Clinical effect of endoscopic dense ligation in treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding
-
摘要: 目的观察内镜下密集套扎法治疗食管静脉曲张破裂出血的临床疗效。方法选取石家庄市第五医院2015年7月-2016年6月因肝硬化门静脉高压食管静脉曲张破裂出血首次行内镜下套扎治疗的156例患者的临床资料,根据治疗方法不同分为密集套扎组(n=76)和非密集套扎组(n=80)。对患者随访观察12年,统计患者的静脉曲张根除或基本消失率、套扎次数、早期再出血率、迟发性再出血率及不良反应发生率等。计量资料2组间比较采用t检验;计数资料2组间比较采用χ2检验或Fisher精确检验。结果密集套扎组与非密集套扎组静脉曲张根除或基本消失率(71.05%vs 55.00%)、套扎次数比较,差异均有统计学意义(χ2值分别为4.300、8.511,P值分别为0.038、0.014),2组患者早期再出血率(5.26%vs 2.50%)、迟发性再出血率(7.89%vs10.00%)、静脉曲张复发率(13.16%vs 18.75%)及不良反应发生率(26.32%vs 21.25%)比较,差异均无统计学意义(P值均>0.05);静脉曲张复发时间比较,差...Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical effect of endoscopic dense ligation in the treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding. Methods A total of 156 patients who underwent endoscopic ligation for the first time due to esophageal variceal bleeding caused by cirrhotic portal hypertension in Shijiazhuang Fifth Hospital from July 2015 to June 2016 were enrolled, and according to the treatment method, they were divided into dense ligation group with 76 patients and non-dense ligation group with 80 patients. The patients were followed up for 1-2 years, and a statistical analysis was performed for the eradication or disappearance rate of varices, the number of times of ligation, early rebleeding rate, late-onset rebleeding rate, and the incidence rate of adverse reactions. The t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups, and the chi-square test or Fisher's exact test was used for comparison of categorical data between two groups. Results There were significant differences between the dense ligation group and the non-dense ligation group in the eradication or disappearance rate of varices ( 71. 05% vs 55. 00%, χ2= 4. 300, P = 0. 038) and number of times of ligation ( χ2= 8. 511, P = 0. 014) , and there were no significant differences between the two groups in early rebleeding rate ( 5. 26% vs 2. 50%, P > 0. 05) , late-onset rebleeding rate ( 7. 89% vs 10. 00%, P > 0. 05) , recurrence rate of varices ( 13. 16% vs 18. 75%, P > 0. 05) , and incidence rate of adverse reactions ( 26. 32% vs 21. 25%, P > 0. 05) . There was a significant difference in the time to recurrence of varices between the two groups ( 11. 90 ±1. 89 months vs 7. 07 ± 1. 17 months, t = 2. 295, P = 0. 031) . Of all 156 patients, 2 ( 1. 28%) died during follow-up, with 1 patient in the dense ligation group and 1 in the non-dense ligation group. There was no significant difference in mortality rate between the two groups ( P > 0. 05) . Conclusion Endoscopic dense ligation is a safe technique for the treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding and is better than non-dense ligation in terms of the disappearance rate of varices and number of times of ligation. Endoscopic dense ligation also allows a longer time to recurrence of varices than non-dense ligation.
-
Key words:
- liver cirrhosis /
- esophageal and gastric varices /
- ligation /
- treatment outcome
-
在我国,原发性肝癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。外科手术是肝癌患者的首选治疗方式。然而,外科术后肿瘤复发是影响患者预后的重要因素[1]。近年来,微创介入治疗因其独特的优点,被肝癌患者尤其是复发性肝癌患者所接受。经肝动脉化疗栓塞(transcatheter arterial chemoembolization, TACE)联合局部消融被越来越多地应用于治疗外科术后复发性肝癌患者[2]。研究[2-3]显示,TACE联合局部消融治疗外科术后复发性肝癌具有较好的疗效。本研究对TACE联合局部消融治疗外科术后复发性肝癌患者的临床资料进行回顾性分析,现报道如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性分析2017年1月—2020年12月于宁夏医科大学总医院接受TACE联合局部消融治疗外科术后复发性肝癌患者的资料。纳入标准:(1)既往因肝癌行外科手术治疗,术后影像学检查提示肝内出现新的病灶,具备典型的肝癌影像学特征;(2)复发性肝癌以TACE联合局部消融为首选治疗;(3)肝内单发病灶直径≤5 cm,或者多发结节病灶≤3个,且每个结节病灶直径≤3 cm;(4)肝功能Child-Pugh分级为A级或B级。排除标准:(1)BCLC分期C期或者D期;(2)合并有全身急性疾病或自身免疫系统疾病者;(3)消融治疗前肝功能Child-Pugh C级;(4)随访信息不全或者失访者。
1.2 TACE联合局部消融治疗
患者完善相关检查后行TACE术式。采用Seldinger技术行股动脉穿刺插管,行腹腔干、肝固有动脉或其分支造影。通过造影结果明确肿瘤局部情况后,超选择插管至肿瘤主要供血动脉,进行化疗药物灌注治疗,并用碘化油(用量10~20 mL)进行栓塞,根据肿瘤局部情况行个体化治疗。灌注药物有盐酸吡柔比星20 mg,洛铂30 mg。患者在TACE术后2~4周行射频消融或者微波消融。术前通过影像学检查(B超、CT、MRI)明确病灶部位及形态,确定穿刺位点,制订个体化治疗计划。术中在CT引导下行经皮穿刺肝内病灶,逐步进行病灶消融术,消融后立即行CT平扫了解消融范围是否基本覆盖病灶。若消融范围覆盖不完全,则可立即再次消融。于一次消融中完成所有病灶消融。
1.3 随访及疗效评价
局部消融治疗后开始随访。术后前3个月,患者每个月行肝脏增强CT或者MRI。之后间隔3个月1次,1年后间隔半年1次,行上述影像学检查。随访患者的总体生存时间(overall survival time, OS)。OS定义为:患者接受初次联合治疗至其死亡或随访截止时间(2020年10月)。随访过程中若局部病灶存活或者复发,可根据个体情况给予相应治疗(TACE、局部消融等)。疗效评价:依据美国肝病学会颁布的改良实体瘤疗效评价标准(mRECIST),评价患者的近期疗效(首次联合治疗术后3个月)。该标准内容包括:完全缓解(CR),影像学检查提示肝内所有病灶动脉期不增强,即肿瘤病灶完全坏死;部分缓解(PR),影像学检查提示肝内病灶部分坏死(病灶直径缩小≥30%),但仍有部分病灶存活;疾病进展(PD),影像学检查提示肝内病灶直径较前增大(病灶直径增加≥20%),或肝内出现新的病灶;疾病稳定(SD),经影像学检查评估后,肝内病灶变化情况介于部分缓解与疾病进展之间,即病灶缩小程度不及部分缓解,增加程度不及疾病进展。总体有效率(ORR)=(CR+PR)/总例数×100%;疾病控制率(DCR)=(CR+PR+SD)/总例数×100%。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 24.0软件进行分析。运用Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析,采用log-rank检验分析组间差异。采用Cox比例风险回归模型评估影响外科术后复发性肝癌患者OS的可能危险因素。单因素分析结果有意义的变量被用于多因素分析检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料
共纳入47例患者,其中男33例,女14例。肝功能Child-Pugh A级29例,B级18例。单结节患者33例,多结节患者(肿瘤数目2~3个)14例。
2.2 近期疗效和不良反应
TACE联合局部消融治疗外科术后复发性肝癌47例,其中CR 33例,PR 9例,SD 3例,PD 2例,ORR为89.3%,DCR为95.7%。
47例复发性肝癌患者共行TACE 53次,局部消融67次。TACE及消融术后并发症均为轻度不良反应,其中TACE术后疼痛33例,恶心呕吐29例,发热19例;局部消融术后疼痛28例,发热23例。予以对症处理后均得以缓解。治疗中未发生与手术直接相关的死亡事件。
2.3 生存情况
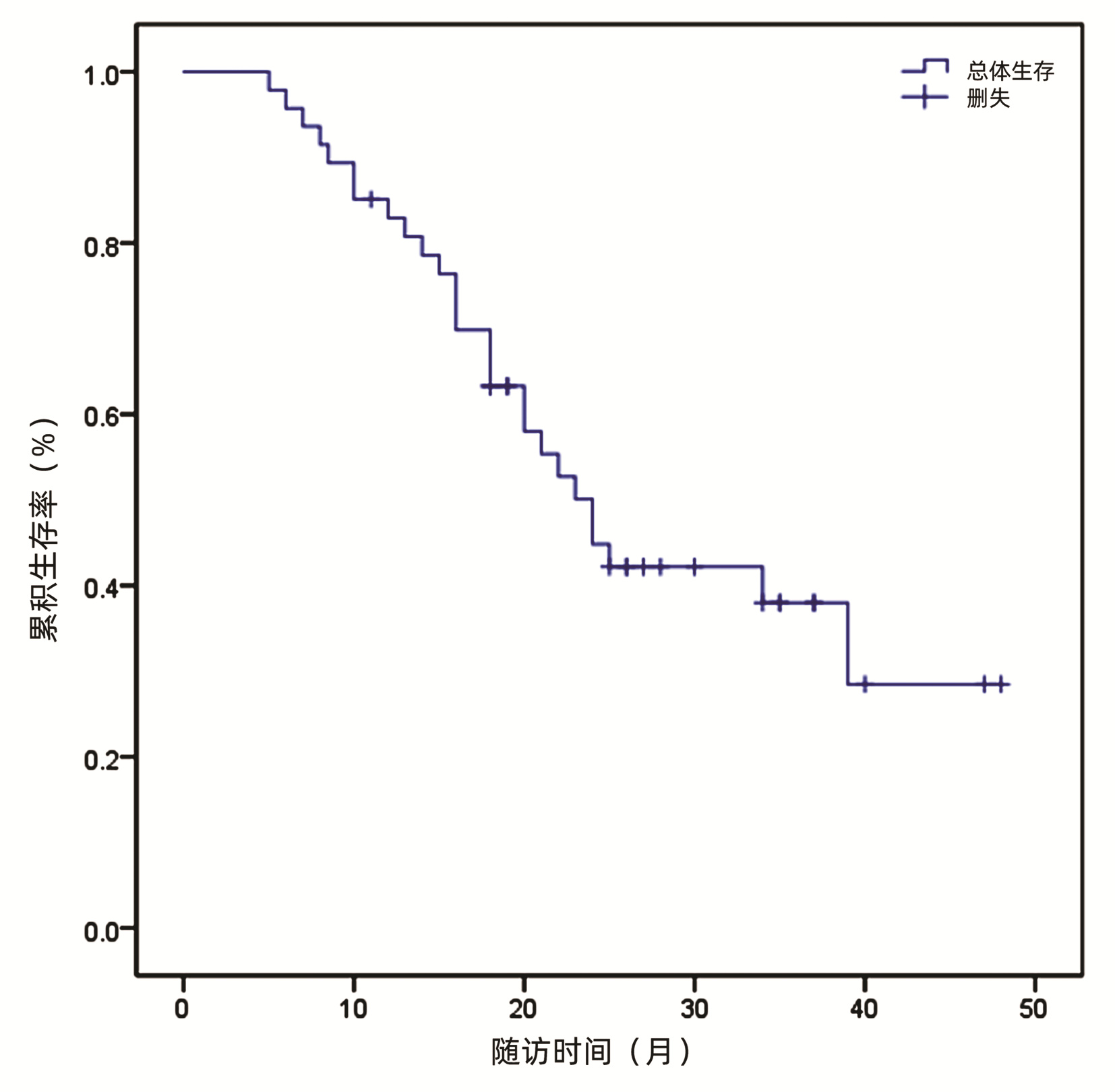
47例患者中位OS为24个月。6、12、18、24个月总生存率分别为95.70%、76.40%、63.30%、58.00%。截至研究终点(即随访截止时间),27例患者死亡,尚有20例患者存活(图 1)。
2.4 影响患者OS的单因素和多因素分析
Kaplan-Meier单因素分析显示外科术后复发性肝癌患者TACE联合局部消融治疗后OS与AFP≥40 ng/mL、肿瘤直径≥3 cm、肿瘤边界不规整和肿瘤位置临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等)相关,差异均有统计学意义(P值均<0.05)。与性别、年龄、PLT、ALT、AST、肝功能分级和肿瘤数目无关(P值均>0.05)(表 1)。将单因素分析有意义的因素(AFP、肿瘤直径、肿瘤边界和肿瘤位置是否临近危险区域)导入Cox比例风险回归模型,结果显示:肿瘤边界不规整和肿瘤位置临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等)是影响外科术后复发性肝癌患者TACE联合局部消融术后生存的危险因素(P值均<0.05)(表 2)。
表 1 影响患者OS的单因素分析Table 1. Univariate analysis of affecting patient OS因素 例数 中位OS(月) χ2值 P值 性别 0.754 0.385 男 33 22 女 14 25 年龄 0.003 0.953 ≥60岁 23 23 <60岁 24 24 PLT 0.066 0.798 ≥100×109/L 32 23 <100×109/L 15 22 ALT 0.294 0.588 ≥40 U/L 11 24 <40 U/L 36 22 AST 0.459 0.498 ≥45 U/L 30 24 <45 U/L 17 22 Child-Pugh分级 0.479 0.489 A级 29 25 B级 18 22 AFP 3.861 0.049 ≥40 ng/mL 20 16 <40 ng/mL 27 25 肿瘤直径 3.933 0.047 ≥3 cm 19 16 <3 cm 28 25 肿瘤数目 0.508 0.476 单个 32 23 2~3个 15 34 肿瘤边界 5.531 0.021 规整 28 25 不规整 19 18 肿瘤位置是否临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等) 7.920 0.005 是 11 18 否 36 34 表 2 影响患者OS的多因素分析Table 2. Multivariate analysis of affecting patient OS因素 RR B值 SE Wald 95%CI P值 肿瘤边界(规整/不规整) 3.938 1.164 0.417 7.804 1.709~9.073 0.005 肿瘤位置是否临近危险区域(是/否) 3.202 1.371 0.426 10.361 1.415~7.245 0.001 3. 讨论
对于复发性肝癌,手术切除或者肝移植可能是最为理想的治疗方式。然而复发性肝癌患者常受剩余肝脏体积、远处转移、静脉侵犯、基础条件、个人意愿等情况的影响而难以耐受再次手术切除[4-5]。因而临床中多采用微创介入的治疗方式[6-7]。TACE被视为非手术治疗肝癌的首选方式[8]。然而多次行TACE对患者肝功能损害较大,且TACE受肿瘤乏血供、肿瘤直径等因素的影响[9],单一TACE治疗效果欠佳。
局部消融因具备微创、可重复等优势被广泛应用于原发性肝癌与复发性肝癌患者的治疗中。相较于外科手术,局部消融具备安全性能高、术后并发症少、住院时间短等优势[10-11]。但有研究[12]显示,两者的治疗效果与肿瘤直径存在一定的关系。就患者术后生存率而言,当肿瘤直径较小时(≤3 cm),两者在患者术后生存率方面无明显差异;当肿瘤直径较大时(>3 cm),局部消融组患者的生存率低于外科手术组。
近年来为改善肝癌患者微创化治疗的疗效,TACE联合局部消融被越来越广泛应用于临床[13-14]。本研究结果显示,复发性肝癌患者治疗后3个月ORR为89.3%,DCR为95.7%,且治疗后无严重手术直接相关并发症发生,提示对于外科术后复发性肝癌患者,TACE联合局部消融治疗可获得较好的的近期疗效及安全性。临床研究[12]显示,对于复发性肝癌患者远期生存率,TACE联合消融组与手术组治疗相比,其预后相近,两组在统计学上无明显差异。Peng等[15]亦称在患者1、3、5年生存率方面,TACE联合消融组与再次手术组无统计学差异。在本研究中,47例复发性肝癌患者TACE联合局部消融治疗后,中位OS可达到24个月,且12、24个月总生存率分别为76.40%、58.00%,与张辉等[16]的研究结果相近。提示对于接受TACE联合局部消融治疗的外科术后复发性肝癌患者,该治疗方式可获得较好的生存率。
本研究显示肿瘤边界不规整和肿瘤位置临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等)是影响外科术后复发性肝癌患者TACE联合局部消融术后生存的危险因素(P值均<0.05),肿瘤边界不规整,肿瘤位置临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等)的患者,治疗后生存率较低。当肿瘤位置临近大血管时,因管内血液对管壁的快速冲刷作用,即所谓的“热沉效应”,导致消融过程热量损减,使得消融效果降低,可能导致肿瘤消融不完全从而影响预后。当肿瘤位置临近空腔脏器时,消融过程可能因注意保护脏器而折损消融效果,且术前肿瘤可能已经对临近脏器产生微浸润现象[17],从而影响治疗效果及预后。
肿瘤边界不规整常由于癌组织的树突状生长或者癌细胞的不规则浸润引起[18],使得病灶更容易临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等),且消融过程受到局部汽化的影响,可能导致消融范围不能完全覆盖病灶,从而引发肿瘤复发及转移,对患者的预后造成影响。因此对于复发性肝癌需要个体化治疗,在适宜情况下可联合其他治疗方式,以期延长患者的生存期。
付元等[19]探讨了TACE联合射频消融及索拉非尼在外科术后复发性肝癌患者中的治疗效果。结果显示,相较于对照组(TACE联合射频消融组),治疗组(TACE联合射频消融及口服索拉非尼)可明显延长患者的中位生存时间。然而在1、2、3年生存率方面,尽管治疗组均高于对照组,但其差异无统计学意义。笔者认为,如何选用适合的治疗方式以求最大程度延长复发性肝癌患者的生存,是临床研究需要突破的一个关键点。就本研究而言,在合并有危险因素的情形下(肿瘤边界不完整或肿瘤位置临近危险区域),局部消融过程可能存在“盲区”或“遗漏区”,对于此类患者是否可以联合一些其他的治疗手段,如靶向治疗等,进而降低局部复发率,目前尚未有这方面的研究。
综上所述,TACE联合局部消融治疗外科术后复发性肝癌安全可靠,可以成为此类患者的一种治疗方式。本研究还发现,肿瘤边界不完整和肿瘤位置临近危险区域(大血管、空腔脏器等)是影响患者联合治疗术后生存的危险因素。对于合并有此类危险因素的患者,术后应密切随访。本研究不足之处在于此研究为单一中心回顾性研究,纳入患者数量较少,随访时间较短,且分析的危险因素较少,结果可能存在一定偏倚。仍需多中心大样本的研究来进一步验证。
-
[1]Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association;Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association;Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association.Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2016, 32 (2) :203-219. (in Chinese) 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会内镜学分会.肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2016, 32 (2) :203-219. [2]HERRERA JL.Management of acute variceal bleeding[J].Clin Liver Dis, 2014, 18 (2) :347-357. [3]de FRANCHIS R, Baveno VI Faculty.Expanding consensus in portal hypertension:Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop:Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J].J Hepatol, 2015, 63 (3) :743-752. [4] Committee of esophageal varicosity, Society of Digestive Endoscopy of Chinese Medical Association.Tentative guidelines for endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of varicosity and variceal bleeding in digestive tract (2009) [J].Chin J Dig Endosc, 2010, 27 (1) :1-4. (in Chinese) 中华医学会消化内镜学分会食管胃静脉曲张学组.消化道静脉曲张及出血的内镜诊断和治疗规范试行方案 (2009年) [J].中华消化内镜杂志, 2010, 27 (1) :1-4. [5] Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association;Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association;Chinese Society of Endoscopy, Chinese Medical Association.Consensus on prevention and treatment for gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in liver cirrhosis (2008, Hangzhou) [J].Chin J Dig, 2008, 28 (8) :551-558. (in Chinese) 中华医学会消化病学分会, 中华医学会肝病学分会, 中华医学会内镜学分会.肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治共识 (2008, 杭州) [J].中华消化杂志, 2008, 28 (8) :551-558. [6]CHEN P.Clinical effect of endoscopic ligation of esophageal veins in treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding:An analysis of 67 cases[J].Shandong Med J, 2011, 51 (7) :69-70. (in Chinese) 陈萍.内镜下食管静脉结扎术治疗食管静脉曲张破裂出血67例分析[J].山东医药, 2011, 51 (7) :69-70. [7]DAI C, LIU WX, JIANG M, et al.Endoscopic variceal ligation compared with endoscopic injection sclerotherapy for treatment of esophageal variceal hemorrhage:A meta-analysis[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21 (8) :2534-2541. [8]ZHANG DX, LUO ZY.Clinical effect of esophageal variceal ligation in treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with liver cirrhosis[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33 (1) :76-81. (in Chinese) 张东旭, 骆子义.食管静脉曲张套扎术治疗肝硬化食管静脉曲张破裂出血的效果观察[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33 (1) :76-81. [9]YE ZS, CHEN LG.Clinical effect of endoscopic variceal ligation in treatment of patients with severe esophageal varices[J].Chin Foreign Med Res, 2016, 14 (32) :36-37. (in Chinese) 叶震世, 陈立刚.内镜下曲张静脉套扎用于食管静脉重度曲张患者治疗的临床效果[J].中外医学研究, 2016, 14 (32) :36-37. [10]XUE DY, QU SX, WANG L, et al.Clinical effect of endoscopic dense versus non-dense ligation in treatment of severe esophageal varices[J].Chin Community Doct, 2012, 14 (17) :140-141. (in Chinese) 薛冬云, 曲少贤, 王玲, 等.内镜密集与非密集套扎治疗重度食管静脉曲张的疗效比较[J].中国社区医师, 2012, 14 (17) :140-141. [11]ZHANG H, YAN DM, FAN HZ.Application of endoscopic variceal ligation in the treatment of patients with esophagus and gastric;varices bleeding:An analysis of sixty cases[J].J Pract Hepatol, 2013, 16 (4) :330-331. (in Chinese) 张鸿, 严冬梅, 范合璋.内镜下曲张静脉套扎治疗食管静脉重度曲张患者60例[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2013, 16 (4) :330-331. [12]YANG KZ, ZHU ZM, CHEN B.Comparison of the efficacy of non-dense ligation and dense ligation of esophageal varices on patients with severe esophageal varices[J].J Hunan Normal Univ:Med Sci, 2017, 14 (6) :133-135. (in Chinese) 杨昆政, 朱增民, 陈波.内镜下非密集套扎与密集套扎对重度食管静脉曲张的疗效比较[J].湖南师范大学学报:医学版, 2017, 14 (6) :133-135. [13]GARCIA-PAGAN JC, REVERTER E, ABRALDES JG, et al.Acute variceal bleeding[J].Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2012, 33 (1) :46-54. [14]LEE SW, LEE TY, CHANG CS.Independent factors associated with recurrent bleeding in cirrhotic patients with esophageal variceal hemorrhage[J].Dig Dis Sci, 2009, 54 (5) :1128-1134. [15]XU L, JI F, XU QW, et al.Risk factors for predicting early variceal rebleeding after endoscopic variceal ligation[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17 (28) :3347-3352. [16]ZHOU JN, WEI Z, SUN ZQ.Risk factors for early rebleeding after esophageal variceal ligation in patients with liver cirrhosis[J].Chin J Hepatol, 2016, 24 (7) :486-492. (in Chinese) 周嘉宁, 魏志, 孙自勤.肝硬化食管静脉曲张套扎后早期再出血相关危险因素的多中心研究[J].中华肝脏病杂志, 2016, 24 (7) :486-492. [17]JIN Y, WANG X, ZHANG LJ, et al.Risk factors for early rebleeding after esophageal variceal ligation in patients with liver cirrhosis[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2017, 33 (11) :2147-2151. (in Chinese) 金燕, 王雪, 张玲娟, 等.肝硬化患者食管静脉曲张套扎术后早期再出血的危险因素分析[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2017, 33 (11) :2147-2151. [18]GU C, LI L, WANG J, et al.Study on efficacy of endoscopic ligation therapy for esophageal varices and risk factors for postoperative rebleeding[J].J Clin Hepatol, 2014, 30 (12) :1279-1282. (in Chinese) 古川, 李璐, 王军, 等.内镜下套扎术治疗肝硬化食管静脉曲张的疗效及术后再出血的危险因素分析[J].临床肝胆病杂志, 2014, 30 (12) :1279-1282. [19]LUZ GO, MALUF-FILHO F, MATUGUMA SE, et al.Comparison between endoscopic sclerotherapy and band ligation for hemostasis of acute variceal bleeding[J].World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2011, 3 (5) :95-100. [20]ZHANG JP, JIANG LY, SHEN YJ.Endoscopic ligation of multiple serial for treatment of esophageal varices[J].J Changchun Univ Chin Med, 2016, 32 (4) :816-818. (in Chinese) 张金萍, 姜连英, 沈玉杰.内镜下多连环结扎术治疗食管静脉曲张的护理[J].长春中医药大学学报, 2016, 32 (4) :816-818. [21]AUGUSTIN S, GONZALEZ A, GENESCAJ.Acute esophageal variceal bleeding:Current strategies and new perspectives[J].World J Hepatol, 2010, 2 (7) :261-274. [22]LUO CQ, LI M, LI MH, et al.Comparison of endoscopic dense ligation and spiral ligation on esophageal varices[J].Mod Digest Interv, 2009, 14 (3) :153-155. (in Chinese) 罗炽权, 李明, 李明华, 等.密集套扎法与螺旋形套扎法治疗食管静脉曲张的疗效对比[J].现代消化及介入诊疗, 2009, 14 (3) :153-155. [23]PEREZ-AYUSO RM, VALDERRAMA S, ESPINOZA M, et al.Endoscopic band ligation versus propranolol for the primary prophylaxis of variceal bleeding in cirrhotic patients with high risk esophageal varices[J].Ann Hepatol, 2010, 9 (1) :15-22. [24]LAHBABI M, MELLOUKI I, AQODAD N, et al.Esophageal variceal ligation in the secondary prevention of variceal bleeding:Result of long term follow-up[J].Pan Afr Med J, 2013, 15:3. [25]FRANCO MC, GOMES GF, NAKAO FS, et al.Efficacy and safety of endoscopic prophylactic treatment with undiluted cyanoacrylate for gastric varices[J].World J Gastrointest Endosc, 2014, 6 (6) :254-259. [26]MASALAITE L, VALANTINAS J, STANAITIS J.The role of collateral veins detected by endosonography in predicting the recurrence of esophageal varices after endoscopic treatment:A systematic review[J].Hepatol Int, 2014, 8 (3) :339-351. [27]TRIANTOS C, KALAFATELI M.Endoscopic treatment of esophageal varices in patients with liver cirrhosis[J].World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20 (36) :13015-13026. [28]MOSTAFA EF, MOHAMMAD AN.Incidence and predictors of rebleeding after band ligation of oesophageal varices[J].Arab J Gastroenterol, 2014, 15 (3-4) :135-141. [29]KAPOOR A, DHAREL N, SANYAL AJ.Endoscopic diagnosis and therapy in gastroesophageal variceal bleeding[J].Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am, 2015, 25 (3) :491-507. [30]LO EA, WILBY KJ, ENSOM MH, et al.Use of proton pump inhibitors in the management of gastroesophageal varices:A systematic review[J].Ann Pharmacother, 2015, 49 (2) :207-219. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 卢冰. 再次肝切除术和射频消融术在治疗肝切除术后早期复发性小肝癌中的疗效比较. 医药论坛杂志. 2024(06): 620-623+628 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 尚敏杰,张军港,顾宗庭,魏芳强,陶然,吴国清,文阳,沈坚,唐雨琪. 免疫联合靶向治疗预防肝细胞癌行ALPPS术后复发的临床疗效. 中华消化外科杂志. 2023(02): 281-285 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 姚爱武,廖和壁,张璟. 血清AFP、AFP-L3与肝细胞癌经肝动脉化疗栓塞术后疗效的关系分析. 分子诊断与治疗杂志. 2023(04): 690-693+698 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 蔡泽丰,祖庆泉,周春高,施海彬,王杰. TACE联合MWA治疗肝切除术后复发性肝癌的疗效及预后分析. 现代生物医学进展. 2023(23): 4578-4583 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1649 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1649 KB)


 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: