经内镜鼻胆管引流术与经内镜胆道支架置入术在低位恶性梗阻性黄疸术前胆道引流效果比较的Meta分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.04.027
Clinical effect of endoscopic nasobiliary drainage versus endoscopic biliary stenting in preoperative biliary drainage for low-level malignant obstructive jaundice: A Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
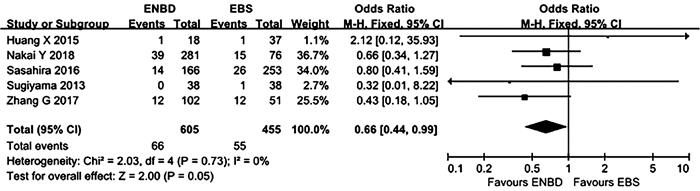
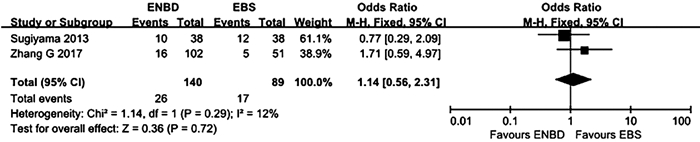
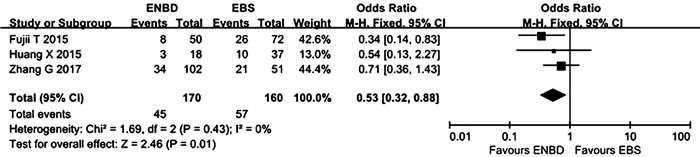
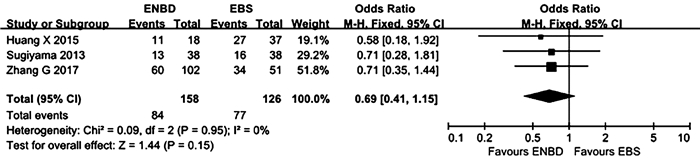
目的 比较经内镜鼻胆管引流术(ENBD)和经内镜胆道支架置入术(EBS)在低位恶性梗阻性黄疸术前胆道引流中的有效性及安全性。 方法 在中英文数据库中检索从建库至2020年8月发表的有关ENBD与EBS在低位恶性梗阻性黄疸术前胆道引流疗效对照研究的所有中英文文献,对纳入的研究进行质量评价和数据提取后,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行Meta分析,比较ENBD与EBS术前胆管炎发生率、术前胰腺炎发生率、支架障碍率、术前术后总并发症发生率、术后胰漏率的差异。 结果 最终纳入6项研究,包括1182例患者。Meta分析结果显示,在术前胰腺炎发生率、支架障碍率、术前术后总并发症发生率方面,ENBD组与EBS组比较差异均无统计学意义(OR分别为0.66、1.14、0.69,95%CI分别为0.44~0.99、0.56~2.31、0.41~1.15,P值分别为0.05、0.72、0.15)。但是,ENBD组相较于EBS降低了术前胆管炎发生率和术后胰漏率,差异均有统计学意义(OR分别为0.34、0.53,95%CI分别为0.23~0.50、0.32~0.88,P值分别为 < 0.000 01、0.01)。 结论 对于诊断明确的低位恶性胆道梗阻患者,术前胆道引流使用ENBD优于使用EBS。未来需要更多的多中心大样本随机对照试验来验证这一结论。 -
关键词:
- 黄疸, 梗阻性 /
- 引流术 /
- 支架 /
- Meta分析(主题)
Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical effect and safety of endoscopic nasobiliary drainage (ENBD) versus endoscopic biliary stenting (EBS) in preoperative biliary drainage for low-level malignant obstructive jaundice. Methods Chinese and English databases were searched for control studies on the clinical effect of ENBD versus EBS in preoperative biliary drainage for low-level malignant obstructive jaundice published up to August 2020. After quality assessment and data extraction were performed for the studies included, RevMan 5.3 software was used to perform the meta-analysis. ENBD and EBS were compared in terms of incidence rates of preoperative cholangitis and preoperative pancreatitis, stent dysfunction rate, overall incidence rate of complications before and after surgery, and rate of postoperative pancreatic leakage. Results Six studies involving 1182 patients were included. The meta-analysis showed that there were no significant differences between the ENBD group and the EBS group in incidence rate of preoperative pancreatitis (odds ratio [OR]=0.66, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.44-0.99, P=0.05), stent dysfunction rate (OR=1.14, 95% CI: 0.56-2.31, P=0.72), and overall incidence rate of complications before and after surgery (OR=0.69, 95% CI: 0.41-1.15, P=0.15). Compared with the EBS group, the ENBD group had significant reductions in incidence rate of preoperative cholangitis (OR=0.34, 95% CI: 0.23-0.50, P < 0.000 01) and rate of postoperative pancreatic leakage (OR=0.53, 95% CI: 0.32-0.88, P=0.01). Conclusion Preoperative biliary drainage with ENBD is superior to EBS in patients with well-diagnosed low-level malignant obstructive jaundice. More large multicenter randomized controlled trials are needed in the future to verify this conclusion. -
Key words:
- Jaundice, Obstructive /
- Drainage /
- Stents /
- Meta-Analysis as Topic
-
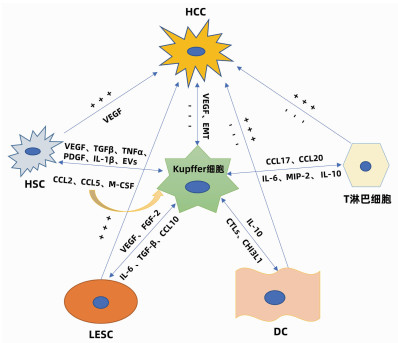
近来,肝细胞癌(HCC)的发病率在全球范围内均有上升的趋势,其治疗方式仍是以手术为主的综合治疗,但由于其高复发率和转移率,5年生存率仅有19%[1]。越来越多的研究发现Kupffer细胞对于HCC的发生发展具有关键性作用,但相关作用及机制尚未完全阐明。鉴于Kupffer细胞在HCC中的特殊作用,本文就Kupffer细胞参与调控HCC的相关机制作一综述。
Kupffer细胞是一种由血液单核细胞黏附于肝窦壁上分化而成的肝脏常驻巨噬细胞,其数量占非实质细胞的35%, 单核-巨噬细胞系总数的80%~90%[2],是肝脏固有免疫系统的一个重要组成部分。Kupffer细胞具有很高的可塑性,可以根据肝脏微环境的变化改变其表型[3],是肝脏免疫防御的第一道防线。Kupffer细胞作为HCC微环境的重要成员,能够分泌细胞因子及其他化学成分共同调控HCC。
1. Kupffer细胞对HCC的双重作用
随着肿瘤相关巨噬细胞概念的提出,人们对Kupffer细胞的双重作用越来越重视。研究[4]表明Kupffer细胞被来自肠道的内毒素激活后可活化为M1型、M2型。M1型Kupffer细胞主要分泌高水平的炎性因子和趋化因子,并通过吞噬作用将肿瘤细胞杀死,呈现出抗肿瘤表型。而M2型Kupffer细胞仅有较弱抗原递呈能力,并通过分泌抑制性细胞因子如IL-10、TGFβ等下调免疫应答,同时分泌IL-6和IL-8来促进HCC干细胞的增殖和上皮-间充质转化[5],进而促进组织重塑,呈现出促肿瘤表型。
1.1 Kupffer细胞抑制HCC的发生发展
Kupffer细胞是机体杀伤肝癌细胞的主要效应细胞,生物学反应修饰激活的Kupffer细胞可通过非特异性细胞毒作用、吞噬作用、抗体依赖细胞介导的细胞毒作用及抗原递呈作用参与细胞免疫清除癌细胞[6-7]。同时,Kupffer细胞也能够分泌TNFα、一氧化氮等细胞因子参与体液免疫以间接杀伤肝癌细胞。血管对于实体瘤是至关重要的,没有足够的血管,肿瘤也无法长期生存[8]。激活的M1型Kupffer细胞能够分泌成纤维细胞生长因子2和血管内皮生长因子(vascular permeability factor, VEGF)A来诱导内皮细胞生成血管抑制因子进而抑制肿瘤的侵袭、转移[9-10]。Kupffer细胞亦可表达表面受体蛋白抑制HCC的发生发展。Li等[11]发现癌组织中Kupffer细胞表面CD16a数量显著低于癌旁组织和邻近的正常肝组织,且随着癌症分化程度的降低而降低,而加入免疫血清后CD16a表达增加,这说明Kupffer细胞表面的CD16a有助于杀灭肿瘤细胞。此外,Kupffer细胞表面还有很多相关的抑癌受体蛋白,如IgG Fc受体、补体受体、甘露糖受体等。
1.2 Kupffer细胞促进HCC的发生发展
HCC的发生与炎性反应-组织修复密不可分。炎性反应时,M1型Kupffer细胞可释放大量氧化物及活性氧导致微环境改变,致使肝细胞大量死亡以及存活的肝细胞大量增殖,成为促进HCC形成和进展的重要因素。新生血管的形成在肿瘤的侵袭和转移中起着关键作用。研究发现Kupffer细胞既能抑制又能促进血管生成,激活的Kupffer细胞能够分泌大量的促血管生长因子如VEGF、巨噬细胞集落刺激因子(macrophage colony-stimulating factor, M-CSF)、IL-18、血小板衍生生长因子(platelet derived growth factor, PDGF)、成纤维细胞生长因子(fibroblast growth factor, FGF)、血管趋化生成因子等促进血管的生成,研究[12-16]发现M1、M2型Kupffer细胞均能分泌促血管生长因子,但主要由M2型Kupffer细胞分泌。血小板可增强肿瘤细胞增殖、促进肿瘤新生血管的形成,并影响肿瘤与间质之间的通讯,从而促进转移。Malehmir等[17]发现血小板黏附和活化是肝癌发生的关键,其中,血小板衍生的抗原对HCC的发展至关重要。Kupffer细胞能够通过分泌血小板活化因子,以及表达CD11b/CD18等影响其激活过程,进而促进HCC的发生发展。而上皮间质化是HCC获得迁移和侵袭能力的重要改变。活化的M2型Kupffer细胞能够分泌IL-6、IL-8、TNFα、TGFβ、VEGF等诱发上皮间质化[18]。同时M2型Kupffer细胞还可通过自分泌及旁分泌的方式释放巨噬细胞移动抑制因子抑制自身的组织穿透能力,并且巨噬细胞移动抑制因子还可加强VEGF的表达从而促进HCC中新生血管的形成[19-20]。此外,Kupffer细胞分泌大量基质金属蛋白酶2和基质金属蛋白酶9,可溶解细胞外基质并破坏基底膜的完整性,协助肿瘤细胞破坏周围组织及周围组织的重塑。
2. Kupffer细胞在HCC中与其他非肝实质细胞的相互作用
肝细胞包括实质细胞和非实质细胞,非实质细胞又包括Kupffer细胞、肝星状细胞(HSC)、肝窦内皮细胞(liver sinusoidal endothelial cell, LESC)、树突状细胞(dendritic cell, DC)以及淋巴细胞等。在HCC发生发展中,Kupffer细胞能够通过细胞因子与其他非实质细胞产生联系,发生相互作用、相互影响共同调控HCC(图 1)。
2.1 Kupffer细胞与HSC的相互作用
研究者在动物实验中观察到为了响应生长因子和炎性介质,HSC被激活并触发类似于肝脏肿瘤的早期修复事件; 在临床标本中则发现了HCC癌组织以及癌旁组织中的胶原蛋白Ⅳ明显增加。在HCC中,癌细胞能够促进Kupffer细胞和HSC中促血管生成基因的表达,此外,Kupffer细胞和HSC均能够促进彼此分泌促血管生成因子,共同促进HCC的发生发展。Brodt[21]还发现活化的Kupffer细胞能够通过释放TGFβ、TNFα、PDGF、IL-1β等细胞因子维持HSC的活性来促进HCC的发展。同时,衰老的HSC还可以分泌大量的细胞外囊泡,促进Kupffer细胞分泌表皮生长因子降低其抗肿瘤作用[22]。而另一方面,活化的Kupffer细胞亦可产生趋化因子CCL2、CCL5诱导HSC的迁移和募集,且HSC衍生的趋化因子CCL2和M-CSF能够进一步激活并募集Kupffer细胞,以此形成Kupffer细胞- CCL2-Kupffer细胞的正反馈环改变免疫微环境,从而放大免疫反应调控HCC[23],同时HSC还能通过旁分泌作用调节Kupffer细胞的积累和增值。
2.2 Kupffer细胞与LESC的相互作用
LSEC作为肝脏的重要生理结构,在HCC的发生发展中发挥着重要作用。在HCC中Kupffer细胞分泌的VEGF上调,上调的VEGF能通过缝隙连接蛋白促进肝窦内皮祖细胞的迁移和增殖。此外,VEGF可以刺激并维持LESC特异性生长活性[24],进而修复受损的肝窦功能发挥抑癌作用。而相反,Kupffer细胞分泌的碱性成纤维细胞因子对于肝窦的窦壁毛细血管化至关重要,并可以加剧HCC的进展。同时,HCC分泌的另一种生长因子FGF2可以诱导LSEC上的T-钙黏附素的表达。在体外,T-钙黏附素已经被证明可以通过与脂联素结合和激活NF-κB来增加肝癌的侵袭作用。此外,在HCC进展中,LSEC分泌的IL-6与Kupffer细胞分泌的IL-6受体相互作用共同促进血管的形成[25],已经明确的是Kupffer细胞与HSC可以促进彼此分泌促血管因子,而Kupffer细胞、HSC与LSEC三者之间的促血管生成关系还需进一步研究。Manzi等[26]还发现TGFβ可能通过上调Gal1(一种β-半乳糖苷结合蛋白)的表达和促进肝癌细胞与LESC的黏附而促进肝癌的转移,这与M2型Kupffer细胞的促肿瘤作用是一致的。同时,在HCC的进展中,Kupffer细胞的骤减及其分泌的CCL10[27]导致LESC通透性增加,癌细胞逃逸并大量增殖形成恶性循环。总之,Kupffer细胞与LESC的相互作用对于HCC的发生发展亦有双重作用。
2.3 Kupffer细胞与DC的相互作用
DC的组织募集作用对于抗原递呈至关重要,DC能和T淋巴细胞相互联系发挥对抗HCC的作用,同时DC与免疫耐受密切相关。Uwatoku等[28]发现DC可以选择性结合Kupffer细胞,在Kupffer细胞衰竭的大鼠中,DC既不能募集到肝脏,也不能黏附在肝窦窦壁上。Kupffer细胞还可分泌C型凝集素(CTLs)来促进DC向肝脏的募集,Lo等[29]发现凝集素受体基因敲除小鼠的DC迁移的频率和数量减少。Kupffer细胞还与DC的发育密切相关, Kupffer细胞能够分泌CHI3L1(一种糖基水解酶,在DC免疫反应中发挥关键作用)促进DC的分化和成熟[30]。研究[31]发现DC可分泌IL-10来抑制Kupffer细胞产生TNFα、IL-6及活性氧改变肿瘤微环境。而在HCC中由于Kupffer细胞的衰竭导致DC的迁移、发育受阻,HCC得以快速演变。
2.4 Kupffer细胞与淋巴细胞等相互作用
在病理状态下,Kupffer细胞的衰竭可以通过下调肝炎相关细胞因子/趋化因子(例如CXCL10)抑制浸润的免疫细胞(单核细胞、T淋巴细胞、B淋巴细胞和NK细胞)。而Kupffer细胞能够分泌细胞因子促进淋巴细胞分化成不同的亚型,发挥促肿瘤的功能。M2型Kupffer细胞可以分泌CCL17和CCL22来促进CD4+调节性T淋巴细胞的聚集[32],并通过抑制细胞毒性T淋巴细胞的免疫应答而损害机体的免疫监测能力,从而促进HCC的发生。另一方面CD4+T淋巴细胞又可以通过释放细胞因子反作用于Kupffer细胞,进一步促进肿瘤的生长和免疫抑制性微环境的形成。同时M2型Kupffer细胞通过分泌IL-6、MIP-2等细胞因子抑制CD8+T淋巴细胞的增殖。研究[33]还发现在HCC中,Kupffer细胞可通过与T淋巴细胞之间的相互作用促进T淋巴细胞的耗竭来阻碍抗肿瘤反应。此外,Kupffer细胞还可以通过IL-10诱导T淋巴细胞耐受和功能障碍来抑制抗肿瘤活性。
3. 以Kupffer细胞为靶点的HCC治疗
Kupffer细胞在HCC中的关键性决定了针对Kupffer细胞的治疗是一个十分热门的研究。Kupffer细胞分泌的肝细胞生长因子能够促进细胞增殖、存活和侵袭而参与HCC的进展。而c-Met是肝细胞生长因子的唯一受体,替波替尼是一种高度选择性的三磷酸腺苷竞争性c-Met抑制剂; 在临床前模型中发现其能够抑制MHCC97H小鼠的皮下和原位肿瘤生长并诱导完全消退[34]。而伯瑞替尼是一种新型、高度选择性的小分子c-Met抑制剂,已经使肝癌患者获得了一些初步疗效。抗VEGFR抗体如贝伐珠单抗、卡博替尼、索拉非尼、4-甲基伞形酮[35-38]能够针对Kupffer细胞分泌的VEGF,不仅可以使免疫抑制的肿瘤血管正常化,还能激活DC,减少调节性T淋巴细胞和髓源抑制性细胞[39]; 并且还通过下调转录因子TOX[40],使效应性T淋巴细胞免于衰竭。TGFβ可以调节细胞活动,包括增殖、迁移、黏附、分化以及调节HCC微环境,同时还可调节T淋巴细胞的存活、增殖和效应功能[41],影响Kupffer细胞的转化,促进上皮间充质转化、肿瘤侵袭和转移,一些TGFβ途径抑制剂如加尼西替尼[42]已经进入临床。FGF在癌细胞的生长增殖、血管生成中发挥着重要作用,Ⅱ期临床试验已经证明英非替尼能够抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和诱导凋亡从而抑制肿瘤生长[34],于此同时一种广泛成纤维细胞生长因子受体抑制剂伊达非替尼也正在临床试验中。针对Kupffer细胞的治疗,仍有许多难题困扰着研究者,深入研究Kupffer细胞相关性治疗还需更多的科研成果。
4. 小结
综上所述,Kupffer细胞在HCC的发生发展中具有密切作用。Kupffer细胞对于HCC的调控具有双向作用,既能抑制HCC的发生发展,又能促进HCC的侵袭转移。目前,在HCC中针对Kupffer细胞的治疗多种多样,但由于客观缓解率低、不良反应多和耐药问题等,总体临床效果欠佳。相信未来会有疗效更好的Kupffer细胞靶向药物及规范化、个体化的综合治疗方案,从而为HCC患者带来新的曙光和希望。
-
[1] PU LZ, SINGH R, LOONG CK, et al. Malignant biliary obstruction: Evidence for best practice[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2016, 2016: 3296801. DOI: 10.1155/2016/3296801. [2] CHEN WW, HUANG K, LIU R, et al. Clinical effect of percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage combined with biliary stent implantation in treatment of high malignant obstructive jaundice and the influencing factors for prognosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(3): 559-564. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.03.021.陈伟伟, 黄坤, 刘锐, 等. 经皮肝穿刺胆管引流术联合胆道支架植入术治疗高位恶性梗阻性黄疸的效果及预后影响因素分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(3): 559-564. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.03.021. [3] BERGQUIST A, VON SETH E. Epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, 2015, 29(2): 221-232. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpg.2015.02.003. [4] YOSHIDA Y, AJIKI T, UENO K, et al. Preoperative bile replacement improves immune function for jaundiced patients treated with external biliary drainage[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2014, 18(12): 2095-2104. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-014-2674-2. [5] GUNDRY SR, STRODEL WE, KNOL JA, et al. Efficacy of preoperative biliary tract decompression in patients with obstructive jaundice[J]. Arch Surg, 1984, 119(6): 703-708. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390180065011. [6] COATES JM, BEAL SH, RUSSO JE, et al. Negligible effect of selective preoperative biliary drainage on perioperative resuscitation, morbidity, and mortality in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Arch Surg, 2009, 144(9): 841-847. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.152. [7] ZHAO SW, SHEN ZY, WANG JC, et al. Effect of biliary drainage methods on patients with obstructive jaundice undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. J Surg Concepts Pract, 2020, 25(4): 301-305. DOI: 10.16139/j.1007-9610.2020.04.007.赵诗葳, 沈子贇, 王建承, 等. 术前胆道引流方式对合并梗阻性黄疸病人胰十二指肠切除术的影响[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2020, 25(4): 301-305. DOI: 10.16139/j.1007-9610.2020.04.007. [8] CHOI SH, GWON DI, KO GY, et al. Hepatic arterial injuries in 3110 patients following percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage[J]. Radiology, 2011, 261(3): 969-975. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.11110254. [9] MOHER D, LIBERATI A, TETZLAFF J, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement[J]. PLoS Med, 2009, 6(7): e1000097. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [10] LUCHINI C, STUBBS B, SOLMI M, et al. Assessing the quality of studies in Meta-analyses: Advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa Scale[J]. World J Meta-Analysis, 2017, 5(4): 80-84. DOI: 10.13105/wjma.v5.i4.80. [11] FUJII T, YAMADA S, SUENAGA M, et al. Preoperative internal biliary drainage increases the risk of bile juice infection and pancreatic fistula after pancreatoduodenectomy: A prospective observational study[J]. Pancreas, 2015, 44(3): 465-470. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000265. [12] HUANG X, LIANG B, ZHAO XQ, et al. The effects of different preoperative biliary drainage methods on complications following pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015, 94(14): e723. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000723. [13] NAKAI Y, YAMAMOTO R, MATSUYAMA M, et al. Multicenter study of endoscopic preoperative biliary drainage for malignant hilar biliary obstruction: E-POD hilar study[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 33(5): 1146-1153. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14050. [14] SASAHIRA N, HAMADA T, TOGAWA O, et al. Multicenter study of endoscopic preoperative biliary drainage for malignant distal biliary obstruction[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(14): 3793-3802. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i14.3793. [15] SUGIYAMA H, TSUYUGUCHI T, SAKAI Y, et al. Preoperative drainage for distal biliary obstruction: Endoscopic stenting or nasobiliary drainage?[J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2013, 60(122): 231-234. DOI: 10.5754/hge12621. [16] ZHANG GQ, LI Y, REN YP, et al. Outcomes of preoperative endoscopic nasobiliary drainage and endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage for malignant distal biliary obstruction prior to pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(29): 5386-5394. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i29.5386. [17] van der GAAG NA, RAUWS EA, van EIJCK CH, et al. Preoperative biliary drainage for cancer of the head of the pancreas[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(2): 129-137. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0903230. [18] SEWNATH ME, KARSTEN TM, PRINS MH, et al. A meta-analysis on the efficacy of preoperative biliary drainage for tumors causing obstructive jaundice[J]. Ann Surg, 2002, 236(1): 17-27. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-200207000-00005. [19] KARNABATIDIS D, SPILIOPOULOS S, KATSAKIORI P, et al. Percutaneous trans-hepatic bilateral biliary stenting in Bismuth Ⅳ malignant obstruction[J]. World J Hepatol, 2013, 5(3): 114-119. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i3.114. [20] BARKAY O, MOSLER P, SCHMITT CM, et al. Effect of endoscopic stenting of malignant bile duct obstruction on quality of life[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2013, 47(6): 526-531. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318272440e. [21] YAGIOKA H, HIRANO K, ISAYAMA H, et al. Clinical significance of bile cytology via an endoscopic nasobiliary drainage tube for pathological diagnosis of malignant biliary strictures[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2011, 18(2): 211-215. DOI: 10.1007/s00534-010-0333-x. [22] HONG SK, JANG JY, KANG MJ, et al. Comparison of clinical outcome and cost-effectiveness after various preoperative biliary drainage methods in periampullary cancer with obstructive jaundice[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2012, 27(4): 356-362. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.4.356. [23] CORTES A, SAUVANET A, BERT F, et al. Effect of bile contamination on immediate outcomes after pancreaticoduodenectomy for tumor[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2006, 202(1): 93-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2005.09.006. [24] YU PH, SU S, CHEN S, et al. Clinical effect of pancreaticoduodenectomy with total mesopancreas excision versus traditional pancreaticoduodenecto-my in treatment of pancreatic head carcinoma and periampullary cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(8): 1811-1815. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.026.余佩和, 苏松, 陈诗, 等. 胰十二指肠联合全系膜切除术与胰十二指肠切除术治疗胰头癌及壶腹周围癌效果比较的Meta分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(8): 1811-1815. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.08.026. [25] VELANOVICH V, KHEIBEK T, KHAN M. Relationship of postoperative complications from preoperative biliary stents after pancreaticoduodenectomy. A new cohort analysis and meta-analysis of modern studies[J]. JOP, 2009, 10(1): 24-29. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19129611 [26] KAWAI M, TANI M, HIRONO S, et al. Association of preoperative biliary drainage related complications with postoperative complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy[J]. HPB, 2014, 16: 111-112. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 于艳艳. 基于决策曲线分析超声造影血流灌注参数评估PHC介入治疗后肿瘤活性的价值. 罕少疾病杂志. 2025(03): 97-99 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2745 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2745 KB)


 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术