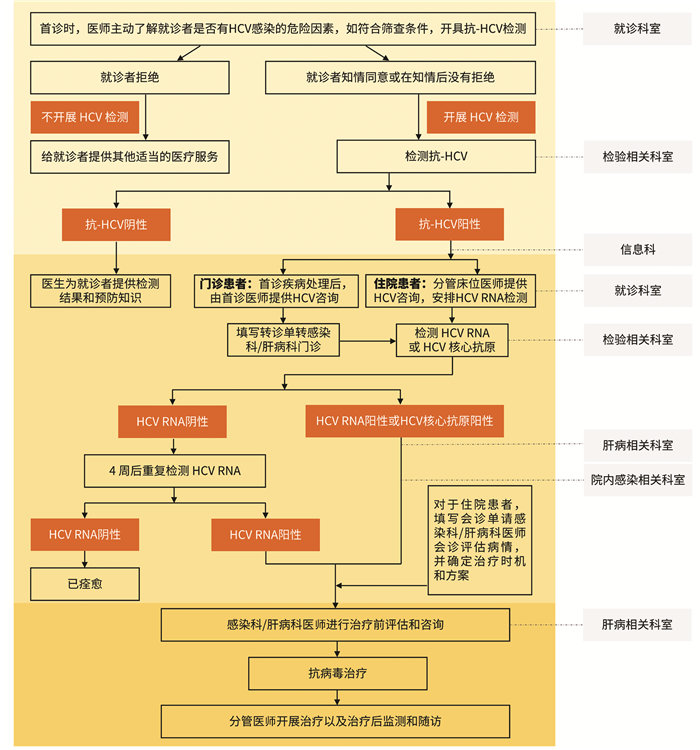
中国丙型病毒性肝炎院内筛查管理流程(试行)
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.07.011
庄 辉 北京大学医学部中联肝健康促进中心
李明阳 中联肝健康促进中心
陈仲丹 世界卫生组织驻华代表处
关秀茹 哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院
李军 南京医科大学第一附属医院江苏省人民医院
封 波 北京大学肝病研究所
陈仲丹 世界卫生组织驻华代表处
关秀茹 哈尔滨医科大学附属第一医院
王传新 山东大学第二医院
郑 磊 南方医科大学南方医院
封 波 北京大学肝病研究所
俞云松 浙江大学医学院附属邵逸夫医院
陈仲丹 世界卫生组织驻华代表处
李六亿 北京大学第一医院
张欣欣 上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院
侯铁英 广东省人民医院
高 燕 北京大学人民医院
潘世扬 南京医科大学第一附属医院江苏省人民医院
南月敏 河北医科大学第三医院
主审:
参与修订、讨论和定稿的专家(按姓氏拼音排序)
魏 来 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院中联肝健康促进中心
任 红 重庆医科大学附属第二医院
张静萍 中国医科大学附属第一医院
李伯安 解放军总医院第五医学中心
高 燕 北京大学人民医院
段钟平 首都医科大学附属北京佑安医院
吴 超 南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院
执笔者(按姓氏拼音排序):
刘运喜 解放军总医院第一医学中心
庄 辉 北京大学医学部中联肝健康促进中心
李明阳 中联肝健康促进中心
崔丽艳 北京大学第三医院
胡必杰 复旦大学附属中山医院
欧启水 福建医科大学附属第一医院
庄 辉 北京大学医学部中联肝健康促进中心
徐小元 北京大学第一医院
王 磊 山东大学第二医院
魏 来 清华大学附属北京清华长庚医院中联肝健康促进中心
利益冲突声明:专家组所有成员均声明不存在利益冲突
In-hospital process for viral hepatitis C screening and management in China (Draft)
-
摘要: 丙型病毒性肝炎是肝硬化、肝细胞癌的重要病因之一。我国约有1000万例慢性HCV感染者,但是,我国仍有大约70%以上的HCV感染者并没有被发现。根据世界卫生组织提出到2030年消除病毒性肝炎作为公共卫生危害的目标,以及医疗机构是目前我国发现HCV感染者和患者的主要场所,我们制定了《中国丙型病毒性肝炎院内筛查管理流程》,希望促进医疗机构管理、临床、检验、感染控制的多学科、多部门联合,加强医疗机构对检出抗-HCV阳性就诊者的咨询和转诊,促进慢性丙型肝炎患者的诊断和抗病毒治疗。Abstract: Viral hepatitis C is one of the important causes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. There are approximately 10 million cases of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in China. However, over 70% of HCV infections of China have not yet been detected. According to the goal of "eliminating viral hepatitis as a public health threat by 2030" of the World Health Organization Viral Hepatitis Stratrgy, and the fact that medical institutions remain the main places for detecting HCV infections or patients in China at present, we established the " In-hospital process for viral hepatitis C screening and management in China(Draft)", with intention to promote multidisciplinary collaboration and cooperation among the departments of clinic, laboratory, infection control, management, and etc. in medical institutions, and strengthen consultation and referral of patients with detected HCV antibodies and advance the diagnosis and antiviral treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C.
-
Key words:
- Hepatitis C /
- Algorithm /
- Screen /
- Diagnosis /
- Treatment
-
附件5 目前国内治疗慢性丙型肝炎的主要DAAs方案及其用法
方案 规格 用法 泛基因型 索磷布韦/维帕他韦 索磷布韦400 mg/维帕他韦100 mg 1片,1次/d 索磷布韦/可洛派韦 索磷布韦400 mg /可洛派韦60 mg 索磷布韦1片,1次/d; 可洛派韦1粒,1次/d 特异基因型 来迪派韦/索磷布韦 来迪派韦90 mg/索磷布韦400 mg 1片,1次/d 艾尔巴韦/格拉瑞韦 艾尔巴韦50 mg/格拉瑞韦100 mg 1片,1次/d 拉维达韦/达诺瑞韦/利托那韦/RBV** 拉维达韦200 mg/达诺瑞韦100 mg/利托那韦100 mg/RBV 拉维达韦1片,1次/d;达诺瑞韦1片,2次/d;利托那韦1片,2次/d;RBV 磷酸依米他韦/索磷布韦 磷酸依米他韦100 mg/索磷布韦400 mg 磷酸依米他韦1粒,1次/d;索磷布韦1片,1次/d 注:RBV,利巴韦林,体质量>75 kg,1200 mg/d;体质量≤75 kg,1000 mg/d,均分为2~3次服用。 -
[1] World Health Organization. Guidelines for the care and treatment of persons diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C virus infection[EB/OL]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/hepatitis-c-guidelines-2018/en/. [2] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of hepatitis C (2019 version)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(12): 2670-2686. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.008.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 丙型肝炎防治指南(2019版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2670-2686. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.008. [3] World Health Organization. Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016-2021[EB/OL]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2016. https://www.who.int/hepatitis/strategy2016-2021/ghss-hep/en/. [4] LIU L, XU H, HU Y, et al. Hepatitis C screening in hospitals: Find the missing patients[J]. Virol J, 2019, 16(1): 47. DOI: 10.1186/s12985-019-1157-1. [5] ORKIN C, LEACH E, FLANAGAN S, et al. High prevalence of hepatitis C (HCV) in the emergency department (ED) of a London hospital: Should we be screening for HCV in ED attendees?[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2015, 143(13): 2837-2840. DOI: 10.1017/S0950268815000199. [6] OLAFSSON S, TYRFINGSSON T, RUNARSDOTTIR V, et al. Treatment as prevention for hepatitis C (TraP Hep C)- a nationwide elimination programme in Iceland using direct-acting agents[J]. J Intern Med, 2018, 283(5): 500-507. DOI: 10.1111/joim.12740. [7] CHEN YX, WU C. Establishment and implementation of hepatitis C screening and referral channels in the hospitals[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2020, 28(10): 820-823. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200925-00531.陈雨欣, 吴超. 医院内丙型肝炎筛查和转诊路径的建立与实施[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2020, 28(10): 820-823. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20200925-00531. [8] FENG B, ZHANG J, WEI L. Inadequate awareness of hepatitis C among nonspecialist physicians in China[J]. Adv Med Educ Pract, 2011, 2: 209-214. DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S23887. [9] GHANY MG, MORGAN TR, AASLD-IDSA Hepatitis C Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C guidance 2019 update: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases-Infectious Diseases Society of America Recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C virus infection[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(2): 686-721. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31060. [10] National Health and Family Planning Commission, The People's Republic of China. Screening and management of hepatitis C[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2015, 28(1): 1-2, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CRBX201501001.htm中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 丙型病毒性肝炎筛查及管理[J]. 传染病信息, 2015, 28(1): 1-2, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CRBX201501001.htm -



 PDF下载 ( 3399 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3399 KB)

 下载:
下载:


