SpyGlass单人操作胆道镜系统对胆道疾病的诊治价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.10.027
Value of SpyGlass single-operator choledochoscopy system in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with biliary tract diseases
-
摘要:
目的 评估SpyGlass单人操作胆道镜系统对不明原因的胆管狭窄、复杂胆管结石及其他胆道疾病的诊疗价值。 方法 回顾性收集2017年12月—2020年6月在南京医科大学第二附属医院行SpyGlass下诊治胆道疾病患者的临床资料。胆管狭窄患者在SpyGlass引导下对病灶部位进行充分可视化,必要时取活检;胆管结石患者行SpyGlas胆道镜直视下激光碎石;胆囊病变患者通过SpyGlass辅助下超选胆囊管。分析SpyGlass系统诊治的敏感度、特异度、准确度、碎石成功率、结石清除率、操作成功率以及并发症发生率。 结果 共有58例患者进行SpyGlass操作。44例(76%)用于评估性质不明的胆道狭窄,SpyGlass视觉印象的诊断敏感度为92%(24/26),特异度为94%(17/18),准确度为93%(41/44),SpyBite直视活检的诊断敏感度为71%(15/21),特异度为92%(11/12),准确度为79%(26/33);8例(14%)用于胆管结石的治疗,碎石成功率为83%(5/6),结石清除率为88%(7/8);5例(9%)用于SpyGlass下引导导丝超选胆囊管,操作成功率为80%(4/5);1例(1%)用于肝移植术后合并胆总管结石的辅助取石及胆管吻合口狭窄的治疗。术后共有5例(9%)患者出现并发症。 结论 SpyGlass胆道镜系统能准确、安全、有效地应用于不明原因的胆管狭窄、复杂胆管结石以及其他胆道疾病的诊治。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the value of SpyGlass single-operator choledochoscopy system in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with unexplained biliary stricture, complex bile duct stones, or other biliary tract diseases. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of the patients with biliary tract diseases who were diagnosed and treated with SpyGlass in The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from December 2017 to June 2020. For the patients with biliary stricture, the biliary lesions were fully visualized under the guidance of SpyGlass, and SpyBite biopsy was performed if necessary; the patients with bile duct stones were treated with SpyGlass-guided direct-view laser lithotripsy; for the patients with gallbladder disease, the cystic duct was superselected with the assistance of SpyGlass. The SpyGlass system was analyzed in terms of its sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy rate in diagnosis and treatment, lithotripsy success rate, stone clearance rate, procedure success rate, and incidence rate of complications. Results A total of 58 patients underwent SpyGlass procedure. SpyGlass was used to evaluate biliary stricture of unknown nature in 44 (76%) patients; SpyGlass visual impression had a diagnostic sensitivity of 92% (24/26), a specificity of 94% (17/18), and an accuracy of 93% (41/44), and SpyBite biopsy had a diagnostic sensitivity of 71% (15/21), a specificity of 92% (11/12), and an accuracy of 79% (26/33). SpyGlass was used for the treatment of bile duct stones in 8 patients (14%), with a lithotripsy success rate of 83% (5/6) and a stone clearance rate of 88% (7/8). A guide wire under the SpyGlass system was to superselect the cystic duct in 5 patients (9%), with a procedure success rate of 80% (4/5). In one patient (1%), SpyGlass was used to assist the removal of common bile duct stones after liver transplantation and the treatment of bile duct anastomotic stricture. A total of 5 patients (9%) experienced complications after surgery. Conclusion The SpyGlass choledochoscopy system is accurate, safe, and effective in the diagnosis and treatment of unexplained biliary stricture, complex bile duct stones, and other biliary tract diseases. -
Key words:
- SpyGlass /
- Biliary Tract Diseases /
- Diagnosis /
- Therapeutics
-
目前,经内镜逆行胰胆管造影(ERCP)已成为胆胰管疾病的主要诊疗手段,但其对于不明原因胆管狭窄及复杂胆管结石患者存在一定的局限性。2007年,Chen[1]报道了第一代SpyGlass系统应用于胆道疾病中的可能性,证实了其腔内可视性及靶向活检的可行性。由于其存在工作孔径较小、光纤易受损害、图像质量欠佳等缺陷,未能在临床上广泛应用。近年来,随着内镜器械的逐步发展,第二代SpyGlass系统的问世有效地弥补了以上不足,其具有即插即用、图片成像质量高、更大的工作通道、双注水孔径的优点,为胆胰疾病的患者带来诊断和治疗上的益处[2-3]。国外有较多文献报道第二代SpyGlass系统在胆道疾病中的诊断及治疗效果,但我国由于开展单位较少,相关文献报道并不多。本院自2017年应用该系统对胆管狭窄及胆管结石的患者进行诊治,取得较好的疗效,现报道如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2017年12月—2020年6月在本院行SpyGlass下诊治胆胰管疾病的患者,通过电子病历及内镜系统查询患者资料,包括性别、年龄、临床症状、实验室检查、诊断、操作时长、并发症等。纳入标准: 接受第二代SpyGlass系统进行胆道相关疾病诊断或治疗的患者。排除标准: (1)年龄<18岁; (2)妊娠、哺乳期、资料不全的患者; (3)合并严重血液系统疾病; (4)合并胆道广泛性出血或管壁新鲜坏死; (5)合并急性梗阻性化脓性胆管炎。所有SpyGlass胆道镜系统及内镜相关操作均由本院消化中心有丰富临床经验的医师完成。
1.2 操作器械
Olympus公司JF240或JF260十二指肠侧视镜,相关附件包括造影导管、导丝、针形及弓形切开刀、鼻胆引流管、胆道扩张球囊、取石网篮、碎石网篮、胆管塑料支架及胆道全覆膜金属支架等。SpyGlass内镜直视系统(Boston Scientific Corp, Natick, MA, USA)、U-100 Plus双频激光仪及相关消耗性附件如SpyBite活检钳、光纤摄像头、钬激光碎石探头等。
1.3 操作方法
1.3.1 术前准备
常规ERCP术前准备,术前禁食水12 h,便于操作。
1.3.2 操作过程
所有患者术中均匀氧气吸入及心电监护。在行SpyGlass前根据术中情况行内镜下乳头括约肌切开术(endoscopic sphincterotomy, EST)及内镜下柱状气囊扩张术(endoscopic papillary balloon dilation, EPBD)。将十二指肠镜送至十二指肠降部,经十二指肠乳头插入胆管,造影观察胆道系统,显示病变轮廓,留置导丝,SpyGlass系统传送导管连同光纤摄像头经十二指肠镜的工作孔道置入,并缓慢送至胆管病变部位进行直视下观察,拔除导丝,对病灶处进行诊断及治疗。对于胆道结石的患者,将预装激光光纤的SpyGlass外套管推送至结石处,直视下将光纤末端对准结石表面,启用U-100 Plus双频激光仪进行碎石,直至结石完全碎裂;对于性质不明的胆道狭窄患者,根据患者意愿及术中情况通过活检孔道置入SpyBite活检钳对病灶处进行直视下活检,观察胆道无出血后退镜;对于胆囊病变的患者,通过SpyGlass辅助下超选胆囊管,循导丝插入柱状扩张球囊扩张胆囊管,退出球囊后置入胆囊冲洗管或鼻胆囊引流管。
1.3.3 术后处理
术后禁食48 h,予补液、抑酸、预防感染等对症疗法,术后2 h和24 h监测血尿淀粉酶及血常规,同时注意观察生命体征、腹部体征及鼻胆管引流的量、颜色等,及时进行对症处理。
1.4 观察指标
主要观察指标是病变部位在SpyGlass胆道镜系统下达到治疗或诊断目的,包括碎石成功率、结石清除率、操作成功率以及SpyGlass引导下诊断良恶性胆管狭窄的敏感度、特异度和准确度。次要观察指标是并发症发生率的评估,包括急性胰腺炎、高淀粉酶血症、出血、急性胆管炎及胆道穿孔等。活检样本由本院病理科2位有丰富临床经验的病理医生审查。
1.5 随访情况
对所有患者进行半年以上的随访。若在随访过程中出现恶性肿瘤征象,如影像学检查发现肿瘤转移性表现或实验室检查提示肿瘤指标的持续性增长,判别为恶性狭窄。最终诊断是由病理诊断、影像学检查、实验室检查及随访情况综合判断。
1.6 伦理学审查
本研究方案经由南京医科大学第二附属医院伦理委员会审批,批号:[2021]-KY-120-01。患者在术前均被告知手术风险并签署知情同意书。
1.7 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0进行数据分析。符合正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示。计算SpyGlass视觉印象和直视下活检对良恶性胆管狭窄鉴别的敏感度、特异度和准确度。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
本研究共纳入了58例患者,其中男30例,女28例,年龄23~84岁,平均(63±13)岁;总操作时间29.9~189 min,平均(71±36) min。所有患者均行EST和EPBD,大部分(71%)患者以腹痛和皮肤黄染为主要临床表现,且多数(57%)患者合并基础疾病。58例患者中,44例(76%)采用SpyGlass系统诊断性质不明的胆道狭窄。最终,通过病理诊断、影像学及实验室检查、随访发现等综合诊断为良性狭窄的患者有18例,诊断为恶性狭窄的有26例,包括壶腹部肿瘤4例(15%), 十二指肠乳头腺癌2例(8%), 胆管癌13例(50%), 胰腺癌1例(4%), 肝癌2例(8%),胆囊癌多发转移1例(4%),胆管乳头状黏液腺癌1例(4%),胆管乳头状黏液腺瘤1例(4%),胰腺导管内乳头状黏液腺瘤1例(4%)。此外,14例患者进行SpyGlass胆道镜系统治疗,包括8例(57%)胆总管取石,5例(36%)辅助下超选胆囊管,1例(7%)肝移植术后吻合口狭窄合并胆总管结石的治疗。
2.2 SpyGlass系统在胆管狭窄中的诊断情况
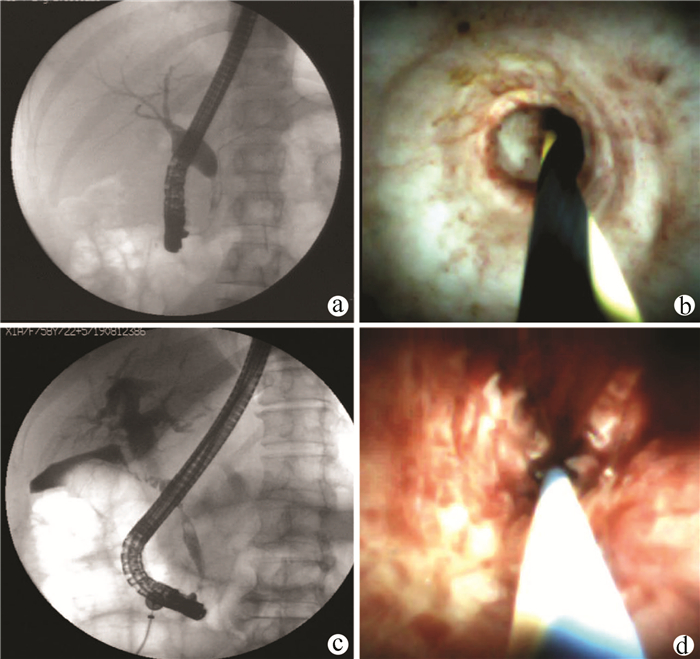
共44例胆管狭窄的患者进行SpyGlass胆道镜系统诊断,所有患者均行狭窄处球囊扩张,放置胆管或胰管支架的患者有23例(52%)。44例胆管狭窄的患者中,16例术中直视下考虑为炎性狭窄,表现为胆管内表面结构光滑、呈细颗粒样、无新生血管或肿块、表面发白并呈皱襞样集中;28例术中直视下考虑为恶性狭窄,表现为胆管内结节样或乳头状隆起、表面见扭曲扩张或粗细不均的血管、易自发性出血。共有33例患者行胆道镜直视下(SpyBite)活检,术后病理提示:良性病变12例,恶性病变20例,恶性病变的患者有8例经过外科手术病理证实,此外,1例患者因术中病变组织取材不充分,在随访过程中出现与恶性肿瘤相一致的疾病进展(肿瘤指标持续性升高及肿块持续性增长),诊断为恶性狭窄。在对11例未取活检患者的随访过程中,2例患者后续行外科手术治疗,术后病理为壶腹部中低分化腺癌和胆管绒毛状腺癌,1例患者在随访过程中影像学资料证实为转移性肿瘤,其余患者在随访过程中均未发现狭窄处进展。SpyGlass视觉印象的诊断敏感度为92%(24/26),特异度为94%(17/18),准确度为93%(41/44),SpyBite直视活检的诊断敏感度为71%(15/21),特异度为92%(11/12),准确度为79%(26/33)。图 1展示胆管良恶性狭窄的SpyGlass镜下图片。视频1和2(附录1和2)分别展现良性和恶性胆管狭窄的镜下过程。
2.3 SpyGlass系统在胆管结石中的治疗情况
共8例患者接受SpyGlass用于胆管结石的治疗,其中多数(6/8,75%)位于远端胆总管,25%(2/8)在左肝内胆管中。所有胆管结石的患者均被归类为困难取石病例。8例患者均顺利将SpyGlass激光探头置入胆道对准结石,6例患者采用狄激光碎石,5例患者的结石被碎成多块大小不等结石,随后予网篮或取石球囊取石,1例患者的结石表面呈裂纹状但未能碎裂,随访过程中未再行内镜下取石术。其余患者均取石成功,总碎石成功率为83%(5/6),总结石清除率为88%(7/8)。
2.4 SpyGlass系统在其他胆道疾病中的治疗情况
5例患者行SpyGlass下引导导丝超选胆囊管,其中2例系胆总管结石合并胆囊结石患者,3 d前均行ERCP胆管下段取石术,此次SpyGlass辅助下超选至胆囊管,循导丝置入胆囊冲洗管,冲洗出胆囊内结石,操作成功率为100%。另外3例患者因急性胆囊炎行SpyGlass下辅助胆囊减压引流,1例患者因胆囊管开口角度较大,多次尝试未能深插入胆囊管,总操作成功率为80%(4/5)。
1例患者系肝移植术后吻合口狭窄合并胆总管结石,予SpyGlass胆道镜系统激光碎石,取石网篮取出,置入两枚塑料胆管支架,术后恢复良好,无结石残余。
2.5 并发症发生情况
术后共有5例(9%)患者出现不同程度并发症,3例出现高淀粉酶血症,予保守治疗后好转;1例出现急性胰腺炎,予禁食、抑酶后缓解;1例出现轻度急性胆管炎,经抗感染治疗后得到控制。无穿孔、出血等其他并发症发生。
3. 讨论
SpyGlass系统的问世为部分胆道疾病患者提供了新的诊疗策略,在临床中发挥了越来越重要的作用。据文献[4-5]报道,该系统已逐渐应用于以下临床范围中:难治性胆石症的治疗;残余结石碎片的治疗;胆管癌及壶腹部肿瘤的分期;胆管狭窄的诊治;原发性硬化性胆管炎的评估;胆道出血的诊断;插管困难者直视下导丝超选;胆胰管异物/支架的取出;肝移植术后并发症的评估与治疗;胰腺导管内乳头黏液性肿瘤、狭窄性病变以及结石的诊治;胆囊的减压引流;胆囊结石的治疗;妊娠妇女的无射线胆道取石;肿瘤的射频消融治疗等。
既往对于胆管狭窄性质的诊断多数依靠于ERCP下细胞刷检和X线下活检,但因其无法直视下操作易发生出血、穿孔等并发症,敏感度约为45%和48%,即使将这两项技术结合使用时,敏感度仅提高到59.4%[6]。近年来,多项研究[7-9]表明SpyGlass直视化系统在诊断恶性胆管狭窄的敏感度高达97%,特异度高达100%,具有较高的准确度。Sun等[10]和Navaneethan等[11]对胆管狭窄的患者进行SpyGlass直视下活检,提示SpyBite直视活检的诊断敏感度为60%~69%,特异度为98%。本研究中共44例患者应用第二代SpyGlass系统进行胆道狭窄性质的判别,诊断为恶性狭窄的敏感度为92%,特异度为94%,操作成功率为100%,这与既往的研究结果相类似。de Oliveira等[12]纳入了6篇关于SpyGlass系统诊断胆管狭窄的文献进行系统综述,结果同样表明SpyGlass总体印象下具有较高的敏感度(94%)和特异度(95%)。作者注意到操作过程中SpyGlass活检钳很容易受损,作者的经验是在进行SpyBite活检时,动作一定要轻柔,当活检钳伸至十二指肠乳头附近时,因角度问题活检钳无法继续送至胆管内,此时需推送SpyGlass胆道镜,以便活检钳可以顺利进入胆管,减少或避免活检钳的损伤。
SpyGlass系统对于复杂或困难胆管结石的处理也同样被证实为是一种安全有效的治疗手段。困难结石的特征通常包括结石的大小(>1.5 cm)、形状(铸形结石)、数量(≥ 3枚)、位置(肝内胆管或胆囊管)以及解剖因素(S型胆总管、胆管狭窄、结石嵌顿、成角<135°)等,这些难治性结石往往不能通过常规ERCP方式成功取石[13]。2015年发表的关于SpyGlass胆道镜检查的亚洲专家共识[14]中提出以下建议:在常规取石失败或对于困难结石者,推荐采用胆道镜辅助下的腔内碎石术(电力液压或激光)。先前的研究报道第二代SpyGlass系统在治疗困难胆管结石的成功率为86%~100%[15],相比ERCP下体外冲击波碎石的成功率(64.4%)大大提高[16]。目前临床上主要选择Spyglass直视下液电碎石或激光碎石来处理胆总管复杂结石,两者在碎石率及并发症发生率上无明显差异,但激光碎石一般产生较小的热效应,对胆道组织及胆管壁的损伤相对较轻,采用激光碎石可能会更加安全高效[17]。Bokemeyer等[18]近期发表的一个单中心回顾性研究,纳入了75例胆管结石的患者,使用SpyGlass系统一次取石成功率约为85%,其中15%的患者需要二次取石,激光取石和液电取石具有相似的成功率(66% vs 68%)。本研究均采用狄激光碎石,碎石成功率为83%,取石成功率为88%,与国内外文献相符。
本研究中共有9%的患者出现不同程度的并发症,经对症治疗后均好转。既往文献报道SpyGlass的操作并发症发生率为7%~11%,ERCP相关并发症为2.9%,且SpyGlass操作后胆管炎发生率也较ERCP高(1.0% vs 0.2%),这可能是因为SpyGlass操作期间予胆管内冲洗导致细菌逆行,尤其在胆管狭窄或胆管结石易引起液体潴留的患者中更为明显[19-21]。研究[8]表明SpyGlass术前常规使用抗生素预防感染可能会降低胆管炎的发生率。因此对于预计手术时间较长的患者,术前可预防性使用抗生素,术中予间断性生理盐水冲洗,以减少胆管炎的发生率。关于SpyGlass操作的成本效益也是患者及内镜医师一直关注的问题,有研究[22-23]比较了用于诊断原发性硬化性胆管炎引起的胆管狭窄导致胆管癌的5种不同技术的成本效益,使用蒙特卡洛模拟来评估结果,提示SpyGlass镜下活检是最经济有效的诊断方式。
总之,SpyGlass系统具备微创、直视化、安全、高效、成功率高等优势,已逐步成为胆道疾病诊治的重要手段。准确选择SpyGlass系统的适应证能够为患者及医师减少不必要的操作与费用,在患者的精确诊断及安全治疗方面发挥了关键作用。建立标准而完整的视觉化分类系统仍是亟需解决的问题。当然,本研究也存在一定的局限性,是回顾性研究且样本量较小,未来仍需大样本、多中心的试验来进一步证实。

-
[1] CHEN YK. Preclinical characterization of the Spyglass peroral cholangiopancreatoscopy system for direct access, visualization, and biopsy[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2007, 65(2): 303-311. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.07.048. [2] DERDEYN J, LALEMAN W. Current role of endoscopic cholangioscopy[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2018, 34(5): 301-308. DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000457. [3] XU W, MIAO L, WANG ZF, et al. Application of SpyGlassTM DS Direct Visualization System in the diagnosis and treatment of biliary tract diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36(11): 2626-2629. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.052.徐雯, 苗龙, 王正峰, 等. SpyGlassTM DS直视化系统在胆道疾病诊疗中的应用[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(11): 2626-2629. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.052. [4] KARAGYOZOV P, BOEVA I, TISHKOV I. Role of digital single-operator cholangioscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of biliary disorders[J]. World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2019, 11(1): 31-40. DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i1.31. [5] YODICE M, CHOMA J, TADROS M. The expansion of cholangioscopy: Established and investigational uses of SpyGlass in biliary and pancreatic disorders[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2020, 10(3): 132. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10030132. [6] NAVANEETHAN U, NJEI B, LOURDUSAMY V, et al. Comparative effectiveness of biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015, 81(1): 168-176. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.017. [7] SHAH RJ, RAIJMAN I, BRAUER B, et al. Performance of a fully disposable, digital, single-operator cholangiopancreatoscope[J]. Endoscopy, 2017, 49(7): 651-658. DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-106295. [8] TUROWSKI F, HVGLE U, DORMANN A, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic single-operator cholangiopancreatoscopy with SpyGlassDSTM: Results of a multicenter retrospective cohort study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2018, 32(9): 3981-3988. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-018-6141-0. [9] LENZE F, BOKEMEYER A, GROSS D, et al. Safety, diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic efficacy of digital single-operator cholangioscopy[J]. United European Gastroenterol J, 2018, 6(6): 902-909. DOI: 10.1177/2050640618764943. [10] SUN X, ZHOU Z, TIAN J, et al. Is single-operator peroral cholangioscopy a useful tool for the diagnosis of indeterminate biliary lesion? A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015, 82(1): 79-87. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.12.021. [11] NAVANEETHAN U, HASAN MK, LOURDUSAMY V, et al. Single-operator cholangioscopy and targeted biopsies in the diagnosis of indeterminate biliary strictures: A systematic review[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2015, 82(4): 608-614. e2. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.04.030. [12] de OLIVEIRA P, DE MOURA D, RIBEIRO IB, et al. Efficacy of digital single-operator cholangioscopy in the visual interpretation of indeterminate biliary strictures: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34(8): 3321-3329. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-020-07583-8. [13] YASUDA I, ITOI T. Recent advances in endoscopic management of difficult bile duct stones[J]. Dig Endosc, 2013, 25(4): 376-385. DOI: 10.1111/den.12118. [14] RAMCHANDANI M, REDDY DN, LAKHTAKIA S, et al. Per oral cholangiopancreatoscopy in pancreatico biliary diseases-expert consensus statements[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(15): 4722-4734. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4722. [15] BREWER GUTIERREZ OI, BEKKALI N, RAIJMAN I, et al. Efficacy and safety of digital single-operator cholangioscopy for difficult biliary stones[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 16(6): 918-926. e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.10.017. [16] ALJEBREEN AM, ALHARBI OR, AZZAM N, et al. Efficacy of spyglass-guided electrohydraulic lithotripsy in difficult bile duct stones[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(6): 366-370. DOI: 10.4103/1319-3767.145329. [17] ABURAJAB M, DUA K. Endoscopic management of difficult bile duct stones[J]. Curr Gastroenterol Rep, 2018, 20(2): 8. DOI: 10.1007/s11894-018-0613-1. [18] BOKEMEYER A, GERGES C, LANG D, et al. Digital single-operator video cholangioscopy in treating refractory biliary stones: A multicenter observational study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34(5): 1914-1922. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-019-06962-0. [19] SETHI A, CHEN YK, AUSTIN GL, et al. ERCP with cholangiopancreatoscopy may be associated with higher rates of complications than ERCP alone: A single-center experience[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2011, 73(2): 251-256. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.08.058. [20] NGUYEN NQ. Getting most out of SpyGlass cholangio-pancreatoscopy: How and when?[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 27(8): 1263-1265. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2012.07178.x. [21] LALEMAN W, VERRAES K, VAN STEENBERGEN W, et al. Usefulness of the single-operator cholangioscopy system SpyGlass in biliary disease: A single-center prospective cohort study and aggregated review[J]. Surg Endosc, 2017, 31(5): 2223-2232. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-016-5221-2. [22] NJEI B, MCCARTY TR, VARADARAJULU S, et al. Cost utility of ERCP-based modalities for the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gastrointest Endosc, 2017, 85(4): 773-781. e10. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.08.020. [23] ANG TL, KWEK A. Safety and efficacy of SpyGlass cholangiopancreatoscopy in routine clinical practice in a regional Singapore hospital[J]. Singapore Med J, 2019, 60(10): 538-544. DOI: 10.11622/smedj.2018158. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 王旋,陈雪雯,黄金鑫,陈佳骏,曲岩,高浩,龚彪,张晞文,李甫. 取石球囊在内镜逆行胰胆管造影术治疗肝移植术后胆管吻合口狭窄中的特殊应用. 中国内镜杂志. 2024(03): 7-13 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 马丽娜·阿新拜,张立平,王林恒,王允亮,陈润花,孟捷,胡立明,姚玉璞. 经ERCP联合SpyGlass DS治疗的74例不明原因胆管狭窄患者的临床特征分析. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志. 2024(08): 1037-1044 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 艾合买江·库尔班江,布娅·米然别克,王秋玲,李得阳,高峰. SpyGlass DS系统联合激光碎石法与常规分次治疗胆总管大结石的效果和安全性的对比分析. 中国内镜杂志. 2024(08): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 邝文熙,岑瑜,谢春晓,卢洁霞,姜海行,覃山羽. SpyGlass直视化系统联合肿瘤标志物对恶性胆管狭窄的诊断价值. 广西医科大学学报. 2023(03): 492-496 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 王旋,李甫,唐睿,黄金鑫,刘加康,龚彪,张晞文. SpyGlass内镜直视系统在原位肝移植术后复杂胆道并发症中的应用. 器官移植. 2023(03): 404-410 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 江贵,王林恒,丁玄,张春双,张丽杰. SpyGlass~(TM)DS在70岁以上胆管疾病患者中的诊疗价值及安全性分析. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志. 2023(08): 875-879 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 刘炯,汪向飞,江斌. SpyGlass系统在困难胆囊腹腔镜胆囊切除术中的应用价值. 临床外科杂志. 2023(10): 925-927 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 云逸飞,王林恒,江贵,卢心毓,黄朔,何寅家,张丽杰. 单人经口胆道镜系统直视下与传统X线下非困难性胆总管结石取石的对比研究. 中华消化内镜杂志. 2023(09): 707-712 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 蒙钊. SpyGlass系统监视在胆总管结石辅助液电碎石中的应用. 中国医学物理学杂志. 2023(11): 1428-1432 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2327 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2327 KB)


 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术