靶向共价闭合环状DNA抗HBV治疗的研究进展
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.044
利益冲突声明:所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突。
作者贡献声明:王艺颖负责资料分析、撰写论文;刘熙称负责收集数据,修改论文;朴荣利负责课题设计、拟定写作思路;秦俊杰负责撰写文章并最后定稿。
Research advances in anti-hepatitis B virus therapy targeting covalently closed circular DNA
-
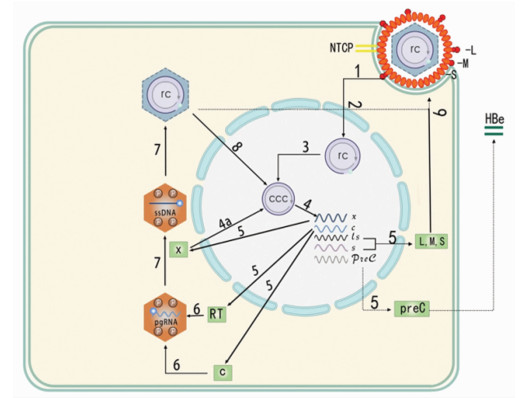
摘要: HBV引起尚未治愈的慢性感染,是世界范围内的主要健康负担。共价闭合环状DNA作为稳定的微染色体存在于受感染细胞的细胞核中,当新型治疗手段实现灭活或消除感染肝细胞中持久存在的共价闭合环状DNA,慢性感染自然过程和长期抗病毒治疗将不复存在。介绍了通过基因编辑、表观遗传修饰等方法靶向共价闭合环状DNA, 以期完全性治愈HBV感染。Abstract: The incurable chronic infection caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) is the major health burden worldwide. Covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) exists in the nucleus of infected cells as a stable minichromosome, and when a new therapy realizes inactivation or eliminates persistent cccDNA in infected hepatocytes, the natural process of chronic infection and long-term antiviral therapy will no longer exist. This article introduces the methods targeting cccDNA, such as gene editing and epigenetic modification, so as to achieve the complete cure of HBV infection.
-
Key words:
- Covalently Closed Circular DNA /
- Hepatitis B Virus /
- Gene Editing
-
表 1 新研发的抗HBV感染的代表药物
类型 药物名称 作用机理 类别 临床阶段 进入抑制剂 Myrcludex B 阻断NTCP 肽类 Ⅱ CRV431 阻断NTCP和蛋白质折叠 小分子 Ⅰ 翻译抑制剂 JNJ3989 mRNA降解 siRNA Ⅱ GSK3389404 mRNA降解 反义寡核苷酸 Ⅱ 衣壳装配抑制剂 RO7049389 结合核心蛋白 小分子 Ⅱ ABI-H0731 结合核心蛋白 小分子 Ⅱ JNJ0440 结合核心蛋白 小分子 HBsAg分泌抑制剂 REP 2139、REP 2165 结合HBsAg 核酸基聚合物 Ⅱ 先天性免疫激活剂 Inarigivir RIG-Ⅰ激动剂和聚合酶抑制剂 小分子 Ⅱ 适应性免疫激活剂 TG-1050 疫苗 5型腺病毒抗体 Ⅰ -
[1] World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report[R]. Geneva: WHO, 2017: 1-83. [2] BLUMBERG BS, ALTER HJ, VISNICH S. A "NEW" antigen in leukemia sera[J]. JAMA, 1965, 191: 541-546. DOI: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080070025007. [3] SUMMERS J, MASON WS. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B-like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate[J]. Cell, 1982, 29(2): 403-415. DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [4] HU J, PROTZER U, SIDDIQUI A. Revisiting hepatitis B virus: Challenges of curative therapies[J]. J Virol, 2019, 93(20): e01032-19. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01032-19. [5] GUO JT, GUO H. Metabolism and function of hepatitis B virus cccDNA: Implications for the development of cccDNA-targeting antiviral therapeutics[J]. Antiviral Res, 2015, 122: 91-100. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.08.005. [6] ZHU A, LIAO X, LI S, et al. HBV cccDNA and its potential as a therapeutic target[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2019, 7(3): 258-262. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2018.00054. [7] LIN CL, KAO JH. Review article: Novel therapies for hepatitis B virus cure - advances and perspectives[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 44(3): 213-222. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13694. [8] LIU S, XIN Y. HBV cccDNA: The stumbling block for treatment of HBV infection[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2019, 7(3): 195-196. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2019.00047. [9] TANG L, COVERT E, WILSON E, et al. Chronic hepatitis B infection: A review[J]. JAMA, 2018, 319(17): 1802-1813. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2018.3795. [10] BARTENSCHLAGER R, URBAN S, PROTZER U. Towards curative therapy of chronic viral hepatitis[J]. Z Gastroenterol, 2019, 57(1): 61-73. DOI: 10.1055/a-0824-1576. [11] BLOCK TM, GUO H, GUO JT. Molecular virology of hepatitis B virus for clinicians[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2007, 11(4): 685-706, vii. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.08.002. [12] DONG J, YING J, QIU X, et al. Advanced strategies for eliminating the cccDNA of HBV[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2018, 63(1): 7-15. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-017-4842-1. [13] SETO WK, LO YR, PAWLOTSKY JM, et al. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10161): 2313-2324. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31865-8. [14] TU T, BUDZINSKA MA, VONDRAN F, et al. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration occurs early in the viral life cycle in an in vitro infection model via sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide-dependent uptake of enveloped virus particles[J]. J Virol, 2018, 92(11): e02007-e02017. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02007-17. [15] HU J, SEEGER C. Hepadnavirus genome replication and persistence[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2015, 5(7): a021386. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021386. [16] SEEGER C, MASON WS. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Virology, 2015, 479-480: 672-686. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.031. [17] NASSAL M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Gut, 2015, 64(12): 1972-1984. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309809. [18] GAO W, HU J. Formation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA: Removal of genome-linked protein[J]. J Virol, 2007, 81(12): 6164-6174. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02721-06. [19] WU M, LI J, YUE L, et al. Establishment of Cre-mediated HBV recombinant cccDNA (rcccDNA) cell line for cccDNA biology and antiviral screening assays[J]. Antiviral Res, 2018, 152: 45-52. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.02.007. [20] BLOOM K, MAEPA MB, ELY A, et al. Gene therapy for chronic HBV-can we eliminate cccDNA?[J]. Genes (Basel), 2018, 9(4). DOI: 10.3390/genes9040207. [21] KITAMURA K, QUE L, SHIMADU M, et al. Flap endonuclease 1 is involved in cccDNA formation in the hepatitis B virus[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2018, 14(6): e1007124. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007124. [22] SLAGLE BL, BOUCHARD MJ. Role of HBx in hepatitis B virus persistence and its therapeutic implications[J]. Curr Opin Virol, 2018, 30: 32-38. DOI: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.01.007. [23] SEKIBA K, OTSUKA M, OHNO M, et al. Inhibition of HBV transcription from cccDNA with nitazoxanide by targeting the HBx-DDB1 interaction[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 7(2): 297-312. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.10.010. [24] LEWANDOWSKA M, PIEKARSKA A. New directions in hepatitis B therapy research[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2017, 3(3): 119-126. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2017.68831. [25] KENNEDY EM, KORNEPATI AV, CULLEN BR. Targeting hepatitis B virus cccDNA using CRISPR/Cas9[J]. Antiviral Res, 2015, 123: 188-192. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.10.004. [26] SEEGER C, SOHN JA. Complete spectrum of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutations on HBV cccDNA[J]. Mol Ther, 2016, 24(7): 1258-1266. DOI: 10.1038/mt.2016.94. [27] YANG HC, CHEN PJ. The potential and challenges of CRISPR-Cas in eradication of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA[J]. Virus Res, 2018, 244: 304-310. DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2017.06.010. [28] KOSTYUSHEV D, BREZGIN S, KOSTYUSHEVA A, et al. Orthologous CRISPR/Cas9 systems for specific and efficient degradation of covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(9): 1779-1794. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-019-03021-8. [29] WEBER ND, STONE D, SEDLAK RH, et al. AAV-mediated delivery of zinc finger nucleases targeting hepatitis B virus inhibits active replication[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e97579. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097579. [30] BLOOM K, ELY A, MUSSOLINO C, et al. Inactivation of hepatitis B virus replication in cultured cells and in vivo with engineered transcription activator-like effector nucleases[J]. Mol Ther, 2013, 21(10): 1889-1897. DOI: 10.1038/mt.2013.170. [31] DREYER T, NICHOLSON S, ELY A, et al. Improved antiviral efficacy using TALEN-mediated homology directed recombination to introduce artificial primary miRNAs into DNA of hepatitis B virus[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 478(4): 1563-1568. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.152. [32] BELLONI L, ALLWEISS L, GUERRIERI F, et al. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome[J]. J Clin Invest, 2012, 122(2): 529-537. DOI: 10.1172/JCI58847. [33] PARK HK, MIN BY, KIM NY, et al. Short hairpin RNA induces methylation of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA in human hepatoma cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 436(2): 152-155. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.04.108. [34] QIAN G, HU B, ZHOU D, et al. NIRF, a novel ubiquitin ligase, inhibits hepatitis B virus replication through effect on HBV core protein and H3 histones[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2015, 34(5): 327-332. DOI: 10.1089/dna.2014.2714. [35] WEI ZQ, ZHANG YH, KE CZ, et al. Curcumin inhibits hepatitis B virus infection by down-regulating cccDNA-bound histone acetylation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2017, 23(34): 6252-6260. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6252. [36] SONG M, SUN Y, TIAN J, et al. Silencing retinoid X receptor alpha expression enhances early-stage hepatitis B virus infection in cell cultures[J]. J Virol, 2018, 92(8). DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01771-17. [37] YUAN Y, ZHAO K, YAO Y, et al. HDAC11 restricts HBV replication through epigenetic repression of cccDNA transcription[J]. Antiviral Res, 2019, 172: 104619. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104619. [38] FANNING GC, ZOULIM F, HOU J, et al. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18(11): 827-844. DOI: 10.1038/s41573-019-0037-0. [39] ZAI WJ, CHEN JL, YUAN ZH. Regulatory mechanisms of the transcription and metabolism of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA and strategies for silencing and elimination[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(5): 983-988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.006.宰文静, 陈捷亮, 袁正宏. HBV cccDNA转录代谢调控机制及沉默清除策略[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(5): 983-988. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05.006. -




 PDF下载 ( 2143 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2143 KB)

 下载:
下载:


