRNA-335在肝脏疾病发生、发展中的生物学调控功能,以期为肝病的诊治提供新思路。
 图 1 miRNA-335及其宿主基因MEST[5]
图 1 miRNA-335及其宿主基因MEST[5]1. miRNA-335与肝脏炎症
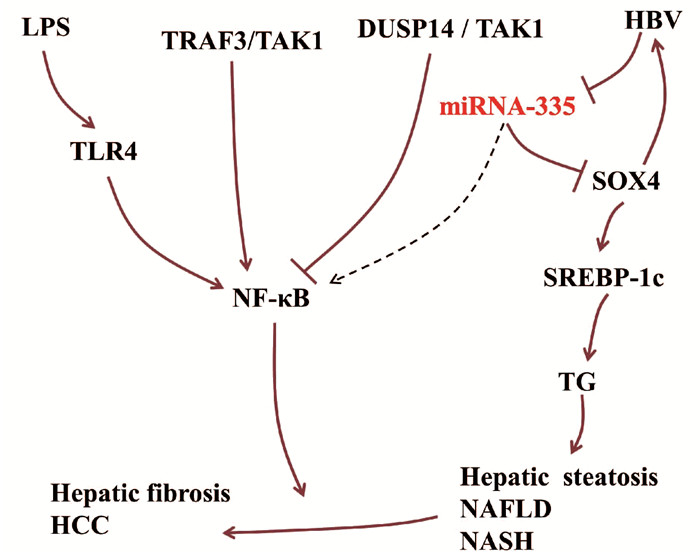
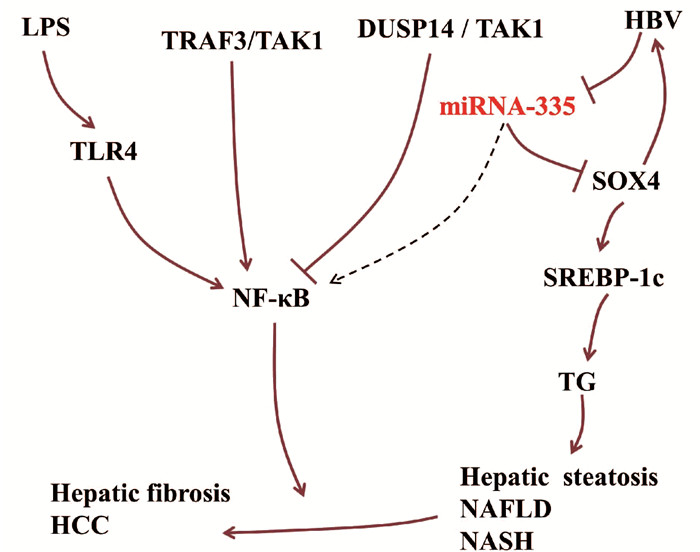
miRNA-335参与调控肝脏炎症。作为决定细胞命运和组织形态形成的上游调控因子,Y盒上的性别决定区(sex-determining region on Y box, SOX)转录因子已被选为肝脏疾病的干预靶点[10]。HBV感染能够激活SOX转录因子家族成员SOX4的转录,激活的SOX4又可以促进HBV复制。在HBV感染的肝脏中,miRNA-335靶向抑制SOX4的表达。因此,HBV感染过程中可能存在HBV/miRNA-335/SOX4正反馈回路[6]。在NAFLD中,SOX4直接靶向调控甾醇调节因子原件结合转录因子1c(sterol regulator element binding transcription factor 1c, SREBP-1c)基因的转录活性,从而调控甘油三脂(TG)的水平[11]。研究[12]显示,miRNA-335在肥胖小鼠ob/ob肝脏与脂肪组织中表达上调,参与脂肪代谢。SREBP-1c属于SREBP1s转录因子家族,能够促进IL-1β产生,也可以阻断脂多糖(LPS)激活的TLR4信号通路,在肝脏脂肪炎症的调控中具有双重作用[13]。
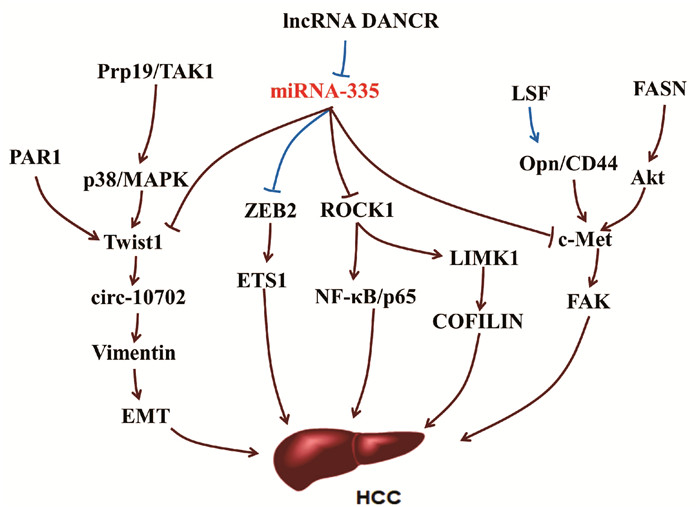
NF-κB信号通路是肝损伤、肝纤维化与肝细胞癌的调控枢纽,可被LPS诱导的TLR4激活,在肝病进展中具有重要作用。NF-κB可被上游的双特异性磷酸酶14(dual specificity phosphatase, DUSP14)抑制,DUSP14直接与TGFβ激酶1(TGFβ acvivated kinase 1, TAK1)结合并使其去磷酸化,降低TAK1活性以及下游信号分子JNK、p38和NF-κB的活性[14]。在肝脏炎症中,NF-κB受肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3(TNF receptor associated factor 3, TRAF3)的正向调控作用[15]。肝细胞中的TRAF3结合TAK1诱导其泛素化和自磷酸化,从而增强下游IKKβ/NF-κB和MKK/JNK/IRS1级联反应[16]。在下肢静脉血栓中,miRNA-335能够抑制NF-κB通路[17]。在肝脏疾病中,miRNA-335能否调控NF-κB信号通路有待进一步研究(图 2)。
2. miRNA-335与肝纤维化
肝纤维化是肝脏对病毒感染、酒精滥用、代谢性疾病等各种病因引起慢性损伤的一种反应, 以肝星状细胞(HSC)活化迁移和细胞外基质(ECM)过度沉积为特征,伴随多种氧化应激因子、炎症促进和抑制因子等的产生与调控。miRNA-335在调控HSC活化、ECM形成等过程中具有重要作用。
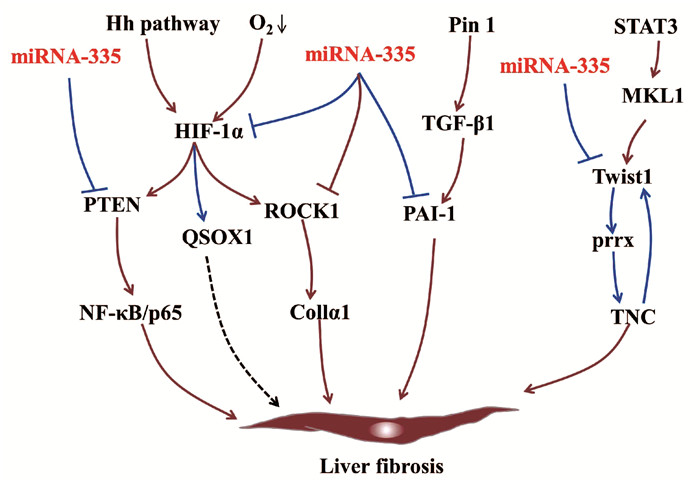
miRNA-335的靶基因缺氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha, HIF-1α)[18]、磷酸酶和紧张素同系物(phosphatase and tensin homologue, PTEN)[19]及ROCK1[9]具有促纤维化作用。缺氧反应及经典的Hh信号通路活化均可上调HSC中HIF-1α的表达[20-21]。在NAFLD向肝纤维化的进展过程中,肝细胞分泌的HIF-1α通过激活PTEN/NF-κB/p65信号通路正向调控肝纤维化[22]。当氧浓度较低时,HSC中HIF-1α的表达水平随着时间不断增加,并上调ROCK1的表达,增加胶原的合成和沉积,促进纤维化进展[20]。ROCK1能够被上调的受体相互作用蛋白3(receptor-interacting protein 3,RIP3)激活,并激活下游TLR4/NF-κB信号通路促进肝脏炎症和肝纤维化[23]。在低氧环境中,HIF-1α与巯基氧化酶1(quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1, QSOX1)基因两个HRE区结合诱导QSOX1表达,进而促进基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-2和MMP-9分泌,有利于胰腺癌细胞的侵袭[24-25],QSOX1在肝纤维化中的作用尚未明晰。另外,纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1(plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, PAI-1)作为miRNA-335的靶基因, 是一种与肝纤维化相关的急性期蛋白,可被肽基-脯氨基异构酶活化的TGFβ1诱导,进而抑制MMP9活性,加速肝纤维化[17, 26-27]。
miRNA-335的靶基因碱性螺旋-环-螺旋转录因子家族(Twist family bHLH transcription factor 1, Twist1)是一种成纤维细胞调控转录因子,参与上皮-间质转化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT)[28]。Twist1能够与配对相关同源框(paired related homebox1, Prrx1)、细胞黏合素C(tenascin, TNC)相互作用组成正反馈回路Twist1-Prrx-TNC,抑制成纤维细胞活化[29]。TNC是一种ECM糖蛋白,可促进HSC迁移[8]。在肝窦内皮细胞中,巨核细胞性白血病因子1结合到Twist1启动子区,并以信号转换器和转录激活剂3依赖的方式激活Twist1转录,促进肝窦内皮细胞的EMT过程[30]。而在急性损伤的肾脏中,炎性浸润巨噬细胞中的Twist1可促进CD11b+Ly6Clo髓样细胞中MMP13的表达,促进ECM的降解,进而抑制肾纤维化进展[31](图 3)。
3. miRNA-335与肝癌
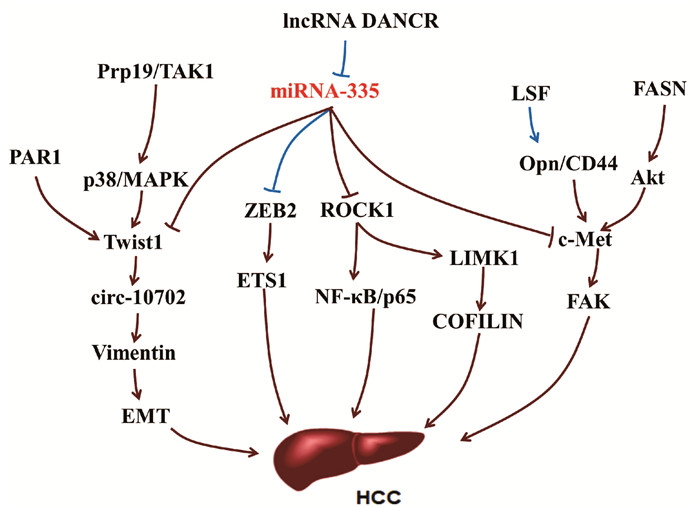
miRNA-335作为一种肿瘤抑制剂能够靶向抑制间质-上皮细胞转化因子(mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor, c-Met),c-Met的异常激活与肝癌发生有关,通过肝细胞分泌的黏着斑激酶(focal adhesion kinase, FAK)活性诱发肝癌,是具有肝细胞生长因子(HGF)/c-Met活性的肝癌潜在治疗靶点[32-35]。肝癌发生时,c-Met可被细胞转录因子(late SV40 factor, LSF)介导的Opn激活,Opn与其细胞表面受体CD44结合上调c-Met诱发肝癌[36]。c-Met还能够通过脂肪酸合成酶(fatty acid synthase, FASN)依赖的方式被丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(Serine/threonine kinase, Akt)激活[34]。FASN是脂肪从头合成的主要调控因子,在Akt诱导的肝癌发生中必不可少[37]。
miRNA-335能够通过靶向抑制ROCK1进而抑制肝癌细胞的增殖、迁徙和侵袭[9]。在肝癌细胞中ROCK1的下调可抑制NF-κB信号通路,从而抑制细胞周期,促进细胞凋亡,阻滞肝癌进展[38]。在结直肠癌和骨肉瘤中,miRNA-335的上游调控分子长链非编码RNA(long noncoding RNA, lncRNA DANCR),能够通过与miRNA-335竞争性结合,阻断miRNA-335对ROCK1的抑制作用[39-40],但是该过程在肝癌中并未见报道。lncRNA DANCR还能够通过ROCK1/LIMK1/CIFILIN1通路调节肝癌生长和EMT形成[41]。作为诱导EMT形成的重要转录因子,Twist1在多种癌症中表达上调。在肝癌中,Twist1可结合到Cul2启动子区激活其转录活性,并选择性促进Cul2环状RNA circ-10720的表达水平,进而促进波形蛋白Vimentin表达,有利于EMT形成[42]。Twist1的上游调控因子蛋白酶激活受体1 (protease-activated receptor-1, PAR1)能够通过上调Twist1促进肝癌细胞通过上皮-内皮细胞转化向内皮细胞转化[43]。Twist1诱导肝癌EMT过程中,还可被信使RNA前体加工因子19(pre-mRNA processing factor 19, Prp19)正向调控,Prp19直接与TAK1结合,促进p38 /MAPK活化,抑制Twist1降解[44]。另外,miRNA-335还能够通过靶向抑制E盒结合锌指蛋白2(zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2,ZEB2)/ETS1通路调控癌细胞侵袭和迁移[45-46](图 4)。
4. 总结与展望
肝病是一个全球性的公共卫生问题,严重危害了人们的身心健康,造成了巨大的经济损失,肝纤维化是慢性肝炎发展为肝硬化、肝癌的必经阶段,逆转肝纤维化将大大降低肝硬化、肝癌的发病率。miRNA-335作为一种抑癌分子被广泛研究,外泌体miRNA-335能够减小肝肿瘤体积,显著抑制肝癌细胞的侵袭、增殖和迁移,进一步研究[47]显示,miRNA-335能够靶向调控ROCK1抑制肝癌。另外,miRNA-335在结直肠癌细胞、非小细胞肺癌细胞和甲状腺癌细胞的增殖及迁移中也具有明显的抑制作用[46, 48-49]。目前,已证实的miRNA-335靶基因主要有HIF-1α、ROCK1以及Twist1等,这些基因在纤维化相关信号通路的调控中发挥重要作用。笔者前期研究(未发表)表明青蒿琥酯抗血吸虫性肝纤维化有效且与HSC的增殖活化抑制密切相关,进一步全转录组分析显示,miRNA-335及其候选靶基因QSOX1的表达与青蒿琥酯抗血吸虫性肝纤维化具有显著相关性。据文献[24]报道,QSOX1可被HIF-1α上调,使MMP-2和MMP-9的分泌增加,促进胰腺癌细胞侵袭。因此,miRNA-335/QSOX1调控轴可能通过抑制HSC活化介导青蒿琥酯抗血吸虫性肝纤维化。进一步围绕miRNA-335在肝纤维化调控中的深入研究,能够有望为肝纤维化等肝病的防治提供新思路。
-
图 1 miRNA-335及其宿主基因MEST[5]
-
[1] THOMAS DL. Global elimination of chronic hepatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(21): 2041-2050. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1810477 [2] SARIN SK, KUMAR M, ESLAM M, et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A lancet gastroenterology & hepatology commission[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5(2): 167-228. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30342-5 [3] ESTES C, ANSTEE QM, ARIAS-LOSTE MT, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(4): 896-904. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036 [4] SEKI E, BRENNER DA. Recent advancement of molecular mechanisms of liver fibrosis[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2015, 22(7): 512-518. DOI: 10.1002/jhbp.245 [5] DOHI O, YASUI K, GEN Y, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miR-335 and its host gene MEST in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Oncol, 2013, 42(2): 411-418. DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1724 [6] SHANG J, ZHENG Y, GUO X, et al. Hepatitis B virus replication and sex-determining region Y box 4 production are tightly controlled by a novel positive feedback mechanism[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 10066. DOI: 10.1038/srep10066 [7] HAN S, TANG Q, LU X, et al. Dysregulation of hepatic microRNA expression profiles with Clonorchis sinensis infection[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2016, 16(1): 724. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-2058-1 [8] CHEN C, WU CQ, ZHANG ZQ, et al. Loss of expression of miR-335 is implicated in hepatic stellate cell migration and activation[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2011, 317(12): 1714-1725. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.001 [9] LIU H, LI W, CHEN C, et al. MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2015, 36(8): 6313-6319. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-015-3317-2 [10] YIN C. Molecular mechanisms of Sox transcription factors during the development of liver, bile duct, and pancreas[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2017, 63: 68-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.08.015 [11] JIAO Y, ZHAO J, ZHANG Z, et al. SRY-Box containing gene 4 promotes liver steatosis by upregulation of SREBP-1c[J]. Diabetes, 2018, 67(11): 2227-2238. DOI: 10.2337/db18-0184 [12] NAKANISHI N, NAKAGAWA Y, TOKUSHIGE N, et al. The up-regulation of microRNA-335 is associated with lipid metabolism in liver and white adipose tissue of genetically obese mice[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2009, 385(4): 492-496. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.058 [13] OISHI Y, SPANN NJ, LINK VM, et al. SREBP1 contributes to resolution of pro-inflammatory TLR4 signaling by reprogramming fatty acid metabolism[J]. Cell Metab, 2017, 25(2): 412-427. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.11.009 [14] WANG X, MAO W, FANG C, et al. Dusp14 protects against hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury via Tak1 suppression[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68(1): 118-129. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.08.032 [15] HU J, ZHU XH, ZHANG XJ, et al. Targeting TRAF3 signaling protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusions injury[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(1): 146-159. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.08.021 [16] WANG PX, ZHANG XJ, LUO P, et al. Hepatocyte TRAF3 promotes liver steatosis and systemic insulin resistance through targeting TAK1-dependent signalling[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7: 10592. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10592 [17] BAO CX, ZHANG DX, WANG NN, et al. MicroRNA-335-5p suppresses lower extremity deep venous thrombosis by targeted inhibition of PAI-1 via the TLR4 signalingpathway[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(6): 4692-4710. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.26647 [18] LIU FJ, KAUR P, KAROLINA DS, et al. MiR-335 regulates Hif-1α to reduce cell death in both mouse cell line and rat ischemic models[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(6): e0128432. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128432 [19] KABIR TD, LEIGH RJ, TASENA H, et al. A miR-335/COX-2/PTEN axis regulates the secretory phenotype of senescent cancer-associated fibroblasts[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2016, 8(8): 1608-1635. DOI: 10.18632/aging.100987 [20] HU Y, HU D, YU H, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α and ROCK1 regulate proliferation and collagen synthesis in hepatic stellate cells under hypoxia[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(4): 3997-4003. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30132575 [21] ZHANG F, HAO M, JIN H, et al. Canonical hedgehog signalling regulates hepatic stellate cell-mediated angiogenesis in liver fibrosis[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2017, 174(5): 409-423. DOI: 10.1111/bph.13701 [22] HAN J, HE Y, ZHAO H, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor-1 promotes liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by activating PTEN/p65 signaling pathway[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(9): 14735-14744. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.28734 [23] WEI S, ZHOU H, WANG Q, et al. RIP3 deficiency alleviates liver fibrosis by inhibiting ROCK1-TLR4-NF-κB pathway in macrophages[J]. FASEB J, 2019, 33(10): 11180-11193. DOI: 10.1096/fj.201900752R [24] SHI CY, FAN Y, LIU B, et al. HIF1 contributes to hypoxia-induced pancreatic cancer cells invasion via promoting QSOX1 expression[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2013, 32(3): 561-568. DOI: 10.1159/000354460 [25] KATCHMAN BA, ANTWI K, HOSTETTER G, et al. Quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase 1 promotes invasion of pancreatic tumor cells mediated by matrix metalloproteinases[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2011, 9(12): 1621-1631. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0018 [26] YANG JW, HIEN TT, LIM SC, et al. Pin1 induction in the fibrotic liver and its roles in TGF-β1 expression and Smad2/3 phosphorylation[J]. J Hepatol, 2014, 60(6): 1235-1241. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.02.004 [27] FLEVARIS P, VAUGHAN D. The role of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in fibrosis[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2017, 43(2): 169-177. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/82f79194318957c4b32216c05179ee37 [28] WANG J, WANG X, LIU F, et al. microRNA-335 inhibits colorectal cancer HCT116 cells growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process by targeting Twist1[J]. Pharmazie, 2017, 72(8): 475-481. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29441907 [29] YEO SY, LEE KW, SHIN D, et al. A positive feedback loop bi-stably activates fibroblasts[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 3016. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-05274-6 [30] LI Z, CHEN B, DONG W, et al. MKL1 promotes endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and liver fibrosis by activating TWIST1 transcription[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(12): 899. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-2101-4 [31] REN J, ZHANG J, RUDEMILLER NP, et al. Twist1 in infiltrating macrophages attenuates kidney fibrosis via matrix metallopeptidase 13-mediated matrix degradation[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2019, 30(9): 1674-1685. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018121253 [32] CHEN S, XIA X. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 suppresses sorafenib sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating miR-335-c-Met[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019.[Epub ahead of print] [33] BOUATTOUR M, RAYMOND E, QIN S, et al. Recent developments of c-Met as a therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(3): 1132-1149. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29496 [34] HU J, CHE L, LI L, et al. Co-activation of AKT and c-Met triggers rapid hepatocellular carcinoma development via the mTORC1/FASN pathway in mice[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 20484. DOI: 10.1038/srep20484 [35] YOU H, DING W, DANG H, et al. c-Met represents a potential therapeutic target for personalized treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54(3): 879-889. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24450 [36] YOO BK, GREDLER R, CHEN D, et al. c-Met activation through a novel pathway involving osteopontin mediates oncogenesis by the transcription factor LSF[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 55(6): 1317-1324. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.02.036 [37] LI L, PILO GM, LI X, et al. Inactivation of fatty acid synthase impairs hepatocarcinogenesis driven by AKT in mice and humans[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(2): 333-341. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.10.004 [38] WANG RK, SHAO XM, YANG JP, et al. MicroRNA-145 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of HepG2 cells by targeting ROCK1 through the ROCK1/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(7): 2777-2785. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31002128 [39] WANG Y, ZENG XD, WANG NN, et al. Long noncoding RNA DANCR, working as a competitive endogenous RNA, promotes ROCK1-mediated proliferation and metastasis via decoying of miR-335-5p and miR-1972 in osteosarcoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 89. DOI: 10.1186/s12943-018-0837-6 [40] LIANG H, ZHANG C, GUAN H, et al. LncRNA DANCR promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating ROCK1 via sponging miR-335-5p[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5): 7266-7278. DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27484 [41] GUO D, LI Y, CHEN Y, et al. DANCR promotes HCC progression and regulates EMT by sponging miR-27a-3p via ROCK1/LIMK1/COFILIN1 pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(4): e12628. [42] MENG J, CHEN S, HAN JX, et al. Twist1 regulates vimentin through Cul2 circular RNA to promote EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(15): 4150-4162. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-3009 [43] XIAO T, ZHANG Q, ZONG S, et al. Protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR1) promotes epithelial-endothelial transition through Twist1 in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 185. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0858-4 [44] YIN J, WANG L, ZHU JM, et al. Prp19 facilitates invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/twist1 pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(16): 21939-21951. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7877 [45] YALIM-CAMCI I, BALCIK-ERCIN P, CETIN M, et al. ETS1 is coexpressed with ZEB2 and mediates ZEB2-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human tumors[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2019, 58(6): 1068-1081. DOI: 10.1002/mc.22994 [46] KAN QE, SU Y, YANG HH. MicroRNA-335 is downregulated in papillary thyroid cancer and suppresses cancer cell growth, migration and invasion by directly targeting ZEB2[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(6): 7622-7628. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/320190432_MicroRNA-335_is_downregulated_in_papillary_thyroid_cancer_and_suppresses_cancer_cell_growth_migration_and_invasion_by_directly_targeting_ZEB2 [47] WANG F, LI L, PIONTEK K, et al. Exosome miR-335 as a novel therapeutic strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(3): 940-954. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29586 [48] DU WW, TANG HC, LEI Z, et al. miR-335-5p inhibits TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer via ROCK1[J]. Respir Res, 2019, 20(1): 225. DOI: 10.1186/s12931-019-1184-x [49] SUN ZF, ZHANG Z, LIU ZD, et al. MicroRNA-335 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting ZEB2[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31(6): 982. DOI: 10.1007/s12032-014-0982-8 -




 PDF下载 ( 2858 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2858 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载: