| [1] |
YE Q, ZOU BY, YEO YH, et al. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5( 8): 739- 752. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30077-7. |
| [2] |
A RH, JIA HY, DING YH, et al. Research advances in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 5): 1154- 1159. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.05. 046.
|
| [3] |
DELA CRUZ AC, BUGIANESI E, GEORGE J, et al. Characteristics and long-term prognosis of lean patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146( 5): S909. DOI: 10.1016/s0016-5085(14)63307-2. |
| [4] |
YOUNES R, GOVAERE O, PETTA S, et al. Caucasian lean subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease share long-term prognosis of non-lean: Time for reappraisal of BMI-driven approach?[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 2): 382- 390. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322564. |
| [5] |
HAGSTRÖM H, NASR P, EKSTEDT M, et al. Risk for development of severe liver disease in lean patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A long-term follow-up study[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2018, 2( 1): 48- 57. DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1124. |
| [6] |
WANG QY, YOU H, OU XJ, et al. Non-obese histologically confirmed NASH patients with abnormal liver biochemistry have more advanced fibrosis[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 6): 766- 776. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09982-z. |
| [7] |
LI CL, GUO PP, OKEKUNLE AP, et al. Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients had comparable total caloric, carbohydrate, protein, fat, iron, sleep duration and overtime work as obese non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34( 1): 256- 262. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14360. |
| [8] |
SCHWARZ JM, LINFOOT P, DARE D, et al. Hepatic de novo lipogenesis in normoinsulinemic and hyperinsulinemic subjects consuming high-fat, low-carbohydrate and low-fat, high-carbohydrate isoenergetic diets[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2003, 77( 1): 43- 50. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/77.1.43. |
| [9] |
DONNELLY KL, SMITH CI, SCHWARZENBERG SJ, et al. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Invest, 2005, 115( 5): 1343- 1351. DOI: 10.1172/JCI23621. |
| [10] |
XIA Y. Dietary patterns associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Tianjin population: a case-control study[C]// The 12th National Nutrition Science Conference, Beijing, 2015.
夏阳. 膳食模式在天津人群中与非酒精性脂肪肝关联:病例-对照研究[C]// 第十二届全国营养科学大会, 北京, 2015.
|
| [11] |
Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association, National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines of prevention and treatment for alcoholic liver disease: a 2018 update[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2018, 34( 5): 939- 946. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2018.05.006. |
| [12] |
ZHAO C, LI MF, XIAO W, et al. Selection of calculation methods for daily total calories of overweight and obese adults[J]. Guangdong Med J, 2004, 25( 5): 577- 578. DOI: 10.13820/j.cnki.gdyx.2004.05.064. |
| [13] |
LIANG J, JIANG ZQ, HE YM, et al. Estimated equations of basal metabolic rate in Chinese healthy adults[J]. Chin J Sch Dr, 2008, 22( 4): 372- 374. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7062.2008.04.002. |
| [14] |
YAO M, MCCRORY MA, MA G, et al. Energy requirements of urban Chinese adults with manual or sedentary occupations, determined using the doubly labeled water method[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2002, 56( 7): 575- 584. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601361. |
| [15] |
MA LC. Analysis of the intervention effect of low-carb diet on patients with metabolic-related fatty liver disease[D]. Yan’an: Yan’an University, 2021.
马立翠. 低碳水化合物饮食对MAFLD患者的干预效果分析[D]. 延安: 延安大学, 2021.
|
| [16] |
WU LX, WANG WJ, TANG X, et al. Diagnostic value of FibroTouch controlled attenuation parameters for hepatic steatosis in NAFLD patients[J]. J New Chin Med, 2019, 50( 8): 579- 583. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9802.2019.08.004. |
| [17] |
SHEN F, ZHENG RD, MI YQ, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter for non-invasive assessment of hepatic steatosis in Chinese patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20( 16): 4702- 4711. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4702. |
| [18] |
SASSO M, BEAUGRAND M, de LEDINGHEN V, et al. Controlled attenuation parameter(CAP): A novel VCTE™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2010, 36( 11): 1825- 1835. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.07.005. |
| [19] |
CHEN JN, CHEN AP, PAN Q, et al. Influential factors and clinical value of controlled attenuation parameters in the evaluation of hepatic steatosis using FibroScan[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2016, 21( 10): 805- 809. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2016.10.001. |
| [20] |
KIM NH, KIM JH, KIM YJ, et al. Clinical and metabolic factors associated with development and regression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in nonobese subjects[J]. Liver Int, 2014, 34( 4): 604- 611. DOI: 10.1111/liv.12454. |
| [21] |
ISOURA Y, CHO Y, FUJIMOTO H, et al. Effects of obesity reduction on transient elastography-based parameters in pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Obes Res Clin Pract, 2020, 14( 5): 473- 478. DOI: 10.1016/j.orcp.2020.08.005. |
| [22] |
WANG Y, ZHENG JF. Research progress of nutritional intervention in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Med Postgrad, 2014, 27( 1): 99- 101. DOI: 10.16571/j.cnki.1008-8199.2014.01.012. |
| [23] |
MOORE MP, CUNNINGHAM RP, DASHEK RJ, et al. A fad too far? dietary strategies for the prevention and treatment of NAFLD[J]. Obesity, 2020, 28( 10): 1843- 1852. DOI: 10.1002/oby.22964. |
| [24] |
SANTESSO N, AKL EA, BIANCHI M, et al. Effects of higher- versus lower-protein diets on health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Clin Nutr, 2012, 66( 7): 780- 788. DOI: 10.1038/ejcn.2012.37. |
| [25] |
WANG Y, JIANG MX, XU Q, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diet on obese adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Mil Med J Southeast China, 2015, 17( 1): 5- 7, 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-271X.2015.01.002. |
| [26] |
FAN JG, CAO HX. Role of diet and nutritional management in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2013, 28( Suppl 4): 81- 87. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12244. |
| [27] |
WANG CE, XU WT, GONG J, et al. Research progress in treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2022, 50( 9): 897- 899, 903. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2022.09.06. |
| [28] |
MOYER VA, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for and management of obesity in adults: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2012, 157( 5): 373- 378. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-157-5-201209040-00475. |



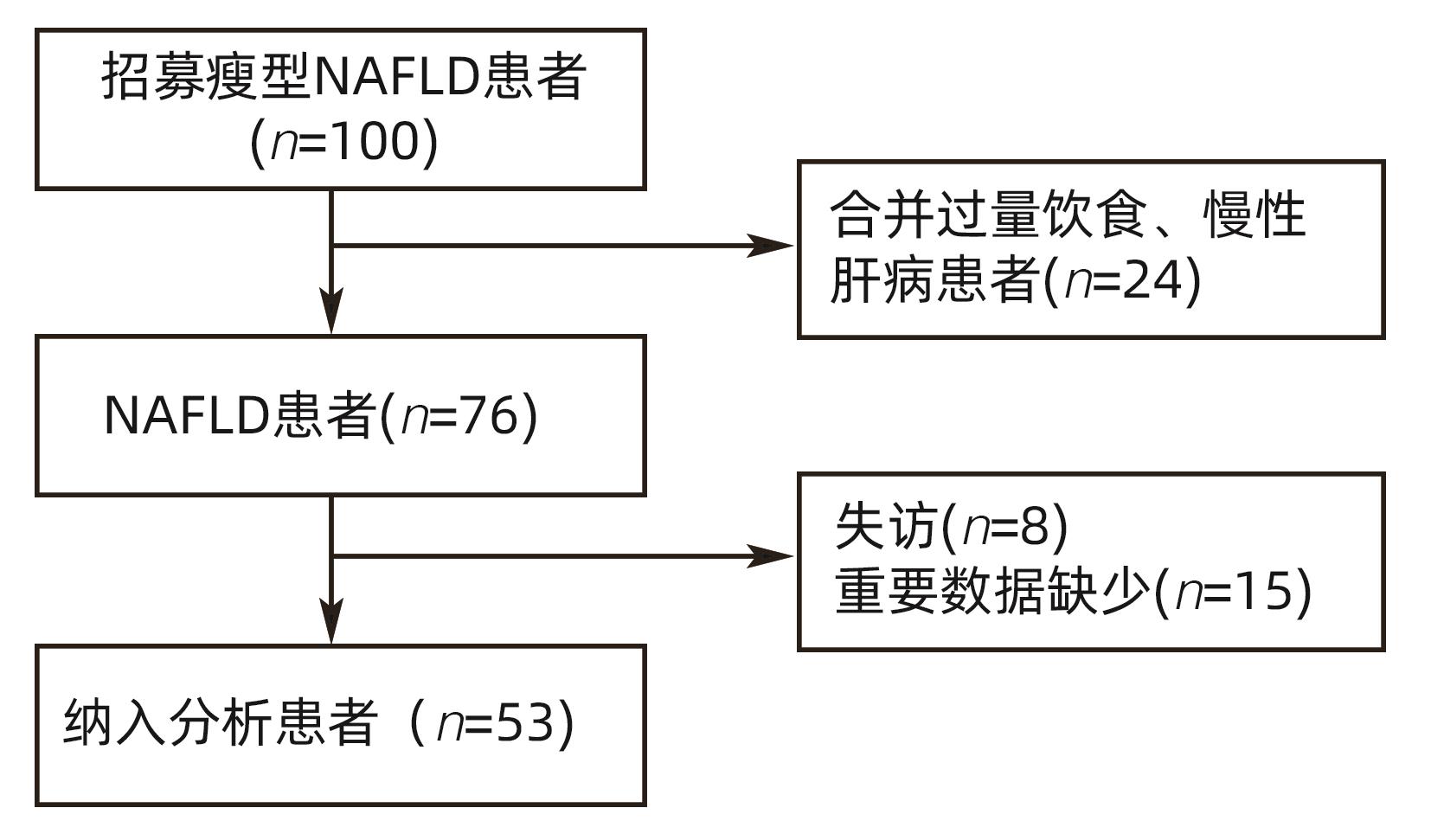




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: