FibroTouch、FibroScan及ARFI在原发性胆汁性胆管炎相关肝纤维化中的诊断价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.04.019
Diagnostic value of FibroTouch, FibroScan, and acoustic radiation force impulse for liver fibrosis in patients with primary biliary cholangitis
-
摘要:
目的 评估FibroTouch与FibroScan、声辐射力脉冲成像(ARFI)对原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)患者肝纤维化程度的诊断效能。 方法 回顾性纳入2014年9月—2018年10月在首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院行肝穿刺活检明确诊断为PBC的患者。采用METAVIR评分系统评估肝纤维化和炎症程度。在肝活检1周内分别应用瞬时弹性成像(FibroTouch和FibroScan)和ARFI技术检测肝脏硬度值(LS);以病理结果作为金标准,采用受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)比较3种超声弹性成像技术对PBC肝纤维化的诊断价值,并分析其影响因素;采用Youden指数计算不同程度肝纤维化的诊断界值。多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni法校正P值。采用Spearman进行相关性分析,采用多重线性回归模型进行多因素分析。 结果 研究共纳入68例PBC患者,其中肝纤维化F0、F1、F2、F3和F4分别为13、15、18、12和10例。FibroTouch获得的LS(FT-LS)、FibroScan获得的LS(FS-LS)和ARFI获得的LS (ARFI-LS)与肝纤维化程度均呈强正相关(r值分别为0.798、0.782和0.742,P值均<0.001)。FT-LS诊断F≥2、F≥3、F=4 AUC分别为0.922、0.881、0.926,对应的cut-off值分别为10.5、15.8和17.5 kPa;FS-LS诊断F≥2、F≥3、F=4 AUC分别为0.918、0.878、0.939,对应的cut-off值分别为10.1、12.9和18.2 kPa;ARFI-LS诊断F≥2、F≥3、F=4 AUC分别为0.904、0.869、0.928,对应的cut-off值分别为1.45、1.83和2.08 m/s。3种超声成像技术对各期纤维化程度的诊断差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。多因素分析结果显示,FT-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.399,P<0.001)、TBil水平(β=0.466,P<0.001)和PTA(β=-0.195,P=0.020);FS-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.370,P<0.001)、AST(β=0.450,P<0.001)、PTA(β=-0.303,P=0.001)和ALP(β=-0.187,P=0.042);而ARFI-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.489,P<0.001)、AST(β=0.467,P<0.001)和PLT(β=-0.188,P=0.028)。 结论 FibroTouch与FibroScan和ARFI在诊断PBC肝纤维化程度的效能相似,特别是对显著纤维化(F≥2)和肝硬化(F=4)具有较高的诊断效能,可作为诊断PBC患者肝纤维化程度的可靠手段。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the diagnostic efficiency of FibroTouch, FibroScan, and acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) for liver fibrosis in patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the patients who underwent liver biopsy and were then diagnosed with PBC in Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University, from September 2014 to October 2018, and the METAVIR scoring system was used to evaluate the degree of liver fibrosis and inflammation. Within 1 week after liver biopsy, FibroTouch, FibroScan, and ARFI were used to measure liver stiffness (LS); with pathological results as the gold standard, the area under the ROC curve (AUC) was used to compare the value of FibroTouch, FibroScan, and ARFI in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in PBC patients, and related influencing factors were analyzed; Youden index was used to calculate the cut-off values of LS for different degrees of liver fibrosis. The Kruskal-Wallis H test was used for comparison between multiple groups, and P value corrected by the Bonferroni method was used for further comparison between two groups. A Spearman correlation analysis was performed, and a multiple linear regression model was used for multivariate analysis. Results A total of 68 patients with PBC were enrolled in the study, among whom 13 had F0 liver fibrosis, 15 had F1 liver fibrosis, 18 had F2 liver fibrosis, 12 had F3 liver fibrosis, and 10 had F4 liver fibrosis. LS obtained by FibroTouch (FT-LS), LS obtained by FibroScan (FS-LS), and LS obtained by ARFI (ARFI-LS) were strongly positively correlated with the degree of liver fibrosis (r=0.798, 0.782, and 0.742, all P < 0.001). FT-LS had AUCs of 0.922, 0.881, and 0.926, respectively, in the diagnosis of F≥2, F≥3, and F=4 liver fibrosis, and the corresponding cut-off values were 10.5 kPa, 15.8 kPa, and 17.5 kPa, respectively; FS-LS had AUCs of 0.918, 0.878, and 0.939, respectively, in the diagnosis of F≥2, F≥3, and F=4 liver fibrosis, and the corresponding cut-off values were 10.1 kPa, 12.9 kPa, and 18.2 kPa, respectively; ARFI-LS had AUCs of 0.904, 0.869, and 0.928, respectively, in the diagnosis of F≥2, F≥3, and F=4 liver fibrosis, and the corresponding cut-off values were 1.45 m/s, 1.83 m/s, and 2.08 m/s, respectively. There was no significant difference in diagnosing the same stage of liver fibrosis between FibroTouch, FibroScan, and ARFI (P > 0.05). The multivariate analysis showed that degree of liver fibrosis (β=0.399, P < 0.001), total bilirubin (β=0.466, P < 0.001), and prothrombin time activity (β=-0.195, P=0.020) were influencing factors for FT-LS; degree of liver fibrosis (β=0.370, P < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (β=0.450, P < 0.001), prothrombin time activity (β=-0.303, P=0.001), and alkaline phosphatase (β=-0.187, P=0.042) were influencing factors for FS-LS; degree of liver fibrosis (β=0.489, P < 0.001), aspartate aminotransferase (β=0.467, P < 0.001), and platelet count (β=-0.188, P=0.028) were influencing factors for ARFI-LS. Conclusion FibroTouch has similar efficiency to FibroScan and ARFI in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in PBC patients, with relatively high diagnostic efficiency for significant liver fibrosis (F≥2) and liver cirrhosis (F=4), and therefore, it can be used as a reliable method for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in PBC patients. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis, Biliary /
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Elasticity Imaging Techniques /
- Diagnosis
-
原发性胆汁性胆管炎(PBC)是一种慢性肝内胆汁淤积为主的免疫性肝病,其病理特点为进行性、非化脓性、破坏性肝内小胆管炎。持续胆管炎症导致汇管区胆管周围纤维化,逐步扩展到肝实质。同病毒性肝炎一样,PBC亦可发展至纤维化、肝硬化,甚至肝细胞癌、肝衰竭等,严重影响患者预后。肝纤维化是肝病进展的关键环节。对患者纤维化的准确评估,及时发现显著肝纤维化、进展期肝纤维化和早期肝硬化,对防治肝病相关终点事件及改善预后具有重要的意义。
肝活检是诊断PBC疾病分期和肝纤维化的“金标准”,由于其存在有创、取样体积小、判读误差等局限,不易被患者接受且不适长期随访。近年来,瞬时弹性成像(transient elastrography, TE)和声辐射力脉冲成像技术(acoustic radiation force impulse,ARFI)等超声弹性成像技术成为无创评估肝纤维化的研究热点。通过测定组织弹性,快速获得的肝脏硬度值(liver stiffness,LS), 可作为评估肝纤维化的替代指标。上述方法已广泛用于慢性病毒性肝炎、非酒精性脂肪性肝病相关的纤维化诊断和长期随访[1-4]。其中,基于TE技术有两种仪器:FibroScan(法国Echosens公司)和FibroTouch。FibroTouch是我国自主研发的新型肝纤维化无创诊断仪,在PBC人群肝纤维化的诊断效能的研究很少。因此,本研究比较FibroTouch与其他两种超声弹性成像技术评估PBC患者肝纤维化的诊断效能,并分析其影响因素,以期为其临床应用提供依据。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性纳入2014年9月—2018年10月在首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院就诊并经肝穿刺活检病理证实的PBC患者,符合2015年修订的《原发性胆汁性肝硬化(又名原发性胆汁性胆管炎)诊断和治疗共识》[5]的诊断标准。纳入标准:(1)在肝活检1周内行FibroTouch、FibroScan和ARFI检测LS,并检测血清学指标;(2)患者同意参加本研究,并签署知情同意书。排除标准:(1)有病毒性肝炎、酒精性肝病、非酒精性脂肪性肝病、自身免疫性肝炎、原发性硬化性胆管炎、IgG4相关胆管炎、重叠综合征、肝豆状核变性、血色病及药物肝损伤者;(2)有恶性肿瘤史或其他终末期疾病者;(3)孕产妇;(4)近期右上腹及左上腹有创口未愈合者;(5)TE和ARFI测量失败或结果不可靠者;(6)不能或不愿参加本研究者。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 一般信息及实验室指标
收集患者性别、年龄、身高、体质量、BMI等一般资料以及WBC、PLT、ALT、AST、ALP、GGT、TBil、Alb、PTA、肌酐(Cr)等实验室指标。
1.2.2 仪器与测量方法
FibroTouch: 应用FibroTouch (无锡海斯凯尔公司,中国)检测前,操作医师首先使用设备配有的超声探头进行定位,避开大血管、胆管和囊肿等位置,对所选择的最佳检查部位进行肝脏硬度测定10次,检测成功率≥60%,检测结果的四分位数间距/中位数≤30%被认为结果可靠[6]。获取的数据记录为FT-LS,单位为kPa。FibroScan:应用FibroScan M型探头(Echosens公司,法国)进行肝脏硬度测定10次,检测成功率≥60%,检测结果的四分位数间距/中位数≤30%被认为结果可靠[7]。获取的数据记录为FS-LS,单位为kPa。ARFI:应用Acuson S2000彩色超声仪(Siemens公司,美国)进行肝脏硬度测定,反复测量10次取中位数[8];检测成功率≥60%,检测结果的四分位数间距/中位数≤30%被认为结果可靠。获取的数据记录为ARFI-LS,单位为m/s。
1.2.3 肝穿病理评估
肝穿刺病理由经皮肝穿刺或经颈静脉穿刺获得。病理评估由1位有经验的副主任医师级别以上的病理专家独立阅片。采用METAVIR评分系统评估肝纤维化和坏死炎症活动[9]。其中F2~F4定义为显著肝纤维化(即F≥2);F3~4定义为进展期肝纤维化(即F≥3);F=4定义为肝硬化(即F=4)。
1.3 伦理学审查
本研究方案经由首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院伦理委员会审批,批号:2018-P2-050-01。
1.4 统计学方法
采用IBM SPSS 22.0统计软件及MedCalc软件对数据进行统计学分析。计量资料不满足正态分布的以M(P25~P75)表示,多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni法校正P值。通过绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC曲线)对肝纤维化的诊断效能进行评估,采用Youden指数确定诊断界值(cut-off值),ROC曲线下面积(AUC)的比较采用DeLong法。采用Spearman进行相关性分析,采用多重线性回归模型进行多因素分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 PBC患者的基本特征
共纳入68例肝活检明确诊断为PBC的患者,患者的临床基本特征见表 1。
表 1 68例PBC患者的临床基本特征指标 参数 男/女(例) 8/60 年龄(岁) 51.5(44.3~58.8) BMI(kg/m2) 22.7(20.3~24.8) ALT(U/L) 44(27~75) AST(U/L) 58.9(34.0~95.9) ALP(U/L) 198.0(117.3~334.3) GGT(U/L) 162.0(78.8~260.8) TBil(μmol/L) 16.11(11.88~24.93) Alb(g/L) 36.8(34.1~40.8) Cr(mmol/L) 58.5(52.6~65.3) PLT(×109/L) 178.5(99.8~236.3) PTA(%) 98.4(98.3~112.4) 肝纤维化分期[例(%)] F0 13(19.1) F1 15(22.1) F2 18(26.5) F3 12(17.6) F4 10(14.7) 2.2 FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS与肝纤维化分期的相关性分析
FibroScan、FibroTouch和ARFI测得的LS与肝纤维化分期存在较强的正相关,并随着肝纤维化程度的增加而增加,Spearman相关系数分别为0.798、0.782和0.742(P值均<0.000 1)。
不同肝纤维化分期的FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS的水平见表 2。多组间FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS的总体差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.001); 进一步两两比较采用Bonferroni法校正,FT-LS、FS-LS、ARFI-LS的分布在F0和F2、F3、F4之间的差异均有统计学意义(调整后P值均<0.05);FT-LS和FS-LS的分布在F1和F3、F4之间的差异具有统计学意义(调整后P值均<0.05);ARFI-LS的分布在F1和F2、F3、F4的差异均具有统计学意义(调整后P值均<0.05);余各组之间差异均无统计学意义(调整后P值均>0.05)。
表 2 不同肝纤维化分期的FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS水平指标 F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 H值 P值 FT-LS(kPa) 5.5(4.6~7.5) 8.0(7.0~10.5) 13.7(11.3~16.1) 16.9(11.7~25.4) 43.2(19.9~51.2) 43.242 <0.001 FS-LS(kPa) 5.6(4.9~8.0) 7.0(6.5~8.3) 11.9(8.8~15.0) 15.1(9.5~29.9) 34.4(24.9~46.1) 42.110 <0.001 ARFI-LS(m/s) 1.27(1.09~1.57) 1.35(1.19~1.53) 1.81(1.55~2.08) 1.92(1.86~2.19) 2.42(2.15~2.61) 38.798 <0.001 2.3 FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS对PBC不同肝纤维化分期的诊断效能
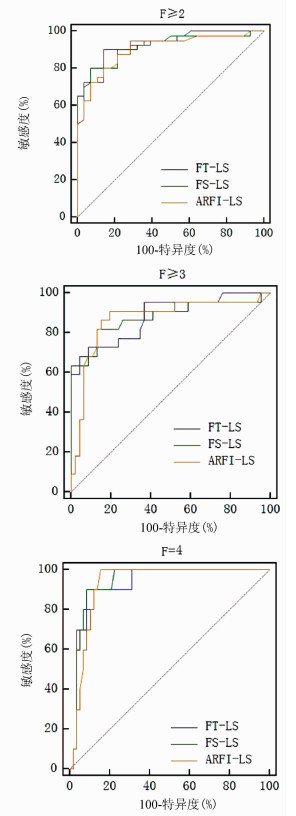
ROC曲线结果分析显示,FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS在评估肝纤维化分期上具有较好的准确性(AUC均>0.85);FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS诊断F≥2、F≥3和F=4的cut-off值见表 3。对3种方法的诊断效能进行统计学分析,结果显示差异并无统计学意义(P值均>0.05)(图 1)。
表 3 FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS对PBC肝纤维化的诊断效能纤维化分期 AUC(95%CI) cut-off值 敏感度 特异度 F≥2 FT-LS 0.922(0.831~0.973) 10.5 kPa 0.900 0.857 FS-LS 0.918(0.826~0.971) 10.1 kPa 0.800 0.929 ARFI-LS 0.904(0.808~0.962) 1.45 m/s 0.950 0.714 F≥3 FT-LS 0.881(0.780~0.947) 15.8 kPa 0.727 0.913 FS-LS 0.878(0.776~0.945) 12.9 kPa 0.818 0.869 ARFI-LS 0.869(0.765~0.939) 1.83 m/s 0.909 0.804 F=4 FT-LS 0.926(0.836~0.975) 17.5 kPa 0.900 0.879 FS-LS 0.939(0.853~0.982) 18.2 kPa 0.900 0.914 ARFI-LS 0.928(0.838~0.976) 2.08 m/s 1.000 0.845 2.4 FT-LS、FS-LS及ARFI-LS的影响因素分析
多因素分析结果显示,FT-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.399,P<0.001)、TBil水平(β=0.466,P<0.001)和PTA(β=-0.195,P=0.020);FS-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.370,P<0.001)、AST(β=0.450,P<0.001)、PTA(β=-0.303,P=0.001)和ALP(β=-0.187,P=0.042);而ARFI-LS的影响因素有肝纤维化程度(β=0.489,P<0.001)、AST(β=0.467,P<0.001)和PLT(β=-0.188,P=0.028)。
3. 讨论
评估肝纤维化是慢性肝病患者管理的重要部分[3]。超声弹性成像技术弥补了肝穿刺活检的不足,具有无创、操作简便、可快速获得结果、重复性较好、易随访监测等优势,给临床慢性肝病肝纤维化的评估提供了重要手段。TE和ARFI是研究较多的超声弹性成像技术,在慢性病毒性肝炎、非酒精性脂肪性肝病、酒精性肝病等慢性肝病相关纤维化中均具有较高的诊断价值,但在PBC患者的研究文献有限,亦缺乏统一的诊断界值,尤其是FibroTouch在我国PBC人群中的诊断效能尚待评估。
本研究发现,在PBC患者中,FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS均随着纤维化进展而增加,并与纤维化分期呈较强的正相关性,相关系数均在0.74~0.79。这与之前多数利用FibroScan和ARFI测定的研究[10-13]结果一致。此外,采用的病理标准不同,可能影响评估结果。在一项纳入了包括26例PBC患者在内的自身免疫性和胆汁淤积性肝病患者的回顾性研究[14]中,未发现ARFI与PBC纤维化程度之间存在相关性(r=0.019,P=0.927),其原因可能与采用的病理分期方法不同有关,该研究中采用Ishak评分的病理标准,且研究对象中不含Ishak≥4以上的病例,纳入的病例较少。本研究采用了METAVIR病理标准,各组纤维化病例分布相对平衡。
本研究发现,FT-LS、FT-LS和ARFI-LS对F≥2、F≥3和F=4的诊断效能均良好,AUC均在0.85以上,其中F≥2和F=4时AUC均在0.90以上,并具有较高的敏感度和特异度。这也提示,3种无创超声弹性成像技术的LS,一定程度上可作为肝活检评估肝纤维化程度的替代指标。但总体来说,3种技术获得的LS在诊断各级纤维化的效能之间并无显著统计学差异。大量研究[1-2]证据表明,FibroScan在显著肝纤维化(F≥2)和肝硬化(F=4)效能较高,被广泛推荐用于临床评估肝纤维化的常规方法。ARFI和FibroScan在F ≥ 2和F=4的诊断效能的差异无统计学意义[4]。在新近发表的关于FibroTouch诊断慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化的多中心研究[6]中,FT-LS在F≥2和F=4的AUC分别达0.850和0.874。目前国内仅1篇研究[15]评估了FT-LS对PBC的诊断效能,同样显示在F(S)≥2和F(S)=4时诊断效能更高,AUC分别为0.981和0.902,但在该研究中并未提及到所采用的病理分期方法。关于ARFI对PBC诊断效能的研究数据相对有限,且采用的病理标准多为PBC的临床病理分期,即Ⅰ期(胆管炎期)、Ⅱ期(汇管区周围炎期)、Ⅲ期(进行性纤维化期)和Ⅳ期(肝硬化期)。Zhang等[13]采用PBC临床病理分期,ARFI-LS诊断≥Ⅲ和Ⅳ期的AUC为0.93和0.91。国内一项关于ARFI的研究[16]同样采用PBC临床病理分期标准,ARFI-LS在肝硬化时AUC为0.81。因此,本研究首次采用了肝纤维化METAVIR病理分期法对ARFI的诊断效能进行了评价。
国内仅有1篇研究[15]提到了FT-LS诊断F(S)≥2、F(S)≥3、F(S)=4的界值,依次为9.05、11.75和18.95 kPa。而本研究显示F≥3时界值高达15.8 kPa,在F=4时界值为17.5 kPa。其原因可能与病例的分布组成及病理标准有关。该研究中患者的ALP、GGT水平偏高,纤维化分期中缺乏F(S)0病例,可能影响各期界值的界定。此外,该研究未提及到所采用的病理分期方法[15]。同样的情况也发生在FibroScan的研究中。在一项纳入103例PBC患者的前瞻性研究中发现,FS-LS在F≥2、F≥3和F=4的诊断界值分别为8.8、10.7和16.9 kPa[11]。而本研究中,FS-LS对应三期的诊断界值均高于该研究。对比后发现,本研究中纳入病例的AST>ALT,病理分期F≥2的比例较高(59% vs 50%),这可能跟患者当时的治疗状态有关,即混杂了初治和经治效果不佳的病例,部分甚至有自身免疫性肝炎倾向,入组时患者病情较重,纤维化程度高,因此获得诊断界值较高。国内一项探讨FS-LS对PBC纤维化的诊断研究[17]采用了Scheuer标准的病理纤维化分期,结果发现,FS-LS在F≥2、F≥3和F=4的诊断界值分别为12.9、16.1和19.7 kPa。现有研究[13-14, 16]显示,ARFI对PBC肝硬化期时的诊断界值为2.01~2.05 m/s,与本研究类似(2.08 m/s),但由于采用不同病理分期,缺乏其他纤维化阶段的诊断界值。因此,病理分期标准的不同及各阶段患者的分布不均匀,是造成诊断界值不一致的主要原因。
相关研究[1, 14, 18]发现,影响TE和ARFI获得LS准确性的因素包括肝脏炎症坏死、ALT、胆汁淤积、胆红素、性别(男性更高)、BMI、肝脂肪变性等。本研究发现,与FS-LS和ARFI-LS的影响因素略有不同,组织纤维化程度、TBil和PTA是影响FT-LS的独立因素,主要区别在于炎症及TBil对结果的影响。考虑与回顾性研究中病例入组条件、检测方法和操作者有关。在一项FibroTouch诊断慢性乙型肝炎纤维化的多中心研究[6]中,严格排除了ALT≥5倍正常值上限和TBil≥1.5倍正常值上限的病例,获得各期的FT-LS界值要比本研究更低。因此,应采用更加严格的病例入排标准,排除混杂因素的影响。另外,ALP亦可能影响LS,考虑PBC是胆汁淤积为主的疾病,胆汁淤积造成肝细胞进行性损伤,进一步加重炎性浸润和纤维化范围,亦可致LS较高。因此在制订入排标准时应根据PBC的特点进行确定。另外,各种仪器本身的成像特点存在不同。FibroScan属于一维超声技术,无法实时二维图像观察肝脏并定位目标, 且受肥胖、腹水等影响,测量成功率下降;FibroTouch增加了二维超声影像引导,比FibroScan具有更高的检测成功率。不同于FibroScan的固定频率探头(本研究所用3.5 Hz的M探头),FibroTouch采用宽频探头,有效降低皮下脂肪导致的信号衰减,可能导致LS值的差异。且研究中采用病理评分系统或患者的疾病状态不同,获得的LS受不同因素影响,可能存在一定的变异度,因此在解释这些数据时还需慎重。
本研究为单中心的回顾性研究,入组病例数有限,仅为住院患者,导致存在选择偏倚;同时作为回顾性研究,在入排标准的制订和掌握上不及前瞻性研究,因此在诸如影响因素及诊断界值等问题上存在偏差。未来应开展多中心、前瞻性和大样本量的临床研究,减少上述偏倚及混杂因素的影响。
综上所述,FibroTouch与FibroScan和ARFI获得LS对诊断PBC相关肝纤维化的效能相当,特别是在F≥2和F=4时具有较高的诊断效能,可作为诊断PBC患者肝纤维化程度的可靠手段。
-
表 1 68例PBC患者的临床基本特征
指标 参数 男/女(例) 8/60 年龄(岁) 51.5(44.3~58.8) BMI(kg/m2) 22.7(20.3~24.8) ALT(U/L) 44(27~75) AST(U/L) 58.9(34.0~95.9) ALP(U/L) 198.0(117.3~334.3) GGT(U/L) 162.0(78.8~260.8) TBil(μmol/L) 16.11(11.88~24.93) Alb(g/L) 36.8(34.1~40.8) Cr(mmol/L) 58.5(52.6~65.3) PLT(×109/L) 178.5(99.8~236.3) PTA(%) 98.4(98.3~112.4) 肝纤维化分期[例(%)] F0 13(19.1) F1 15(22.1) F2 18(26.5) F3 12(17.6) F4 10(14.7) 表 2 不同肝纤维化分期的FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS水平
指标 F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 H值 P值 FT-LS(kPa) 5.5(4.6~7.5) 8.0(7.0~10.5) 13.7(11.3~16.1) 16.9(11.7~25.4) 43.2(19.9~51.2) 43.242 <0.001 FS-LS(kPa) 5.6(4.9~8.0) 7.0(6.5~8.3) 11.9(8.8~15.0) 15.1(9.5~29.9) 34.4(24.9~46.1) 42.110 <0.001 ARFI-LS(m/s) 1.27(1.09~1.57) 1.35(1.19~1.53) 1.81(1.55~2.08) 1.92(1.86~2.19) 2.42(2.15~2.61) 38.798 <0.001 表 3 FT-LS、FS-LS和ARFI-LS对PBC肝纤维化的诊断效能
纤维化分期 AUC(95%CI) cut-off值 敏感度 特异度 F≥2 FT-LS 0.922(0.831~0.973) 10.5 kPa 0.900 0.857 FS-LS 0.918(0.826~0.971) 10.1 kPa 0.800 0.929 ARFI-LS 0.904(0.808~0.962) 1.45 m/s 0.950 0.714 F≥3 FT-LS 0.881(0.780~0.947) 15.8 kPa 0.727 0.913 FS-LS 0.878(0.776~0.945) 12.9 kPa 0.818 0.869 ARFI-LS 0.869(0.765~0.939) 1.83 m/s 0.909 0.804 F=4 FT-LS 0.926(0.836~0.975) 17.5 kPa 0.900 0.879 FS-LS 0.939(0.853~0.982) 18.2 kPa 0.900 0.914 ARFI-LS 0.928(0.838~0.976) 2.08 m/s 1.000 0.845 -
[1] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007 [2] Foundation for Hepatitis Prevention and Control; Chinese society of Infectious Disease and Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Liver Disease Committee of Chinese Research Hospital Association. Consensus on clinical application of transient elastrography detecting liver fibrosis: A 2018 update[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2019, 27(3): 182-191. (in Chinese)中国肝炎防治基金会, 中华医学会感染病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会和中国研究型医院学会肝病专业委员会. 瞬时弹性成像技术诊断肝纤维化专家共识(2018年更新版)[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2019, 27(3): 182-191. [3] LOOMBA R, ADAMS LA. Advances in non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(7): 1343-1352. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317593 [4] DIETRICH CF, BAMBER J, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of liver ultrasound elastography, update 2017 (long version)[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2017, 38(4): e48. DOI: 10.1055/a-0641-0076 [5] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chines Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and management of primary biliary cirrhosis(cholangitis) (2015)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(12): 1980-1988. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.004中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 原发性胆汁性肝硬化(又名原发性胆汁性胆管炎)诊断和治疗共识(2015)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31 (12) : 1980-1988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.12.004 [6] DUAN WJ, WANG XZ, MA AL, et al. Multicenter prospective study to validate a new transient elastography device for staging liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Dig Dis, 2020, 21(9): 519-525. DOI: 10.1111/1751-2980.12924 [7] FERRAIOLI G, WONG VW, CASTERA L, et al. Liver ultrasound elastography: An update to the world federation for ultrasound in medicine and biology guidelines and recommendations[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2018, 44(12): 2419-2440. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.07.008 [8] BARR RG, WILSON SR, RUBENS D, et al. Update to the society of radiologists in ultrasound liver elastography consensus statement[J]. Radiology, 2020, 296(2): 263-274. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2020192437 [9] BEDOSSA P, POYNARD T. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group[J]. Hepatology, 1996, 24(2): 289-293. DOI: 10.1002/hep.510240201 [10] CORPECHOT C, EL NAGGAR A, POUJOL-ROBERT A, et al. Assessment of biliary fibrosis by transient elastography in patients with PBC and PSC[J]. Hepatology, 2006, 43(5): 1118-1124. DOI: 10.1002/hep.21151 [11] CORPECHOT C, CARRAT F, POUJOI-ROBERT A, et al. Noninvasive elastography-based assessment of liver fibrosis progression and prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2012, 56(1): 198-208. DOI: 10.1002/hep.25599 [12] GÓMEZ-DOMINGUEZ E, MENDOZA J, GACIA-BUEY L, et al. Transient elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2008, 27(5): 441-447. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/18081731 [13] ZHANG DK, CHEN M, LIU Y, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for non-invasive assessment of disease stage in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis: A preliminary study[J]. Clin Radiol, 2014, 69(8): 836-840. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2014.03.019 [14] GOERTZ RS, GABMANN L, STROBEL D, et al. Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse (ARFI) elastography in autoimmune and cholestatic liver diseases[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2019, 18(1): 23-29. DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.7858 [15] ZHANG YG, ZHAO SX, ZHOU GD, et al. Correlation of FibroTouch and FibroScan with the stage of primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2016, 24(12): 902-906. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.12.005张玉果, 赵素贤, 周光德, 等. FibroTouch、FibroScan与原发性胆汁性肝硬化分期的相关性分析[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2016, 24(12): 902-906. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.12.005 [16] ZHANG DK, ZHAO YY, CHEN M, et al. The initial clinical study of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in quantitative evaluating the degree of primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. J Chin Clin Med Imaging, 2014, 25(4): 248-251. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201404010.htm张大鹍, 赵媛媛, 陈敏, 等. 声脉冲辐射力成像在原发性胆汁性肝硬化定量诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2014, 25(4): 248-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYYX201404010.htm [17] LI B, JI D, NIU XX, et al. Diagnostic value of FibroScan for liver fibrosis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2014, 19(8): 585-587. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUAN201408008.htm李冰, 纪冬, 牛小霞, 等. FibroScan对原发性胆汁性肝硬化患者肝纤维化的诊断价值[J]. 肝脏, 2014, 19(8): 585-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZUAN201408008.htm [18] GUO H, LIAO M, JIN J, et al. How intrahepatic cholestasis affects liver stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A study of 1197 patients with liver biopsy[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(2): 1096-1104. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06451-x 期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王大龙,王涛,王康娥. 瞬时弹性成像及血清HBsAg、HBV DNA联合评估乙型肝炎肝纤维化程度的价值. 肝脏. 2024(01): 56-59+63 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 张兆辉,庄轶超,杨文宪. 瞬时弹性成像技术对原发性胆汁性肝硬化、自身免疫性肝炎的鉴别及与肝脏纤维化程度、肝功能的相关性研究. 世界华人消化杂志. 2023(11): 464-469 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 王轶佳,李绍军,郝卫刚,高元平. 丁二磺酸腺苷蛋氨酸联合熊去氧胆酸治疗原发性胆汁性胆管炎的临床效果. 中国医药. 2023(07): 1030-1034 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 边娜娜,王辉,孙荣荣,张心怡,王梓依,贺娜. 肝硬化及相关不良事件进行无创诊断和预测的价值. 肝脏. 2023(10): 1158-1161+1174 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王文亮,魏宁,徐浩,王兴田,张庆桥,祖茂衡,刘洪涛. 肝脏剪切波速检测及与门静脉压力相关性研究在布-加综合征介入疗效评价中的应用. 介入放射学杂志. 2023(12): 1178-1183 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 朱敏嘉,辛琳琳,端木文雯,朱捷,杨璐璇,张迎春. FibroScan对低水平ALT乙肝患者肝纤维化程度的诊断价值. 江苏大学学报(医学版). 2022(01): 58-62 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 黄艳梅,陈成彩,陈洁华,陈必武,黄婷. 超声弹性成像在无创性肝纤维化诊断中的研究进展. 影像研究与医学应用. 2022(11): 4-6 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 朱立娜,唐源,赵秋燕,黄初军,夏显旺,周林波. 不同病因对Fibrotouch检测慢性肝病患者纤维化分级的影响研究. 临床消化病杂志. 2022(06): 466-469 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2599 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2599 KB)

 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术