突变型KRAS在胰腺导管腺癌代谢中的作用
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.043
-
摘要: 胰腺癌作为一种致死率高、预后差的恶性肿瘤,肿瘤代谢相关的基因突变被认为是其进展和预后不良的基础。胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)是最常见的胰腺癌类型,86%的PDAC患者被检测出KRAS突变,KRAS作为多种信号通路和转录因子上游的“分子开关”,对肿瘤细胞代谢过程起着重要的调控作用。突变型KRAS可影响营养物质和能量代谢重编程、巨胞饮作用和自噬,调节肿瘤微环境中的成分相互作用,维持癌细胞的生存和增殖。目前,临床上对PDAC的KRAS靶向治疗大多停留在试验阶段,未来能否真正应用于治疗仍需进一步临床研究。Abstract: Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor with high fatality rate and poor prognosis, and gene mutations involved in tumor metabolism are considered as the basis of its progression and poor prognosis. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the most common type of pancreatic cancer, and it is reported that KRAS mutations are detected in 86% of PDAC patients. As a molecular switch in the upstream of various signaling pathways and transcription factors, KRAS plays an important role in the regulation of tumor cell metabolism. KRAS mutations may affect the metabolic reprogramming of nutrients and energy, macropinocytosis, and autophagy, regulate the interaction between components in tumor microenvironment, and maintain the survival and proliferation of cancer cells. At present, KRAS-targeting therapies for PDAC still remain in an experimental stage, and further clinical studies are needed to determine whether they can be safely applied in treatment.
-
Key words:
- Pancreatic Neoplasms /
- Metabolism /
- Tumor Microenvironment
-
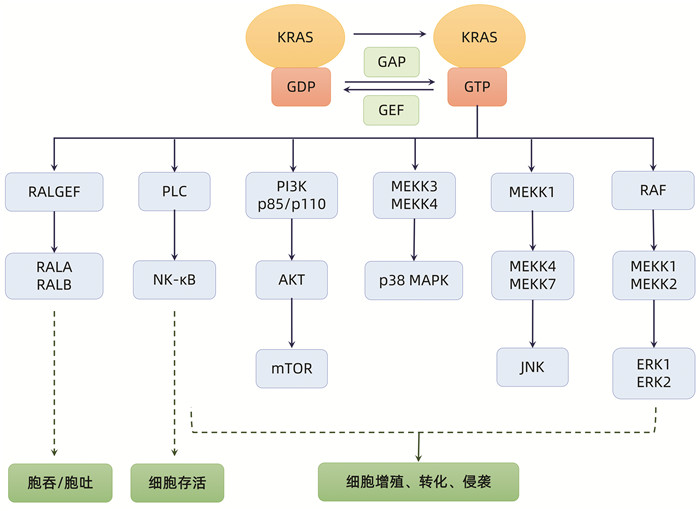
注:KRAS在与GTP结合时被激活,启动下游多种信号通路,最终促进细胞存活、增殖、转化、侵袭、胞吞/胞吐功能。KRAS的突变破坏RAS的内在GTP酶活性,使GAP失去对GTP的失活作用,促进GTP向GDP转化,导致KRAS及其下游信号通路的持续激活。GEF:鸟苷酸交换因子;RALGEF:鸟嘌呤核苷酸交换因子;RALA:Ras样蛋白A;RALB:Ras样蛋白B;PLC:磷酯酶C;NK-κB:核因子κB;MEKK1/2/3/4:MAPK激酶1/2/3/4;JNK:c-Jun氨基末端激酶。
图 1 KRAS信号通路及其对细胞功能的作用
Figure 1. KRAS signaling pathway and its effects on cell function
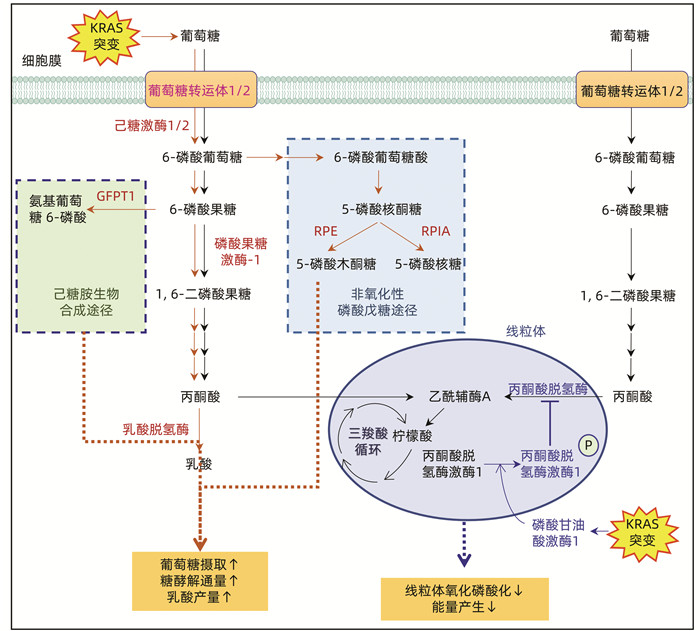
注:葡萄糖在胞液中可裂解为丙酮酸,是葡萄糖无氧氧化和有氧氧化的共同起始途径。在正常细胞中,氧供充足,丙酮酸主要进入线粒体,经历三羧酸循环,遵循糖的有氧氧化途径(黑色箭头路线所示)。(1)KRAS突变,致使葡萄糖转运体、糖酵解限速酶、糖代谢分支途径的关键酶(棕色)上调,糖代谢以无氧氧化为主(棕色箭头路线所示),从而促进葡萄糖摄取,增加糖酵解通量。(2)KRAS突变,刺激磷酸甘油酸激酶1向线粒体易位,致使癌细胞中丙酮酸脱氢酶激酶1磷酸化,抑制丙酮酸脱氢酶(蓝色箭头路线所示),从而抑制胰腺癌细胞中线粒体氧化磷酸化,产能减少。GFPT1:谷氨酰胺6-磷酸果糖转移酶;RPE:5-磷酸核丁糖-3-差向异构酶;RPIA:5-磷酸核丁糖异构酶。
图 2 KRAS突变影响胰腺导管腺癌代谢重编程
Figure 2. KRAS mutation affects metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
表 1 KRAS突变对PDAC代谢的影响
Table 1. Effects of KRAS mutations on PDAC metabolism
影响类型 涉及机制 分子水平改变 最终效应 肿瘤细胞代谢重编程 糖代谢 上调:葡萄糖转运体、己糖激酶、磷酸果糖激酶1、乳酸脱氢酶、谷氨酰胺6-磷酸果糖转移酶、5-磷酸核丁糖-3-差向异构酶、5-磷酸核丁糖异构酶 葡萄糖摄取↑乳酸产量↑糖酵解通量↑ 磷酸甘油酸激酶1线粒体易位 氧化磷酸化↓能量产生↓ 脂代谢 以细胞外脂质供应占主导 避免损耗,限制细胞死亡 过度表达酰基辅酶A合成酶长链3 抑制细胞自噬 氨基酸代谢 诱导:磷酸戊糖途径的代谢重组、天冬氨酸转氨酶的表达 谷氨酰胺代谢↑ 抑制:苹果酸脱氢酶1精氨酸甲基化、谷氨酸脱氢酶的表达、线粒体解耦连蛋白2的表达 维持肿瘤细胞活力 巨胞饮与自噬作用 巨胞饮 突变型KRAS与肿瘤细胞表面的αvβ3和半乳糖凝集素3形成复合物 癌细胞巨胞饮作用↑ 促进关键效应因子V-ATPase向质膜易位 维持癌细胞的氧化还原平衡 自噬 激活YAP-TAZ途径及其下游JAK-STAT3信号转导 诱导细胞自噬相关的MHC-I降解 -
[1] SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21654. [2] BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21492. [3] HUANG L, JANSEN L, BALAVARCA Y, et al. Resection of pancreatic cancer in Europe and USA: an international large-scale study highlighting large variations[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(1): 130-139. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314828. [4] HENRIKSEN A, DYHL-POLK A, CHEN I, et al. Checkpoint inhibitors in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2019, 78: 17-30. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.06.005. [5] INDINI A, RIJAVEC E, GHIDINI M, et al. Targeting KRAS in solid tumors: Current challenges and future opportunities of novel KRAS inhibitors[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(5): 653. DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13050653. [6] HOSEIN AN, BREKKEN RA, MAITRA A. Pancreatic cancer stroma: an update on therapeutic targeting strategies[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(8): 487-505. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-0300-1. [7] SUN H, ZHANG B, LI H. The Roles of frequently mutated genes of pancreatic cancer in regulation of tumor microenvironment[J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2020, 19: 1533033820920969. DOI: 10.1177/1533033820920969. [8] HOLLINSHEAD K, PARKER SJ, EAPEN VV, et al. Respiratory supercomplexes promote mitochondrial efficiency and growth in severely hypoxic pancreatic cancer[J]. Cell Rep, 2020, 33(1): 108231. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108231. [9] DEY P, LI J, ZHANG J, et al. Oncogenic KRAS-Driven metabolic reprogramming in pancreatic cancer cells utilizes cytokines from the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Discov, 2020, 10(4): 608-625. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0297. [10] BUSCAIL L, BOURNET B, CORDELIER P. Role of oncogenic KRAS in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(3): 153-168. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-019-0245-4. [11] ENCARNACIÓN-ROSADO J, KIMMELMAN AC. Harnessing metabolic dependencies in pancreatic cancers[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18(7): 482-492. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-021-00431-7. [12] NAGDAS S, KASHATUS JA, NASCIMENTO A, et al. Drp1 promotes KRas-driven metabolic changes to drive pancreatic tumor growth[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 28(7): 1845-1859.e5. DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.031. [13] HOU P, KAPOOR A, ZHANG Q, et al. Tumor microenvironment remodeling enables bypass of oncogenic KRAS dependency in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Discov, 2020, 10(7): 1058-1077. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0597. [14] SANTANA-CODINA N, ROETH AA, ZHANG Y, et al. Oncogenic KRAS supports pancreatic cancer through regulation of nucleotide synthesis[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4945. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-07472-8. [15] LI X, JIANG Y, MEISENHELDER J, et al. Mitochondria-translocated PGK1 functions as a protein kinase to coordinate glycolysis and the TCA cycle in tumorigenesis[J]. Mol Cell, 2016, 61(5): 705-719. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.009. [16] ROZEVELD CN, JOHNSON KM, ZHANG L, et al. KRAS controls pancreatic cancer cell lipid metabolism and invasive potential through the lipase HSL[J]. Cancer Res, 2020, 80(22): 4932-4945. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-1255. [17] ROSSI SEBASTIANO M, POZZATO C, SALIAKOURA M, et al. ACSL3-PAI-1 signaling axis mediates tumor-stroma cross-talk promoting pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(44): eabb9200. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb9200. [18] ROSSI SEBASTIANO M, KONSTANTINIDOU G. Targeting long chain Acyl-CoA synthetases for cancer therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(15): 3624. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20153624. [19] SALIAKOURA M, SEBASTIANO MR, NIKDIMA I, et al. Restriction of extracellular lipids renders pancreatic cancer dependent on autophagy[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 16. DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02231-y. [20] WANG YP, ZHOU W, WANG J, et al. Arginine methylation of MDH1 by CARM1 inhibits glutamine metabolism and suppresses pancreatic cancer[J]. Mol Cell, 2016, 64(4): 673-687. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.028. [21] RAHO S, CAPOBIANCO L, MALIVINDI R, et al. KRAS-regulated glutamine metabolism requires UCP2-mediated aspartate transport to support pancreatic cancer growth[J]. Nat Metab, 2020, 2(12): 1373-1381. DOI: 10.1038/s42255-020-00315-1. [22] ZHANG Y, COMMISSO C. Macropinocytosis in cancer: A complex signaling network[J]. Trends Cancer, 2019, 5(6): 332-334. DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.04.002. [23] RAMIREZ C, HAUSER AD, VUCIC EA, et al. Plasma membrane V-ATPase controls oncogenic RAS-induced macropinocytosis[J]. Nature, 2019, 576(7787): 477-481. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1831-x. [24] KINSEY CG, CAMOLOTTO SA, BOESPFLUG AM, et al. Publisher correction: Protective autophagy elicited by RAF→MEK→ERK inhibition suggests a treatment strategy for RAS-driven cancers[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(5): 861. DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0433-3. [25] HUMPTON TJ, ALAGESAN B, DENICOLA GM, et al. Oncogenic KRAS induces NIX-mediated mitophagy to promote pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Discov, 2019, 9(9): 1268-1287. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1409. [26] YAMAMOTO K, VENIDA A, YANO J, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7806): 100-105. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2229-5. [27] POMMIER A, ANAPARTHY N, MEMOS N, et al. Unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress engenders immune-resistant, latent pancreatic cancer metastases[J]. Science, 2018, 360(6394). DOI: 10.1126/science.aao4908. [28] DAI E, HAN L, LIU J, et al. Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis drives tumor-associated macrophage polarization via release and uptake of oncogenic KRAS protein[J]. Autophagy, 2020, 16(11): 2069-2083. DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1714209. [29] MONTERAN L, EREZ N. The dark side of fibroblasts: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as mediators of immunosuppression in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1835. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01835. [30] HAMARSHEH S, GROβ O, BRUMMER T, et al. Immune modulatory effects of oncogenic KRAS in cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5439. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-19288-6. [31] WANG T, NOTTA F, NAVAB R, et al. Senescent carcinoma-associated fibroblasts upregulate IL8 to enhance prometastatic phenotypes[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2017, 15(1): 3-14. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0192. [32] HAFEZI S, SABER-AYAD M, ABDEL-RAHMAN WM. Highlights on the role of KRAS mutations in reshaping the microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(19): 10219. DOI: 10.3390/ijms221910219. [33] NOLLMANN FI, RUESS DA. Targeting mutant KRAS in pancreatic cancer: Futile or promising?[J]. Biomedicines, 2020, 8(8): 281. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines8080281. [34] CANON J, REX K, SAIKI AY, et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity[J]. Nature, 2019, 575(7781): 217-223. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1694-1. [35] HALLIN J, ENGSTROM LD, HARGIS L, et al. The KRASG12C inhibitor MRTX849 provides insight toward therapeutic susceptibility of KRAS-mutant cancers in mouse models and patients[J]. Cancer Discov, 2020, 10(1): 54-71. DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-1167. [36] HONG DS, FAKIH MG, STRICKLER JH, et al. KRASG12C inhibition with sotorasib in advanced solid tumors[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(13): 1207-1217. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1917239. [37] JONCKHEERE N, VASSEUR R, VAN SEUNINGEN I. The cornerstone K-RAS mutation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma: From cell signaling network, target genes, biological processes to therapeutic targeting[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2017, 111: 7-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.01.002. [38] DROSTEN M, BARBACID M. Targeting the MAPK pathway in KRAS-driven tumors[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 37(4): 543-550. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.03.013. [39] TERRELL EM, MORRISON DK. Ras-mediated activation of the raf family kinases[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2019, 9(1): a033746. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a033746. [40] NAGASAKA M, POTUGARI B, NGUYEN A, et al. KRAS Inhibitors- yes but what next? Direct targeting of KRAS-vaccines, adoptive T cell therapy and beyond[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2021, 101: 102309. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2021.102309. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李正优,李荷,周俊. 预见性护理结合舒适护理干预在肝移植术后患者中的应用. 西藏医药. 2024(06): 123-125 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 李珊珊,王媛,高春辉. 早期下床活动对肝移植术后患者胃肠功能及下肢血流的影响. 国际移植与血液净化杂志. 2023(01): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 张欣悦,王海刚,王昊,杨传伟. 他克莫司治疗1例肝移植术后患者的药学监护. 中国医药导报. 2023(14): 183-187 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 种庚,彭晓春,吴若林,赵红川,邵敏. 成人肝移植术后早期严重并发症相关危险因素分析. 肝胆外科杂志. 2022(06): 454-459 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-




 PDF下载 ( 3776 KB)
PDF下载 ( 3776 KB)

 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

