经皮胆道支架植入术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的发生率及危险因素分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.04.031
Incidence rates of hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting and related risk factors
-
摘要:
目的 分析经皮肝穿刺胆道支架植入(PTBS)术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的临床特征,探讨其相关危险因素。 方法 回顾性收集2016年3月—2020年2月于南京医科大学第一附属医院介入放射科收治且接受PTBS治疗的249例恶性胆道梗阻患者的临床资料。根据术后患者有无高淀粉酶血症或急性胰腺炎,将所有患者分为高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=55)、无高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=194),并分析其发生率、严重程度及相关危险因素。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验或Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。将上述单因素分析中P < 0.1的因素纳入多因素logistic回归分析,探究PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的独立危险因素。 结果 PTBS术后,共55例(22.1%)发生血清淀粉酶异常升高,其中26例(10.4%)诊断为高淀粉酶血症,29例(11.7%)诊断为急性胰腺炎。所有胰腺炎均表现为轻度。多因素logistic回归分析发现,年龄(≤60岁)(OR=2.2,95%CI:1.07~4.52,P=0.033)、碘-125粒子条植入(OR=2.8,95%CI:1.21~6.45,P=0.016)、胆道支架跨乳头释放(OR=6.3,95%CI:2.85~14.05,P < 0.001) 及术中胰管显影(OR=13.9,95%CI:5.64~34.03,P < 0.001)是PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的危险因素。 结论 高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎是PTBS术后相对常见的并发症。年龄≤60岁、同期碘粒子条植入、胆道支架跨乳头释放及术中胰管显影是PTBS术后发生高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的独立风险因素。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors of hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting (PTBS). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 249 patients with malignant biliary obstruction who were admitted to Department of Interventional Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, and underwent PTBS from March 2016 to February 2020, and according to the presence or absence of postoperative hyperamylasemia or acute pancreatitis, the patients were divided into two groups to analyze incidence rate, severity, and related risk factors. The t-test or the Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparison of continuous data between groups, and the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between groups. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed for the factors with P < 0.1 in the univariate analysis to investigate independent risk factors for hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after PTBS. Results After PTBS, 55 patients (22.1%) patients had abnormally elevated serum amylase, among whom 26 (10.4%) were diagnosed with hyperamylasemia and 29 (11.7%) were diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. All patients with acute pancreatitis had mild manifestations. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age ≤60 years (odds ratio [OR]=2.2, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07-4.52, P=0.033), iodine-125 seed strand implantation (OR=2.8, 95%CI: 1.21-6.45, P=0.016), biliary stent placement across the papilla (OR=6.3, 95%CI: 2.85-14.05, P < 0.001), and visualization of the pancreatic duct during surgery (OR=13.9, 95%CI: 5.64-34.03, P < 0.001) were risk factors for hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after PTBS. Conclusion Hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis are relatively common complications after PTBS. Age ≤60 years, iodine-125 seed strand implantation, biliary stent placement across the papilla, and visualization of the pancreatic duct during surgery are independence risk factors for hyperamylasemia and acute pancreatitis after PTBS. -
Key words:
- Hyperamylasemia /
- Pancreatitis /
- Risk Factors
-
近年来,胆道金属支架植入术因其符合生理性胆汁流向,提高患者生存质量,已逐渐成为恶性胆道梗阻(malignant biliary obstruction, MBO) 患者的主要姑息性治疗手段[1-2]。胆道金属支架可通过经内镜逆行胰胆管造影(endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, ERCP) 或经皮肝穿刺胆道支架植入(percutaneous transhepatic biliary stenting, PTBS)途径释放,两种方式各有优劣。有文献[3-4]报道PTBS的技术成功率更高,特别是病灶累及肝门部及其上级分支。高淀粉酶血症是ERCP术后最常见的并发症之一,可能进一步发展为胰腺炎,其中重症急性胰腺炎还可能诱发全身炎性反应综合征和多器官功能衰竭,甚至危及生命[5]。Sugawara等[6]和Kim等[7]报道PTBS术后急性胰腺炎的发生率为6.4%~24.2%,但这些研究的样本量较小且均为远端胆道梗阻患者,同时未提及高淀粉酶血症。目前,与ERCP相比,关于MBO患者PTBS术后高淀粉酶和胰腺炎的发生率和严重程度鲜有较大样本的临床报道,相关危险因素尚未得到充分评估。
本研究旨在分析MBO患者PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的发生率和危险因素,以便于临床工作中及时辨别高危患者,降低其发生风险。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
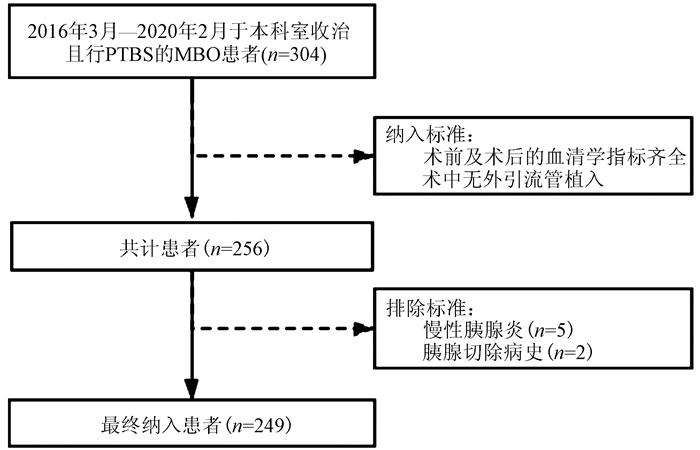
回顾性收集2016年3月—2020年2月于本院介入放射科收治且进行PTBS的MBO患者临床资料。纳入标准: (1)患者术前及术后的血清学指标齐全; (2)术中无外引流管植入。排除标准: (1)慢性胰腺炎病史; (2)胰腺切除病史。最终共纳入249例患者(图 1)。所有患者通过肿瘤病理或影像学、实验室检查诊断为MBO。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 术前准备
患者禁食12 h同时于术前2 h测定血清淀粉酶水平。采用增强CT和/或磁共振胰胆管造影评估胆管狭窄及肿瘤情况。术中静脉使用羟考酮镇静并缓解疼痛。
1.2.2 操作步骤
经右腋中线第9肋和/或剑突下用22G Chiba针(Cook, Bloomington,IN) 穿刺肝内胆管,引入套管造影了解胆管情况,选择合适胆道分支,透视下调整穿刺路径,穿刺成功后,植入0.018微导丝,退出Chiba针,交换入6F三件套管鞘,将三件套管鞘分别送入肝内肝管内,植入0.038超滑导丝,经导丝试探通过胆管梗阻段进入十二指肠,退出6F三件套管鞘,交换入6F导管鞘。经鞘在导丝引导下植入金属支架释放系统,支架末端应比狭窄节段长1.5~2 cm,透视下精确定位,跨过狭窄处释放金属支架,使其位于狭窄部位。若行粒子植入,则经另一导丝同时引入碘-125粒子条,后经外鞘注入少量稀释造影剂,显示金属支架开放良好,造影剂顺畅进入肠道,粒子条与支架重叠。最后用明胶海绵条装入鞘内,边退鞘边推进海绵条以充填穿刺路径。术后常规予以保肝、护胃及抗感染等支持治疗,并于3 h及24 h后再次检测血清淀粉酶。若出现血清淀粉酶异常升高,则予以生长抑素(6 mg,500 ml 0.9%生理盐水,静脉滴注) 及禁食处理。本研究中使用3种裸自膨胀金属支架[E-Luminexx (Bard Peripheral Vascular, Tempe, AZ)、S.M.A.R.T(Cordis, Milpitas, CA)、Zilver(Cook, Bloomington, IN)], 直径8 mm,长度40~100 mm。
1.2.3 定义和标准
急性胰腺炎的诊断标准[8]: (1) PTBS术后血淀粉酶超过正常测定值3倍及以上; (2) 急性出现的持续性腹痛; (3) 影像学表现。以上3项标准中符合2项及以上即诊断为术后急性胰腺炎。急性胰腺炎严重程度的诊断标准[8]: (1) 轻度为无局部或全身并发症,无器官衰竭; (2) 中度为48 h内好转的器官衰竭和/或其他并发症; (3) 重度为持续存在的器官衰竭。高淀粉酶血症的诊断标准[5]: PTBS术后血淀粉酶超过正常测定值且无急性的持续性腹痛。
1.3 伦理学审查
本研究方案经由南京医科大学附属第一医院伦理委员会审批通过,批号:2020-SR-200。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0软件分析数据。计量资料若符合正态分布采用x±s表示,两组间比较采用t检验,若不符合正态分布采用M(P25~P75)表示,两组间比较采用Mann-Whitney U检验。计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。将上述单因素分析中P < 0.1的因素纳入多因素logistic回归分析,探究PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的独立危险因素。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入249例患者,年龄36~92岁,平均(64.6±9.9)岁,所有患者基线资料见表 1。
表 1 患者基线特征基本特征 数值 男/女(例) 131/118 年龄(岁) 64.6±9.9 肿瘤类型[例(%)] 胰腺癌 33(13.3) 胆囊癌 23(9.2) 胆管细胞癌 108(43.4) 肝细胞癌 57(22.9) 其他恶性肿瘤 28(11.2) 基础疾病[例(%)] 高血压 96(38.6) 糖尿病 37(14.9) 冠心病 22(8.8) 术前肝功能 ALT(U/L) 73.1(42.7~127.4) AST(U/L) 88.8(56.2~144.8) TBil(μmol/L) 190.7(113.2~311.3) 术前感染[例(%)] 68(27.3) 既往胆道引流手术史[例(%)] 103(41.4) 手术时长[例(%)] ≤60 min 194(77.9) >60 min 55(22.1) 支架数量[例(%)] 1个 164(65.9) 2个 76(30.5) ≥3个 9(3.6) 支架类型[例(%)] Cordis 136(54.6) Bard 72(28.9) Cook 41(16.5) 支架释放位置[例(%)] 乳头上方 140(56.2) 跨乳头 109(43.8) 胰管显影[例(%)] 39(15.7) 碘-125粒子条植入[例(%)] 51 (20.5) 2.2 发生率及严重程度
所纳入的249例患者术前血清淀粉酶均属于正常范围,共55例(22.1%) 发生术后血清淀粉酶异常升高,其中26例(10.4%) 诊断为高淀粉酶血症,29例(11.6%) 诊断为急性胰腺炎。55例患者均予以生长抑素及禁食治疗,没有高淀粉酶血症进展为胰腺炎,没有中重度胰腺炎发生。术后3 h血清淀粉酶水平>1000 U/L的患者恢复至正常水平所需的时间明显高于其他患者[(3.9±1.1)d vs (3.1±1.3)d, t=2.186,P=0.036]。
2.3 危险因素
将单因素分析中P < 0.1的因素纳入多因素logistic回归分析,最后显示年龄(≤60岁)、碘-125粒子条植入、胆道支架跨乳头释放及术中胰管显影为PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的独立危险因素(P值均 < 0.05)(表 2、3)。
表 2 PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的单因素分析因素 高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=55) 无高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=194) 统计值 P值 性别(例) χ2=0.082 0.775 男 28 103 女 27 91 年龄(例) χ2=3.135 0.077 ≤60岁 28 73 >60岁 27 121 肿瘤类型(例) χ2=2.914 0.088 胰腺癌 3 30 非胰腺癌 52 164 高血压(例) χ2=0.004 0.949 是 21 75 否 34 119 糖尿病(例) χ2=0.616 0.433 是 10 27 否 45 167 冠心病(例) χ2=0.377 0.539 是 6 16 否 49 178 术前肝功能 ALT(U/L) 73.0(44.4~134.0) 75.3(41.4~116.0) Z=-0.433 0.433 AST(U/L) 92.2(57.2~144.4) 82.5(48.2~173.6) Z=-0.387 0.699 TBil(μmol/L) 185.4(116.8~310.6) 191.6(90.7~306.3) Z=-0.364 0.716 术前感染(例) χ2=1.044 0.307 是 18 50 否 37 144 既往胆道引流手术史(例) χ2=0.295 0.587 是 21 82 否 34 112 手术时长(例) χ2=0.003 0.956 ≤60 min 43 151 >60 min 12 43 支架数量(例) χ2=0.156 0.693 1个 35 129 ≥2个 20 65 支架类型(例) χ2=0.401 0.818 Cordis 28 108 Bard 17 55 Cook 10 31 支架释放位置(例) χ2=18.382 < 0.001 乳头上方 17 123 跨乳头 38 71 胰管显影(例) χ2=41.819 < 0.001 是 24 15 否 31 179 碘-125粒子条植入(例) χ2=3.212 0.073 是 16 35 否 39 159 表 3 多因素logistic回归分析结果因素 B值 P值 OR 95%CI 胰腺癌 -0.893 0.174 0.4 0.11~1.49 年龄(≤ 60岁) 0.786 0.033 2.2 1.07~4.52 碘-125粒子条植入 1.026 0.016 2.8 1.21~6.45 支架跨乳头释放 1.845 < 0.001 6.3 2.85~14.05 胰管显影 2.628 < 0.001 13.9 5.64~34.03 3. 讨论
近年来,对于MBO患者,PTBS因其安全有效在临床得到广泛运用[1, 9-11]。有荟萃分析[12]表明经皮肝穿刺途径与内镜途径术后发生急性胰腺炎的风险相似。高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎作为PTBS术后的并发症,目前临床认知不足。本研究通过回顾性收集249例MBO患者的临床资料发现,高淀粉酶血症的发生率约10.4%,急性胰腺炎的发生率约11.8%。所有患者经抑酸抑酶及禁食治疗后没有发生高淀粉酶血症进展为胰腺炎,没有中重度胰腺炎发生。此外,本研究还发现术后3 h血清淀粉酶水平>1000 U/L的患者恢复至正常水平所需的时间明显高于其他患者。因此,对于此类患者,即使无典型的胰腺炎式腹痛和影像学表现,笔者建议术后使用抑酶药物以降低其恢复时间。
本研究中,老年患者(>60岁) PTBS术后发生高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的概率明显低于年轻患者(P=0.010)。这可能是由于随着患者年龄增长,其胰腺萎缩的可能性增大。Sugawara等[6]认为由于萎缩胰腺的外分泌功能低下且组织纤维化增加,往往在支架植入之前,其胰液流出道已发生梗阻,因此不容易发生胰液反流,胰腺实质组织也不容易受影响。此外,由于肿瘤侵犯,胰腺癌患者亦容易发生流出道的梗阻。既往有文献[13]报道原发肿瘤类型非胰腺癌是ERCP术后急性胰腺炎的危险因素之一。然而,在本研究的多因素分析中,其未见统计学意义(P=0.174)。推测由于本研究中胰腺癌患者的比例较小(13.3%),远低于既往研究的52%~82%[14-19]。应开展更多的研究以验证胰腺癌是否可以降低PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的发生。
本研究表明PTBS术中行碘-125粒子条植入的患者发生高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的风险更高(P=0.016)。在PTBS操作过程中,此类患者导丝对管壁造成的摩擦性损伤更多,乳头水肿的可能性更大。此外,碘粒子向邻近肿瘤组织提供高剂量辐射的同时不可避免伴随着一部分放射性损伤。
本研究中,支架跨十二指肠乳头释放的患者术后发生高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的风险明显高于不跨乳头患者(P < 0.001)。Jo等[20]报道经乳头上方释放胆道支架的患者术后急性胰腺炎的发生率(4.1%) 明显低于跨乳头释放的患者(25.0%)。Tarnasky等[21]表示由于胆道支架压迫了胰管流出口,胰液引流不畅,引起胰液反流,导致胰腺炎的发生。近年有文献[22-23]报道,与支架跨乳头释放相比,经乳头上方释放胆道支架的患者术后支架再狭窄及胆管炎的发生率两者并无明显差异,因此笔者认为在条件允许的情况下,经乳头上方释放胆道支架更合理。
术中胰管的意外显影被认为是PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的危险因素之一(P < 0.001)。Kawakubo等[13]表明胰管受到的压力过高可导致胰腺炎发生。然而,PTBS术中胰管的意外显影常常正是胰管压力过高的表现。同时,造影剂的注入对胰管及其内容物也不可避免的造成了损伤。根据上述结果,建议术者在操作时尽量避免以过高的压力注射造影剂,避免其意外流入胰管。此外,对于术中出现上述高危因素的患者,如胰管显影、支架需要跨乳头或需同期进行碘-125粒子条植入,笔者建议可术后予以生长抑素静脉滴注进行预防性治疗或暂予以禁食处理,及时复查血清淀粉酶水平,以降低术后高淀粉酶血症及胰腺炎发生风险。
本研究存在一定的局限性。首先,本文属于回顾性研究,这可能会影响数据的可靠性。其次,临床中有时难以区分不典型的胰腺炎腹痛和术后支架腹痛,并且非所有患者的术后CT图像均可获得。因此研究中可能将部分高淀粉酶血症诊断为胰腺炎,导致两者发生率存在误差。最后,本研究所用支架直径均为8 mm且胰腺癌患者比例较低,因此关于支架直径及胰腺癌对于PTBS术后高淀粉酶和急性胰腺炎的影响有待于更一步研究。
综上所述,高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎是PTBS术后相对常见的并发症。所有患者予以禁食、抑酸抑酶治疗,并无中重度胰腺炎发生。年龄≤60岁、同期碘-125粒子条植入、支架跨乳头释放及术中胰管显影是PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和急性胰腺炎的独立危险因素。
-
表 1 患者基线特征
基本特征 数值 男/女(例) 131/118 年龄(岁) 64.6±9.9 肿瘤类型[例(%)] 胰腺癌 33(13.3) 胆囊癌 23(9.2) 胆管细胞癌 108(43.4) 肝细胞癌 57(22.9) 其他恶性肿瘤 28(11.2) 基础疾病[例(%)] 高血压 96(38.6) 糖尿病 37(14.9) 冠心病 22(8.8) 术前肝功能 ALT(U/L) 73.1(42.7~127.4) AST(U/L) 88.8(56.2~144.8) TBil(μmol/L) 190.7(113.2~311.3) 术前感染[例(%)] 68(27.3) 既往胆道引流手术史[例(%)] 103(41.4) 手术时长[例(%)] ≤60 min 194(77.9) >60 min 55(22.1) 支架数量[例(%)] 1个 164(65.9) 2个 76(30.5) ≥3个 9(3.6) 支架类型[例(%)] Cordis 136(54.6) Bard 72(28.9) Cook 41(16.5) 支架释放位置[例(%)] 乳头上方 140(56.2) 跨乳头 109(43.8) 胰管显影[例(%)] 39(15.7) 碘-125粒子条植入[例(%)] 51 (20.5) 表 2 PTBS术后高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎的单因素分析
因素 高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=55) 无高淀粉酶血症和胰腺炎组(n=194) 统计值 P值 性别(例) χ2=0.082 0.775 男 28 103 女 27 91 年龄(例) χ2=3.135 0.077 ≤60岁 28 73 >60岁 27 121 肿瘤类型(例) χ2=2.914 0.088 胰腺癌 3 30 非胰腺癌 52 164 高血压(例) χ2=0.004 0.949 是 21 75 否 34 119 糖尿病(例) χ2=0.616 0.433 是 10 27 否 45 167 冠心病(例) χ2=0.377 0.539 是 6 16 否 49 178 术前肝功能 ALT(U/L) 73.0(44.4~134.0) 75.3(41.4~116.0) Z=-0.433 0.433 AST(U/L) 92.2(57.2~144.4) 82.5(48.2~173.6) Z=-0.387 0.699 TBil(μmol/L) 185.4(116.8~310.6) 191.6(90.7~306.3) Z=-0.364 0.716 术前感染(例) χ2=1.044 0.307 是 18 50 否 37 144 既往胆道引流手术史(例) χ2=0.295 0.587 是 21 82 否 34 112 手术时长(例) χ2=0.003 0.956 ≤60 min 43 151 >60 min 12 43 支架数量(例) χ2=0.156 0.693 1个 35 129 ≥2个 20 65 支架类型(例) χ2=0.401 0.818 Cordis 28 108 Bard 17 55 Cook 10 31 支架释放位置(例) χ2=18.382 < 0.001 乳头上方 17 123 跨乳头 38 71 胰管显影(例) χ2=41.819 < 0.001 是 24 15 否 31 179 碘-125粒子条植入(例) χ2=3.212 0.073 是 16 35 否 39 159 表 3 多因素logistic回归分析结果
因素 B值 P值 OR 95%CI 胰腺癌 -0.893 0.174 0.4 0.11~1.49 年龄(≤ 60岁) 0.786 0.033 2.2 1.07~4.52 碘-125粒子条植入 1.026 0.016 2.8 1.21~6.45 支架跨乳头释放 1.845 < 0.001 6.3 2.85~14.05 胰管显影 2.628 < 0.001 13.9 5.64~34.03 -
[1] WANG WJ, YU CH. Improvement in liver function in patients with malignant obstructive jaundice after endoscopic biliary metallic stent drainage[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(8): 1295-1298. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.08.027.王文君, 于聪慧. 胆道支架引流术对恶性梗阻性黄疸患者肝功能的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(8): 1295-1298. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.08.027. [2] ZHANG K, ZHANG MF, REN JZ, et al. Efficacy of percutaneous intraductal radiofrequency ablation combined with biliary stenting in treatment of malignant biliary obstruction[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2015, 31(5): 737-740. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.05.025.张凯, 张萌帆, 任建庄, 等. 经皮肝穿刺胆道腔内射频消融联合胆道支架治疗恶性胆道梗阻的临床观察[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2015, 31(5): 737-740. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2015.05.025. [3] LEE SH, PARK JK, YOON WJ, et al. Optimal biliary drainage for inoperable Klatskin's tumor based on Bismuth type[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2007, 13(29): 3948-3955. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i29.3948. [4] CHEN BY, PANG LY. Implantation of biliary metallic stent for malignant obstructive jaundice: Technical comparison study between via ERCP route and via PTCD route[J]. J Intervent Radiol, 2016, 25(10): 880-884. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2016.10.011.陈保银, 庞林元. 两种不同途径胆道金属支架植入治疗恶性阻塞性黄疸的对比研究[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2016, 25(10): 880-884. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2016.10.011. [5] PAN HW, WANG C, ZHANG Y. Risk factors of post-operative pancreatitis and hyperamylosis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography[J]. China J Endosc, 2018, 24(7): 26-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1989.2018.07.005.潘宏伟, 王晨, 张艳. 经内镜逆行胰胆管造影术后并发胰腺炎和高淀粉酶血症的危险因素分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2018, 24(7): 26-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1989.2018.07.005. [6] SUGAWARA S, ARAI Y, SONE M, et al. Frequency, severity, and risk factors for acute pancreatitis after percutaneous transhepatic biliary stent placement across the papilla of vater[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2017, 40(12): 1904-1910. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-017-1730-1. [7] KIM ET, GWON DI, KIM JW, et al. Acute pancreatitis after percutaneous insertion of metallic biliary stents in patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer[J]. Clin Radiol, 2020, 75(1): 57-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.crad.2019.07.014. [8] BANKS PA, BOLLEN TL, DERVENIS C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut, 2013, 62(1): 102-111. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779. [9] QIAN Z, LIU HC, PANG Q, et al. The clinical efficacy and prognostic factors of percutaneous biliary stent implantation combined with 125Ⅰ seed intracavitary irradiation in the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Chin J Radiol, 2018, 52(8): 640-643. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2018.08.014.钱震, 刘会春, 庞青, 等. 胆道支架联合125Ⅰ粒子腔内照射治疗胆管癌的临床疗效及预后因素分析[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2018, 52(8): 640-643. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1005-1201.2018.08.014. [10] YIN JY, YANG K. Nonsurgical treatment of malignant biliary obstructive diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(3): 226-230. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.03.052.尹靖阳, 杨慷. 胆道恶性梗阻性疾病的非手术治疗[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(3): 681-685. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.03.052. [11] LIU R, HUANG K, CHEN WW, et al. Clinical effect of biliary stenting combined with percutaneous transhepatic cholangial drainage in treatment of different types of malignant obstructive jaundice[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(1): 131-137. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.025.刘锐, 黄坤, 陈伟伟, 等. 胆道支架植入术联合经皮肝穿刺胆管引流术治疗不同类型恶性梗阻性黄疸的效果观察[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(1): 131-137. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.025. [12] ZHAO XQ, DONG JH, JIANG K, et al. Comparison of percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage and endoscopic biliary drainage in the management of malignant biliary tract obstruction: A meta-analysis[J]. Dig Endosc, 2015, 27(1): 137-145. DOI: 10.1111/den.12320. [13] KAWAKUBO K, ISAYAMA H, NAKAI Y, et al. Risk factors for pancreatitis following transpapillary self-expandable metal stent placement[J]. Surg Endosc, 2012, 26(3): 771-776. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-011-1950-4. [14] TELFORD JJ, CARR-LOCKE DL, BARON TH, et al. A randomized trial comparing uncovered and partially covered self-expandable metal stents in the palliation of distal malignant biliary obstruction[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010, 72(5): 907-914. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.08.021. [15] KAHALEH M, TOKAR J, CONAWAY MR, et al. Efficacy and complications of covered Wallstents in malignant distal biliary obstruction[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2005, 61(4): 528-533. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02593-3. [16] KULLMAN E, FROZANPOR F, SÖDERLUND C, et al. Covered versus uncovered self-expandable nitinol stents in the palliative treatment of malignant distal biliary obstruction: Results from a randomized, multicenter study[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010, 72(5): 915-923. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.07.036. [17] COTÉ GA, KUMAR N, ANSSTAS M, et al. Risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis with placement of self-expandable metallic stents[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2010, 72(4): 748-754. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.05.023. [18] ARTIFON EL, SAKAI P, ISHIOKA S, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy before deployment of covered metal stent is associated with greater complication rate: A prospective randomized control trial[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42(7): 815-819. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31803dcd8a. [19] YOON WJ, LEE JK, LEE KH, et al. A comparison of covered and uncovered Wallstents for the management of distal malignant biliary obstruction[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2006, 63(7): 996-1000. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2005.11.054. [20] JO JH, PARK BH. Suprapapillary versus transpapillary stent placement for malignant biliary obstruction: Which is better?[J]. J Vasc Interv Radiol, 2015, 26(4): 573-582. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2014.11.043. [21] TARNASKY PR, CUNNINGHAM JT, HAWES RH, et al. Transpapillary stenting of proximal biliary strictures: Does biliary sphincterotomy reduce the risk of postprocedure pancreatitis?[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 1997, 45(1): 46-51. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5107(97)70301-8. [22] COSGROVE N, SIDDIQUI AA, ADLER DG, et al. A comparison of bilateral side-by-side metal stents deployed above and across the sphincter of oddi in the management of malignant hilar biliary obstruction[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2017, 51(6): 528-533. DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000584. [23] ZHANG JX, ZU QQ, LIU S, et al. Differences in efficacy of uncovered self-expandable metal stent in relation to placement in the management of malignant distal biliary obstruction[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2018, 24(2): 82-86. DOI: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_326_17. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 殷将领,赵茗茗,王尧,李红玲. 不同时期重症急性胰腺炎临床特点及疾病转归的影响因素分析. 临床和实验医学杂志. 2024(07): 698-702 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 武振东,金鹏飞,董源. 经内镜逆行胰胆管造影术后胰腺炎发生的预测模型及关键因子研究. 腹腔镜外科杂志. 2024(12): 903-908 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 李汛,韩恒通,岳平. 迟发性医源性胆道损伤的内镜外科治疗策略. 中华消化外科杂志. 2022(07): 866-872 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 孙伟,王强,董韶华. 胆总管结石患者ERCP术中不同取石器械取石效果的差异性研究及术后并发症预测模型的建立. 中国中西医结合消化杂志. 2022(09): 613-619 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2066 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2066 KB)


 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术