Influencing factors for hepatic venous pressure gradient in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension
-
摘要: 目的探讨行经颈静脉肝内门体静脉分流术(TIPS)治疗的肝硬化门静脉高压患者肝静脉压力梯度(HVPG)的临床影响因素。方法选取2015年1月-2018年12月在中国人民解放军西部战区总医院接受TIPS治疗的肝硬化门静脉高压患者158例。在TIPS过程中,分别测量肝静脉楔压、肝静脉自由压及门静脉压,计算得出HVPG与门静脉压力梯度(PVPG)。计量资料2组间比较采用t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。HVPG与PVPG相关性采用Pearson相关分析,采用多元线性逐步回归法分析影响HVPG的独立危险因素。结果 HVPG与PVPG呈正相关(r=0. 796,P <0. 001)。单因素方差分析显示年龄、病因是HVPG的影响因素(F值分别为19. 900、10. 287,P值均<0. 001)。多元线性逐步回归分析显示,年龄及病因是HVPG的独立影响因素(t值分别为7. 870、-2. 178,P值均<0. 001)。结论肝硬化门静脉高压患者的年龄和病因是HVPG的独立影响因素,年龄≥60岁或慢性丙型肝炎肝硬化门静脉高压患者具有更高的HVP...
-
关键词:
- 门体分流术,经颈静脉肝内 /
- 肝硬化 /
- 高血压,门静脉 /
- 危险因素
Abstract: Objective To investigate the influencing factors for hepatic venous pressure gradient(HVPG) in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt(TIPS). Methods A total of 158 patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension who underwent TIPS in The General Hospital of Western Theater Command of the Chinese PLA from January 2015 to December 2018 were enrolled. Wedged hepatic venous pressure(WHVP),free hepatic venous pressure(FHVP),and portal venous pressure(PVP) were measured during TIPS,and HVPG and portal venous pressure gradient(PVPG) were calculated. The t-test was used for comparison of continuous data between two groups; a one-way analysis of variance was used for comparison between multiple groups,and the least significant difference t-test was used for further comparison between two groups. The Pearson correlation coefficient was used to analyze the correlation between HVPG and PVPG,and a multivariate linear stepwise regression analysis was used to investigate the independent risk factors for HVPG. Results HVPG was positively correlated with PVPG(r = 0. 796,P < 0. 001). The one-way analysis of variance showed that age and etiology were influencing factors for HVPG(F = 19. 900 and 10. 287,both P < 0. 001). The multivariate linear stepwise regression analysis showed that age and etiology were independent influencing factors for HVPG(t = 7. 870 and-2. 178,both P < 0. 001). Conclusion Age and etiology are independent influencing factors for HVPG in patients with cirrhotic portal hypertension,and the patients aged ≥60 years or the patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis tend to have higher HVPG. -
肝纤维化是指各种慢性肝病向肝硬化发展时肝脏损伤修复愈合反应的一种病理生理过程[1],其中肝细胞凋亡在肝纤维化的形成过程中具有重要作用[2]。关于肝细胞凋亡与肝纤维化的联系,目前主要有2种机制[3]:(1)肝细胞凋亡后产生的凋亡小体被肝脏中的Kupffer细胞、肝星状细胞、肝窦周细胞吞噬,促进纤维化进展;(2)凋亡的肝细胞会释放核苷酸腺苷三磷酸、脂质溶血磷脂胆碱等促纤维化介质从而促进肝纤维化。
目前国内已有多种中成药应用于肝纤维化的治疗,如扶正化瘀胶囊、鳖甲软肝片等。这些方药中大多含有虫草菌丝或冬虫夏草。笔者在既往针对扶正化瘀胶囊有效组分的研究[4-6]中发现,虫草多糖具有显著的抗肝纤维化作用,其可通过抑制肝星状细胞活化和抑制TGFβ/Smads信号通路而发挥抗肝纤维化作用[7],同时体内研究[8]也发现,虫草多糖有抗肝细胞凋亡的作用,因此,本文拟运用体外TNFα诱导的L02细胞凋亡模型,进一步探讨虫草多糖对肝细胞凋亡的影响及可能的机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
1.1.1 细胞株
人正常肝细胞株L02,购自中国科学院上海细胞生物学研究所细胞库。
1.1.2 实验药物
虫草多糖(批号180316,纯度≥45%UV)购自上海融禾医药科技发展有限公司,称取0.028 g虫草多糖,加入1 ml细胞全培养基后进行冰水浴超声5 min混匀,配置为12.8 mg/ml的虫草多糖母液储存在超低温冰箱备用,后续根据所需实验药物浓度进行配置。
1.1.3 实验试剂
细胞培养基DMEM(1X,货号11965-092,购自GibcoTM);胎牛血清(货号10099141C,购自GibcoTM);青霉素和链霉素(10 000 U/ml,货号15140122,购自GibcoTM);PBS(货号21-040-CV,购自Corning公司);TNFα(货号210-TA,购自美国R & D公司);CCK8试剂盒(货号CCK02-181102,购自上海博谷生物科技有限公司);Annexin V/PI凋亡检测试剂盒[货号E606336-0100,购自生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司];兔cleaved-caspase3单克隆抗体(货号9664)和兔cleaved-caspase8单克隆抗体(货号9496)均购自cell signaling technology公司;兔GAPDH多克隆抗体(货号10494-1-AP,购自Proteintech公司);UNIQ-10柱式Trizol总RNA抽提试剂盒(货号B511321-0100,购自生工生物工程上海股份有限公司);TB Green Rremix Ex Taq(货号PK0445,购自TaKaRa Bio公司);iScriptTM cDNA Synthesis Kit(货号1708891,购自TaKaRa Bio公司);RT-PCR使用引物以及片段长度详见表 1。
表 1 引物序列及片段长度引物名称 引物序列 产物长度(bp) Bax 5′TCG CCC TTT TCT ACT TTG CC 3′ 97 caspase3 5′CTG GTA TGT GTG GAT GAT GCT 3′ 100 caspase8 5′CTG GGA GAA GGA AAG TTG GAC 3′ 68.5 caspase9 5′TGC CTC AAT GCC AGT AAC 3′ 129 Fas 5′ATT TTT GCC TTG GTG CTC A 3′ 94 GAPDH 5′GGG AAG GTG AAG GTC GGA GT 3′ 105 ACTB 5′AAG GTG ACA GCA GTC GGT T 3′ 195 1.1.4 实验仪器及设备
细胞孵育箱(型号Galasxy170s,购于美国NewBrunswick公司);细胞超净操作台(型号HR50-IIA2,购自中国海尔公司);PCR机(型号Applied Biosystems ViiA7,购自美国赛默飞公司);Odyssey双色红外激光成像系统(购自Li-COR公司);高内涵系统(购自美国赛默飞公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
L02正常肝细胞在提前配置好的完全DMEM培养基中培养,其中添加1%青霉素-链霉素和10%胎牛血清。于37 ℃、5%CO2的恒温细胞培养箱中培养,取对数生长期,生长状态良好的细胞进行后续实验。
1.2.2 造模方法
将细胞按照所需组数接种于96孔板或6孔板,每孔细胞密度根据后续具体实验方法进行选择,TNFα造模浓度为0、5、10、20、40 ng/ml,干预时间为24 h,使用CCK8细胞增殖毒性检测法和Annexin V/PI双染法以确定最佳造模浓度。
1.2.3 细胞给药
细胞按照所需组数接种于96孔板或者6孔板,虫草多糖设置浓度为50、100、200 μg/ml共3组,在造模前预作用时间为12 h。
1.2.4 实验分组
不经任何药物和TNFα处理的正常培养细胞为正常组(N),通过实验筛选确定TNFα造模浓度并作用24 h的细胞为模型组(M),根据实验设计,50、100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖预作用12 h并给予TNFα造模浓度作用24 h为实验组。
1.2.5 检测内容和方法
1.2.5.1 细胞增殖:CCK8法
细胞按照5×103 /孔接种于96孔板,每组10孔,待细胞生长至80%以上时,弃上清,按照实验设计进行分组并待药物干预以及造模后,使用PBS缓冲液0.1 ml/孔清洗1次,加入CCK8工作液(CCK8试剂∶细胞全培养基=1∶ 10)0.1 ml/孔,然后于培养箱内继续培养,选取最佳时间放入多功能酶标仪内(450 nm和630 nm波长)读取各孔吸光度值。
1.2.5.2 肝细胞凋亡流式细胞仪检测:Annexin V/PI双染法
细胞按照2×106/孔接种于6孔板,每组3孔,待细胞生长至80%以上时弃上清,按照实验设计进行分组并待药物干预以及造模后,使用PBS洗涤收集不同组细胞,将细胞悬液摇匀后用195 μl的1×Binding Buffer重悬细胞;使细胞密度为2×105细胞/ml,分别加入5 μl的Annexin V和FITC染液至195 μl细胞重悬液,避光,混匀,4 ℃孵育15 min后进行上机检测,为防止荧光衰变,在1 h内进行流式细胞检测。
1.2.5.3 细胞凋亡内源性线粒体途径(Bax、caspase9)、外源性死亡受体途径(caspase8、Fas)和关键执行蛋白酶caspase3的mRNA表达:RT-PCR法
取生长状态良好的细胞接种于6孔板,每组3孔,按照实验设计进行分组并待药物干预以及造模后,弃上清,使用PBS缓冲液清洗,加入Trizol裂解细胞,按照说明书使用总RNA抽提试剂盒进行细胞内总RNA提取,逆转录后进行RT-PCR检测。
1.2.5.4 细胞内cleaved-caspase3、cleaved-caspase8蛋白表达: Western Blot法
将生长状态良好的细胞接种于6孔板中,每组3孔,待药物干预以及造模后,4 ℃预冷离心取细胞沉淀,加入60 μl RIPA细胞裂解液后置于冰上进行细胞总蛋白提取并使用100 ℃加热器致蛋白变性3次,每次10 min后取相应样本进行SDS-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳,使用Odyssey双色红外激光成像系统(Li-COR)进行蛋白印迹显影并分析。
1.2.6 统计学方法
应用SPSS 20.0统计软件进行数据分析。正态分布的计量资料以x±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。非正态分布的计量资料M(P25~P75)表示,多组间比较采用Kruskal-Wallis H检验,进一步两两比较采用Dunnett-t检验。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 TNFα诱导L02正常肝细胞凋亡模型的建立
2.1.1 不同浓度TNFα对L02肝细胞增殖的影响
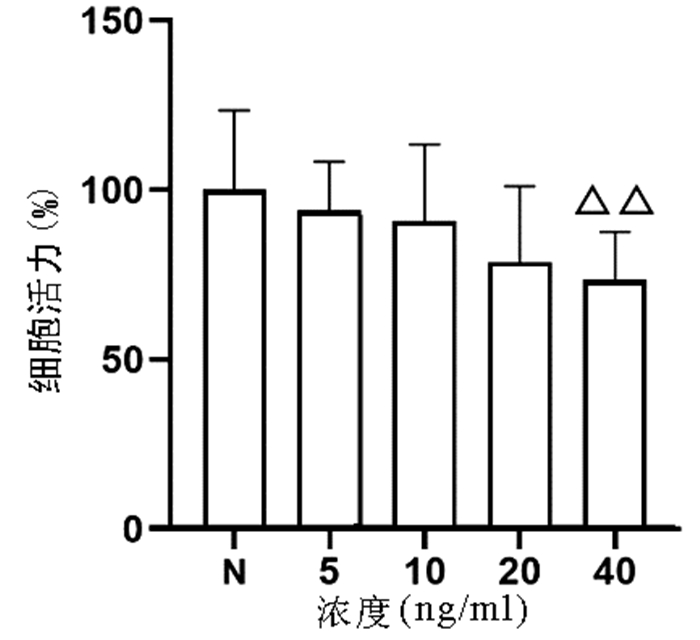
以不同浓度(0、5、10、20、40 ng/ml)TNFα作用于L02细胞24 h,结果显示,随着浓度的增加,细胞增殖逐渐受到抑制,其中40 ng/ml浓度TNFα对L02细胞的增殖具有显著抑制作用(P<0.01)(图 1)。
2.1.2 不同浓度TNFα对L02肝细胞凋亡数的影响
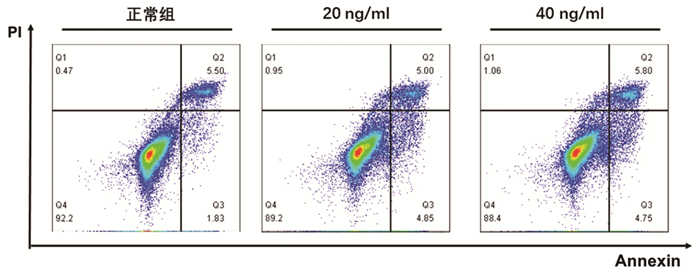
根据增殖实验结果,选用0、20、40 ng/ml的TNFα浓度,通过Annexin V/PI双染法检测其诱导L02肝细胞24 h的细胞凋亡作用。结果显示,细胞凋亡数量随TNFα浓度升高而增加,其中40 ng/ml组与正常组比较差异具有统计学意义(9.85%±0.87% vs 7.71%±1.20%,P<0.05)(图 2)。因此,后续实验以40 ng/ml的TNFα浓度作为诱导L02肝细胞凋亡的造模浓度。
2.2 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导的L02肝细胞凋亡的影响
2.2.1 不同浓度虫草多糖的肝细胞毒性试验
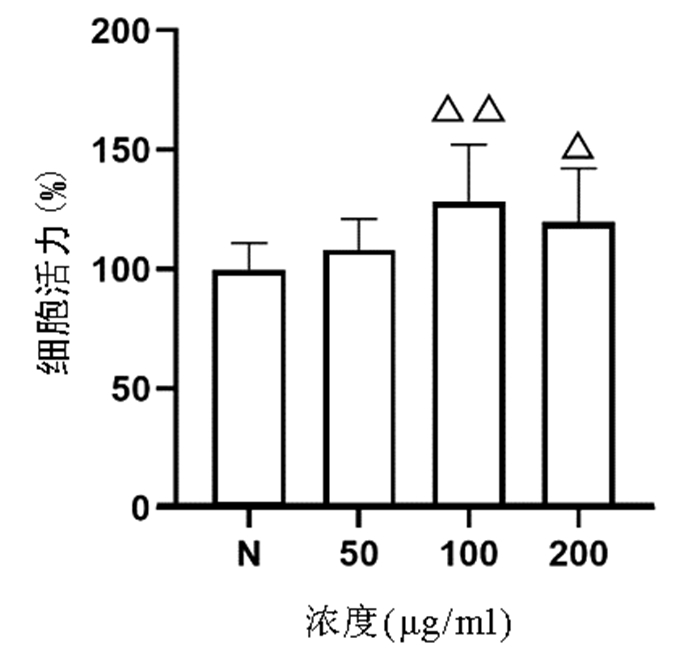
CCK8法检测结果显示,与正常组比较,50、100、200 μg/ml的虫草多糖均对L02肝细胞无明显细胞毒性,其中100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖显著促进L02肝细胞增殖(P值均<0.05)(图 3)。
2.2.2 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导L02肝细胞增殖的影响
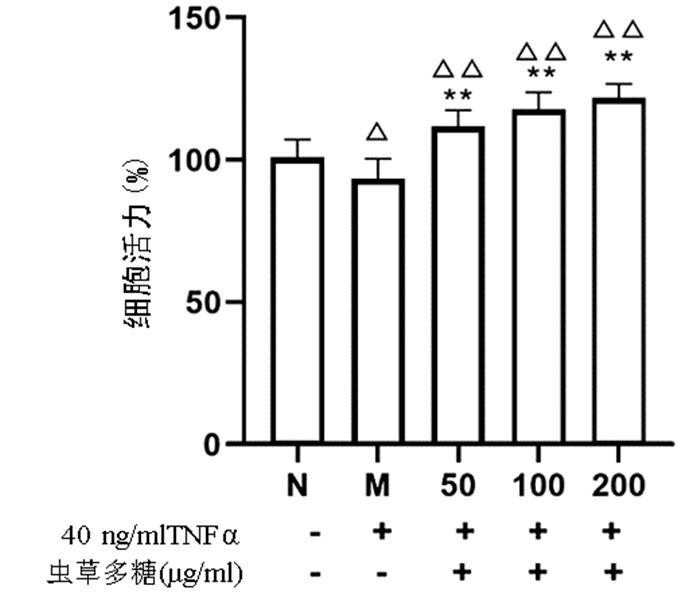
与正常组比较,模型组细胞增殖活力显著下降(P<0.05),而50、100、200 μg/ml的虫草多糖组增殖活力均显著高于正常组和模型组(P值均<0.01)(图 4)。
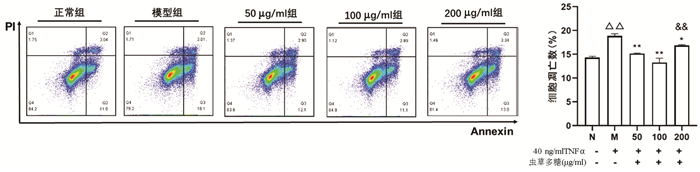
2.3 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导L02肝细胞凋亡数的影响
Annexin V/PI双染法检测结果显示,与正常组比较,模型组凋亡细胞数量显著增加(P<0.01);与模型组比较,50、100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖组凋亡细胞数量均明显降低(P值均<0.05);100 μg/ml组作用效果最优,其与200 μg/ml组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)(图 5)。
2.4 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导L02肝细胞凋亡的mRNA表达影响
RT-PCR结果显示,与正常组比较,模型组的内源性线粒体途径(Bax)、外源性死亡受体途径Fas的mRNA表达均显著升高(P值均<0.05);50、100、200 μg/ml的虫草多糖均可显著降低模型组内源性线粒体途径caspase9的mRNA表达和关键执行蛋白酶caspase3的mRNA表达(P值均<0.05);50、100 μg/ml的虫草多糖可显著降低Bax mRNA表达(P值均<0.05);100、200 μg/ml的虫草多糖可明显降低Fas、caspase8 mRNA表达(P值均<0.05)(表 3)
表 3 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导L02肝细胞凋亡的Bax、caspase 9、caspase 8、Fas、caspase 3的mRNA表达影响组别 Bax caspase 9 Fas caspase 8 caspase 3 正常组 0.92(0.63~1.90) 1.00±0.05 0.97(0.85~1.14) 1.01(0.83~1.15) 0.94(0.87~1.20) 模型组 2.38(1.46~4.14)1) 1.11±0.32 1.66(1.20~3.87)1) 1.33(0.92~4.44) 1.41(1.03~2.80) 50 μg/ml 0.81(0.78~1.11)3) 0.83±0.142) 1.06(0.86~3.18) 0.90(0.83~1.40) 0.90(0.66~1.16)2) 100 μg/ml 1.09(0.65~1.64)2) 0.75±0.073) 0.83(0.77~1.19)2) 0.85(0.76~1.02) 0.83(0.68~0.95)3) 200 μg/ml 1.88(0.90~3.69) 0.77±0.103) 0.77(0.72~0.88)3) 0.82(0.75~0.84)2) 0.79(0.65~0.95)3) 统计值 H=14.17 F=5.298 H=15.88 H=10.45 H=14.63 P值 0.006 <0.001 0.003 0.003 0.005 注:与正常组比较,1)P<0.05;与模型组比较,2)P<0.05,3)P<0.01。 2.5 不同浓度虫草多糖对TNFα诱导L02肝细胞凋亡的相关蛋白表达影响
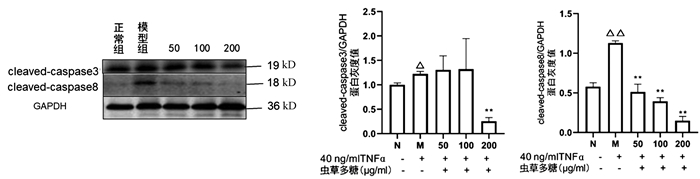
与正常组比较,模型组cleaved-caspase3(P<0.05)、cleaved-caspase8(P<0.01)均显著升高,200 μg/ml虫草多糖组与模型组比较,cleaved-caspase3蛋白表达显著降低(P<0.01);与模型组比较,50、100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖组的cleaved-caspase8蛋白表达均明显降低(P值均<0.01)(图 6)。
3. 讨论
外源性死亡受体通路和内源性线粒体通路介导细胞凋亡的发生,外源性死亡受体途径主要由TNF超家族成员介导,涉及半胱氨酸蛋白酶的层联级激活,包括caspase8、caspase7、caspase10、caspase3。caspase3的激活导致肝细胞凋亡事件的发生,包括核DNA片段化,磷脂酰丝氨酸外露至细胞膜表面等。内源性线粒体途径中线粒体促凋亡蛋白Bax通过拮抗抗凋亡蛋白Bcl2导致线粒体膜通透性改变,从而介导细胞色素C的释放并激活caspase9和凋亡小体的形成,然后caspase9直接激活半胱氨酸蛋白酶3,后续步骤同外源性死亡受体途径[9]。越来越多的研究[10]表明细胞凋亡的失调广泛参与了各种疾病和病理过程,包括药物毒性损伤、免疫反应所导致的损伤、感染以及肿瘤的发生、代谢紊乱、各种肝脏疾病等。
虫草多糖是一种重要的机体稳态调节剂,基于肝细胞凋亡与肝纤维化的关系,本实验重点研究虫草多糖对TNFα诱导的肝细胞凋亡模型的具体影响以及作用机制。CCK8细胞增殖毒性实验和流式细胞检测结果显示:(1) 不同浓度的虫草多糖对L02正常肝细胞均无明显细胞增殖毒性,其中100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖对L02正常肝细胞具有显著的促增殖作用,且可以明显恢复TNFα抑制的L02正常肝细胞的细胞增殖毒性;(2)100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖能够显著减少TNFα诱导的细胞凋亡数量。此外,TNFα诱导L02正常肝细胞发生细胞凋亡的外源性途径中死亡受体Fas的mRNA以及激活形式cleaved-caspase8的蛋白表达均升高,Fas被激活后可激活caspase8和细胞凋亡执行关键酶caspase3从而导致细胞凋亡;同时,对于内源性线粒体途径,Bax作为重要的线粒体促凋亡蛋白,可导致线粒体功能障碍;关键酶caspase9功能与caspase8相近,同样可激活caspase3导致细胞凋亡。TNFα诱导L02正常肝细胞Bax、caspase9、caspase3的mRNA和激活形式cleaved-caspase3的蛋白表达均升高,而100、200 μg/ml虫草多糖可显著抑制外源性途径和内源性途径中的Fas、caspase8、caspase9的mRNA以及激活形式cleaved-caspase8的蛋白表达,200 μg/ml虫草多糖还可以显著抑制激活形式cleaved-caspase3的蛋白表达,虫草多糖对肝细胞凋亡的抑制作用可能随药物浓度升高而逐渐增强,因此,在安全药物浓度的前提下,100、200 μg/ml可能是虫草多糖抑制TNFα诱导肝细胞凋亡的最优浓度,未来仍需进一步实验证实。
综上所述,虫草多糖抑制肝细胞凋亡的具体机制可能涉及如下:(1)抑制内源性线粒体途径中的促凋亡相关蛋白功能,保护线粒体功能完整性;(2)抑制肝细胞凋亡相关的半胱氨酸蛋白酶激活;(3)抑制外源性死亡受体的表达。总之,该研究结果为虫草多糖及其复方制剂在抗肝纤维化中的临床应用提供了一定依据。
-
[1] BOSCH J,IWAKIRI Y. The portal hypertension syndrome:Etiology,classification,relevance,and animal models[J]. Hepatol Int,2017,12(4):1-10. [2] BOSCH J,ABRALDES JG,BERZIGOTTI A,et al. The clinical use of HVPG measurements in chronic liver disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol,2009,6(10):573-582. [3] THALHEIMER U,LEANDRO G,SAMONAKIS DN,et al. Assessment of the agreement between wedge hepatic vein pressure and portal vein pressure in cirrhotic patients[J]. Dig Liver Dis,2005,37(8):601-608. [4] DING HG,XU XY,LINGHU EQ,et al. Interpretation of guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2016,32(2):220-222.(in Chinese)丁惠国,徐小元,令狐恩强,等.《肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南》解读[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2016,32(2):220-222. [5] Group of Gastrointestinal Intervention,Chinese Society of Gastroenterology, Chinese Medical Association. Consensus on transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for treatment of cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2014,30(3):210-213.(in Chinese)中华医学会消化病学分会消化介入学组.经颈静脉肝内门体静脉分流术治疗肝硬化门静脉高压共识意见[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2014,30(3):210-213. [6] THOMAS DB,HASKAL ZJ. The role of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt(TIPS)in the management of portal hypertension:Update 2009[J]. Hepatology,2010,51(1):386-400. [7] Chinese Society of Hepatology,Chinese Medical Association;Chinese Society of Gastroenterolory,Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Endoscopy,Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal and gastric variceal bleeding in cirrhotic portal hypertension[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2016,32(2):203-219.(in Chinese)中华医学会肝病学分会,中华医学会消化病学分会,中华医学会内镜学分会.肝硬化门静脉高压食管胃静脉曲张出血的防治指南[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2016,32(2):203-219. [8] Chinese Society of Hepatology,Chinese Medical Association.Guidelines on the management of ascites and complications in cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2017,33(10):1847-1863.(in Chinese)中华医学会肝病学分会.肝硬化腹水及相关并发症的诊疗指南[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2017,33(10):1847-1863. [9] TANG SH,QIN JP,JIANG MD,et al. The agreement and clinical value of hepatic vein pressure gradient and portal vein pressure in patients with portal hypertension[J]. Chin J Hepatol,2015,23(5):354-357.(in Chinese)汤善宏,秦建平,蒋明德,等.门静脉高压患者肝静脉压力梯度与门静脉压相关性及其临床价值[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2015,23(5):354-357. [10] BOSCH J,GARCIAPAGAN JC,BERZIGOTTI A,et al. Measurement of portal pressure and its role in the management of chronic liver disease[J]. Semin Liver Dis,2006,26(4):348-362. [11] QIN JP,TANG W,TANG SH,et al. Modified tranjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in the treatment of portal hypertension of liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Dig,2014,34(1):33-36.(in Chinese)秦建平,唐文,汤善宏,等.改良经颈静脉肝内门体静脉分流术治疗肝硬化门静脉高压症[J].中华消化杂志,2014,34(1):33-36. [12] QIN JP,JIANG MD,TANG W,et al. Clinical effects and complications of TIPS for portal hypertension due to cirrhosis:A single center[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2013,19(44):8085-8092. [13] ZHANG M,ZHUGE YZ,ZOU XP,et al. Correlation between hepatic venous pressure gradient and clinic features in patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Chin J Dig,2015,35(8):530-533.(in Chinese)张明,诸葛宇征,邹晓平,等.肝静脉压力梯度与肝硬化患者临床特征的相关性[J].中华消化杂志,2015,35(8):530-533. [14] BELLIS LR,MONTAGNESE F,FESTUCCIA F,et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient determination in patients with hepatitis C virus-related and alcoholic cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2003,15(10):1085-1089. [15] WADHAWAN M,DUBEY S,SHARMA BC,et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient in cirrhosis:Correlation with the size of varices,bleeding,ascites,and child’s status[J]. Dig Dis Sci,2006,51(12):2264-2269. [16] GULZAR GM,ZARGAR SA,JALAL S,et al. Correlation of hepatic venous pressure gradient with variceal bleeding,size of esophageal varices,etiology,ascites and degree of liver dysfunction in cirrhosis of liver[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol,2009,28(2):59-61. [17] SUBRAMANIAM R,NIRANJAN K,NAVEEN K,et al. Correlation of HVPG level with CTP score,MELD score,ascites,size of varices,and etiology in cirrhotic patients[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol,2016,22(2):109-115 [18] MAMUN AM,SHEIKH MNEA,MOHAMMAD AR,et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient measurement in bangladeshi cirrhotic patients:A correlation with Child’s status,variceal size,and bleeding[J]. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol,2017,7(2):142-145. [19] XU R,CHANG J,HUANG H,et al. Relationship between clinical parameters and degree of liver fibrosis and risk factors for significant liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B:A Logistic regression analysis[J]. World Chin J Dig,2016,24(2):279-286.(in Chinese)徐瑞,常江,黄华,等.慢性乙型肝炎患者临床指标与肝脏纤维化程度关系及明显肝纤维化危险因素的Logistic回归分析[J].世界华人消化杂志,2016,24(2):279-286. [20] WESTBROOK RH,DUSHEIKO G. Natural history of hepatitis C[J]. J Hepatol,2014,61(1):s58-s68. [21] RASTOGI A,MAIWALL R,BIHARI C,et al. Cirrhosis histology and Laennec staging system correlate with high portal pressure[J]. Histopathology,2013,62(5):731-741. [22] VINCENT JK,STARK C,SHIELDS JT,et al. Hepatic venous pressure gradient correlates with advanced hepatic fibrosis:A retrospective review[J]. Abdom Radiol(NY),2017,42(11):2609-2614. [23] LU LG. Current understanding of the process of liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease[J]. J Diagn Concepts Pract,2005,4(1):9-11.(in Chinese)陆伦根.慢性肝病肝纤维化进程的现今认识[J].诊断学理论与实践,2005,4(1):9-11. [24] Chinese Portal Hypertension Diagnosis and Monitoring Study Group(CHESS); Minimally Invasive Intervention Collaborative Group,Chinese Society of Gastroenterology; Emergency Intervention Committee,Chinese College of Interventionalists,et al. Consensus on clinical application of hepatic venous pressure gradient in China(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol,2018,34(12):2526-2536.(in Chinese)中国门静脉高压诊断与监测研究组(CHESS),中华医学会消化病学分会微创介入协作组,中国医师协会介入医师分会急诊介入专业委员会,等.中国肝静脉压力梯度临床应用专家共识(2018版)[J].临床肝胆病杂志,2018,34(12):2526-2536. 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王雪莹,侯惠宁,安永升,卢佳,李日顺,张才. 甘草多糖对H_2O_2诱导肉鸡肝细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用. 中国兽医学报. 2024(08): 1773-1781 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 马传贵,张志秀,贺宗毅. 虫草属真菌多糖的分离提取、理化性质及生物活性研究进展. 食用菌. 2023(02): 1-3+7 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 李爽,韩淑贞,戴瑜婷,修明慧,杜籼芹,和建政,蔺兴遥. 基于多种化疗肠损伤发生机制的中医药防治进展. 中国临床药理学与治疗学. 2023(05): 583-593 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 韩思婕,潘翔,张梦美,魏琼,叶晓川. 白蔹乙酸乙酯部位体内抗肿瘤的药效作用机制及其成分分析研究. 中药新药与临床药理. 2022(12): 1623-1631 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 常久,张琪,郑宏,季巍巍,向宇雁. 药用真菌抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展. 中国中医药信息杂志. 2021(12): 140-144 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-




 PDF下载 ( 1952 KB)
PDF下载 ( 1952 KB)

 下载:
下载:






 百度学术
百度学术
 下载:
下载: