| [1] |
GRIFFITH JW, SOKOL CL, LUSTER AD. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2014, 32: 659- 702. DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120145. |
| [2] |
EDDERKAOUI B. Potential role of chemokines in fracture repair[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2017, 8: 39. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00039. |
| [3] |
FAHEY S, DEMPSEY E, LONG A. The role of chemokines in acute and chronic hepatitis C infection[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2014, 11( 1): 25- 40. DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2013.37. |
| [4] |
WASMUTH HE, TACKE F, TRAUTWEIN C. Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2010, 30( 3): 215- 225. DOI: 10.1055/s-0030-1255351. |
| [5] |
GUSTAVSSON M. New insights into the structure and function of chemokine receptor: Chemokine complexes from an experimental perspective[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2020, 107( 6): 1115- 1122. DOI: 10.1002/JLB.2MR1219-288R. |
| [6] |
CHARO IF, RANSOHOFF RM. The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006, 354( 6): 610- 621. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra052723. |
| [7] |
BAGGIOLINI M, LOETSCHER P. Chemokines in inflammation and immunity[J]. Immunol Today, 2000, 21( 9): 418- 420. DOI: 10.1016/s0167-5699(00)01672-8. |
| [8] |
SALLUSTO F, MACKAY CR, LANZAVECCHIA A. The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory immune responses[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2000, 18: 593- 620. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.593. |
| [9] |
WHITE GE, IQBAL AJ, GREAVES DR. CC chemokine receptors and chronic inflammation: Therapeutic opportunities and pharmacological challenges[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2013, 65( 1): 47- 89. DOI: 10.1124/pr.111.005074. |
| [10] |
SEEGER C, MASON WS. Molecular biology of hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Virology, 2015, 479-480: 672- 686. DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.031. |
| [11] |
HU LS, ZHU Y, ZHANG JQ, et al. Potential circulating biomarkers of circulating chemokines CCL5, MIP-1β and HA as for early detection of cirrhosis related to chronic HBV(hepatitis B virus) infection[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19( 1): 523. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4130-0. |
| [12] |
LI Y, WANG CM, ZHAO T, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates chemokine CCL15 upregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2021, 21( 16): 2198- 2203. DOI: 10.2174/1871520621666210302083407. |
| [13] |
ZHANG K, LIU YQ, YANG XA, et al. HBV promotes the recruitment of IL-17 secreting T cells via chemokines CCL22 and CCL17[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40( 6): 1327- 1338. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14438. |
| [14] |
ZHUO JY, LU D, LIN ZY, et al. CC motif chemokine ligand 16 inhibits the progression of liver cirrhosis via inactivating hepatic stellate cells[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2020, 19( 5): 440- 448. DOI: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2019.12.006. |
| [15] |
YAN Y, ZHAO W, LIU W, et al. CCL19 enhances CD8 + T-cell responses and accelerates HBV clearance[J]. J Gastroenterol, 2021, 56( 8): 769- 785. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-021-01799-8. |
| [16] |
KHANAM A, GHOSH A, CHUA JV, et al. Blockade of CCR4 breaks immune tolerance in chronic hepatitis B patients by modulating regulatory pathways[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21( 1): 271. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-023-04104-8. |
| [17] |
LIU HJ, GUAN QZ, ZHAO P, et al. TGF-β-induced CCR8 promoted macrophage transdifferentiation into myofibroblast-like cells[J]. Exp Lung Res, 2022: 1- 14. DOI: 10.1080/01902148.2022.2055227. |
| [18] |
LI L, WEI W, LI ZZ, et al. The spleen promotes the secretion of CCL2 and supports an M1 dominant phenotype in hepatic macrophages during liver fibrosis[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 51( 2): 557- 574. DOI: 10.1159/000495276. |
| [19] |
BARTNECK M, SCHRAMMEN PL, MÖCKEL D, et al. The CCR2 + macrophage subset promotes pathogenic angiogenesis for tumor vascularization in fibrotic livers[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 7( 2): 371- 390. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.10.007. |
| [20] |
FLAMINI S, SERGEEV P, VIANA de BARROS Z, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper regulates liver fibrosis by suppressing CCL2-mediated leukocyte recruitment[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12( 5): 421. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03704-w. |
| [21] |
XI S, ZHENG X, LI X, et al. Activated hepatic stellate cells induce infiltration and formation of CD163 + macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 pathway[J]. Front Med(Lausanne). 2021, 8: 627927. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.627927. |
| [22] |
DU PLESSIS J, KORF H, van PELT J, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines but not endotoxin-related parameters associate with disease severity in patients with NAFLD[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11( 12): e0166048. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166048. |
| [23] |
XU L, CHEN YP, NAGASHIMADA M, et al. CC chemokine ligand 3 deficiency ameliorates diet-induced steatohepatitis by regulating liver macrophage recruitment and M1/M2 status in mice[J]. Metabolism, 2021, 125: 154914. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154914. |
| [24] |
GUO YK, ZHAO C, DAI WT, et al. C-C motif chemokine receptor 2 inhibition reduces liver fibrosis by restoring the immune cell landscape[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19( 8): 2572- 2587. DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.83530. |
| [25] |
IGAKI K, KOMOIKE Y, NAKAMURA Y, et al. MLN3126, an antagonist of the chemokine receptor CCR9, ameliorates inflammation in a T cell mediated mouse colitis model[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 60: 160- 169. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.049. |
| [26] |
MORIKAWA R, NAKAMOTO N, AMIYA T, et al. Role of CC chemokine receptor 9 in the progression of murine and human non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 74( 3): 511- 521. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.09.033. |
| [27] |
HANSON A, PIRAS IS, WILHELMSEN D, et al. Chemokine ligand 20(CCL20) expression increases with NAFLD stage and hepatic stellate cell activation and is regulated by miR-590-5p[J]. Cytokine, 2019, 123: 154789. DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154789. |
| [28] |
HEO YJ, CHOI SE, LEE NM, et al. CCL20 induced by visfatin in macrophages via the NF-κB and MKK3/6-p38 signaling pathways contributes to hepatic stellate cell activation[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2020, 47( 6): 4285- 4293. DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05510-7. |
| [29] |
KISSELEVA T, BRENNER D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 18( 3): 151- 166. DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-00372-7. |
| [30] |
KONG M, DONG WH, KANG AQ, et al. Regulatory role and translational potential of CCL11 in liver fibrosis[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 1): 120- 135. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000287. |
| [31] |
PROOST P, WUYTS A, van DAMME J. The role of chemokines in inflammation[J]. Int J Clin Lab Res, 1996, 26( 4): 211- 223. DOI: 10.1007/BF02602952. |
| [32] |
TACKE F. Functional role of intrahepatic monocyte subsets for the progression of liver inflammation and liver fibrosis in vivo[J]. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, 2012, 5( Suppl 1): S27. DOI: 10.1186/1755-1536-5-S1-S27. |
| [33] |
DEBES JD, ROMAGNOLI PA, PRIETO J, et al. Serum biomarkers for the prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2021, 13( 7): 1681. DOI: 10.3390/cancers13071681. |
| [34] |
ZHU MX, XU WY, WEI CY, et al. CCL14 serves as a novel prognostic factor and tumor suppressor of HCC by modulating cell cycle and promoting apoptosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10( 11): 796. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1966-6. |
| [35] |
EHLING J, TACKE F. Role of chemokine pathways in hepatobiliary cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2016, 379( 2): 173- 183. DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.06.017. |
| [36] |
YANG XQ, LU PR, FUJII C, et al. Essential contribution of a chemokine, CCL3, and its receptor, CCR1, to hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. Int J Cancer, 2006, 118( 8): 1869- 1876. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.21596. |
| [37] |
PAN XF, CHIWANDA KAMINGA A, LIU AZ, et al. Chemokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1802. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01802. |
| [38] |
TAN YY, YUE SR, LU AP, et al. The improvement of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by Poria cocos polysaccharides associated with gut microbiota and NF-κB/CCL3/CCR1 axis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 103: 154208. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154208. |
| [39] |
RATZIU V, SANYAL A, HARRISON SA, et al. Cenicriviroc treatment for adults with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis: Final analysis of the phase 2b CENTAUR study[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 72( 3): 892- 905. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31108. |
| [40] |
WIERING L, TACKE F. Treating inflammation to combat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Endocrinol, 2022, 256( 1): e220194. DOI: 10.1530/JOE-22-0194. |
| [41] |
PUENGEL T, LEFERE S, HUNDERTMARK J, et al. Combined therapy with a CCR2/CCR5 antagonist and FGF21 analogue synergizes in ameliorating steatohepatitis and fibrosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 12): 6696. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23126696. |



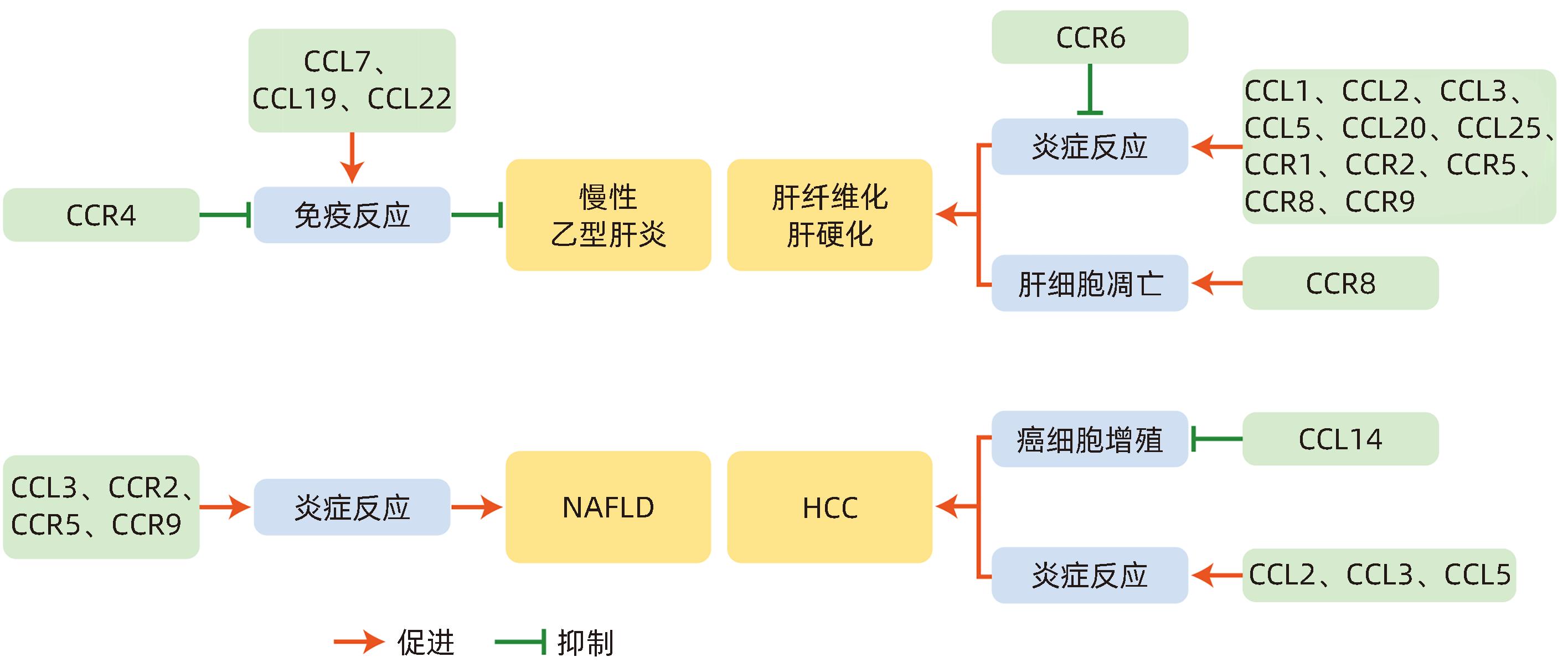




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: