内镜结扎联合中医辨证论治对肝硬化食管静脉曲张破裂出血的二级预防效果
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.05.019
Effect of endoscopic ligation combined with traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation-based treatment in the secondary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis
-
摘要:
目的 观察内镜下结扎联合中医辨证论治防治肝硬化食管静脉曲张破裂出血(EVB)二级预防的疗效。 方法 选取2015年4月—2021年2月上海中医药大学附属曙光医院肝硬化科收治的行内镜下结扎治疗的EVB患者108例,对同时服用中药治疗的患者定义为中西医组(n=59),对未服用中药治疗的患者定义西医组(n=49)。比较两组患者的再出血发生率、病死率以及门静脉高压性胃病的改善率等。计量资料符合正态分布者采用t检验;不符合正态分布者采用Mann-Whitney U秩和检验;计数资料2组间对比采用χ2检验或Fisher确切概率法;并采用Cox回归分析评估影响再出血的危险因素。 结果 中西医组内镜结扎后13~24个月的再出血率显著低于西医组(2% vs 12%, P=0.045);中西医组再出血病死率显著低于西医组(2% vs 12%, P=0.045),且门静脉高压性胃病的总有效率显著高于西医组(90% vs 77%, P=0.04)。基础疾病(主要包括糖尿病、高血压、心脏病)及肝功能Child-Pugh分级是影响再出血的显著危险因素(P值均<0.05)。 结论 内镜结扎联合中医辨证论治可显著降低EVB的迟发性再出血发生率和病死率,改善门静脉高压性胃病的程度,为结扎联合中医药提高EVB二级预防的综合疗效提供了新策略。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the efficacy of endoscopic ligation combined with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome differentiation-based treatment in the secondary prevention of esophageal variceal bleeding (EVB) in patients with liver cirrhosis. Methods A total of 108 EVB patients who were admitted to Department of Liver Cirrhosis, Shuguang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine from April 2015 to February 2021 and underwent endoscopic ligation were enrolled, among whom 59 patients with TCM treatment were enrolled as Chinese and Western medicine group, and 49 patients without TCM treatment were enrolled as Western medicine group. The two groups were compared in terms of the incidence rate of rebleeding, mortality rate, and the improvement rate of portal hypertensive gastropathy. The t-test was used for comparison of normally distributed continuous data between groups, and the Mann-Whitney U rank sum test was used for comparison of non-normally distributed continuous data between groups; the chi-square test or the Fisher's exact test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups; a Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate the risk factors for rebleeding. Results Compared with the Western medicine group, the Chinese and Western medicine group had a significantly lower rebleeding rate within 13-24 months after ligation (2% vs 12%, P=0.045), a significantly lower mortality rate of rebleeding (2% vs 12%, P=0.045), and a significantly higher overall response rate of portal hypertensive gastropathy (90% vs 77%, P=0.04). Underlying diseases (mainly including diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease) and Child-Pugh class for liver function were significant risk factors for rebleeding (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Ligation combined with TCM treatment can significantly reduce the incidence rate of delayed rebleeding and the mortality rate of EVB and improve the degree of portal hypertensive gastropathy, which provides a new strategy for ligation combined with TCM treatment to improve the overall response of EVB secondary prevention. -
慢性HBV感染的自然史划分为4个期,即免疫耐受期、免疫清除期、免疫控制期和再活动期[1]。目前,对于处于免疫清除期以及再活动期的慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)患者,各大指南均推荐抗病毒治疗,对于免疫耐受期则不推荐抗病毒治疗,建议长期随访[1-4]。然而,有研究[5-11]表明,10%~49%免疫耐受期CHB (Immune-tolerant CHB,IT-CHB) 患者经肝组织病理学检查证实存在明显的肝脏炎症和/或纤维化,若不积极治疗,发展至肝硬化及肝癌的风险增加。IT-CHB患者是否抗病毒治疗尚存在争议[12-18],而评估肝组织学显著肝脏炎症及纤维化对于抗病毒治疗具有重要意义,肝活检仍然是金标准,但其有创性及不易重复等缺点限制了临床应用。本研究通过分析IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)的高危因素,构建无创的个体化列线图预测模型,旨在为指导IT-CHB抗病毒治疗提供参考依据。
1. 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性选取2002年8月—2017年12月在解放军总医院第五医学中心住院的IT-CHB患者。免疫耐受期的诊断标准符合2018年版美国肝病学会CHB指南[2]中的定义。纳入标准:(1)年龄>18岁;(2)HBsAg阳性及HBeAg阳性>1年;(3)ALT水平持续正常(男性35 U/L,女性25 U/L)>1年;(4)HBV DNA>1×106 IU/ml;(5)接受肝活检。排除标准:(1)合并其他病毒感染;(2)其他类型肝脏疾病;(3)失代偿期肝硬化;(4)肝癌或其他恶性肿瘤病史;(5)严重的心脏、肾脏或者其他脏器的原发疾病或精神系统疾病。
1.2 肝组织学检查
采用16G活检针进行超声引导下经皮肝活检,要求肝组织长度≥15 mm,至少包括11个汇管区[19]。由2名经验丰富的病理医师进行双盲法阅片,肝组织炎症分级和纤维化分期标准参照《慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015年版)》[20]。显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)定义为肝组织学存在明显的肝脏炎症(≥G2)或纤维化(≥S2)。
1.3 血清学检测
采用贝克曼库尔特AU5421全自动生化仪检测血清ALT、AST、TBil、PLT等。乙型肝炎血清学标志物采用罗氏E170电化学发光法检测。计算APRI指数和FIB-4指数,APRI = (AST/正常值上限×100)/PLT,FIB-4=(年龄×AST)/(PLT×ALT1/2)[21]。
1.4 伦理学审查
本研究通过解放军总医院第五医学中心伦理委员会审批,批号:2020056D。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 22.0进行统计分析。正态分布的计量数据以x±s表示,2组间比较采用独立样本t检验;非正态分布数据以M(P25~P75)表示,2组间比较采用Mann- Whitney U检验; 多组比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验;计数资料2组间比较采用χ2检验。相关性分析采用Spearman秩相关。通过多因素logistic回归模型进入法筛选显著肝损伤的相关因素,采用R语言(3.6.1)的RMS(Regression Modeling Strategies)程序包构建列线图模型,通过Bootstrap重抽样法对模型进行内部验证,用一致性指数(C-指数)、ROC曲线、校准曲线来评价列线图的区分度及校准度。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入382例IT-CHB患者,其中82例(21.5%)存在显著肝损伤。肝组织炎症活动度分级: G0 29例(7.6%)、G1 301例(78.8%)、G2 50例(13.1%)、G3 2例(0.5%);肝组织纤维化分期: S0 57例(14.9%)、S1 251例(65.7%)、S2 39例(10.2%)、S3 23例(6.0%)、S4 12例(3.1%)。按照是否存在显著肝损伤(≥G2/S2)分为2组,2组年龄、HBV DNA载量、ALT、AST、PLT比较差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)(表 1)。
表 1 患者基线的一般资料指标 总体(n=382) 非显著肝损伤组(n=300) 显著肝损伤组(n=82) 统计值 P值 男性[例(%)] 261(68.3) 201(67.0) 60(73.2) χ2=1.133 0.287 年龄(岁) 33.3±10.2 31.5±9.1 39.9±11.2 t=-7.071 <0.001 年龄段[例(%)] χ2=56.472 <0.001 <30岁 161(42.1) 147(49.0) 14(17.1) 30~39岁 130(34.0) 106(35.3) 24(29.3) 40~49岁 64(16.8) 35(11.7) 29(35.4) ≥50岁 27(7.1) 12(4.0) 15(18.3) 乙型肝炎家族史[例(%)] 221(57.9) 173(57.7) 48(58.5) χ2=0.020 0.888 BMI(kg/m2) 23.2±3.53 23.0±3.4 23.7±3.9 t=-1.021 0.308 HBV DNA(log10IU/ml) 8.4(7.8~8.8) 8.4(8.0~8.8) 7.9(6.9~8.5) Z=-4.924 <0.001 ALT(U/L) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 23.0(18.0~28.0) 25.5(21.0~32.0) Z=-3.693 <0.001 AST(U/L) 23.0(19.0~27.0) 21.0(19.0~26.0) 28.0(23.0~34.0) Z=-6.945 <0.001 TBil(μmol/L) 11.1(8.3~15.3) 10.9(8.3~15.3) 11.5(8.6~15.4) Z=-0.585 0.559 PLT(×109/L) 202(164~234) 208(176~239) 161(137~209) Z=-5.723 <0.001 2.2 年龄与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
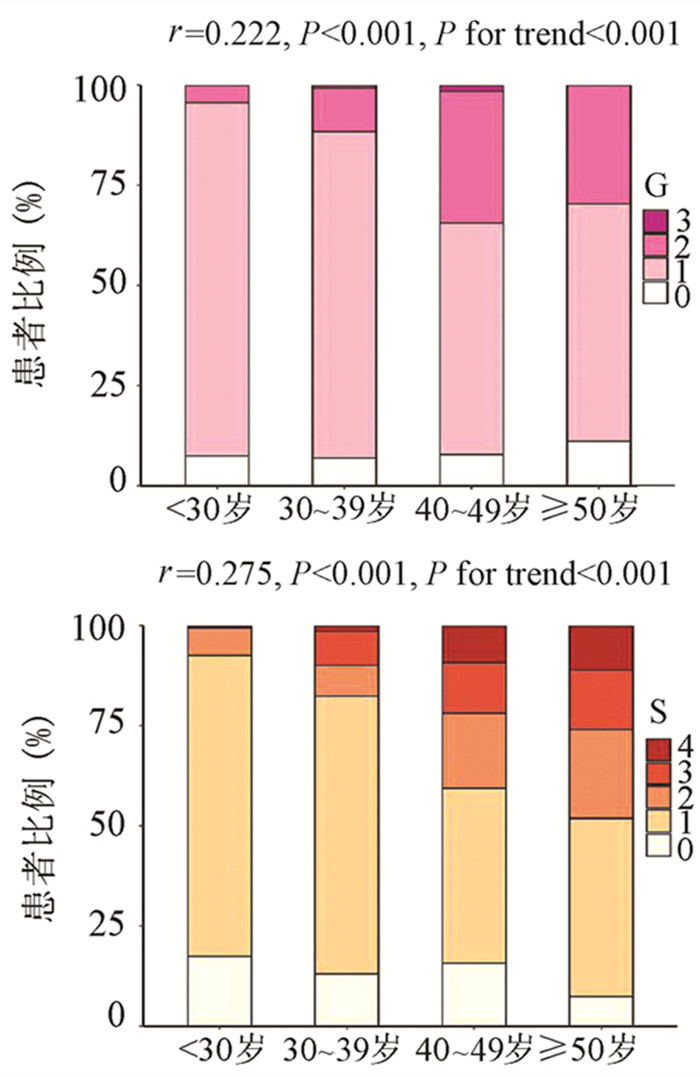
为了评估年龄对IT-CHB显著肝损伤的影响,将患者分为4个年龄段,即<30岁、30~39岁、40~49岁和≥50岁。随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高,趋势性检验结果表明差异均具有统计学意义(P值均<0.001)。Spearman等级相关分析显示,两者呈正相关(r值分别为0.222、0.275,P值均<0.001)(图 1)。Logistic单因素分析结果显示,较年龄<30岁组,30~39岁组、40~49岁组、年龄≥50岁组出现显著肝损伤的可能性分别为2.4倍(95%CI: 1.175~4.811)、8.7倍(95%CI: 4.165~18.175)、13.1倍(95%CI: 5.146~33.477)(P值均<0.05)。
2.3 HBV DNA与肝组织损伤病理学的关系
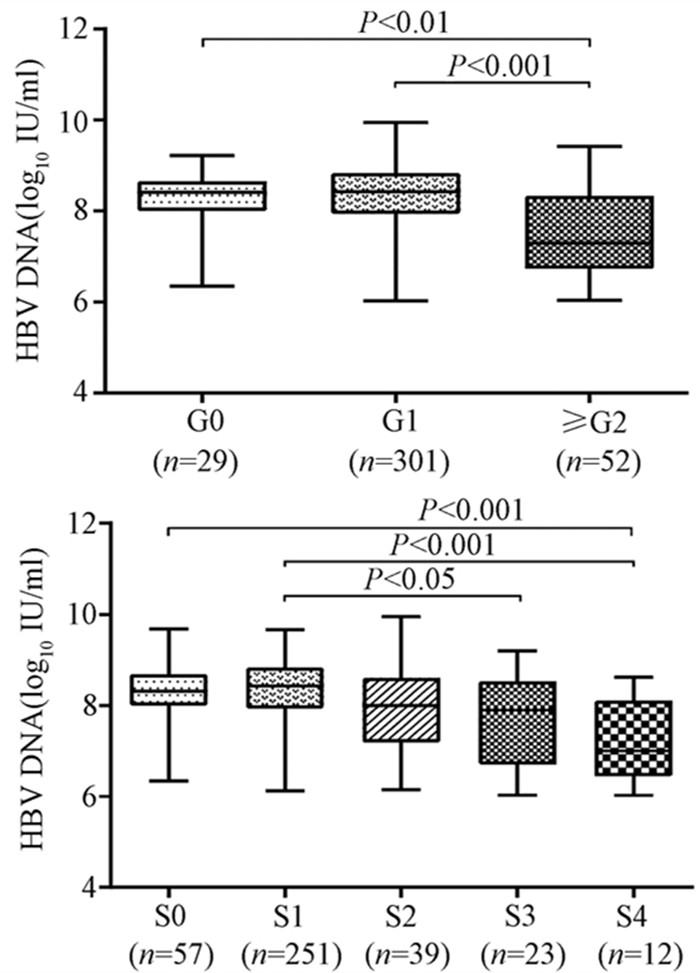
随着肝脏坏死性炎症的加剧,HBV DNA水平呈下降趋势(H=34.161,P<0.001),组间两两比较结果显示:G0组、G1组与≥G2组之间差异有统计学意义(H值分别为80.688、96.903,P值均<0.05),而GO组与G1组无差异(图 2)。伴随肝纤维化的进展,HBV DNA同样表现出下降的趋势(H=26.627,P<0.001),组间两两比较显示,S0与S4、S1与S4、S1与S3之间差异均有统计学意义(H值分别为112.287、125.953、74.354,P值均<0.05)(图 2)。
2.4 显著肝损伤的单因素及多因素分析
为进一步构建无创预测模型,基于无创参数中单因素分析P<0.05的变量作为自变量,以显著肝损伤作为因变量进行logistic回归分析。结果显示,年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT是显著肝损伤的独立影响因素(P值均<0.01)(表 2)。
表 2 显著肝损伤的logistic回归分析因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 OR(95%CI) P值 OR(95%CI) P值 年龄 1.084 (1.057~1.113) <0.001 1.074(1.043~1.107) <0.001 HBV DNA 0.437 (0.324~0.589) <0.001 0.442(0.314~0.624) <0.001 ALT 1.076(1.036~1.119) <0.001 1.009(0.959~1.060) 0.736 AST 1.132 (1.089~1.177) <0.001 1.096(1.051~1.142) <0.001 PLT 0.985 (0.98~0.991) <0.001 0.992(0.986~0.998) 0.006 2.5 列线图的制作与检验
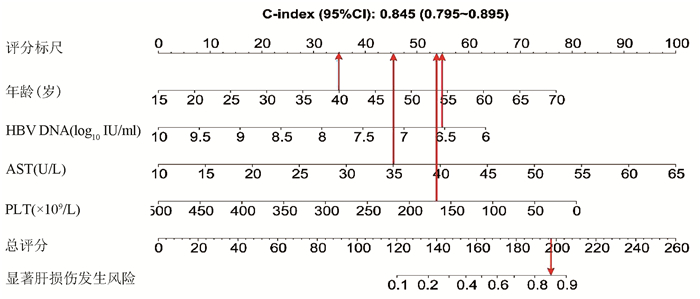
基于logistic回归分析结果,将独立影响因素引入R软件建立预测显著肝损伤的个体化列线图预测模型,并绘制校准曲线和ROC曲线。结果显示,列线图模型预测IT-CHB发生显著肝损伤的C-指数的ROC曲线下面积(AUC)为0.845(95%CI: 0.795~0.895), 明显优于单独使用APRI(AUC=0.781, 95%CI: 0.723~0.840)以及FIB-4(AUC=0.802, 95%CI: 0.746~0.859),差异有统计学意义。校正曲线贴近于理想曲线(对角线),斜率为1.017,Hosmer-Lemeshow拟合优度检验χ2=8.224,P=0.412,提示模型预测值与实际观测值之间的差异无统计学意义,预测模型有良好的校准度。ROC曲线分析显示,列线图的AUC高于APRI、FIB-4,预测IT-CHB患者显著肝损伤的最佳界值为141.4,其敏感度、特异度分别为74.4%、84.7%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表 3, 图 3)。
表 3 列线图、APRI、FIB-4诊断显著肝损伤的效能比较诊断参数 AUC 95%CI 界值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性预测值(%) Youden指数 列线图 0.845 0.795 ~ 0.895 141.4 74.4 84.7 57.0 92.4 0.59 APRI 0.781 0.723 ~ 0.840 0.338 70.7 77.7 46.4 90.7 0.48 FIB-4 0.802 0.746 ~ 0.859 0.882 78.1 72.3 43.5 92.3 0.50 3. 讨论
全球慢性HBV感染者约2.92亿人,其中约5940万处于免疫耐受期,我国的IT-CHB患者约有1584万例[22]。目前国内外指南对于免疫耐受期的定义尚存在争议[1-4, 23-25],ALT正常上限的标准亦不同, 按照美国肝病学会的标准意味我国IT-CHB患者并非全部处于免疫耐受阶段。单纯用病毒学、ALT水平评估免疫耐受可能存在临床误判,“真正”的免疫耐受需在肝活检基础上进一步确诊,目前多项研究[5-9]表明,10%~49% IT-CHB患者存在明显的肝细胞炎症坏死和肝纤维化病理学改变, 此类患者是否应抗病毒治疗逐渐成为热点问题。
本研究发现IT-CHB患者中21.5%(82/382)存在显著肝损伤,19.4%(74/382)呈显著肝纤维化,其中12例患者(3.1%)处于S4期,提示并不是全部IT-CHB患者均不需要治疗,如何筛选出需要治疗的患者尤为重要。本研究筛选出4个显著肝损伤的高危因素,包括年龄、HBV DNA水平、AST以及PLT,其中AST、PLT作为APRI、FIB-4的参数之一,已被充分证实与肝纤维化程度有关[21, 26]。既往研究[27-28]表明,年龄是CHB患者疾病进展的独立危险因素,尤其年龄>30岁时,HBV相关性肝纤维化、肝硬化、肝癌患者的比例显著增加。Xing等[6]发现年龄是影响肝组织炎症及纤维化的独立预测因子,这一点与本研究结果一致,将IT-CHB患者的年龄分为4个年龄亚组,结果表明,随年龄的增加,肝组织炎症及纤维化程度逐渐升高。关于HBV DNA,我国台湾的大样本研究[29]发现高HBV DNA水平CHB患者进展至肝硬化的风险增加,但其中81.6%(2923/3582) 为HBeAg阴性患者,不属于IT-CHB患者,因此该研究无法准确反映高HBV DNA水平与IT-CHB患者肝纤维化的关系。而本研究发现,IT-CHB患者随着肝脏炎症及纤维化程度的加重,HBV DNA呈下降趋势;并且轻度肝损伤(<G2/S2)的IT- CHB患者中位HBV DNA水平更高(8.4 log10 IU/ml),因此单纯HBV DNA水平并不能准确反映出IT-CHB患者纤维化程度。基于上述分析,本研究建立了无创的列线图模型用于预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,该模型具有无创的优势,并将多因素分析结果可视化、量化、个体化,具有可重复性,可作为肝活检的有效替代方式。根据该列线图模型,假设某40岁的IT-CHB患者,HBV DNA水平为6.56 log10 IU/ml,AST 35 U/L,PLT 166×109/L,则该患者总得分为188.6分,发生显著肝损伤的概率高达85%,需积极抗病毒治疗。
综上所述,免疫耐受期具有显著肝损伤的患者比例并不少见,基于年龄、HBV DNA、AST、PLT 4个因素构建的列线图模型具有良好的预测准确性,可用于个体化预测IT-CHB患者的显著肝损伤,减少肝活检,为抗病毒的精准治疗提供参考。
-
表 1 两组基线资料比较
Table 1. Comparison of baselines between the two groups
项目 西医组(n=49) 中西医组(n=59) 统计值 P值 性别[例(%)] χ2=0.02 0.889 男 25(51) 32(54) 女 24(49) 27(46) 年龄(岁) 61.00(50.0~68.0) 57.00(47.0~65.5) Z=1664.5 0.177 病程(年) 4.00(1.00~8.00) 3.00(1.0~9.0) Z=1479 0.838 肝硬化原因[例(%)] 0.882 AIH 1(2) 2(3) PBC 6(12) 6(10) 丙型肝炎肝硬化 1(2) 1(2) 不明原因肝硬化 6(12) 11(19) 混合型肝硬化 6(12) 6(10) 酒精性肝硬化 6(12) 3(5) 血吸虫性肝硬化 3(6) 6(10) 乙型肝炎肝硬化 20(41) 23(39) 重叠综合征(AIH+PBC) 0(0) 1(2) 肝功能指标 TBil(μmol/L) 20.74(11.29~34.50) 20.40(8.80~31.35) Z=1624.5 0.271 ALT(U/L) 31.00(21.00~39.00) 35.00(22.50~53.50) Z=1172 0.092 AST(U/L) 38.00(30.00~45.00) 40.00(30.00~56.50) Z=1248.5 0.224 Alb(g/L) 34.80(30.40~38.41) 35.60(32.15~38.65) Z=1242.5 0.211 Child-Pugh分级[例(%)] 0.304 A级 18(37) 22(37) B级 20(41) 30(51) C级 11(22) 7(12) 食管静脉曲张程度[例(%)] 1.000 中度 5(10) 6(10) 重度 44(90) 53(90) PHG[例(%)] χ2=2.935 0.231 无 23(47) 19(32) 轻度 16(33) 28(47) 重度 10(20) 12(20) 高血压病[例(%)] χ2=0.417 0.518 无 40(82) 44(75) 有 9(18) 15(25) 糖尿病[例(%)] χ2=0.123 0.725 无 35(71) 45(76) 有 14(29) 14(24) 心脏病[例(%)] 1.000 无 48(98) 57(97) 有 1(2) 2(3) 饮酒史[例(%)] χ2=0.101 0.750 无 36(73) 46(78) 有 13(27) 13(22) 吸烟史[例(%)] 1.000 无 41(84) 50(85) 有 8(16) 9(15) 表 2 再出血的发生率
Table 2. Incidence of rebleeding
再出血时间 西医组
(n=49)中西医组
(n=59)P值 早期再出血[例(%)] 6周内 1(2) 1(2) 1.0 迟发性再出血[例(%)] 6周~6个月 3(6) 4(7) 1.0 7~12个月 2(4) 2(3) 1.0 13~24个月 6(12) 1(2) 0.045 25个月以后 0 1(2) 1.0 表 3 Cox回归分析
Table 3. Cox regression analysis
变量 B值 SE Wald Exp(B) P值 组别 -0.037 0.554 0.004 0.964 0.947 性别 0.900 0.826 1.187 2.459 0.276 年龄 0.008 0.030 0.068 1.008 0.795 内镜治疗次数 -0.630 0.372 2.871 0.533 0.090 入组时食管静脉曲张分级 0.738 1.191 0.384 2.091 0.536 是否合并胃底静脉曲张 -1.198 0.898 1.779 0.302 0.182 是否合并PHG 0.367 0.832 轻度 0.184 0.738 0.062 1.202 0.803 重度 0.426 0.707 0.363 1.532 0.547 病程 0.093 0.081 1.343 1.098 0.247 基础疾病 1.546 0.655 5.572 4.693 0.018 饮酒史 0.892 0.847 1.109 2.440 0.292 吸烟史 0.977 0.805 1.475 2.657 0.225 肝硬化原因 0.674 0.700 0.926 1.962 0.336 肝功能Child-Pugh分级 1.550 0.539 8.260 4.713 0.004 -
[1] ZHOU M, WANG H, ZENG X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10204): 1145-1158. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1. [2] CHEN S, LI J, WANG D, et al. The hepatitis B epidemic in China should receive more attention[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10130): 1572. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30499-9. [3] de FRANCHIS R, Baveno VI Faculty. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63(3): 743-752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. [4] XU XY, DING HG, JIA JD, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002.徐小元, 丁惠国, 贾继东, 等. 肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32(2): 203-219. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2016.02.002. [5] LO GH, LAI KH, CHENG JS, et al. Endoscopic variceal ligation plus nadolol and sucralfate compared with ligation alone for the prevention of variceal rebleeding: A prospective, randomized trial[J]. Hepatology, 2000, 32(3): 461-465. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2000.16236. [6] de LA PEÑA J, BRULLET E, SANCHEZ-HERNáNDEZ E, et al. Variceal ligation plus nadolol compared with ligation for prophylaxis of variceal rebleeding: A multicenter trial[J]. Hepatology, 2005, 41(3): 572-578. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20584. [7] ZHANG L. Clinical observation of hemostatic decoction combined tissue adhesive injection(TAI)on treatment of liver cirrhosis complicated by gastric venous bleeding[J]. Hubei J Tradit Chin Med, 2017, 39(11): 25-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBZZ201711009.htm张磊. 止血汤联合内镜下组织胶注射治疗肝硬化并发胃底静脉出血临床观察[J]. 湖北中医杂志, 2017, 39(11): 25-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBZZ201711009.htm [8] NIU SS, ZHANG Q, HOU YX, et al. Primary preventive effect of anti-fibrosis treatment on esophageal and gastric varices bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: A real-world study[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2019, 29(4): 305-309. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2019.04.006.牛帅帅, 张群, 侯艺鑫, 等. 抗肝纤维化治疗对肝硬化食管胃静脉曲张出血的一级预防作用[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志, 2019, 29(4): 305-309. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2019.04.006. [9] HOU YX, ZHANG Q, YANG ZY, et al. Effect of spleen-strengthening, dampness-removing, and hemostatic prescription on rebleeding within one year in cirrhotic patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34(10): 2136-2141. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.015.侯艺鑫, 张群, 杨志云, 等. 健脾化湿止血方对肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张破裂出血患者1年内再出血的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2018, 34(10): 2136-2141. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.10.015. [10] XU XY, DING HG, LI WG, et al. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006.徐小元, 丁惠国, 李文刚, 等. 肝硬化诊治指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(11): 2408-2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. [11] Esophageal and gastric varices group, Digestive Endoscopy Branch, Chinese Medical Association. Tentative guidelines for endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of varicosity and variceal bleeding in digestive tract (2009)[J]. China Contin Med Educ, 2010, 2(6): 21-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2010.06.003.中华医学会消化内镜学分会食管胃静脉曲张学组. 消化道静脉曲张及出血的内镜诊断和治疗规范试行方案(2009年)[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2010, 2(6): 21-26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9308.2010.06.003. [12] MC CORMACK TT, SIMS J, EYRE-BROOK I, et al. Gastric lesions in portal hypertension: Inflammatory gastritis or congestive gastropathy?[J]. Gut, 1985, 26(11): 1226-1232. DOI: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1226. [13] XU LM, LIU P, SHEN XZ, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of liver fibrosis in integrative medicine practice (2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007.徐列明, 刘平, 沈锡中, 等. 肝纤维化中西医结合诊疗指南(2019年版)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(7): 1444-1449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.07.007. [14] Digestive System Diseases Committee, Chinese Association of Integrative Medicine. Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of cirrhosis with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western medicine[J]. Chin J Integr Trad West Med Dig, 2011, 19(4): 277-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXPW201104035.htm中国中西医结合学会消化系统疾病专业委员会. 肝硬化中西医结合诊疗共识[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2011, 19(4): 277-279. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXPW201104035.htm [15] Study Group of Spleen and Portal Hypertension Surgery, Chinese Surgical Society, Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of esophagogastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension (2019 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2019, 39(12): 1241-1247. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.12.01.中华医学会外科学分会脾及门静脉高压外科学组. 肝硬化门静脉高压症食管、胃底静脉曲张破裂出血诊治专家共识(2019版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2019, 39(12): 1241-1247. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2019.12.01. [16] LI Q, ZHOU X, XU KS. The clinical therapeutic effect of Rebamipide on portal hypertensive gastropathy[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2006, 15(3): 264-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX200603011.htm李琪, 周霞, 徐可树. 瑞巴派特对门脉高压性胃病的临床疗效观察[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2006, 15(3): 264-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WCBX200603011.htm [17] GARCIA-TSAO G, BOSCH J. Varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis: A new view of an old problem[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(12): 2109-2117. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.012. [18] VUACHET D, CERVONI J P, VUITTON L, et al. Improved survival of cirrhotic patients with variceal bleeding over the decade 2000-2010[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2015, 39(1): 59-67. DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2014.06.018. [19] WILLIAMS R, ASPINALL R, BELLIS M, et al. Addressing liver disease in the UK: A blueprint for attaining excellence in health care and reducing premature mortality from lifestyle issues of excess consumption of alcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9958): 1953-1997. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61838-9. [20] BOSCH J, SAUERBRUCH T. Esophageal varices: Stage-dependent treatment algorithm[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64(3): 746-748. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.039. [21] LIU P, HU YY, LIU C, et al. Multi-centrally clinical trial of Fuzhenghuayu (Strengthening Healthy Qi to Solve Stagnation) capsules on liver filbrosis caused by chronic hepatitis B[J]. World Sci Technol Modern Tradit Chin Med, 2005, 7(1): 24-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3849.2005.01.006.刘平, 胡义扬, 刘成, 等. 扶正化瘀胶囊干预慢性乙型肝炎肝纤维化作用的多中心临床观察[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2005, 7(1): 24-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3849.2005.01.006. [22] XIAO DH, GU J, CAI H, et al. A randomized placebo-controlled multicentre study of Fuzhenghuayu capsule for prevention of oesophageal variceal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2014, 22(8): 594-599. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2014.08.009.肖定洪, 顾杰, 蔡虹, 等. 扶正化瘀胶囊预防肝硬化患者食管静脉曲张破裂出血的随机对照多中心临床研究[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志, 2014, 22(8): 594-599. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2014.08.009. [23] LIU XD, HUI LM, WANG JH, et al. The clinical effect of endoscopic ligation combined with traditional Chinese and Western medicines on liver cirrhosis esophagogastric variceal bleeding[J]. Chin J Integr Trad West Med Dig, 2019, 27(6): 436-440. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2019.06.08.刘晓东, 回丽妹, 王建华, 等. 内镜套扎联合中西药治疗肝硬化食管静脉曲张破裂出血的临床研究[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2019, 27(6): 436-440. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2019.06.08. [24] YUAN C, HAO JM, WU WP, et al. Clinical study on Prevention of Recent Rebleeding after ligation of esophageal varices with cirrhosis by Yang Zhen's "Heweifugan Decoction"[C]//2019 The fourth Academic Exchange meeting of the first Digestive Endoscopy Professional Committee of Chinese Society of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine. 2019: 24. DOI: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.001223.袁超, 郝建梅, 吴文平, 等. 杨震"和胃复肝汤"预防肝硬化食管静脉曲张套扎术后近期再出血的临床研究[C]//2019中国中西医结合学会消化内镜学专业委员会第一届第四次学术交流会摘要集. 2019: 24. DOI: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.001223. [25] LIU HL, YAN S, LIU Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of carvedilol plus endoscopic variceal ligation for secondly prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients[J]. China J Endosc, 2015, 21(2): 132-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201502005.htm刘浩雷, 燕晟, 刘瑛, 等. 卡维地洛联合内镜套扎术预防食管静脉曲张再次出血的疗效及安全性分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志, 2015, 21(2): 132-135. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGNJ201502005.htm [26] YANG J, GE K, CHEN L, et al. The efficacy comparison of carvedilol plus endoscopic variceal ligation and traditional, nonselective β-blockers plus endoscopic variceal ligation in cirrhosis patients for the prevention of variceal rebleeding: A meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(12): 1518-1526. DOI: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001442. [27] LIU B, FANG ZY, MENG DM, et al. Progress of prevention and treatment of complications of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Chin Pract Diagn Ther, 2016, 30(12): 1152-1155. DOI: 10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2016.12.003.刘斌, 方正亚, 孟冬梅, 等. 肝硬化并发症治疗及预防研究进展[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2016, 30(12): 1152-1155. DOI: 10.13507/j.issn.1674-3474.2016.12.003. [28] SHI ZH, RUAN JJ, HU SP. Clinical observation on 40 cases of portal hypertension gastropathy treated with combined Chinese Drugs[J]. JTCM, 2001, 42(6): 353-354. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1668.2001.06.020.时昭红, 阮景军, 胡少鹏. 中药配合治疗门脉高压性胃病40例临床观察[J]. 中医杂志, 2001, 42(6): 353-354. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1668.2001.06.020 [29] WANG YH, DUAN SS. Effects of weikang mixture on portal hypertensive gastropathy after esophageal varice ligation[J]. J Hunan Univ Chin Med, 2017, 37(9): 982-985. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2017.09.016.王永恒, 段姗姗. 胃康合剂对食管静脉曲张套扎术后门脉高压性胃病的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2017, 37(9): 982-985. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2017.09.016. [30] WEI G, BEI GM, LI HQ. Clinical research of yao minority medical plaster on patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy of deficiency cold of spleen and stomach pattern[J]. World Chin Med, 2016, 11(9): 1807-1810. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2016.09.042.韦刚, 贝光明, 李海强. 瑶医膏药治疗脾胃虚寒型门脉高压性胃病的临床观察[J]. 世界中医药, 2016, 11(9): 1807-1810. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2016.09.042. [31] ALBILLOS A, ZAMORA J, [32] ZHANG SY, HUANG HC, WANG XM. Factors influencing prognosis for cirrhotic patients with esophagogastric variceal bleeding within 1 year after endoscopic variceal ligation[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2021, 26(2): 155-158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2021.02.016.张生燕, 黄宏春, 王秀敏. 肝硬化食管胃底静脉曲张出血内镜套扎术后1年预后的影响因素观察[J]. 肝脏, 2021, 26(2): 155-158. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2021.02.016. 期刊类型引用(9)
1. 李晓蓉,姚家喜,施志斌. SAA、GRP78、miR-21-3p与老年急性胰腺炎Ranson和APACHEⅡ评分的关联性. 中国老年学杂志. 2025(05): 1092-1095 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 赵永红,陈爱荣,胡梦茹,王燚鑫,衣桂荣. 急性胰腺炎伴代谢综合征的临床特点和危险因素分析. 现代消化及介入诊疗. 2024(06): 664-669 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 宋小利,陈璐. 大剂量维生素C联合乌司他丁、生长抑素治疗急性胰腺炎的效果及对肝肾功能的影响. 临床医学研究与实践. 2024(28): 39-42 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 卢景涛,彭琼. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊断联合BISAP评分对急性胰腺炎严重程度的预测价值. 医学信息. 2023(04): 118-122 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 黄雯雪,陈春洁,孙艳. 急性胰腺炎相关危险因素、严重程度评估及临床护理研究进展. 中国基层医药. 2022(03): 473-476 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 刘国雄,匡桥贵,喻欣荷,刘访,王宇,俞洋,陈杨. 加味大承气汤治疗湿热蕴结型高脂血症性急性胰腺炎的疗效及作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2021(05): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 王婷婷,何家俊,杨楚婷,李圆浩,陈炜炜,刘军. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病与急性胰腺炎的关系. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2021(03): 729-732 .  本站查看
本站查看8. 赵冬雨,成丽娅,邵伟,马程,沈宏. 胰胆舒胶囊联合乌司他丁治疗急性胰腺炎的临床研究. 现代药物与临床. 2021(04): 712-716 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 黄莹,苗雨,林晚,刘昊,张飞雄,阮继刚. 急性复发性胰腺炎合并代谢综合征的临床特点及预后分析. 宁夏医学杂志. 2021(11): 968-971 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(7)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1909 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1909 KB)

 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:  百度学术
百度学术