非酒精性脂肪性肝病儿童肝组织病理特征分析
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.021
Histopathological characteristics of the liver in children with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
-
-
Key words:
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease /
- Pathology, Clinical /
- Child
-
HBV感染是一个重大的全球健康问题,据估计2016年全球78个国家的HBV感染者达2.9亿[1]。慢性乙型肝炎(CHB)的自然过程一般可分为免疫耐受期、免疫清除期、免疫控制期和再活跃期。对于免疫耐受期的界定,虽然在一些生化指标如ALT和HBV DNA的数值上仍存在争议,但普遍认为,血清HBsAg和HBeAg阳性、高HBV DNA复制水平、ALT持续或接近正常是免疫耐受期患者的特征[2-4]。这些患者的肝组织活检通常显示肝组织结构良好,没有明显的炎症或纤维化迹象[2-6]。
虽然对CHB的治疗已有基本共识,但对免疫耐受期患者是否应用抗病毒药物仍存在争议。一些研究认为,即使免疫耐受期患者血清ALT水平低于正常值上限,高病毒载量和HBV抗原阳性引起的免疫反应仍会导致肝纤维化的进展并提高肝细胞癌(HCC)的发生风险[7-8],抗病毒治疗可以降低这一风险从而改善患者的预后[9-11]。早期开始抗病毒治疗还可以降低HBV感染病毒池和HBV传播的风险[8-9]。但另一些研究[12-13]结果提示,治疗免疫耐受期CHB患者并不能改变疾病的自然史,一旦停止抗病毒治疗,会发生迅速的病毒学复发,临床复发也很常见。同时,抗病毒治疗降低免疫耐受期患者HCC、肝硬化和肝病相关死亡率的研究证据仍不充分,且持续抗病毒治疗存在潜在的危害,包括治疗成本、药物副作用和耐药性的增加[9]。
为进一步评价抗病毒药物在免疫耐受期CHB患者中的有效性和安全性,本研究对已发表的相关试验进行系统评价,为临床治疗提供参考。
1. 资料与方法
本研究是在系统综述和Meta分析的报告指南(PRISMA)下进行的[14]。
1.1 检索策略
在Cochrane Library、PubMed、EMBASE、中国知网、万方数据库中进行检索,时间为从数据库建立到2020年9月。英文检索词包括:hepatitis B、hepatitis B virus、immune tolerant、antiviral agents等; 中文检索词包括:乙型肝炎、免疫耐受期、抗病毒等。
1.2 纳入及排除标准
纳入标准:(1)随机对照试验、非随机对照试验或队列研究; (2)免疫耐受期CHB患者,无年龄和性别限制; (3)使用抗病毒药物治疗,无论单一用药或联合用药,抗病毒药物包括:IFNα和PEG-IFNα、拉米夫定、替比夫定、恩替卡韦、阿德福韦酯、替诺福韦、富马酸替诺福韦、富马酸丙酚替诺福韦、恩曲他滨和泛昔洛韦; (4)语种限定为中文或英文; (5)仅纳入已正式发表的研究。排除标准:(1)免疫清除期,低(非)复制期或再活跃期的CHB患者; (2)妊娠期女性、移植受者; (3)合并HCV、HDV或HIV感染; (4)接受中药、中成药或除IFN以外的其他免疫调节剂治疗; (5)综述、病例报告; (6)重复报道的文献。
1.3 文献筛选和数据提取
由2名研究者独立筛选文献、提取资料并进行核对。如不一致,则通过第三方意见解决。根据预先制定的表格进行资料提取,提取内容有:(1)研究的基本信息; (2)研究对象的基线特征; (3)研究使用的干预措施; (4)关注的结局指标。
1.4 观察指标
主要的结局指标为HBV DNA阴转率,次要结局指标为HBsAg/HBeAg阴转或血清学转换率、HCC和肝硬化的发生率。安全性评价以药物相关不良反应发生率为主要评价指标。
1.5 文献质量评价
由2名研究者独立评价纳入研究的方法学质量,如不一致,由第3位研究者决定。采用Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具[15]评估随机对照试验、非随机对照试验的偏倚风险,采用纽卡斯-渥太华质量评价量表[16]评估观察性研究的偏倚风险。
2. 结果
2.1 纳入研究概述
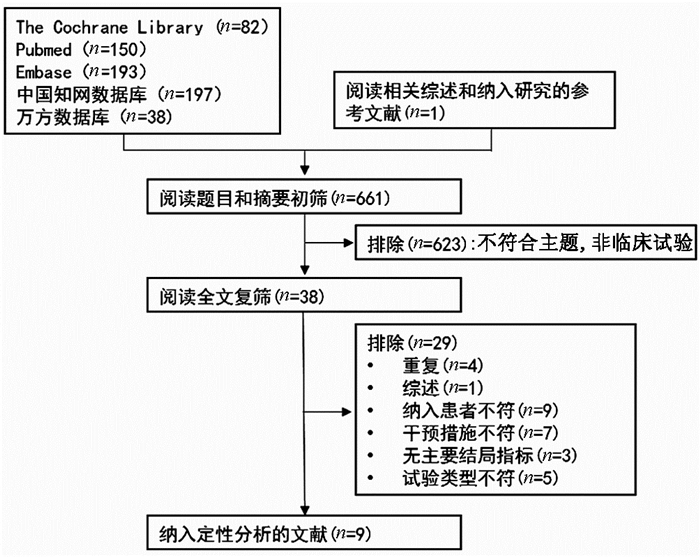
按检索策略,共检索到661篇文章。阅读文章题目和摘要,排除不符合主题、非临床试验文献623篇,剩余38篇。通过阅读原文,排除29篇。最后,共纳入9项研究[13, 15, 17-23]821例患者(均为英文文献)(图 1)。
2.2 纳入研究的基本特征与偏倚风险评价结果
在纳入的研究中,5项研究[11, 17, 19, 21, 23]比较了抗病毒治疗和未治疗,3项研究[18, 22-23]比较了2种抗病毒药物联合治疗和单药治疗,1项研究[13]仅纳入抗病毒治疗组。在研究类型方面,4项研究[18, 20, 22-23]为随机对照研究, 4项研究[13, 17, 19, 21]为非随机对照研究,1项研究[11]为回顾性队列研究。大多数研究中纳入的人数[13, 17, 19-21, 23]少于100人, 但回顾性队列研究[11]纳入了近500例患者。各项研究的抗病毒策略及其他特点见表 1。各研究对免疫耐受期的界定基本一致,具体见表 2。各项研究的偏倚风险评价结果见表 3。
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征纳入研究 国家 例数(男/女) 抗病毒策略 年龄(岁) HBeAg阳性(例) ALT(U/ml) HBV DNA(U/ml) 治疗时间(周) 随访时间(周) 结局指标 研究类型 Artan[17](2005) 土耳其 13/4
3/3拉米夫定
未治疗10.6
917
637.3
30.7NR
NR140
-164
164①③ NRCT Chan[18](2014) 多国 31/33
31/31替诺福韦
替诺福韦+恩曲他滨33
3363
6226.9
26.28.42 log10
8.40 log10192
192192
192①②③④ RCT Chang[11](2017) 韩国 46/41
195/202核苷(酸)类似物
未治疗43.2
41.587
39726.9
26.87.3 log10
7.4 log10NR
NR200
285①③⑥⑦ 队列研究 Feld[13](2019) 加拿大 15/13 恩替卡韦+PEG-IFNα 37.2 28 21 8.2 log10 48 96 ①②③④⑤ 单臂NRCT Lau[19](2002) 中国 12/20
15/17泛昔洛韦
未治疗29
3032
3238
229.04 log10
9.05 log1026
-78
78③ NRCT Leung[20](2014) 中国 9/7
9/5
6/10替比夫定
替诺福韦
替比夫定+替诺福韦28.0
27.3
28.916
14
1631.6
33.9
33.38.98 log10
8.78 log10
8.89 log1012
12
1212
12
12①② RCT Poddar[21](2013) 印度 24/4
27/7拉米夫定+IFNα
未治疗5.92
7.8228
3446.60
50.62NR
NR52
-21.14
28.70①③④ NRCT Wu[22](2019) 中国 26/34
24/37替诺福韦+替比夫定
替诺福韦33
3260
6132.1
31.26.5 log10
7.1 log1048
4848
48①③⑤ RCT Zhu[23](2018) 中国 30/16
13/10IFNα/IFN+拉米夫定
未治疗7
846
2345
489.95×107
1.72×10872
-96
96①③④⑤ RCT 注:NR,未报告; RCT,随机对照研究; NRCT,非随机对照研究; 结局指标中①HBV DNA阴转率; ②HBeAg阴转率; ③HBeAg血清学转换率; ④HBsAg阴转率; ⑤HBsAg血清学转换率; ⑥HCC发生率; ⑦肝硬化发生率。 表 2 纳入研究中对免疫耐受期人群的描述纳入研究 免疫耐受期人群描述 Artan[17](2005) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBeAg(+),抗-HBs(-),抗-HBe(-),HBV DNA>105拷贝/ml,ALT<45 U/L Chan[18](2014) HBsAg(+),HBV DNA>1.7×107 IU/ml,ALT<43 U/L(男)/34 U/L(女) Chang[11](2017) HBeAg(+),HBV DNA>2000 IU/ml,ALT<40 U/L Feld[13](2019) HBsAg(+),HBeAg(+)>12周,HBV DNA>107 IU/ml>12周,ALT<45 U/L(男)/30 U/L(女) Lau[19](2002) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBV DNA>4000 Meq/ml,ALT<1.5倍正常值上限 Leung[20](2014) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBeAg(+)>3月,HBV DNA>107 log10拷贝/ml,ALT<正常值上限,抗-HBc(-) Poddar[21](2013) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBeAg(+),HBV DNA>107拷贝/ml,ALT<2倍正常值上限 Wu[22](2019) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBeAg(+),抗-HBe(-),HBV DNA>107 IU/ml,ALT<40 U/L(男)/30 U/L(女) Zhu[23](2018) HBsAg(+)>6月,HBeAg(+),抗-HBe(-),HBV DNA>107 IU/ml,ALT<60 U/L 表 3 纳入研究的偏倚风险评价结果纳入研究 序列产生 分配隐藏 盲法 结局数据完整性 选择性结局报告 其他偏倚来源 Artan[17](2005) - - 不清楚 是 不清楚 无 Chan[18](2014) 不清楚 不清楚 是 是 不清楚 无 Feld[13](2019) - - 否 是 无 无 Lau[19](2002) - - 不清楚 是 无 无 Leung[20](2014) 不清楚 不清楚 不清楚 是 无 无 Poddar[21](2013) - - 不清楚 是 不清楚 无 Wu[22](2019) 不清楚 - 否 是 无 无 Zhu[23](2018) 随机数字表法 - 否 是 无 无 注:-,未予评估。文献11为回顾性队列研究,未列入表中,偏倚风险评价结果如下,非暴露队列选择(★),暴露资料的确定(★),证实初始无观察结局(★),考虑可比性(★ ★),结局评价(★),随访时限不得分,随访充足性(★),总计7★。 2.3 抗病毒治疗对病毒学应答的影响
8项研究[11, 13, 17-18, 20-23]报告了HBV DNA阴转率, 未治疗组HBV DNA阴转率在0~29.1%,6项研究[11, 13, 18, 21-23]中治疗组HBV DNA阴转率均超过60%,但仍有2项研究[17, 20]治疗组阴转率较低(表 4)。其中1项研究[20]治疗组中虽然HBV DNA阴转率仅为0~6.25%,但3个治疗组均有明显的HBV DNA降低(联合治疗组-4.4 log10拷贝/ml,替比夫定组-3.9 log10拷贝/ml,替诺福韦组-4.2 log10拷贝/ml)。另1项采用拉米夫定治疗的研究[17]中,治疗组在治疗的第12个月HBV DNA全部阴转,但在治疗的第43个月又全部复阳。1项研究[19]虽未报告HBV DNA阴转率,但描述了血清HBV DNA水平在治疗过程中的变化情况:在第28周治疗组HBV DNA下降约80%,非治疗组下降约10%,但随后治疗组HBV DNA反弹,在第78周治疗结束时,2组HBV DNA水平较基线水平下降约20%。在3项对比联合治疗和单药治疗的研究[18, 20, 22]中,2项研究发现联合治疗组HBV阴转率显著升高(P=0.016[18], P=0.028[22])。
表 4 抗病毒治疗的有效性分析纳入研究 纳入人群 抗病毒方案 治疗持续时间(周) HBV DNA阴转率(%) HBeAg阴转率(%) HBeAg血清学转换率(%) HBsAg阴转率(%) HBsAg血清学转换率(%) HCC发生风险(HR) 肝硬化发生风险(HR) Artan[17](2005) 儿童 拉米夫定vs非治疗 150 5.9 vs 0(P=1.000) NR 0 vs 0 NR NR NR NR Chan[18](2014) 成人 替诺福韦+恩曲他滨vs替诺福韦 192 75.8 vs 54.7(P=0.016) 1.6 vs 6.3(P=0.365) 0 vs 4.8(P=0.244) 0 vs 0 NR NR NR Chang[11](2017) 成人 核苷(酸)类似物vs非治疗 NR 70.4 vs 29.1(P<0.001)1) NR 18.3 vs 14.4(P=0.106) NR NR 0.189(P=0.004) 0.347(P=0.036) Feld[13](2019) 成人 恩替卡韦+ PEG-IFNα 48 93 3.57 3.57 0 0 NR NR Lau[19](2002) 成人 泛昔洛韦vs非治疗 78 NR2) NR 0 vs 0 NR NR NR NR Leung[20](2014) 成人 替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替诺福韦vs替比夫定 12 6.25 vs 0 vs 0(P=1.000)3)(P=1.000)4) 6.25 vs 0 vs 0(P=1.000)3)(P=1.000)4) NR NR NR NR NR Poddar[21](2013) 儿童 IFNα+拉米夫定vs非治疗 52 60.75) NR 39.3 vs 0(P<0.001) 17.9 vs 0(P=0.036) NR NR NR Wu[22](2019) 成人 替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替诺福韦 48 96.6 vs 85.2(P=0.028) NR 8.3 vs 3.3(P=0.233) NR 0 vs 0 NR NR Zhu[23](2018) 儿童 IFNα/ IFNα+拉米夫定vs非治疗 72 67.39 vs 4.53(P<0.001) NR 21.74 vs 4.53(P=0.131) 19.75 vs 0(P=0.058) 0 vs 0 NR NR 注:NR,未报告。1)在第48周时的HBV DNA阴转率; 2)文章提供了治疗过程中的HBV DNA水平变化图; 3)替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替诺福韦; 4)替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替比夫定; 5)治疗组中的HBV DNA阴转率。 为明确抗病毒治疗的长期效果, 分析了HBV DNA水平在长期治疗中的变化情况(表 5)。共计6项研究[11, 13, 17-19, 23]被纳入分析,随访时间均超过52周,并在52周后至少报告了1次结果。2项研究[11, 18]表明,在长期持续治疗期间,抗病毒药物对HBV DNA水平具有持续抑制作用,未发生病毒学复发。另1项研究中[17],虽然所有的患者均在拉米夫定治疗期间HBV DNA阴转(平均发生时间7.0±2.7个月),但随后除1例患者外其他所有患者的HBV DNA再次转阳(平均发生时间20.0±9.4个月)。在治疗结束后进行随访的研究中, 2项研究[13, 17]结果表明,治疗停止后患者HBV DNA水平迅速反弹至接近基线水平。只有1项研究[23]报告了在IFNα治疗的儿童中,治疗结束后HBV DNA水平持续下降。
表 5 抗病毒治疗的长期有效性分析纳入研究 研究人群 抗病毒方案 随访时间(周) 治疗时间(周) 治疗结束后随访 治疗中病毒学复发 治疗结束后HBV DNA水平变化 治疗结束后HBeAg转换率变化(%) Artan[17](2005) 儿童 拉米夫定 150 150 否 是 NR NR Chan[18](2014) 成人 替诺福韦+恩曲他滨vs替诺福韦 192 192 否 否 NR NR Chang[11](2017) 成人 核苷(酸)类似物 285 NR 否 否 NR NR Feld[13](2019) 成人 恩替卡韦+ PEG-IFNα 96 48 是 否 上升 稳定 Lau[19](2002) 成人 泛昔洛韦 78 26 是 否 上升 稳定 Zhu[23](2018) 儿童 IFNα/ IFNα+拉米夫定 96 72 是 否 下降 上升 注:NR,未报告。 2.4 抗病毒治疗对血清抗原的影响
3项研究[13, 18, 20]报告了HBeAg阴转,均只发生在治疗组中,且阴转率均<10%。8项研究[11, 13, 17-19, 21-23]报告了HBeAg血清学转换率,共有10个治疗组和5个未治疗组。其中2个治疗组[21, 23]HBeAg血清学转换率>20%,明显高于同研究中的未治疗组,但只有1项研究[21]中差异具有统计学意义,这2组均采用IFNα抗病毒治疗且均纳入了儿童。在队列研究[11]中观察到治疗组和非治疗组HBeAg血清学转换率均>10%,但差异无显著性(表 4)。
4项研究[13, 18, 21, 23]报道了HBsAg阴转率,共有5个治疗组和2个未治疗组。在治疗组中,HBsAg阴转只出现在使用IFNα治疗的儿童中,其他治疗组均未发生,但只有1项研究[21]中观察到治疗组和未治疗组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。3项研究[13, 22-23]报道了HBsAg血清学转换率,均未观察到HBsAg血清学转换。3项研究[18, 20, 22]对比了联合治疗与单药治疗中血清抗原的变化,没有研究显示抗病毒治疗血清学应答在联合治疗组中高于单药治疗组(表 4)。
3项研究[13, 19, 23]报道了结束治疗后随访中HBeAg的变化,未观察到显著的HBeAg复阳(表 5)。
2.5 抗病毒治疗对HCC和肝硬化发病率的影响
1项队列研究[11]报道了HCC和肝硬化的发生率(表 4)。结果表明,接受抗病毒药物治疗的患者HCC和肝硬化的风险明显低于未接受治疗的患者[风险比(HR)分别为0.189(P=0.004)和0.347(P=0.036)]。
2.6 抗病毒治疗的安全性评估
6项研究[13, 18, 20-23]评价了抗病毒药治疗的安全性(表 6)。药物相关不良反应在核苷(酸)类似物治疗组中的发生率从3.3%~25%不等。在IFNα治疗组中,因为轻微的副作用(如发烧),不良反应的发生率达到了100%。3项研究[18, 20, 22]比较了联合治疗和单药治疗的安全性,未发现两组间有显著差异。迫使患者停止该抗病毒药物的使用或导致患者出现生命危险甚至死亡的严重不良反应仅在1篇研究[13]中报告,2例患者的严重不良反应均与PEG-IFNα有关。
表 6 抗病毒治疗的安全性评价纳入研究 抗病毒策略 药物相关不良反应发生率 药物相关严重不良反应发生率(%) Chan[18](2014) 替诺福韦+恩曲他滨vs替诺福韦 8.1% vs 6.3%(P=0.742) 0 Feld[13](2019) 恩替卡韦+PEG-IFNα 33% 4.8 Leung[20](2014) 替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替诺福韦vs替比夫定 25% vs 14.3% vs 0(P=0.6571); P=0.1012)) 0 Poddar[21](2013) IFNα+拉米夫定vs非治疗 100% 0 Wu[22](2019) 替诺福韦+比夫定vs替诺福韦 5.0% vs 3.3% (P=0.66) 0 Zhu[23](2018) IFNα/IFNα+拉米夫定vs非治疗 NR 0 注:1)替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替诺福韦组; 2)替诺福韦+替比夫定vs替比夫定组。NR,未报告。 3. 讨论
免疫耐受期患者的抗病毒治疗一直存在争议,虽有研究发现该类患者仍存在肝组织的破坏,但目前主要的临床指南[2-4]都推荐该类患者应进行进一步的评估或持续检测肝功能而非立即接受治疗。
本研究结果显示:IFNα、PEG-IFN和核苷(酸)类似物均表现出较好的病毒抑制作用,在治疗过程中出现较高的HBV DNA阴转率(>50%)或较大幅度HBV DNA水平下降(>40%)。同时,联合治疗相较于单药治疗有更好的病毒学应答。拉米夫定长期治疗过程中出现了明显的病毒学复发,其他抗病毒药物并未出现这一现象。在治疗结束后,泛昔洛韦和恩替卡韦+PEG-IFN治疗组均出现病毒学复发,仅有IFNα治疗的儿童患者表现出持续性的病毒抑制。对于血清抗原抗体转换,使用IFNα治疗的儿童明显优于使用核苷(酸)类似物或PEG-IFN的患者,但整体而言,HBsAg、HBeAg血清学转换率均不高。核苷(酸) 类抗病毒药物通过抑制HBV的复制增殖发挥抗病毒作用,而不直接影响机体的免疫应答。但IFNα可以通过诱导宿主细胞产生细胞因子而发挥作用,或许可以打破免疫耐受[24-25]。综合考虑,抗病毒治疗总体有效性不显著,长期效果不佳,但IFNα在免疫抑制期儿童患者中似乎有较好的疗效[2-4]。
在纳入的文献中,仅有1篇研究[11]显示抗病毒治疗有助于降低免疫耐受期患者HCC和肝硬化的发生率。Kim等[10]纳入了417例免疫耐受期患者分析发现,10年HCC累计发生率达到12.7%,明显高于抗病毒治疗后的免疫清除期患者(6.1%)。值得注意的是, 这2项研究中纳入患者的平均年龄均为40岁左右,明显大于CHB自然史中免疫耐受期患者,某些患者可能已经进入免疫清除期[10-11]。在1项纳入946例免疫耐受期CHB患者的回顾性研究[26]中,10年的HCC累积发病率为1.7%,表明该类患者发生HCC的风险极低。另1项纳入了126例免疫耐受期患者的研究[27]表明,未治疗的患者5年和9年的累积HCC风险分别为1.1%和1.9%,中等病毒载量(HBV DNA 20 000~1 000 000 IU/ml)患者较高病毒载量(HBV DNA>1 000 000 IU/ml)患者HCC发生率高。综上,抗病毒治疗对免疫耐受期患者长期预后的影响仍不清楚,期待更多高质量的前瞻性研究。
在安全性上,仅有PEG-IFN治疗组中出现了较严重的不良反应,抗病毒治疗整体安全性良好。同时,联合治疗与单药治疗的安全性无显著差异。但1项研究[17]发现拉米夫定治疗导致HBV发生突变,尤其是YMDD变异HBV,从而对抗病毒药物产生耐药性,这一基因的突变率为19%。因此,在抗病毒治疗时不应只关注患者肝功能情况,耐药性的发生同样需要引起重视。
目前免疫耐受期的界定仍以ALT、HBV DNA为参考,但越来越多的研究表明,在评估CHB活动时仅凭ALT和HBV DNA是不充分的。免疫耐受期患者与其他时期患者在循环免疫细胞、细胞因子水平等方面存在显著差异,免疫细胞和细胞因子水平或可更好地反应患者的疾病状态[28]。Gu等[28]研究表明,免疫耐受期CHB患者外周血中细胞因子水平与其他时期具有显著差异:相较于CHB感染的其他时期,免疫耐受期NK细胞和NKT细胞表达的IFNγ表达最低,NK细胞表达的TNFα表达最低。Li等[29]研究也发现免疫耐受期患者IFNα2水平显著低于HBeAg阳性的CHB患者,HBeAg水平与IFNα2水平密切相关。此外,免疫耐受期患者T淋巴细胞表型也不同, 不同表型的T淋巴细胞对HBV的清除作用有差异[30]。综上所述,目前抗病毒治疗对免疫耐受期CHB患者的有效性欠佳,易病毒学复发,但安全性良好,严重不良反应少见。笔者支持现有指南的意见,抗病毒治疗范围可以扩大到基于肝活检或非侵入性检查有活动性或晚期肝病证据的免疫耐受期患者或40岁后仍处于免疫耐受期的患者,但无明确疾病进展证据的免疫耐受期CHB患者应持续随访[2, 31]。
相较于传统综述,本文全面地搜集了已发表的临床研究,进行了严格的文献筛选和评价,结果更为可靠。但由于纳入研究间的差异,定量分析未能进行,且对于HBV感染家族史未能分析,上述结论仍需大样本高质量的研究予以验证。
-
表 1 87例NAFLD病例临床特点分析
Table 1. Clinical characteristics analysis of 87 NAFLD cases
项目 数值 年龄(岁) 11.0(10.0~12.3) 男性[例(%)] 83(95.4) 女性[例(%)] 4(4.6) 代谢综合征[例(%)] 44(50.6) 中心性肥胖[例(%)] 85(97.7) 2型糖尿病[例(%)] 4(4.6) 高血压[例(%)] 4(4.6) 高TG血症[例(%)] 55(63.2) 低HDL-C血症[例(%)] 39(44.8) 高non-HDL-C血症[例(%)] 23(26.4) 胰岛素抵抗[例(%)] 69(79.3) 高尿酸血症[例(%)] 66(75.9) 表 2 87例NAFLD病例实验室数据
Table 2. Laboratory data of 87 NAFLD cases
项目 数值 WBC(×109/L) 7.93±1.98 PLT(×109/L) 321.95±77.20 Hb(g/L) 136.37±10.64 ALT(IU/L) 166.95±113.92 AST(IU/L) 83.82±61.98 GGT(IU/L) 66.09±83.22 ALP(U/L) 150.52±4.83 UA(μmol/L) 426.15±101.36 TG(mmol/L) 1.92±1.12 TC(mmol/L) 4.20±0.96 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.05±0.26 non-HDL-C(mmol/L) 3.11±0.92 FBG(mmol/L) 5.09±1.52 注:UA,尿酸;FBG,空腹血糖。 表 3 87例NAFLD病例病理特点分布情况
Table 3. Distribution of pathological characteristics of 87 NAFLD cases
项目 例数(%) 脂肪变性 1分(5%~33%) 14(16.1) 2分(34%~66%) 10(11.5) 3分(>66%) 63(72.4) 小叶炎症 1分(<2个炎症坏死灶) 29(33.3) 2分(2~4个炎症坏死灶) 55(63.2) 3分(>4个炎症坏死灶) 3(3.4) 气球样变性 0分(无) 1(1.1) 1分(少见) 12(13.8) 2分(多见) 74(85.1) 门静脉区炎症 0分(无) 1(1.1) 1分(轻度) 66(75.9) 2分(中度) 18(20.7) 3分(重度) 2(2.3) 门静脉区纤维化 无 10(11.5) 有 77(88.5) 纤维化分级 F0(无纤维化) 10(11.5) F1(3区窦周/门静脉周围) 42(48.3) F2(窦周和门静脉/门静脉周围) 19(21.8) F3(桥接纤维化) 14(16.1) F4(肝硬化) 2(2.3) NAS评分情况 0~2分 1(1.1) 3~4分 10(11.5) 5~8分 76(87.4) NAFLD模式 非NASH 6(6.9) 1区交界型 13(14.9) 3区交界型 6(6.9) 确定NASH 62(71.3) 表 4 FIB-4对NAFLD肝纤维化、显著肝纤维化、进展期肝纤维化的诊断价值
Table 4. Diagnostic value of FIB-4 in NAFLD fibrosis, significant fibrosis and advanced fibrosis
纤维化阶段 AUC 95%CI 最佳临界值 P值 灵敏度(%) 特异度(%) 阴性预测值(%) 阳性预测值(%) 阴性似然比 阳性似然比 ≥F1 0.636 0.410~0.863 0.16 0.147 79.2 60.0 23.8 92.4 0.35 1.98 ≥F2 0.654 0.538~0.770 0.23 0.015 51.4 75.0 69.6 58.1 0.31 2.06 ≥F3 0.618 0.462~0.774 0.27 0.154 40.0 80.6 86.4 28.6 0.74 2.06 -
[1] YOUNOSSI Z, ANSTEE QM, MARIETTI M, et al. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 15(1): 11-20. DOI: 10.1038/nrgastro.2017.109. [2] ZHANG YP, ZHU YB, YAO Y, et al. Association of high-fructose high-salt diet with metabolic syndrome[J]. J Clin Exp Med, 2022, 21(15): 1569-1572. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.15.001.张雅娉, 朱耀斌, 高琰, 等. 高果糖高盐饮食与代谢综合征的关系研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21(15): 1569-1572. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.15.001. [3] ESTES C, ANSTEE QM, ARIAS-LOSTE MT, et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016-2030[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 69(4): 896-904. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036. [4] ESLAM M, NEWSOME PN, SARIN SK, et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(1): 202-209. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039. [5] XIAO QQ, WANG MY, FAN JG. Brief introduction of APASL clinical practice guidelines on metabolic associated fatty liver disease(Treatment Part)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37(1): 41-45. DOI: 10.3696/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.009.肖倩倩, 王梦雨, 范建高. 亚太肝病研究学会代谢相关脂肪性肝病临床诊疗指南(治疗部分)简介[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(1): 41-45. DOI: 10.3696/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.01.009. [6] OZTURK Y, SOYLU OB. Fatty liver in childhood[J]. World J Hepatol, 2014, 6(1): 33-40. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i1.33. [7] SIMON TG, ROELSTRAETE B, HARTJES K, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and young adults is associated with increased long-term mortality[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(5): 1034-1041. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.034. [8] Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on the diagnosis and therapy of hepatic fibrosis(2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007.中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会感染病学分会. 肝纤维化诊断及治疗共识(2019年)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019, 35(10): 2163-2172. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.10.007. [9] VOS MB, ABRAMS SH, BARLOW SE, et al. NASPGHAN clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: Recommendations from the Expert Committee on NAFLD (ECON) and the North American Society of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (NASPGHAN)[J]. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 2017, 64(2): 319-334. DOI: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000001482. [10] KLEINER DE, BRUNT EM, VAN NATTA M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2005, 41(6): 1313-1321. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20701. [11] SCHWIMMER JB, BEHLING C, NEWBURY R, et al. Histopathology of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2005, 42(3): 641-649. DOI: 10.1002/hep.20842. [12] KLEINER DE, BRUNT EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathologic patterns and biopsy evaluation in clinical research[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2012, 32(1): 3-13. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1306421. [13] ANDERSON EL, HOWE LD, JONES HE, et al. The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(10): e0140908. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140908. [14] DISTEFANO JK. NAFLD and NASH in postmenopausal women: Implications for diagnosis and treatment[J]. Endocrinology, 2020, 161(10): bqaa134. DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa134. [15] WEIHE P, WEIHRAUCH-BLVHER S. Metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents: diagnostic criteria, therapeutic options and perspectives[J]. Curr Obes Rep, 2019, 8(4): 472-479. DOI: 10.1007/s13679-019-00357-x. [16] WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Treatment of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50(9): 897-899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06.王彩娥, 许文涛, 宫建, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病治疗研究进展[J]. 临床军医杂志, 2022, 50(9): 897-899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. [17] MANCO M, MARCELLINI M, DEVITO R, et al. Metabolic syndrome and liver histology in paediatric non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2008, 32(2): 381-387. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803711. [18] DOYCHEVA I, WATT KD, ALKHOURI N. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents and young adults: The next frontier in the epidemic[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 65(6): 2100-2109. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29068. [19] GUO ZQ, WANG QY, QI XS, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (2017)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33(12): 2275-2277. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.12.003.郭泽淇, 王倩怡, 祁兴顺, 等. 《2017年美国肝病学会非酒精性脂肪性肝病诊疗指导》摘译[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33(12): 2275-2277. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2017.12.003. [20] KLEINER DE, MAKHLOUF HR. Histology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in adults and children[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2016, 20(2): 293-312. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.10.011. [21] SEKI S, KITADA T, YAMADA T, et al. In situ detection of lipid peroxidation and oxidative DNA damage in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2002, 37(1): 56-62. DOI: 10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00073-9. [22] CHALASANI N, WILSON L, KLEINER DE, et al. Relationship of steatosis grade and zonal location to histological features of steatohepatitis in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2008, 48(5): 829-834. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.01.016. [23] WANG K, SUN C, DONG C, et al. Analysis of de novo non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in early period after pediatric liver transplantation: a report of 8 cases[J]. Chin J Organ Transplant, 2021, 42(9): 534-538. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn421203-20200728-00261.王凯, 孙超, 董冲, 等. 儿童肝移植术后早期新发非酒精性脂肪性肝病八例临床分析[J]. 中华器官移植杂志, 2021, 42(9): 534-538. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn421203-20200728-00261. [24] WANG XY, WANG LF. Pathological diagnosis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Prac Hepatol, 2013, 16(6): 486-489. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2013.06.003.王晓颖, 王立峰. 非酒精性脂肪性肝炎的病理学诊断[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2013, 16(6): 486-489. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5069.2013.06.003. [25] TAKAHASHI Y, INUI A, FUJISAWA T, et al. Histopathological characteristics of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children: Comparison with adult cases[J]. Hepatol Res, 2011, 41(11): 1066-1074. DOI: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00855.x. [26] SKOIEN R, RICHARDSON MM, JONSSON JR, et al. Heterogeneity of fibrosis patterns in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease supports the presence of multiple fibrogenic pathways[J]. Liver Int, 2013, 33(4): 624-632. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12100. [27] CARTER-KENT C, YERIAN LM, BRUNT EM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children: a multicenter clinicopathological study[J]. Hepatology, 2009, 50(4): 1113-1120. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23133. [28] SINGH S, ALLEN AM, WANG Z, et al. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13(4): 643-654. e1-e9; quiz e39-e40. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.04.014. [29] KANWAR P, KOWDLEY KV. The metabolic syndrome and its influence on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Clin Liver Dis, 2016, 20(2): 225-243. DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2015.10.002. [30] WANG LM, ZHANG HF, DONG Y, et al. Clinical and pathological characteristics of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in children[J]. Chin J Pract Pediatr, 2014, 29(12): 932-935. DOI: 10.7504/ek2014120612.王丽旻, 张鸿飞, 董漪, 等. 儿童非酒精性脂肪性肝炎临床与病理特点分析[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2014, 29(12): 932-935. DOI: 10.7504/ek2014120612. [31] ZHU HH, ZHENG RD, MENG JR, et al. Pathological characteristics of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2007, 12(1): 10-12. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2007.01.005.朱皓皞, 郑瑞丹, 孟加榕, 等. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理特点分析[J]. 肝脏, 2007, 12(1): 10-12. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2007.01.005. [32] ZHOU XL, FU JF. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children[J]. Chin J Pract Pediatr, 2018, 33(7): 487-492. DOI: 10.19538/j.ek2018070602.周雪莲, 傅君芬. 儿童非酒精性脂肪肝病诊断与治疗专家共识[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2018, 33(7): 487-492. DOI: 10.19538/j.ek2018070602. [33] PATTON HM, LAVINE JE, van NATTA ML, et al. Clinical correlates of histopathology in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 135(6): 1961-1971. e2. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.08.050. [34] ABDELMALEK MF, SUZUKI A, GUY C, et al. Increased fructose consumption is associated with fibrosis severity in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(6): 1961-1971. DOI: 10.1002/hep.23535. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张咏红. 2013—2022年徐州市铜山区乙型病毒性肝炎流行病学特征分析. 江苏卫生保健. 2024(01): 15-17 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 胡林慧,王艳. 免疫耐受期HBV感染者抗病毒治疗的临床争议. 临床肝胆病杂志. 2024(05): 875-879 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3065 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3065 KB)


 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:


 百度学术
百度学术