声脉冲辐射力成像技术测量的肝脏硬度对肝硬化门静脉高压的诊断价值
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.11.010
Value of liver stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse in diagnosis of cirrhotic portal hypertension
-
摘要:
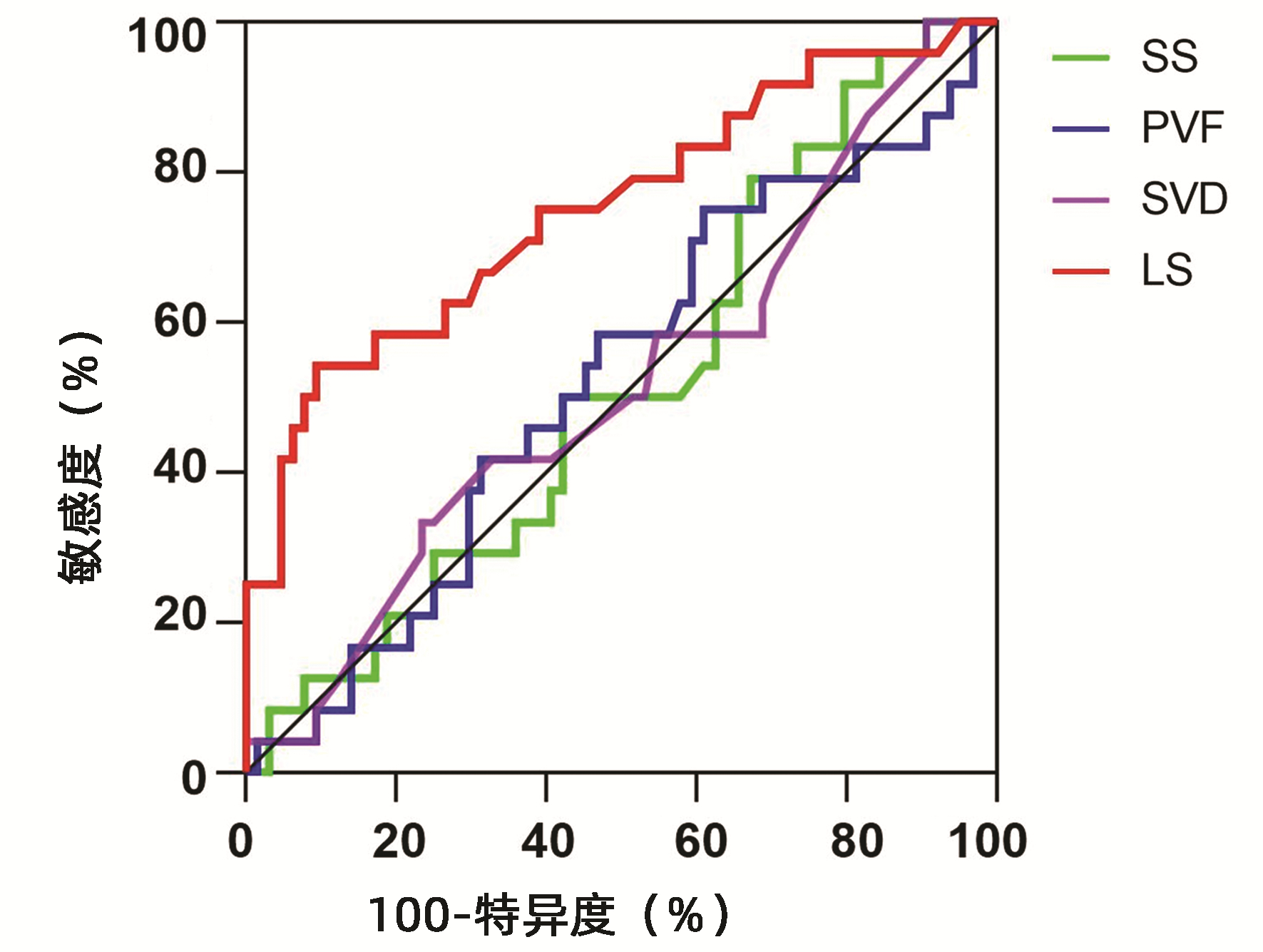
目的 评估肝脏硬度(LS)无创预测失代偿期肝硬化患者肝静脉压力梯度(HVPG)的准确性,探讨LS对失代偿期肝硬化的诊断价值。 方法 回顾性分析2013年4月—2021年6月于南京鼓楼医院消化内科同时接受HVPG测定及声脉冲辐射力成像技术(ARFI)测定LS的88例病毒性肝炎肝硬化失代偿期或酒精性肝硬化失代偿期患者的临床资料,根据HVPG值将患者分为严重门静脉高压(SPH)组(HVPG≥20 mmHg,n=24)和非SPH组(HVPG<20 mmHg,n=64),比较两组间LS、脾脏硬度、门静脉流速及相关生化指标差异。计量资料两组间比较采用t检验或Mann-Whitney U秩和检验;计数资料两组间比较采用χ2检验。不同无创指标与HVPG的相关性采用Pearson相关分析。采用Logistic回归分析不同无创检测指标与SPH发生风险之间的关系。绘制不同无创指标预测HVPG≥20 mmHg发生的受试者工作特征曲线并计算曲线下面积(AUC)、敏感度、特异度、最大约登指数及对应的临界值,以评估各指标对SPH的预测价值。 结果 88例患者中病毒性肝炎相关肝硬化失代偿期76例,酒精性肝硬化失代偿期12例。SPH组与非SPH组患者的年龄、性别、白细胞计数、血红蛋白、血小板计数、凝血酶原时间、谷丙转氨酶、谷草转氨酶、白蛋白、血钠、肌酐、Child-Pugh肝功能分级、脾脏硬度等比较,差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05);两组间LS比较差异有统计学意义(t=-3.970,P<0.01)。相关分析结果显示HVPG与LS呈正相关(r=0.458,P<0.001)。Logistic回归分析结果显示,LS为SPH发生的危险因素(OR=3.941,95%CI:1.245~12.476,P=0.020)。受试者工作特征曲线结果显示,LS预测SPH发生的AUC为0.751,最佳临界值为2.295 m/s,敏感度为54.17%,特异度为90.63%。 结论 在失代偿期肝硬化患者中,ARFI测得的LS与HVPG相关,对肝硬化失代偿期HVPG≥20 mmHg的无创诊断具有一定价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the accuracy of liver stiffness (LS) as a noninvasive index in predicting hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) in patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis and the value of LS in the diagnosis of decompensated liver cirrhosis. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed for the clinical data of 88 patients with decompensated cirrhosis due to viral hepatitis or decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis who received both HVPG measurement and LS measurement by acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) in Department of Gastroenterology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, from April 2013 to June 2021, and according to HVPG, the patients were divided into serious portal hypertension (SPH) (HVPG≥20 mmHg) group with 24 patients and non-SPH (HVPG < 20 mmHg) group with 64 patients. The two groups were compared in terms of LS, spleen stiffness, portal vein velocity, and related biochemical parameters. The t-test or the Mann-Whitney U rank sum test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. A Pearson correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlation of different noninvasive indices with HVPG, and a Logistic regression analysis was used to investigate the association of different noninvasive indices with the risk of SPH. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted for different noninvasive indices in predicting HVPG≥20 mmHg, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, maximum Youden index, and corresponding cut-off value were calculated to investigate the value of each index in predicting SPH. Results Among the 88 patients, 76 had decompensated cirrhosis due to viral hepatitis and 12 had decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. There were no significant differences between the SPH group and the non-SPH group in age, sex, white blood cell count, hemoglobin, platelet count, prothrombin time, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, albumin, serum sodium, creatinine, Child-Pugh class, and spleen stiffness, while there was a significant difference in LS between the two groups (t=-3.970, P < 0.01). The correlation analysis showed that HVPG was positively correlated with LS (r=0.458, P < 0.001). The Logistic regression analysis showed that LS was a risk factor for SPH (odds ratio=3.941, 95% confidence interval: 1.245-12.476, P=0.020). The ROC curve analysis showed that LS had an AUC of 0.751 in predicting the onset of SPH, with a sensitivity of 54.17% and a specificity of 90.63% at the optimal cut-off value of 2.295 m/s. Conclusion In patients with decompensated cirrhosis, LS measured by ARFI is correlated with HVPG and has a certain value in the non-invasive diagnosis of decompensated cirrhosis with HVPG≥20 mmHg. -
Key words:
- Liver Cirrhosis /
- Hypertension, Portal /
- Liver Stiffness /
- Diagnosis
-
肝细胞癌(简称肝癌)术后复发是导致患者死亡的主要原因[1]。对于复发性肝癌,临床上常用的治疗方法包括再次肝切除术、射频消融(radiofrequency ablation,RFA)、肝移植、介入、靶向药物治疗等[2]。然而,目前国内外肝癌诊疗指南均未对复发性肝癌提供具体的诊疗推荐。再次肝切除术和RFA属于根治性治疗方法,临床应用广泛,文献报道较多。但单个研究样本量小,且研究间的结论不统一,临床上对复发性肝癌的根治性治疗方案尚存争议。本文使用Meta分析的方法,客观分析两种治疗措施对复发性肝癌的疗效与安全性。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 文献检索
系统检索PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库,检索日期自建库至2020年6月15日。英文检索词包括:recurrent、recurrence、hepatocellular carcinoma、liver cancer、hepatic resection、hepatectomy、resection、radiofrequency ablation等,中文检索词包括:复发、肝癌、肝细胞癌、手术、再次肝切除术、射频消融等。
1.2 纳入标准
(1) 研究:比较再次肝切除术与RFA治疗复发性肝癌的随机对照试验或队列研究,英文或中文发表。(2)患者:罹患原发性肝癌,接受首次肝切除术治疗后,肝癌复发,复发肿瘤符合米兰标准,且无大血管侵犯及肝外转移。(3)干预措施:肝癌复发后,接受再次肝切除术或RFA治疗。(4)结局指标:报道了总生存期(overall survival,OS)、无瘤生存期(recurrence-free survival,RFS)、围手术期并发症和围手术期病死率中的任何一项。
1.3 排除标准
(1) 肝切除和RFA治疗原发性肝癌、胆管细胞癌或转移性肝癌的研究;(2)单组样本量过小(<10例)或单臂研究;(3)未提供病例具体纳入时间段的研究;(4)肝癌复发后,接受再次肝切除术或RFA治疗前,接受其他的治疗方案(如介入、靶向药物等)。再次肝切除术或RFA治疗后,序贯介入或其他治疗措施,不在排除标准范围之内。对于重复性发表的研究,仅纳入样本量最大的一项。
1.4 数据提取
两位评价者独立检索并提取纳入文献的数据,数据提取过程中若有分歧则通过双方讨论或询问第3位评价者解决。提取的数据包括人口统计学资料及临床基线数据、OS、RFS、围手术期并发症发生率及病死率。若原始文献未详细描述生存数据,则从其Kaplan-Meier生存曲线图估算。
1.5 统计学方法
统计分析采用RevMan 5.4.1软件(Cochrane协作组,牛津,英国)。采用从纳入文献提取的风险比(HR)进行OS和RFS的Meta分析。统计学异质性的评估采用I2检验。I2≥50%时采用随机效应模型,I2<50%时采用固定效应模型。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。采用漏斗图估计发表偏倚。由于纳入文献提供的数据存在一定的局限性,无法根据患者性别、肿瘤大小、肿瘤个数、肿瘤位置等进行亚组分析。
2. 结果
2.1 基线特点
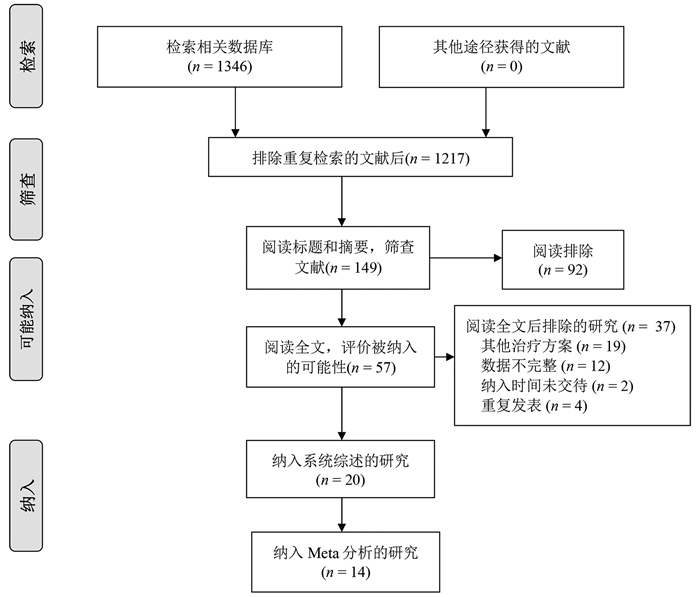
根据纳入和排除标准,18篇回顾性队列研究[3-20]和2篇随机对照试验[21-22]比较了再次肝切除术和RFA治疗复发性肝癌的临床疗效与安全性,共2903例患者(图 1)。全部纳入患者均来自亚洲国家,基线数据详见表 1。
表 1 纳入研究的基线特点第一作者和年份 国家/地区 纳入时间(年) 组别 样本量 男/女(例) 年龄(岁) 单个/多个肿瘤(例) 复发肿瘤直径(cm) 肝硬化[例(%)] CTP分级(A/B/C,例) 随访(月) Wang 2015[3] 中国 2004—2010 肝切除 128 113/15 50.2±10.1 89/39 2.4±0.9 66(51.6) - - RFA 162 148/14 52.7±10.9 107/55 2.3±0.7 - - - Sun 2017[4] 中国台湾 2002—2014 肝切除 43 34/9 60(35~76) - 1.9(0.8~3.0) 36(83.7) 42/1 53 RFA 57 38/19 63(27~81) - 1.8(1.0~3.0) 50(87.7) 57/0 54 Umeda 2011[5] 日本 1998—2007 肝切除 29 - - - 3.20±0.57 - 29/0 48 RFA 58 - - - 2.1±0.3 - 51/7 48 Song 2015[6] 韩国 1994—2012 肝切除 39 31/8 52.5±9.8 32/7 2.2±1.1 23(59) 39/0 36.3(0.8~126.6) RFA 178 145/33 55.4±10.6 156/22 1.7±0.6 130(73.0) 172/6 44.7(5.6~139.8) Liang 2008[7] 中国 1999—2007 肝切除 44 39/5 48.8±12.0 34/10 ≤3 (26) - 44/0 33.5±24.1 RFA 66 54/12 54.6±10.8 48/18 ≤3 (44) - 64/2 21.1±19.1 Ho 2012[8] 中国台湾 2001—2007 肝切除 54 40/14 56.3±12.3 - 2.9±1.8 26(48.1) 51/2/1 32(0~79) RFA 50 39/11 61.0±11.1 - 2.3±1.9 28(56.0) 50/0 27(0~96) Chan 2012[9] 中国香港 2001—2008 肝切除 29 - 52(38~79) 21/8 2.1(0.8~5.5) 25(86.2) 29/0 44.9 RFA 45 - 59(36~80) 29/16 2.2(0.8~6.0) 40(88.9) 40/5 44.9 Chen 2018[10] 中国 2009—2015 肝切除 48 41/7 73.5±3.5 28/20 2.6±1.1 41(85.4) 39/9 36.9(2~78) RFA 57 51/6 73.7±2.9 30/27 2.5±1.2 49(86.0) 45/12 37.3(2~78) 岑峰2016[11] 中国 2011—2015 肝切除 28 22/6 53.6 12/16 - 23(82.1) 18/10 - RFA 24 19/5 55.7 10/14 - 19(79.2) - - 陈康2019[12] 中国 2005—2014 肝切除 77 65/12 - - - 57(74) 76/1 57(2~168) RFA 82 72/10 - - - 50(61) 77/5 51(4~111) 黄新辉2013[13] 中国 2007—2011 肝切除 66 51/15 50.5±10.1 66/0 2.9±1.1 57(86.3) 66/0 - RFA 46 36/10 54.1±12.1 46/0 2.6±0.9 39(84.8) 46/0 - 梁惠宏2011[14] 中国 1999—2009 肝切除 72 65/7 49±12 72/0 2.1±0.1 - 70/2 36±25 RFA 79 69/10 55±11 79/0 2.5±0.1 - 73/6 32±21 任正刚2008[15] 中国 2000—2005 肝切除 145 127/18 51 127/18 2.0 - 145/0 23(3~88) RFA 68 64/4 52 52/16 2.0 - 68/0 23(3~88) 田正灵2016[16] 中国 2012—2015 肝切除 30 28/2 48.8±9.6 24/6 - 24(80) - 17(6.0~42.5) RFA 27 26/1 50.9±10.1 19/8 - 23(85.2) - 17(6.0~42.5) 张辉2013[17] 中国 2003—2011 肝切除 69 - - - 3.5 61(88.4) 54/15 - RFA 99 - - 2.1 76(76.8) 71/28 - 张婷婷2014[18] 中国 1998—2010 肝切除 27 25/2 47±13 25/2 3.2±1.1 - 27/0 32(9~118) RFA 39 37/2 52±13 37/2 2.7±1.1 - 37/2 28(2~79) Peng 2018[19] 中国 2006—2015 肝切除 79 67/2 55 59/20 ≤3(48) - - 53.2(4~96) RFA 107 95/12 57 75/32 ≤3(73) - - 52.3(3~96) Lu 2020[20] 中国 2004—2015 肝切除 138 124/16 50.1±10.9 112/26 2.8±1.9 96(70) 138/0 37.6 RFA 194 172/22 52.9±11.8 162/32 1.9±0.9 134(69) 194/0 41.6 Xia 2019[21] 中国 2010—2013 肝切除 120 107/13 52.4(25.7~60.5) 96/24 2.9(1.0~5.0) 50(41.7) 120/0 44.3(4.3~90.6) RFA 120 109/11 53.5(28.0~59.9) 94/26 2.7(1.0~4.8) 55(45.8) 120/0 44.3(4.3~90.6) 刘嘉龙2019[22] 中国 2016—2017 肝切除 39 38/1 50.0±10.0 37/2 2.1±0.7 37(94.9) 38/1 24 RFA 41 37/4 48.9±11.3 39/2 1.8±0.8 39(95.1) 39/2 24 注:-,未报道。 2.2 围术期并发症及病死率
15篇文献[4, 6-7, 9-17, 19, 21-22]报道了再次肝切除术围手术期并发症发生率为5.5%~68.2%,中位值为22.4%,常见并发症包括肝功能不全、胸腔积液、腹水、胆瘘等。14篇文献[4, 6-7, 9-10, 12-17, 19, 21-22]报道了RFA的围手术期并发症发生率为0~13%,中位值为3.3%,常见并发症包括胆漏、腹腔出血等。16篇文献[4, 6-7, 9-19, 21-22]报道了再次肝切除术和RFA围手术期病死率,其中6篇文献[4, 6, 10, 12, 17, 19]报道再次肝切除术组围手术期病死率为1.3%~2.6%,中位值为2%,其余文献报道发生率为0;仅1篇文献[9]报道RFA围手术期病死率为2.2%,其余文献报道发生率为0(表 2)。
表 2 纳入患者的治疗结局第一作者和年份 组别 并发症发生率(%) 围手术期病死率(%) 复发[例(%)] RFS OS 1年 3年 5年 P值1) 1年 3年 5年 P值1) Wang 2015[3] 肝切除 - - - - - - - 97.7 84.1 64.5 <0.001 RFA - - - - - - 96.9 73.4 37.0 Sun 2017[4] 肝切除 16 2 30(69.8) 57.0 32.1 28.6 0.89 97.6 82.7 56.4 0.69 RFA 7 0 41(71.9) 60.8 26.6 16.6 98.2 77.2 52.6 Umeda 2011[5] 肝切除 - - - - - - - 93.1 66.8 58.1 0.899 RFA - - - - - - 94.7 75.1 48.3 Song 2015[6] 肝切除 64 2.6 18(46.2) 66.1 48.5 43.1 0.834 88.8 88.8 83.9 0.686 RFA 2.2 0 117(65.7) 70.1 40.8 30.0 98.9 82.5 71.0 Liang 2008[7] 肝切除 68.2 0 86.4 - - - - 78.6 44.5 27.6 0.79 RFA 3.0 0 78.8 - - - 76.6 48.6 39.9 Ho 2012[8] 肝切除 - - - - - - - - - 72.0 - RFA - - - - - - - - 83.0 Chan 2012[9] 肝切除 24.1 0 21(72.4) 41.1 24.2 24.2 0.14 89.7 56.5 35.2 0.51 RFA 2.2 2.2 38(84.4) 32.2 12.4 9.3 83.7 43.1 29.1 Chen 2018[10] 肝切除 25 2.1 26(54.2) 73.1 49.7 40.7 0.465 76.3 52.5 42.6 0.413 RFA 0 0 27(47.4) 69.5 37.8 33.1 78.2 40.8 36.7 岑峰2016[11] 肝切除 50 0 - 46.4 0 0 - - - - - RFA - 0 - 20.8 0 0 - - - 陈康2019[12] 肝切除 17.1 1.3 - - - - - 88.8 68.8 51.1 0.258 RFA 9.8 0 - - - - 91.4 73.4 61.1 黄新辉2013[13] 肝切除 18.1 0 - 43.9 14.4 8.2 0.548 89.5 54.3 28.8 0.780 RFA 0 0 - 56.9 12.4 5.0 82.6 50.8 20.5 梁惠宏2011[14] 肝切除 36 0 ≤1年: 39>1年: 33 - - - - 95.3 65.7 54.5 >0.05 RFA 13 0 ≤1年: 37>1年: 42 - - - - 100 79.4 62.1 任正刚2008[15] 肝切除 5.5 0 ≤2年: 71>2年: 74 79.4 48.1 34.4 0.001 88.1 62.6 41.0 0.693 RFA 1.5 0 ≤2年: 37>2年: 31 58.0 27.8 12.4 94.7 65.1 37.3 田正灵2016[16] 肝切除 6.7 0 10(33.3) 73.3 64.3 - 0.002 96.7 93.3 - 0.54 RFA 3.7 0 24(88.9) 46.7 26.7 - 96.3 84.0 - 张辉2013[17] 肝切除 15.9 1.45 - - - - - 68.2 45.4 - >0.05 RFA 0 0 - - - - 73.7 53.6 - 张婷婷2014[18] 肝切除 - 0 22(56.4) 66.7 50.7 43.4 0.323 96.2 76.9 61.2 0.471 RFA - 0 14(52.9) 65.8 28.0 14.0 86.2 73.3 62.2 Peng 2018[19] 肝切除 17.7 1.3 - 64.8 41.6 38.3 0.258 84.8 60.2 51.9 0.871 RFA 4.7 0 - 58.2 35.2 29.6 84.6 66.9 49.1 Lu 2020[20] 肝切除 - - - 91.8 82.0 72.9 0.38 - - - - RFA - - - 94.4 75.4 61.7 - - - Xia 2019[21] 肝切除 22.4 0 60.8 85.0 52.4 36.2 0.09 92.5 65.8 43.6 0.17 RFA 7.3 0 64.2 74.2 41.7 30.2 87.5 52.5 38.5 刘嘉龙2019[22] 肝切除 35.9 0 19(48.7) 69.2 - - <0.001 92.3 - - 0.292 RFA 4.9 0 32(78.0) 26.8 - - 85.4 - - 注:-,未报道;1) P值来源于原文报道。 2.3 RFA与肝切除术OS的比较
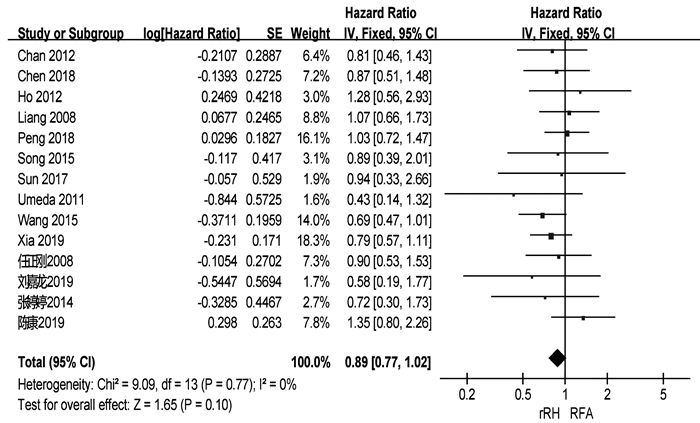
共有18篇研究[3-10, 12-18, 21-22]报道了OS(表 2)。两组患者术后1、3、5年中位OS分别为92.3%、66.3%、51.1%与91.4%、69.2%、39.9%。共有14篇研究[3-10, 12, 15, 18-19, 21-22]可提取数据统计HR,各组间不存在异质性(I2=0,P=0.77),采用固定效应模型进行分析。结果显示,两组患者的OS差异无统计学意义(HR= 0.89,95%CI:0.77~1.02,P=0.10)(图 2)。
2.4 RFA与肝切除术RFS的比较
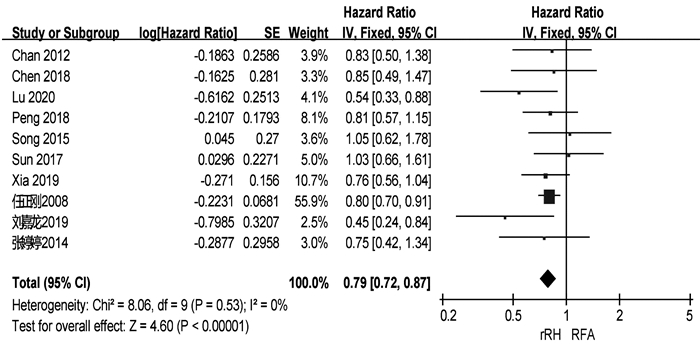
共有13篇研究[4, 6, 9-11, 13, 15-16, 18-19, 20-22]报道了RFS(表 2)。两组患者术后1、3、5年中位RFS分别为67.9%、48.3%、34.4%和57.5%、27.9%、14.0%。共有10篇研究[4, 6, 9-10, 15, 18-22]可提取数据统计HR,各组间不存在异质性(I2=0,P=0.53),采用固定效应模型进行分析。结果显示,再次肝切除术组患者的RFS显著高于RFA组(HR=0.79,95%CI:0.72~0.87,P<0.001)(图 3)。
2.5 发表偏倚
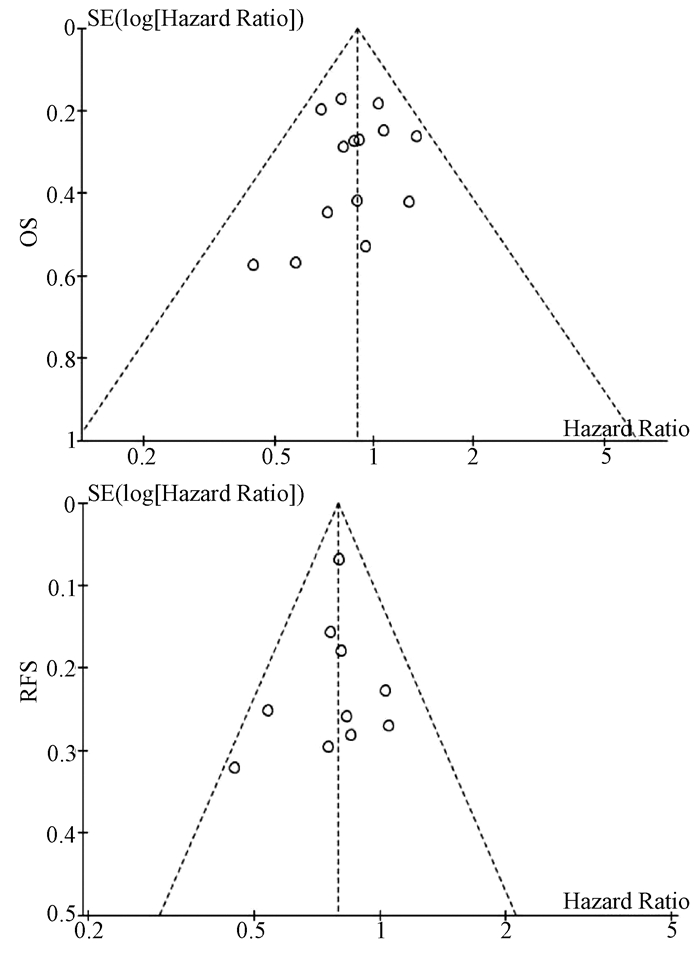
基于OS和RFS HR的漏斗图提示,发表偏倚不明显(图 4)。
3. 讨论
肝癌术后复发是影响患者术后长期生存的主要危险因素。对于复发性肝癌,目前临床上以多学科综合治疗为主。肝移植能显著提高复发性肝癌患者的RFS和远期生存率[23],但肝移植适应证严格、肝源匮乏和费用昂贵等问题仍限制其广泛的临床应用。此外,既往研究[24-25]表明再次肝切除术和RFA对复发性肝癌的疗效均优于介入。因此,针对肝内复发性肝癌患者,再次肝切除术和RFA是目前较为理想的治疗方案。有研究[3]认为再次肝切除术是治疗复发性肝癌的首选治疗方案,即使患者的原发癌更具侵袭性,肝功能水平更差,肝癌复发后行再次肝切除术仍可以获得与RFA相似的疗效。梁惠宏等[14]的研究则发现,RFA治疗复发性小肝癌的长期疗效优于再次肝切除术。因此,关于再次肝切除术和RFA治疗复发性肝癌的选择仍存在较大争议。本研究通过Meta分析的方法,综合评估再次肝切除术和RFA治疗复发性肝癌的疗效和安全性。
本研究结果显示,两组患者的OS无显著性差异,但再次肝切除术组患者的RFS显著高于RFA组。这一结论与肝切除术和RFA治疗原发性肝癌的结果一致[26-27]。RFA组患者RFS偏低的原因可能是:(1)再次肝切除术能将复发肿瘤以及潜在的瘤周子灶及血管癌栓同时切除,减少肿瘤再次局部复发和转移的可能性;(2)RFA后部分患者的肿瘤消融不完全而需进行二次消融或其他治疗;(3)术前影像学检查未能发现主瘤旁的微小卫星灶,导致消融不完全而引起肝癌再次复发。虽然RFA可用于治疗直径≤5 cm的肝癌,但目前认为其最佳适应证为直径≤3 cm的小肝癌[28]。有研究[29]发现,肝癌的直径和数目是导致RFA消融不完全的主要因素,随着肝癌直径的增加,RFA的疗效逐步下降。Livraghi等[30]的研究也表明RFA治疗直径3~5 cm的肝癌时完全消融率显著降低,导致RFA治疗复发性肝癌后局部复发和早期复发的比例明显升高。无论是原发性还是复发性肝癌,肿瘤直径在3~5 cm时经RFA治疗后其RFS和远期生存率均低于再次肝切除术[21, 31]。因此,在选择复发性肝癌治疗方案时,肿瘤直径应作为重要的参考指标。
本研究中,在围手术期并发症方面,再次肝切除术组和RFA组患者的中位发生率分别为22.4%和3.3%,与原发性肝癌接受肝切除术或RFA治疗后的并发症发生率相似[32-33]。此外,本研究还发现RFA治疗复发性肝癌的安全性明显优于再次肝切除术。RFA组患者术后并发症发生率及严重程度更低。虽然再次肝切除术能改善患者的远期生存率及RFS,但再次肝切除术的实施仍受诸多因素的限制,例如复发肿瘤的位置、数量以及肝硬化严重程度等。手术造成较大的创伤导致患者术后更容易发生严重并发症。此外,肝癌患者常伴有不同程度的肝硬化,无疑增加了手术的风险,部分患者最终死于肝衰竭而非肝癌本身带来的肿瘤负担[32]。相比于再次肝切除术,RFA在超声等影像学技术引导下精准地对复发肿瘤进行消融,从而最大限度地避免正常肝组织的破坏。对于手术无法切除、无法耐受手术的患者亦可选择RFA治疗。此外,RFA还可联合介入或无水酒精注射提高患者的OS和RFS[10, 19]。RFA本身具有微创和可重复的优点,肝癌再次复发后相当一部分患者仍可及时接受RFA或其他治疗[12],从而获得与再次肝切除相似的短期OS。
值得注意的是,本研究纳入文献中多数为回顾性研究,仅有2篇随机对照试验,因此本研究结论仍需更多的随机对照试验进行验证。其次,再次肝切除术和RFA治疗复发性肝癌的适应证存在一定的区别。然而,本Meta分析纳入的多数文献均仅纳入符合米兰标准的复发性肝癌,这些患者同时符合再次肝切除术和RFA的适应证。最后,肝癌术后复发(甚至多次)比较常见,对于复发肿瘤的治疗,多采取综合治疗方案(如介入、靶向、免疫治疗等),而非再次肝切除术或RFA等“单一”治疗模式。因此,联合治疗方案可能影响本荟萃分析对患者OS的判断。
总而言之,对于复发性肝癌的治疗,再次肝切除术能提高患者RFS,RFA则具有安全性高的优点。因此,在复发性肝癌患者的治疗中应遵循个体化和多学科治疗原则,合理选择治疗方案。
-
表 1 受试者基线资料
Table 1. Baseline of the patients included
指标 所有患者(n=88) 非SPH组(n=64) SPH组(n=24) 统计值 P值 男/女(例) 65/23 48/16 17/7 χ2=0.157 0.79 年龄(岁) 53.93±11.39 54.35±12.08 53.54±9.68 t=0.132 0.90 病因(病毒性/酒精性,例) 76/12 56/8 20/4 χ2=0.257 0.73 肝右叶斜径(cm) 12.20±1.48 12.56±1.28 12.57±1.66 t=-1.245 0.22 内镜下静脉曲张程度(轻/中/重,例) 4/19/65 3/14/47 1/5/18 χ2=0.025 0.99 白细胞计数(×109/L) 2.25(1.70~3.30) 1.90(1.55~3.30) 2.50(2.05~3.20) Z=-1.918 0.06 血红蛋白(g/L) 86.64±26.66 82.35±25.97 86.64±26.66 t=0.124 0.90 血小板计数(×109/L) 59.49±33.65 60.10±28.95 57.35±30.83 t=0.367 0.72 凝血酶原时间(s) 14.89±2.74 14.35±1.64 15.90±3.10 t=-1.772 0.08 国际标准化比值 1.31±0.20 1.25±0.15 1.39±0.26 t=-1.525 0.07 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) 22.75(16.40~29.40) 24.75(15.90~29.00) 18.75(15.85~29.40) Z=-0.932 0.35 谷草转氨酶(U/L) 26.75(21.25~35.55) 26.80(22.35~36.25) 23.15(20.10~31.50) Z=-1.466 0.14 总胆红素(μmol/L) 16.90(11.00~22.35) 15.85(10.10~20.10) 18.70(13.10~31.70) Z=-1.743 0.08 白蛋白(g/L) 35.43±4.77 36.43±4.45 33.96±5.31 t=1.155 0.25 血肌酐(μmol/L) 67.14±19.23 64.15±14.74 64.29±21.46 t=0.787 0.43 血钠(mmol/L) 141.20±2.60 141.16±3.13 141.23±2.84 t=-0.137 0.89 腹水(有/无,例) 30/58 25/39 5/19 χ2=2.581 0.13 Child-Pugh评分 6.85±1.32 6.40±1.05 7.25±1.29 t=-1.982 0.05 Child-Pugh分级(A/B/C,例) 37/48/3 31/32/1 6/16/2 χ2=5.517 0.06 表 2 SPH组和非SPH组不同无创测定指标的比较
Table 2. The comparison of different noninvasive indexes between SPH group and non-SPH group
指标 所有患者(n=88) 非SPH组(n=64) SPH组(n=24) t值 P值 LS(m/s) 2.00±0.43 1.88±0.34 2.33±0.50 -3.970 <0.01 SS(m/s) 3.48±0.53 3.46±0.56 3.54±0.46 -0.612 0.54 PVF(m/s) 27.56±9.53 27.65±9.59 27.33±9.58 0.139 0.89 SVD(cm) 1.19±0.30 1.18±0.30 1.22±0.30 -0.430 0.67 表 3 SPH发生风险的Logistic回归分析
Table 3. Logistic regression analysis of SPH risk
无创指标 OR 95%CI P值 LS 3.941 1.245~12.476 0.020 SS 0.840 0.281~2.507 0.754 PVF 0.542 0.192~1.527 0.246 SVD 1.452 0.497~4.241 0.496 Child-Pugh分级 B级 0.184 0.011~3.192 0.245 C级 0.402 0.027~5.948 0.507 注:LS≤1.925 m/s赋值为0,LS>1.925 m/s赋值为1;SS≤3.50 m/s赋值为0,SS>3.50 m/s赋值为1;PVF≤25.85 m/s赋值为0,PVF>25.85 m/s赋值为1;SVD≤1.12 cm赋值为0,SVD>1.12 cm赋值为1;Child-Pugh分级以Child-Pugh A级为参考。 -
[1] IWAKIRI Y, TREBICKA J. Portal hypertension in cirrhosis: Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapy[J]. JHEP Rep, 2021, 3(4): 100316. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2021.100316. [2] de FRANCHIS R, BOSCH J, GARCIA-TSAO G, et al. Baveno Ⅶ - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(4): 959-974. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. [3] GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. [4] LEE E, KIM YJ, GOO DE, et al. Comparison of hepatic venous pressure gradient and endoscopic grading of esophageal varices[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2016, 22(11): 3212-3219. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i11.3212. [5] ELKRIEF L, RONOT M, ANDRADE F, et al. Non-invasive evaluation of portal hypertension using shear-wave elastography: analysis of two algorithms combining liver and spleen stiffness in 191 patients with cirrhosis[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2018, 47(5): 621-630. DOI: 10.1111/apt.14488. [6] DING NS, NGUYEN T, ISER DM, et al. Liver stiffness plus platelet count can be used to exclude high-risk oesophageal varices[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36(2): 240-245. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12916. [7] KIM TY, JEONG WK, SOHN JH, et al. Evaluation of portal hypertension by real-time shear wave elastography in cirrhotic patients[J]. Liver Int, 2015, 35(11): 2416-2424. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12846. [8] FLEMING KM, AITHAL GP, CARD TR, et al. The rate of decompensation and clinical progression of disease in people with cirrhosis: a cohort study[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2010, 32(11-12): 1343-1350. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04473.x. [9] LURIE Y, WEBB M, CYTTER-KUINT R, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21(41): 11567-11583. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11567. [10] KENNEDY P, WAGNER M, CASTÉRA L, et al. Quantitative elastography methods in liver disease: current evidence and future directions[J]. Radiology, 2018, 286(3): 738-763. DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2018170601. [11] CORPECHOT C, GAOUAR F, EL NAGGAR A, et al. Baseline values and changes in liver stiffness measured by transient elastography are associated with severity of fibrosis and outcomes of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(4): 970-979. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.030. [12] SINGH S, FUJⅡ LL, MURAD MH, et al. Liver stiffness is associated with risk of decompensation, liver cancer, and death in patients with chronic liver diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 11(12): 1573-1584. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.07.034. [13] BERZIGOTTI A, SEIJO S, ARENA U, et al. Elastography, spleen size, and platelet count identify portal hypertension in patients with compensated cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(1): 102-111. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.001. [14] ABRALDES JG, BUREAU C, STEFANESCU H, et al. Noninvasive tools and risk of clinically significant portal hypertension and varices in compensated cirrhosis: The "Anticipate" study[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(6): 2173-2184. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28824. [15] XIE Q, LI Z, TANG Z, et al. Value of liver/spleen stiffness combined with serum adenosine deaminase in predicting severe esophageal varices in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(6): 1314-1318. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.020.谢青, 李曾, 唐臻, 等. 肝脾硬度联合血清腺苷脱氨酶对乙型肝炎肝硬化重度食管静脉曲张的预测价值分析[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(6): 1314-1318. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.020. [16] COSGROVE D, PISCAGLIA F, BAMBER J, et al. EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 2: Clinical applications[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2013, 34(3): 238-253. DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1335375. [17] D'ONOFRIO M, CROSARA S, de ROBERTIS R, et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse of the liver[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2013, 19(30): 4841-4849. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4841. [18] GARCIA-TSAO G, ABRALDES JG, BERZIGOTTI A, et al. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(1): 310-335. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28906. [19] MIAO CC, ZHUGE YZ, ZHANG M, et al. Correlation analysis between liver and spleen stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse and hepatic venous pressure gradient[J]. Chin J Dig, 2017, 37(1): 30-34. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2017.01.009.缪成成, 诸葛宇征, 张明, 等. 声脉冲辐射力成像测量的肝脏和脾脏硬度与肝静脉压力梯度的相关性分析[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2017, 37(1): 30-34. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2017.01.009. 期刊类型引用(13)
1. 刘新,金子铮,刘宁,陈淑湘,刘辉,于艳华,娄金丽. 乙肝核心相关抗原联合AFP、PIVKA-Ⅱ对乙肝相关肝癌的诊断价值研究. 北京医学. 2023(10): 852-857 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 周莉,陈辰,翟璐,程晓静,韩旭,姚升娟,高敏,李嘉. 血清AFP、PIVKA-Ⅱ、miR-21检测对肝细胞癌的诊断意义. 实用器官移植电子杂志. 2022(02): 135-139 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 董磊. 血清FER、AFP-L3联合检测诊断肝细胞癌的价值分析. 检验医学与临床. 2020(11): 1561-1563+1567 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 李惠军,李彩东,田鹏飞,段正军,雷志萍,张旭强. 乙肝病毒相关肝癌行AFP、PIVKA-Ⅱ和AFU联合检测的价值研究. 中国卫生标准管理. 2020(13): 108-110 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 张莉. 血清铁蛋白、甲胎蛋白异质体3联合腓骨蛋白-1检测诊断肝细胞癌的价值分析. 医学理论与实践. 2020(14): 2247-2249+2240 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 王傲然,李晓玲,门秋爽,孙凤霞. 血清铁蛋白与肝脏疾病研究进展. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版). 2020(04): 34-37 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 许羚雁. GALAD模型在原发性肝细胞癌诊断和预后评估中的价值研究. 循证医学. 2020(05): 277-281 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 高光剑,潘耀振. PIVKA-Ⅱ及AFP对原发性肝癌的诊断价值. 贵州医科大学学报. 2019(01): 100-104 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 董秋月. 慢性乙型肝炎患者32例的肿瘤标志物检测的临床意义. 世界最新医学信息文摘. 2019(53): 13-14 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 孔令希,覃山子,秦雪,陈志坚. PIVKA-Ⅱ、AFP、RDW联合检测在肝细胞癌中的诊断价值. 广西医科大学学报. 2018(06): 839-841 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 张莹,颜学兵. 血清异常凝血酶原Ⅱ对HBV相关肝细胞癌的诊断价值. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2018(07): 1470-1474 .  本站查看
本站查看12. 王欢,陆惠慧,尚琴,徐令清. PIVKA-Ⅱ在乙型肝炎病毒感染者中筛查HCC的应用价值分析. 中国医学创新. 2018(12): 62-65 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 赵芬,郭庆波,曲凯,梁欢. 联合检测PIVKAⅡ、AFP、Ferrtin对肝细胞癌的诊断价值. 国际检验医学杂志. 2018(21): 2615-2617+2621 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-




 PDF下载 ( 2125 KB)
PDF下载 ( 2125 KB)


 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术