Mechanism of action of Xiaochaihu decoction in the treatment of hepatitis B based on network pharmacology
-
摘要:
目的 通过网络药理学研究小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的作用机制。 方法 利用TCMSP数据库收集小柴胡汤中7味中药的主要化学成分和作用靶点;通过GeneCards和OMIM数据库获取乙型肝炎相关靶点,利用STRING在线平台构建潜在靶点PPI网络并利用R语言获取GO功能富集分析及KEGG通路分析;运用Cytoscape3.7.2构建“活性成分-核心靶点”网络并对网络进行拓扑分析;最后利用AutoDock vina等软件对网络中度值较高的活性成分与核心靶点进行分子对接和可视化分析。 结果 筛选到小柴胡汤中槲皮素、山奈酚、汉黄芩素、柚皮素等193种主要化学成分和247个相关靶点,其中关键靶点有RELA、MAPK1、TP53、ESR1、EGFR、AKT1等;GO功能富集分析共得到2612条富集结果,主要涉及细胞对化学应激的反应、对药物的反应、氧化应激反应、对脂多糖的反应等生物过程的调节;KEGG通路分析共得到174条通路富集结果,主要涉及乙型肝炎、PI3K-AKT信号通路、MAPK信号通路等;分子对接结果显示主要活性成分与核心靶点的结合力均较强,蛋白结晶复合物构象稳定。 结论 研究初步表明了小柴胡汤通过多成分、多靶点、多通路发挥治疗乙型肝炎的作用机制。 -
关键词:
- 乙型肝炎 /
- 小柴胡汤 /
- 网络药理学 /
- 药理作用分子作用机制
Abstract:Objective To investigate the mechanism of action of Xiaochaihu decoction in the treatment of hepatitis B based on network pharmacology. Methods The TCMSP database was used to obtain the main chemical components and action targets of the seven traditional Chinese medicines in Xiaochaihu decoction; the GeneCards and OMIM databases were used to obtain the targets associated with hepatitis B; the STRING online platform was used to construct a PPI network of potential targets, and R language was used to perform gene ontology (GO) functional enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis; Cytoscape 3.7.2 was used to construct an "active component-core target" network and perform a topology analysis of this network; AutoDock vina and related software were used to perform molecular docking and visualized analysis of the active components with high value and the core targets in the network. Results A total of 193 main chemical components (including quercetin, kaempferol, wogonin, and naringenin) and 247 related targets were screened out, among which the key targets included RELA, MAPK1, TP53, ESR1, EGFR, and AKT1. A total of 2612 enrichment items were obtained by GO functional enrichment analysis, which were mainly involved in regulating the biological processes such as cell response to chemical stress, response to drugs, oxidative stress response, and lipopolysaccharide response. A total of 174 pathways were obtained by the KEGG pathway analysis, mainly involving hepatitis B, PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, and MAPK signaling pathway. Molecular docking results showed that the main active components had strong binding force to core targets, and the protein crystal complex had a stable conformation. Conclusion This study preliminarily shows that Xiaochaihu decoction exerts a therapeutic effect on hepatitis B through multiple components, targets, and pathways. -
乙型肝炎是由HBV引起,以肝脏损害为主要临床表现的一组全身传染性疾病[1]。据统计[2],我国每年约有30万人死于乙型肝炎相关性疾病。目前,西医在临床中治疗乙型肝炎多使用恩替卡韦、富马酸替诺福韦等药物[3],虽可延缓病情,但有耐药风险,远期预后不佳[4]。中医药治疗乙型肝炎经验丰富,安全性高。其中出自张仲景《伤寒论》中的名方小柴胡汤具有疏肝利胆、和解少阳的功效,临床中常用其治疗肝郁脾虚证乙型肝炎。现代药理学也表明,小柴胡具有显著的抗肝损害、抗炎、抗癌及免疫调节等多种作用[5]。
目前学界内对于小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎有不少研究,但尚未对其作用机制进行系统阐释。网络药理学是基于系统生物学、药理学和药物化学的一门综合性新兴学科,打破了传统的“一个药物,一个靶标,一种疾病”的思维模式及框架[6],与中医治疗疾病的整体观念和辨证论治原则相符[7],是中药发展与研究的新模式[8]。同时,分子对接可揭示药物治疗疾病的分子机制,将药理作用上升到分子水平,为药物机制研究奠定物质基础[9]。因此,本研究基于网络药理学结合分子对接技术,深入阐述小柴胡汤多成分、多靶点、多生物学过程、多通路的协同治疗乙型肝炎的作用机制,为进一步的实验研究提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 药物有效成分筛选及靶点预测
在中药系统药理学数据库和分析平台(TCMSP,http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php)筛选小柴胡汤(柴胡、黄芩、人参、半夏、生姜、大枣、甘草)的全部化学成分,并以口服生物利用度(OB)≥30%、类药性指数(DL)≥0.18为筛选条件,确定药物的活性成分;在Related Targets一栏中找出其所对应的作用靶点,将所有药物靶点进行合并整理,剔除重复靶点;在Uniport数据库(https://www.uniprot.org/)中输入靶点名称获取其对应的标准基因名。
1.2 乙型肝炎疾病靶点获取
以“hepatitis B、hepatitis B virus”为检索词,限制检索条件为“gene”“homo sapiens”,在GeneCards(https://www.genecards.org/)、OMIM(https://omim.org/)数据库中获取乙型肝炎相关靶点基因。将筛选条件定为Relevance score≥10.0,对收集的所有乙型肝炎靶点进行处理,将所有靶点基因进行合并,删除重复靶点。
1.3 小柴胡汤与乙型肝炎交集靶点筛选
将上述获得的药物靶点交集与疾病靶点基因交集通过R语言绘制Venny图,得到药物与疾病交集靶点(Drug-Disease)。
1.4 构建活性成分-核心靶点网络
将上述所得的小柴胡汤所有药物的活性成分和乙型肝炎靶点基因交集数据导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件,并对其参数进行设置,得到活性成分-核心靶点相互作用网络图。
1.5 构建蛋白质相互作用(PPI)网络及核心基因预测
将筛选得到的“Drug-Disease”中的靶点蛋白导入STRING数据库(https://string-db.org/), 限定研究物种为“Homo sapiens”,最低相互作用评分设置为“0.900”,同时设置隐藏游离点,其余参数保持默认,进行蛋白质互作分析,得到PPI网络图。将所得数据导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件,利用CytoNCA插件进行网络拓扑学分析筛选关键基因。
1.6 GO功能富集分析与KEGG通路分析
将筛选得到的“Drug-Disease”中的靶点蛋白通过R语言进行GO功能富集分析和KEGG通路分析,两者均以P<0.05为筛选指标(P<0.01被认定是富集显著,P值越小富集越显著)。
1.7 分子对接
将1.1节和1.5节中整理出degree排名靠前的活性成分与核心靶点进行分子对接。在Pubchem(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)数据库中下载活性成分的小分子配体2D结构,再利用ChemBio3D Ultra 14.0软件生成3D结构,使用优化模块进行分子结构优化,获取最稳定的分子构象,并保存为mol2格式。从PDB(https://www.rcsb.org/)数据库下载靶点蛋白受体三维结构,文件保存为PDB格式并导入PyMOL软件,输入命令删除靶蛋白的水分子和小分子配体,完成蛋白受体准备。将蛋白受体文件导入AutoDock Tools-1.5.6软件中,对蛋白分子加氢及对非完整氨基酸等问题进行矫正,保存文件为pdbqt格式,再将小分子配体文件mol2格式导入AutoDock Tools-1.5.6软件中,把文件转换为pdbqt格式,最后使用Autodock vina软件进行对接并利用PyMOL软件进行可视化分析。
2. 结果
2.1 小柴胡汤有效活性成分筛选及靶点预测
经TCMSP数据库搜索,检索到小柴胡汤7味药材的有效活性成分共有214个,其中柴胡17个、黄芩36个、人参22个、半夏13个、生姜5个、大枣29个、甘草92个,去重后共获得193个有效活性成分(表 1)。将筛选到的193个有效活性成分基于TCMSP搜索并整理后共得到247个作用靶点。
表 1 小柴胡汤部分活性成分信息MOL ID MOL Name OB DL 来源药物 MOL000354 Isorhamnetin 49.6 0.31 柴胡,甘草 MOL000359 Sitosterol 36.91 0.75 黄芩,甘草 MOL000422 Kaempferol 41.88 0.24 柴胡,人参,甘草 MOL000098 Quercetin 46.43 0.28 柴胡,大枣,甘草 MOL000449 Stigmasterol 43.83 0.76 柴胡,半夏,人参,黄芩,甘草 MOL000358 Beta-sitosterol 36.91 0.75 黄芩,人参,半夏,生姜,甘草 MOL005360 Malkangunin 57.71 0.63 人参,甘草 MOL000787 Fumarine 59.26 0.83 人参,大枣 MOL002714 Baicalein 33.52 0.21 半夏,黄芩 MOL002776 Baicalin 40.12 0.75 柴胡,半夏 MOL002879 Diop 43.59 0.39 黄芩,人参 MOL003896 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone 42.56 0.2 甘草 MOL000497 Licochalcone A 40.79 0.29 甘草 MOL000392 Formononetin 69.67 0.21 甘草 MOL004328 Naringenin 59.29 0.21 甘草 MOL012940 Spiradine A 113.52 0.61 甘草 MOL008034 21302-79-4 73.52 0.77 大枣 MOL008647 Moupinamide 86.71 0.26 大枣 MOL002773 Beta-carotene 37.18 0.58 大枣 MOL000096 (-)-catechin 49.68 0.24 大枣 MOL012940 Spiradine A 113.52 0.78 大枣 MOL006936 10, 13-eicosadienoic 39.99 0.2 半夏 MOL006937 12, 13-epoxy-9-hydroxynonadeca-7, 10-dienoic acid 42.15 0.24 半夏 MOL006957 (3S, 6S)-3-(benzyl)-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl) piperazine-2, 5-quinone 46.89 0.27 半夏 MOL003578 Cycloartenol 38.69 0.78 半夏 MOL006967 Beta-D-ribofuranoside, xanthine-9 44.72 0.21 半夏 MOL006129 6-methylgingediacetate2 48.73 0.32 生姜 MOL001771 Poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol 36.91 0.75 生姜 MOL008698 Dihydrocapsaicin 47.07 0.19 生姜 MOL004609 Areapillin 48.96 0.41 柴胡 MOL013187 Cubebin 57.13 0.64 柴胡 MOL004624 Longikaurin A 47.72 0.53 柴胡 MOL004628 Octalupine 47.82 0.28 柴胡 MOL004644 Sainfuran 79.91 0.23 柴胡 MOL003648 Inermin 65.83 0.54 人参 MOL005308 Aposiopolamine 66.65 0.22 人参 MOL005314 Celabenzine 101.88 0.49 人参 MOL005321 Frutinone A 65.9 0.34 人参 MOL005356 Girinimbin 61.22 0.31 人参 MOL000173 Wogonin 30.68 0.23 黄芩 MOL002915 Salvigenin 49.07 0.33 黄芩 MOL002927 Skullcapflavone Ⅱ 69.51 0.44 黄芩 MOL002932 Panicolin 76.26 0.29 黄芩 MOL002934 Neobaicalein 104.34 0.44 黄芩 2.2 药物靶点与疾病靶点交集
经分析得到药物潜在活性成分靶点247个,乙型肝炎疾病基因1655个,二者得出的交集靶点基因为142个(图 1)。
2.3 活性成分-核心靶点相互作用网络
将2.2节得到的142个交集靶点运用Perl相关脚本进行文件处理,所得数据导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件进行可视化网络构建,得到活性成分-核心靶点相互作用网络图(附录1)。
附录1中四周圆形节点代表药物的有效成分,橙、黄、绿、深红、粉红、灰、黑色分别代表小柴胡汤中的半夏、柴胡、大枣、甘草、黄芪、人参、生姜的有效成分,多个颜色代表多个药物共同的有效成分,灰色线条代表边,中间浅蓝色矩形节点代表中药和疾病的交集靶点。图中共有280个节点,其中来源于化合物的有138个,来源于基因的有142个;经统计degree较高的有效成分为槲皮素(quercetin)、山奈酚(kaempferol)、汉黄芩素(wogonin)、柚皮素(naringenin)等(表 2)。
表 2 小柴胡汤度值前10位化学成分基本信息NO. MOL ID MOL Name 化学式 Degree 来源药物 1 MOL000098 槲皮素(quercetin) C15H10O7 100 柴胡,甘草,大枣 2 MOL000422 山奈酚(kaempferol) C15H10O6 32 柴胡,甘草 3 MOL000173 汉黄芩素(wogonin) C16H12O5 31 黄芩 4 MOL004328 柚皮素(naringenin) C15H12O5 25 甘草 5 MOL000392 芒柄花素(formononetin) C16H12O4 20 甘草 6 MOL000497 甘草酮(licochalcone A) C21H22O4 20 甘草 7 MOL002714 黄芩素(baicalein) C15H10O5 19 黄芩,半夏 8 MOL000354 异鼠李素(isorhamnetin) C16H12O7 18 柴胡,甘草 9 MOL003896 7-甲氧基-2-甲基异黄酮
(7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone)C17H13NO5 18 甘草 10 MOL002773 β-胡萝卜素(beta-carotene) C40H56 18 大枣 2.4 PPI网络及核心基因预测
将2.2节的142个交集靶点导入STRING数据库,设定物种为“Homo sapiens”,得出string_interactions文件,并以tsv格式保存。网络图共有142个节点、622条边,平均每个节点的度值为9.32,平均局部聚类系数为0.507,PPI enrichment p-value值为<1.0e-16,邻接节点数目越多,说明这些蛋白在网络中的作用越显著(附录2)。
将tsv格式文件数据导入Cytoscape3.7.2软件中,使用CytoNCA插件对PPI网络进行拓扑分析筛选关键基因,处于核心位置的靶点有RELA、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)1、TP53、ESR1、EGFR、AKT1、JUN、MAPK8、RB1、STAT3、MAPK3、MYC、MAPK14、CCND1等,提示这些基因在PPI中发挥了关键作用,可能是小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的核心靶标基因(附录3)。
2.5 GO富集分析和KEGG通路分析
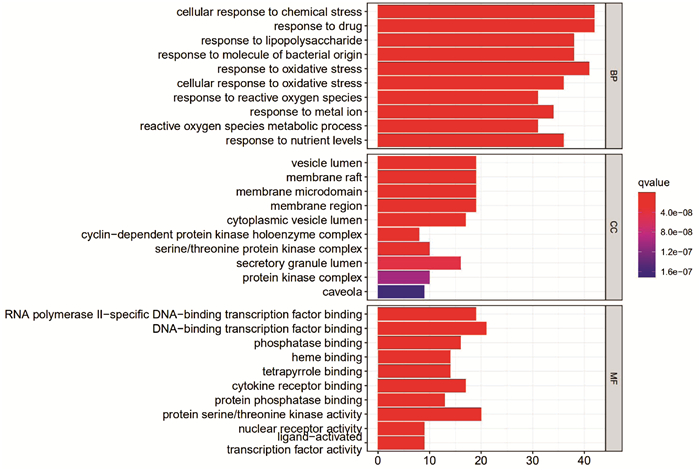
共得到GO富集条目2612条,GO富集条形图主要展示生物过程(BP,共2375个)、细胞组分(CC,共60个)、分子功能(MF,共177个)前10条富集结果(图 2)。KEGG通路分析得到174条富集结果,并绘制KEGG气泡图展示富集通路结果(仅对P值排序后取前30名进行展示,P值越小表明富集越显著,图 3)。在对KEGG结果进行预读后发现,与小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎密切相关的通路有乙型肝炎通路、PI3K-AKT信号通路等。
2.6 潜在活性成分-核心靶点分子对接分析
根据小柴胡汤“活性成分-核心靶点”网络中靶点与成分连接的度值,选取活性化合物中degree排名靠前的主要活性成分槲皮素、山奈酚、汉黄芩素、柚皮素,分别与经拓扑分析筛选后的关键核心靶点MAPK1、RELA、TP53、ESR1进行分子对接。一般认为配体和受体结合能越低结合力越好,结合能≤0 kcal/mol说明两者可以自发结合,结合能≤-5.0 kcal/mol说明有较好的结合力,结合能≤-7.0 kcal/mol说明结合构型具有强烈的活性[10-11]。结果表明以上主要活性成分与关键靶点的结合能均≤-7.0 kcal/mol,展现出良好的结合力(表 3,图 4)。
表 3 关键化合物与核心靶点分子对接有效成分 结合能(kcal/mol) MAPK1 RELA TP53 ESR1 槲皮素(quercetin) -7.4 -7.8 -7.0 -8.6 山奈酚(kaempferol) -7.2 -7.1 -8.1 -7.2 汉黄芩素(wogonin) -9.4 -8.3 -8.9 -7.5 柚皮素(naringenin) -8.6 -7.7 -7.8 -9.1 3. 讨论
小柴胡汤为仲景名方,原方主治少阳病,具有良好的疏肝利胆之效,在临床中防治慢性肝病方面发挥了重要作用[12-13]。近年来运用小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的临床研究[14-16]使用频繁。但目前针对小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的网络药理学与分子层面的研究尚有欠缺。
为深入研究小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的作用机制,本文应用网络药理学的方法,共筛选得到193个活性成分及247个作用靶点,通过构建活性成分-核心靶点相互作用网络可知槲皮素、山奈酚、汉黄芩素、柚皮素等化合物度值较大,对应多个靶点,是小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的主要活性成分。其中槲皮素具有良好的抗炎、抗氧化、抗病毒及抗肝纤维化等作用。研究[17-18]发现,槲皮素能显著降低HBsAg和HBeAg水平,并可抑制人肝癌细胞株HBV抗原分泌和基因组复制,具有显著的抗HBV活性,接近拉米夫定(69%)。乙型肝炎是肝纤维化发生发展的主因之一,肝纤维化可进一步发展成肝硬化,并最终导致危害人类生命、不可逆转的肝细胞癌及肝功能衰竭[19]。槲皮素可通过其抗氧化活性和对NF-κB等信号通路的调节来抑制肝毒性化合物四氯化碳诱导的炎症反应,减弱肝星状细胞的活化并减少自噬,从而达到减少肝脏损伤和预防肝纤维化的目的[20]。由此可见,度值最高(degree:100)且来自小柴胡汤中多味中药(柴胡、甘草、大枣)的活性成分槲皮素在小柴胡汤发挥治疗乙型肝炎的作用机制过程中起着举足轻重的作用。经查阅相关文献发现,富含在柴胡和甘草中的山奈酚[21-23]、黄芩中的汉黄芩素[24-26]、甘草中的柚皮素[27-28]均已被证实具有抗HBV、抗炎、抗肝纤维化、护肝抗癌等作用,与本研究所得主要活性成分作用于乙型肝炎的结果一致。上述主要活性成分均为黄酮类化合物,它们除了具有抗炎、抗病毒等作用,在治疗乙型肝炎的过程中还发挥了抗肝纤维化、护肝抗癌等多种功效,这与中医强调的“未病先防”“既病防变”等理念不谋而合。
通过PPI网络拓扑分析后筛选得到RELA、MAPK1、TP53、ESR1等14个靶点,提示其可能是小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的核心靶标。研究发现在HBV X蛋白(HBx)和HBV介导的肝癌发生的动物模型中,HBx可通过原癌基因RELA与活性DNA脱甲基作用诱导EpCAM表达,由细胞毒性T淋巴细胞分泌的HBx和TNFα激活的RELA在慢性乙型肝炎及其相关肝细胞癌的发病机制中具有重要作用[29]。有研究[30-31]指出在HBV相关肝癌中经常发现肿瘤蛋白p53(TP53)突变,证实HBV感染与肝癌中TP53基因之间表达状态相关的候选单核苷酸多态性和分子途径具有密切关系。HBV是一种性激素应答病毒[32],核受体超家族成员雌激素受体ESR1基因多态性与HBV持续感染显著相关[33]。研究[34]表明,ESR1可以通过调节雌激素稳定在一定的水平来阻止肝纤维化,避免肝细胞炎症损伤,抑制肝细胞凋亡等。小柴胡汤可以作用于雌孕激素受体,充分发挥对肝脏的保护作用。MAPK1、MAPK3、MAPK8、MAPK14等属于MAPK家族, 它们均参与细胞增长、分化、凋亡、免疫及炎症反应等重要生物过程,并在MAPK信号通路中起着举足轻重的作用,已知乙型肝炎及其相关肝细胞癌的发生发展与MAPK信号通路关系密切[35]。此外,这些靶点均对应多个活性成分, 如ESR1对应柚皮素、芒柄花素等89个活性成分,MAPK14对应汉黄芩素、异鼠李素等51个活性成分,这说明小柴胡汤具有多成分、多靶点协同治疗肝炎的作用。
GO功能富集分析结果表明,小柴胡汤中的活性成分可能通过囊腔、膜筏等细胞组分参与氧化应激反应、对脂多糖的反应等生物学过程。这些结果提示小柴胡汤作用于多细胞组分产生不同生物学功能,从而发挥治疗乙型肝炎的作用。KEGG通路分析结果显示,小柴胡汤作用于乙型肝炎的靶点主要涉及乙型肝炎通路、PI3K-AKT信号通路等。其中乙型肝炎通路是本研究预测小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的靶点中富集最多的通路之一,且该通路直接作用于乙型肝炎,在抗HBV感染及抗炎过程中发挥重要作用,进一步提示了本研究的准确性和可靠性。PI3K-AKT信号通路与细胞增殖、周期和凋亡有着密切联系[36-37]。研究[38]发现,几乎所有的病毒都会对PI3K-AKT信号通路进行调控,以调节病毒在感染早期的活力,实现对宿主细胞的感染及介导细胞转化等。在HBV引起的慢性感染性疾病中,HBx可通过激活PI3K-AKT信号通路磷酸化转录因子Bad,抑制caspase 3的活性,进而阻断TGFβ诱导的细胞凋亡[39-40]。此外,PI3K-AKT信号通路的活化同时也是肝细胞癌变的主因之一[41-42]。
根据图 4中的分子对接结果显示,槲皮素与MAPK1上的残基氨基酸LYS-114、ASP-111、GLU-109、MET-108形成氢键作用,山奈酚与RELA上的残基氨基酸GLU-359、GLU-197形成氢键作用,汉芩黄素与TP53上的残基氨基酸THR-97形成氢键作用,柚皮素与ESR1上的残基氨基酸ARG-394、ALA-350、HIS-524形成氢键作用。以上主要活性成分与关键靶点经过分子对接后提示结合能均≤-7.0 kcal/mol,匹配能量较低,说明小分子与大分子结合的构象稳定,结合性好,展现出良好的结合力,进一步验证其可信度,对后续临床及实验研究方向具有重要参考价值。
综上所述,小柴胡汤可能通过槲皮素、山奈酚、汉黄芩素、柚皮素等主要活性成分作用于MAPK1、RELA、TP53、ESR1等关键靶点,通过囊腔、膜筏等细胞组分参与氧化应激反应、对脂多糖的反应等多种生物学过程,激活或抑制乙型肝炎、PI3K-AKT等主要信号通路,产生抗病毒、抑制炎症、调节免疫、抗肝纤维化、护肝抗癌等功效,从而发挥治疗乙型肝炎的作用。本文通过网络药理学结合分子对接的方法,阐释了小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的主要有效成分、作用靶点、相关通路及协同作用的分子机制,有助于从新的角度挖掘小柴胡汤治疗乙型肝炎的潜在价值,为后续进一步生物实验研究与临床应用提供了一定的理论基础。

-
表 1 小柴胡汤部分活性成分信息
MOL ID MOL Name OB DL 来源药物 MOL000354 Isorhamnetin 49.6 0.31 柴胡,甘草 MOL000359 Sitosterol 36.91 0.75 黄芩,甘草 MOL000422 Kaempferol 41.88 0.24 柴胡,人参,甘草 MOL000098 Quercetin 46.43 0.28 柴胡,大枣,甘草 MOL000449 Stigmasterol 43.83 0.76 柴胡,半夏,人参,黄芩,甘草 MOL000358 Beta-sitosterol 36.91 0.75 黄芩,人参,半夏,生姜,甘草 MOL005360 Malkangunin 57.71 0.63 人参,甘草 MOL000787 Fumarine 59.26 0.83 人参,大枣 MOL002714 Baicalein 33.52 0.21 半夏,黄芩 MOL002776 Baicalin 40.12 0.75 柴胡,半夏 MOL002879 Diop 43.59 0.39 黄芩,人参 MOL003896 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone 42.56 0.2 甘草 MOL000497 Licochalcone A 40.79 0.29 甘草 MOL000392 Formononetin 69.67 0.21 甘草 MOL004328 Naringenin 59.29 0.21 甘草 MOL012940 Spiradine A 113.52 0.61 甘草 MOL008034 21302-79-4 73.52 0.77 大枣 MOL008647 Moupinamide 86.71 0.26 大枣 MOL002773 Beta-carotene 37.18 0.58 大枣 MOL000096 (-)-catechin 49.68 0.24 大枣 MOL012940 Spiradine A 113.52 0.78 大枣 MOL006936 10, 13-eicosadienoic 39.99 0.2 半夏 MOL006937 12, 13-epoxy-9-hydroxynonadeca-7, 10-dienoic acid 42.15 0.24 半夏 MOL006957 (3S, 6S)-3-(benzyl)-6-(4-hydroxybenzyl) piperazine-2, 5-quinone 46.89 0.27 半夏 MOL003578 Cycloartenol 38.69 0.78 半夏 MOL006967 Beta-D-ribofuranoside, xanthine-9 44.72 0.21 半夏 MOL006129 6-methylgingediacetate2 48.73 0.32 生姜 MOL001771 Poriferast-5-en-3beta-ol 36.91 0.75 生姜 MOL008698 Dihydrocapsaicin 47.07 0.19 生姜 MOL004609 Areapillin 48.96 0.41 柴胡 MOL013187 Cubebin 57.13 0.64 柴胡 MOL004624 Longikaurin A 47.72 0.53 柴胡 MOL004628 Octalupine 47.82 0.28 柴胡 MOL004644 Sainfuran 79.91 0.23 柴胡 MOL003648 Inermin 65.83 0.54 人参 MOL005308 Aposiopolamine 66.65 0.22 人参 MOL005314 Celabenzine 101.88 0.49 人参 MOL005321 Frutinone A 65.9 0.34 人参 MOL005356 Girinimbin 61.22 0.31 人参 MOL000173 Wogonin 30.68 0.23 黄芩 MOL002915 Salvigenin 49.07 0.33 黄芩 MOL002927 Skullcapflavone Ⅱ 69.51 0.44 黄芩 MOL002932 Panicolin 76.26 0.29 黄芩 MOL002934 Neobaicalein 104.34 0.44 黄芩 表 2 小柴胡汤度值前10位化学成分基本信息
NO. MOL ID MOL Name 化学式 Degree 来源药物 1 MOL000098 槲皮素(quercetin) C15H10O7 100 柴胡,甘草,大枣 2 MOL000422 山奈酚(kaempferol) C15H10O6 32 柴胡,甘草 3 MOL000173 汉黄芩素(wogonin) C16H12O5 31 黄芩 4 MOL004328 柚皮素(naringenin) C15H12O5 25 甘草 5 MOL000392 芒柄花素(formononetin) C16H12O4 20 甘草 6 MOL000497 甘草酮(licochalcone A) C21H22O4 20 甘草 7 MOL002714 黄芩素(baicalein) C15H10O5 19 黄芩,半夏 8 MOL000354 异鼠李素(isorhamnetin) C16H12O7 18 柴胡,甘草 9 MOL003896 7-甲氧基-2-甲基异黄酮
(7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone)C17H13NO5 18 甘草 10 MOL002773 β-胡萝卜素(beta-carotene) C40H56 18 大枣 表 3 关键化合物与核心靶点分子对接
有效成分 结合能(kcal/mol) MAPK1 RELA TP53 ESR1 槲皮素(quercetin) -7.4 -7.8 -7.0 -8.6 山奈酚(kaempferol) -7.2 -7.1 -8.1 -7.2 汉黄芩素(wogonin) -9.4 -8.3 -8.9 -7.5 柚皮素(naringenin) -8.6 -7.7 -7.8 -9.1 -
[1] SONG QW, LI KL, ZHANG GM, et al. Spatial analysis on hepatitis B in China, 2005-2014[J]. Chin J Vacc Immun, 2015, 21(6): 601-605. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2009.12.003.宋全伟, 李克莉, 张国民, 等. 中国2005~2014年乙型病毒性肝炎空间流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2015, 21(6): 601-605. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2009.12.003. [2] YAN LB, TANG H. Progression and prospect in the diagnosis and treatment of chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Practical Internal Med, 2016, 13(2): 5-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2016.02.002.严丽波, 唐红. 慢性乙型肝炎诊治进展和展望[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2016, 13(2): 5-9. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2016.02.002. [3] LIU L, LI L. Interpretation of 2019 guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Trop Dis Parasitol, 2020, 18(2): 75-80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2302.2020.02.003.刘磊, 李磊. 《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》(2019年版)解读与思考[J]. 热带病与寄生虫学, 2020, 18(2): 75-80. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2302.2020.02.003. [4] ZHAO LR, DOU XG. Withdrawal criteria of antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B[J]. Mod Med Health, 2019, 35(22): 3411-3413. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2019.22.002.赵连荣, 窦晓光. 慢性乙型肝炎抗病毒治疗的停药标准[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2019, 35(22): 3411-3413. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5519.2019.22.002. [5] QI XM, LI Y, QIN XM. Research Progress on clinical application and pharmacological action of Xiaochaihu Decoction[J]. J Shanxi College Tradit Chin Med, 2007, 8(3): 59-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0258.2007.03.040.柒小梅, 李英, 秦雪梅. 小柴胡汤临床应用与药理作用研究进展[J]. 山西中医学院学报, 2007, 8(3): 59-60. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0258.2007.03.040. [6] ZHOU WX, CHENG XR, ZHANG YX. Network pharmacology- a new philosophy for understanding of drug action and discovery of new drugs[J]. Chin J Pharmacol Toxicol, 2012, 26(1): 4-9. DOI: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2012.01.002.周文霞, 程肖蕊, 张永祥. 网络药理学: 认识药物及发现药物的新理念[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2012, 26(1): 4-9. DOI: 10.3867/j.issn.1000-3002.2012.01.002. [7] LIU ZH, SUN XB. Network pharmacology: New opportunity for the modernization of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica, 2012, 47(6): 696-703. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2012.06.001.刘志华, 孙晓波. 网络药理学: 中医药现代化的新机遇[J]. 药学学报, 2012, 47(6): 696-703. DOI: 10.16438/j.0513-4870.2012.06.001. [8] WANG Y, ZHANG J, XIN FR, et al. Prediction of target and pathway of berberine in the treatment of atrial fibrillation based on network pharmacology[J]. Traum Crit Med, 2021, 9(3): 165-170. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2021.03.01.王洋, 张建, 辛芳冉, 等. 基于网络药理学预测小檗碱治疗心房颤动作用靶点及通路[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学, 2021, 9(3): 165-170. DOI: 10.16048/j.issn.2095-5561.2021.03.01. [9] YE DY. Introduction to computer aided drug design[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 52-56.叶德永. 计算机辅助药物设计导论[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004: 52-56. [10] XIE LH, LIN XY, HE P, et al. Research on Shuanghuanglian Oral Liquid for treatment of COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology[J]. J Tradit Chin Med Univ Hunan, 2020, 40(9): 1123-1131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2020.09.016.谢丽华, 蔺晓源, 何飘, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接法探寻双黄连口服液治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎的有效成分及机制研究[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2020, 40(9): 1123-1131. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2020.09.016. [11] ZHOU WJ, ZHANG M, YAN YC, et al. Molecular mechanism of Huoxiang(Pogostemonis Herba) in treatment of corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19) based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. J Pract Trad Chin Int Med, 2020, 34(9): 1-4. DOI: 10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.Z20200366.周文静, 张萌, 闫宇晨, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接探讨藿香防治新型冠状病毒肺炎的分子机制[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 1-4. DOI: 10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.Z20200366. [12] LU TT, ZHAO GP. Advances in mechanisms of Xiao Chaihu Tang preventing and treating liver diseases[J]. World Chin J Dig, 2008, 16(9): 971-974. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3079.2008.09.012.陆婷婷, 赵国平. 小柴胡汤防治肝病机制研究进展[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2008, 16(9): 971-974. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3079.2008.09.012. [13] WU FR, NING LJ, ZHOU R. Protective effects of Xiaochaihu Decoction on chemical hepatic fibrosis in mice[J]. Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 25(5): 481-488. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2020.05.001.吴芙蓉, 宁丽娟, 周冉. 小柴胡汤对化学性肝纤维化小鼠的保护作用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2020, 25(5): 481-488. DOI: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2020.05.001. [14] XU T, CHEN X. Clinical application of Xiaochaihu Decoction in digestive system diseases[J/CD]. J Cardiov Dis Integr Tradit Western Med, 2020, 8(29): 153, 156. DOI: 10.16282/j.cnki.cn11-9336/r.2020.29.106.徐仝, 陈旭. 小柴胡汤在消化系统疾病中的临床应用[J/CD]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2020, 8(29): 153, 156. DOI: 10.16282/j.cnki.cn11-9336/r.2020.29.106. [15] SHI HJ. Clinical efficacy of entecavir combined with Xiaochaihu Decoction in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. Shenzhen J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2020, 30(15): 40-42. DOI: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2020.15.020.师会杰. 恩替卡韦联合小柴胡汤治疗慢性乙型肝炎肝硬化临床疗效[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志, 2020, 30(15): 40-42. DOI: 10.16458/j.cnki.1007-0893.2020.15.020. [16] ZHAI XZ. Clinical observation of Xiaochaihu Decoction combined with entecavir in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B with liver depression and spleen deficiency[J]. J Pract Tradit Chin Med, 2020, 36(1): 39-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYAO202001034.htm翟雪珍. 小柴胡汤加减联合恩替卡韦治疗慢性乙型病毒性肝炎肝郁脾虚型疗效观察[J]. 实用中医药杂志, 2020, 36(1): 39-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYAO202001034.htm [17] CHENG Z, SUN G, GUO W, et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by quercetin in human hepatoma cell lines[J]. Virol Sin, 2015, 30(4): 261-268. DOI: 10.1007/s12250-015-3584-5. [18] PARVEZ MK, AL-DOSARI MS, ARBAB AH, et al. Bioassay-guided isolation of anti-hepatitis B virus flavonoid myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside along with quercetin from Guiera senegalensis leaves[J]. Saudi Pharm J, 2020, 28(5): 550-559. DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.03.006. [19] SAMUEL VT, SHULMAN GI. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a nexus of metabolic and hepatic diseases[J]. Cell Metab, 2018, 27(1): 22-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.002. [20] WU L, ZHANG Q, MO W, et al. Quercetin prevents hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation and reducing autophagy via the TGF-β1/Smads and PI3K/Akt pathways[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 9289. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-09673-5. [21] CHEN YH, ZHOU KY, YUAN HY. Research progress on pharmacodynamics of kaempferol[J]. Guangdong Med, 2010, 31(8): 1064-1066. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2010.08.058.陈育华, 周克元, 袁汉尧. 山奈酚药效的研究进展[J]. 广东医学, 2010, 31(8): 1064-1066. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2010.08.058. [22] KIM JK, PARK SU. Recent studies on kaempferol and its biological and pharmacological activities[J]. EXCLI J, 2020, 19: 627-634. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/342243289_Recent_studies_on_kaempferol_and_its_biological_and_pharmacological_activities/download [23] WANG ZH, LIANG T, LI T, et al. Effect of kaempferol on growth and apoptosis of human hepatoma cell line Huh7[J]. Guangdong Med, 2014, 35(2): 192-194. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2014.02.009.王铮华, 梁统, 李涛, 等. 山奈酚对人肝癌细胞Huh7生长及凋亡的影响[J]. 广东医学, 2014, 35(2): 192-194. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2014.02.009. [24] HUANG RL, CHEN CC, HUANG HL, et al. Anti-hepatitis B virus effects of wogonin isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis[J]. Planta Med, 2000, 66(8): 694-698. DOI: 10.1055/s-2000-9775. [25] GUO Q, ZHAO L, YOU Q, et al. Anti-hepatitis B virus activity of wogonin in vitro and in vivo[J]. Antiviral Res, 2007, 74(1): 16-24. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2007.01.002. [26] SI LL, LI L, CHEN RJ, et al. Combination inhibitory effect of baicalein and wogonin on entecavir-resistant HBV and the optimal ratio between the two components[J]. Shandong Med J, 2019, 59(36): 22-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.36.006.思兰兰, 李乐, 陈容娟, 等. 黄芩素和汉黄芩素联合应用对恩替卡韦耐药乙型肝炎病毒的抑制作用及最佳配比观察[J]. 山东医药, 2019, 59(36): 22-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2019.36.006. [27] REHMAN K, KHAN Ⅱ, AKASH M, et al. Naringenin downregulates inflammation-mediated nitric oxide overproduction and potentiates endogenous antioxidant status during hyperglycemia[J]. J Food Biochem, 2020. DOI: 10.1111/jfbc.13422.[Online ahead of print] [28] LI PB, WANG YG, WU H, et al. An overview of pharmacological actions of naringin and its aglycone naringenin on respiratory diseases[J]. J PHARM Research Med, 2020, 39(5): 249-255. DOI: 10.13506/j.cnki.jpr.2020.05.001.李沛波, 王永刚, 吴灏, 等. 柚皮苷及其苷元柚皮素的呼吸系统药理作用研究概述[J]. 药学研究, 2020, 39(5): 249-255. DOI: 10.13506/j.cnki.jpr.2020.05.001. [29] FAN H, ZHANG H, PASCUZZI PE, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein induces EpCAM expression via active DNA demethylation directed by RelA in complex with EZH2 and TET2[J]. Oncogene, 2016, 35(6): 715-726. DOI: 10.1038/onc.2015.122. [30] YU L, LIU X, HAN C, et al. XRCC1 rs25487 genetic variant and TP53 mutation at codon 249 predict clinical outcomes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: A cohort study for 10 years' follow up[J]. Hepatol Res, 2016, 46(8): 765-774. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12611. [31] ZHOU HB, HU HP. Challenges in precise treatment for primary liver cancer based on gene mutation[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(7): 1209-1210. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.07.001.周华邦, 胡和平. 基于基因突变的原发性肝癌精准治疗的挑战[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(7): 1209-1210. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.07.001. [32] WANG SH, CHEN PJ, YEH SH. Gender disparity in chronic hepatitis B: Mechanisms of sex hormones[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 30(8): 1237-1245. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12934. [33] GAO YF, WEI SF, ZHANG YF, et al. Association of estrogen receptor α polymorphisms with chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2009, 12(2): 95-97, 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2009.02.005.郜玉峰, 魏少峰, 张亚飞, 等. 雌激素受体基因α多态性与乙型肝炎病毒感染慢性化的相关性研究[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2009, 12(2): 95-97, 100. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2009.02.005. [34] REN W, WANG X, LI P, et al. Association of Pvu Ⅱ and Xba I polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) gene with the chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Prog Mod Biomed, 2018, 18(24): 4607-4613. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2018.24.002.任雯, 王霞, 李平, 等. 雌激素受体α(ESR1)基因PvuⅡ和XbaⅠ位点基因多态性与HBV慢性感染的相关性研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2018, 18(24): 4607-4613. DOI: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2018.24.002. [35] MA X, XIA W. Research progress on signaling pathways of Chinese medicine in inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis of hepatoma carcinoma cells[J]. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med, 2018, 52(8): 98-101. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2018.06.026.马星, 夏伟. 中药抗肝癌细胞增殖和诱导细胞凋亡的信号通路研究进展[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2018, 52(8): 98-101. DOI: 10.16305/j.1007-1334.2018.06.026. [36] YU ZH, CAI M, XIANG J, et al. PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to neuroprotective effect of Tongxinluo against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2016, 181: 8-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.01.028. [37] SHI J, ZHENG L, LIN Z, et al. Study of pharmacokinetic profiles and characteristics of active components and their metabolites in rat plasma following oral administration of the water extract of Astragali radix using UPLC-MS/MS[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 169: 183-194. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.04.019. [38] COORAY S. The pivotal role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signal transduction in virus survival[J]. J Gen Virol, 2004, 85(Pt 5): 1065-1076. DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.19771-0. [39] KANG-PARK S, IM JH, LEE JH, et al. PTEN modulates hepatitis B virus-X protein induced survival signaling in Chang liver cells[J]. Virus Res, 2006, 122(1-2): 53-60. DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2006.06.010. [40] SHIH WL, KUO ML, CHUANG SE, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein inhibits transforming growth factor-beta -induced apoptosis through the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(33): 25858-25864. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M003578200. [41] LIU RD, RUAN LW. PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and viral infection[J]. Biot Bulletin Med, 2013, 6: 53-62. DOI: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2013.06.023.刘荣雕, 阮灵伟. PI3K-Akt信号通路与病毒感染[J]. 生物技术通报, 2013, 6: 53-62. DOI: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2013.06.023. [42] LIU Y, WEI J, XIAO B, et al. Effect of hepatitis B X-interacting protein on proliferation and migration of hepatoma cells by regulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chin J Immunol, 2020, 36(7): 837-841. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.07.014.刘阳, 魏俊, 肖贝, 等. 乙型肝炎病毒X蛋白结合蛋白可能通过PI3K/Akt信号通路影响肝癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(7): 837-841. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.07.014. 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 赵越,王文萍,李晓斌,王华伟,曹莹. 小柴胡汤在恶性肿瘤全程管理中的应用研究进展. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2024(12): 219-231 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 王慧丽,秦文昊,杨档档,宁雅倩,林杉,代崧霖,胡冰. 黄连素对肝脏疾病的防治作用及其机制. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2024(11): 2326-2331 .  本站查看
本站查看3. 王淑惠,刘泽干,黄小凤,雷攀,王莉博,江明珠,蔡华,杜士明. 柴胡4种活性成分的体外抗氧化作用. 医药导报. 2023(09): 1318-1325 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 马利节,朱晓骏,林佳成,王芳,孙学华,高月求. 基于网络药理学和动物实验研究灵猫方治疗慢性乙型肝炎的机制. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2022(07): 1503-1508 .  本站查看
本站查看5. 黄武明,谢林发. 小柴胡汤加味联合恩替卡韦片治疗慢性乙型肝炎临床研究. 河南中医. 2022(09): 1305-1308 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(6)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3600 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3600 KB)

 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术





