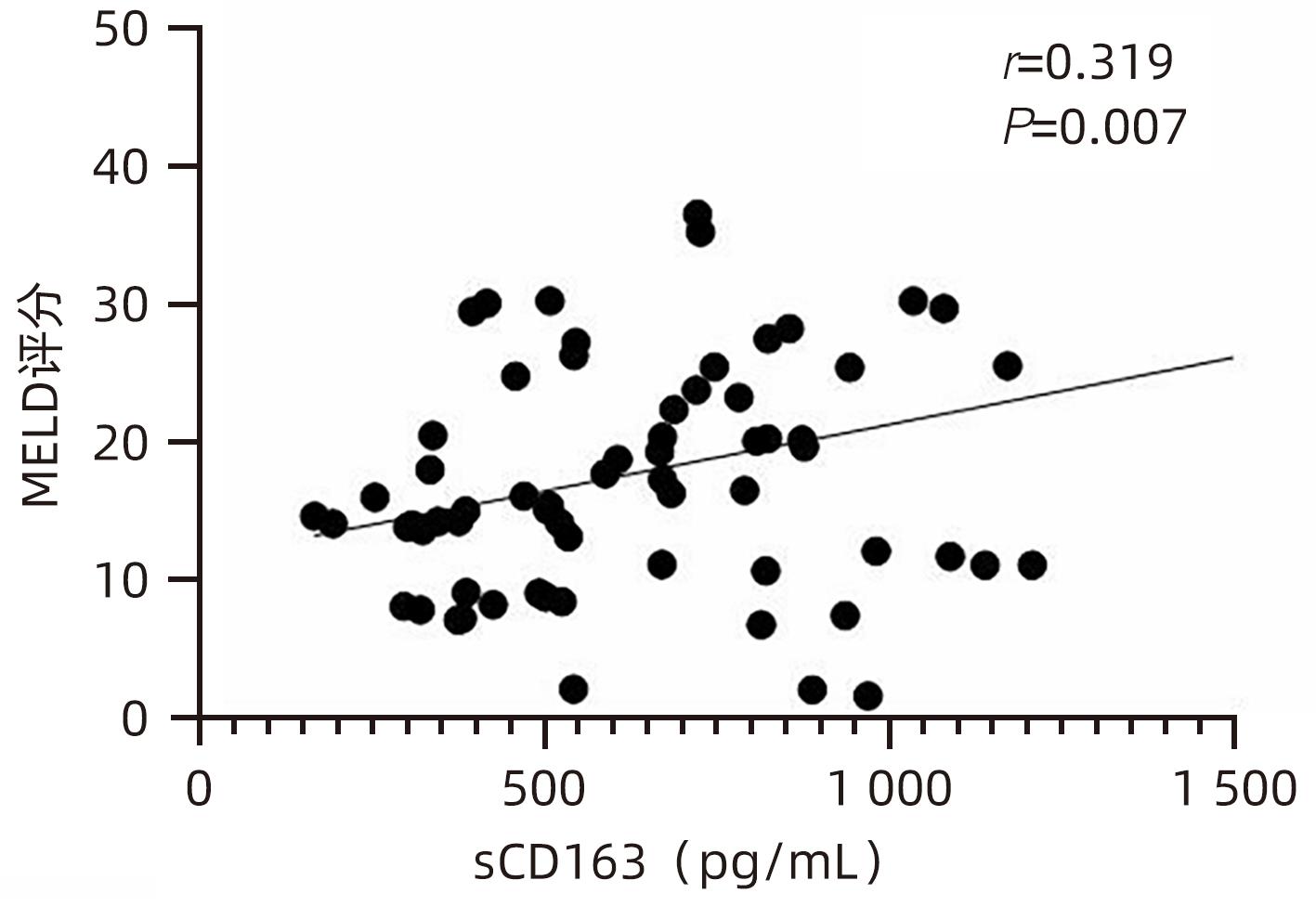
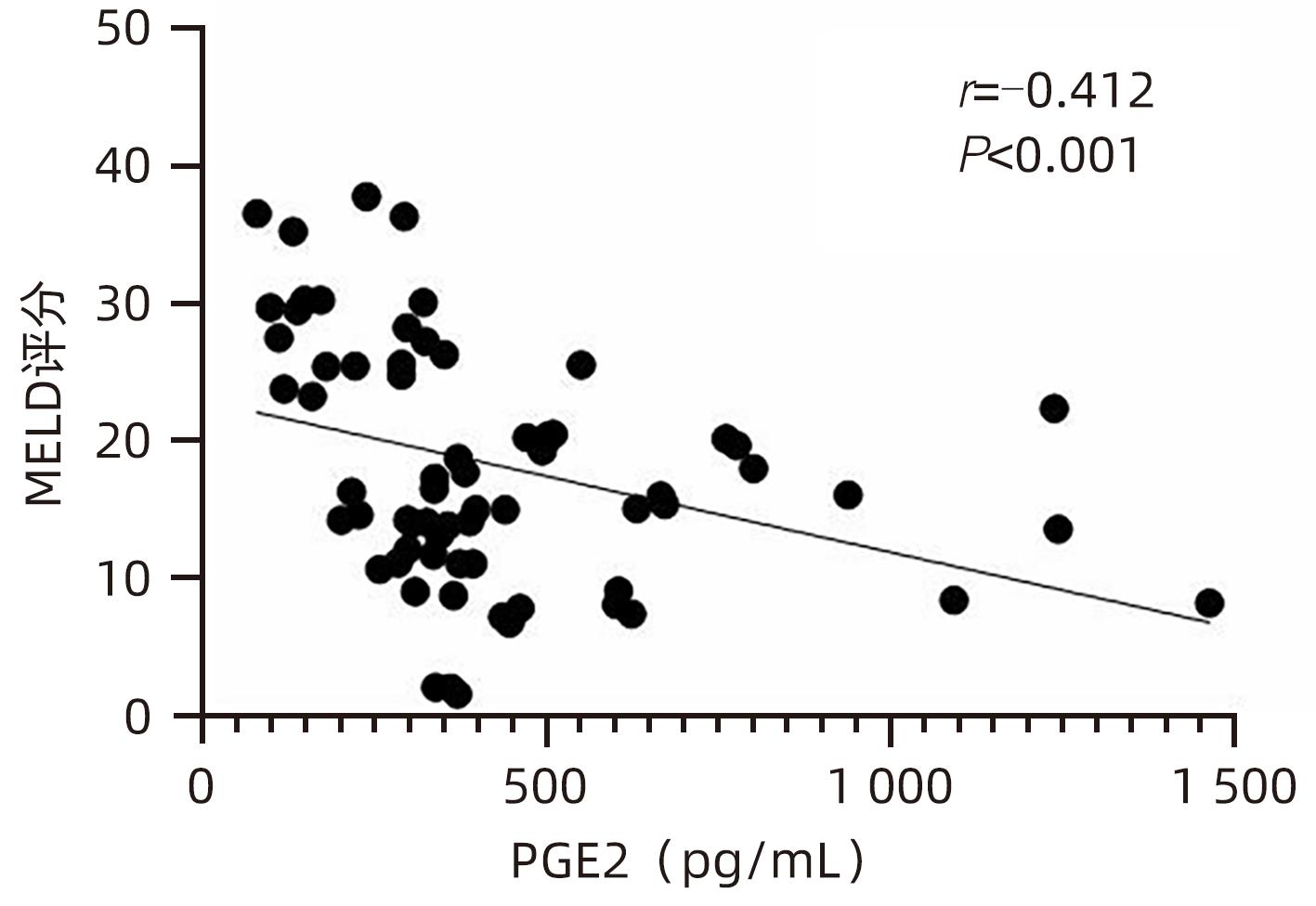
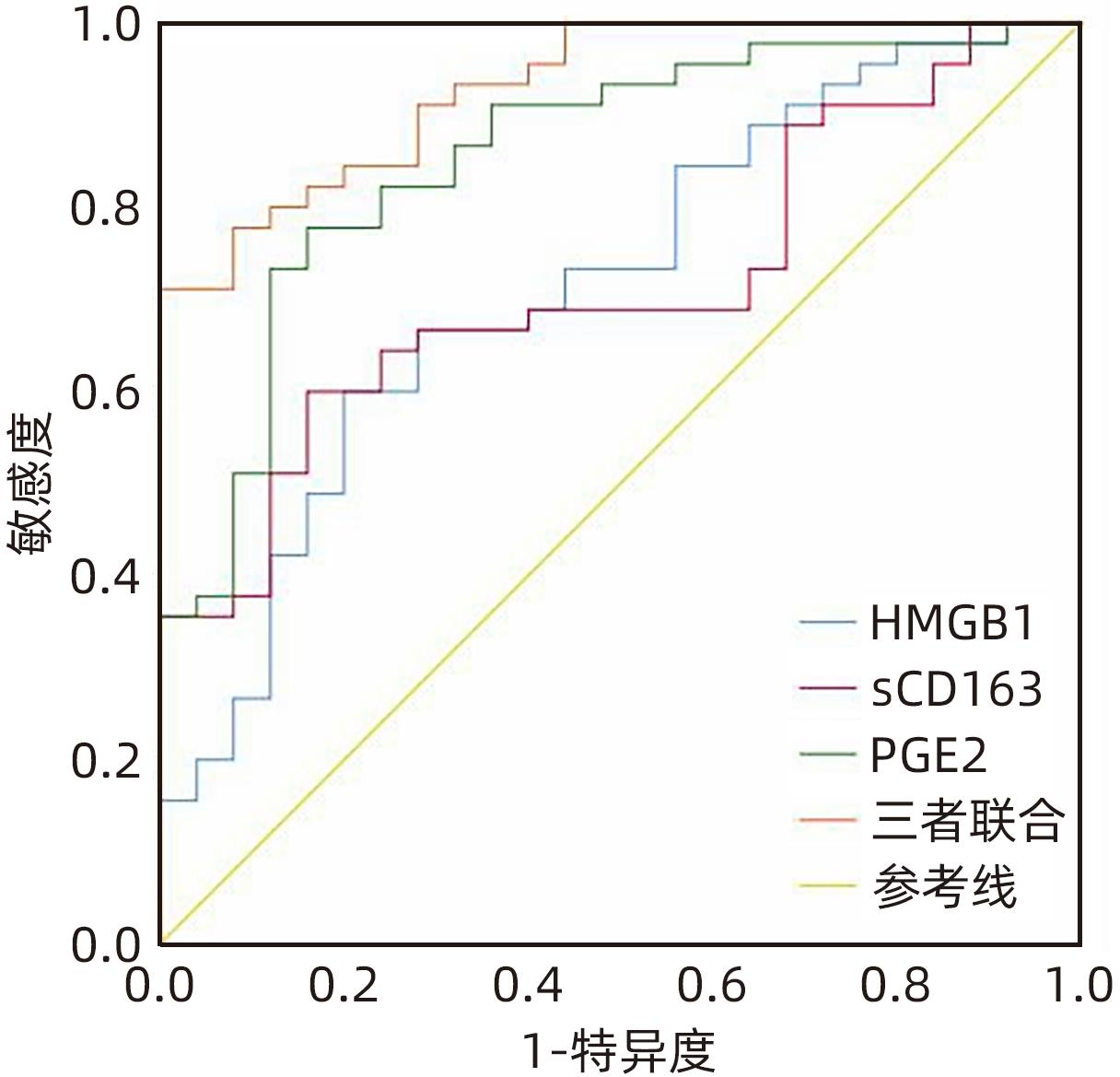
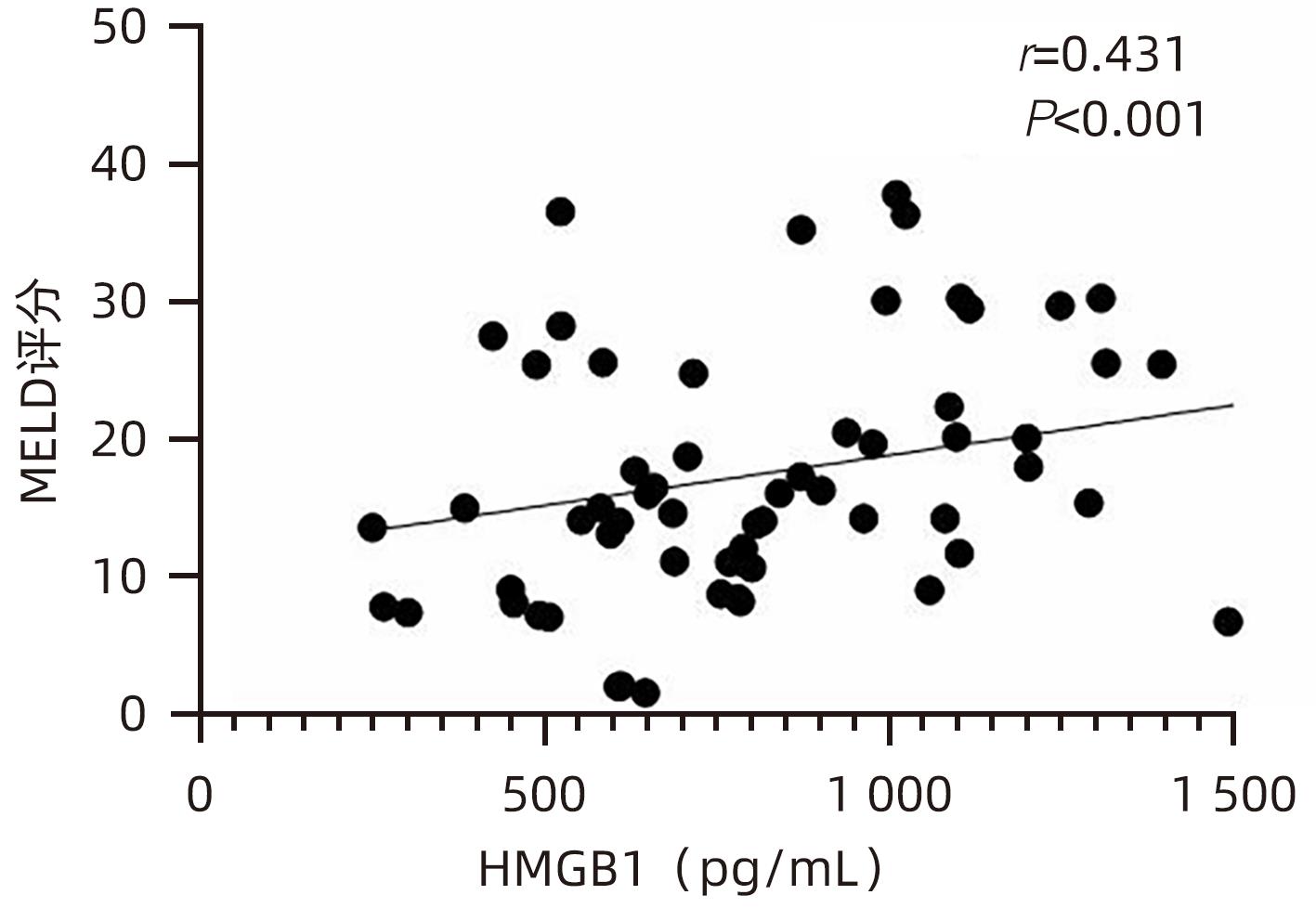
| [1] |
XU MM, KONG M, YU PF, et al. Clinical course and outcome patterns of acute-on-chronic liver failure: a multicenter retrospective cohort study[J]. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2021, 9( 5): 626- 634. DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00179. |
| [2] |
ABUDEIF A, SAYED E, GALAL GM. Characteristics and predictors of short-term mortality in decompensated cirrhotic patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 8( 4): 300- 308. DOI: 10.5114/ceh.2022.122332. |
| [3] |
ABBAS N, RAJORIYA N, ELSHARKAWY AM, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) in 2022: have novel treatment paradigms already arrived?[J]. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 16( 7): 639- 652. DOI: 10.1080/17474124.2022.2097070. |
| [4] |
CHEN MJ, LI X, TANG SH. Research progress on multidimensional evaluation of liver function in the prognosis of liver failure patients[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05. |
| [5] |
LIU Y, YUAN W, FANG M, et al. Determination of HMGB1 in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure patients with acute kidney injury: Early prediction and prognostic implications[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1031790. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1031790. |
| [6] |
GRØNBAEK H, MØLLER HJ, SALIBA F, et al. Improved prediction of mortality by combinations of inflammatory markers and standard clinical scores in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure and acute decompensation[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2021, 36( 1): 240- 248. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15125. |
| [7] |
HUANG XP, WANG Y, CHEN L, et al. Elevated serum prostaglandin E2 predicts the risk of infection in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure patients[J]. Asian Pac J Trop Med, 2017, 10( 9): 916- 920. DOI: 10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.08.008. |
| [8] |
Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Society of Hepatology. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(version 2019)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [9] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [10] |
HERNAEZ R, KRAMER JR, LIU Y, et al. Prevalence and short-term mortality of acute-on-chronic liver failure: A national cohort study from the USA[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 70( 4): 639- 647. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.018. |
| [11] |
CHEN KD. Serum levels of miR-122 and HMGB1 and their relationship with disease condition and prognosis in patients with HBV-ACLF[J]. Infect Dis Info, 2022, 35( 2): 135- 140. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8134.2022.01.007. |
| [12] |
LAI M, WANG X, YAO QW, et al. Predictive value of the initial MELD score and its derivative scores for early survival rate after liver transplantation in patients with liver failure[J]. Ogran Transplant, 2022, 13( 4): 489- 494. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2022.04.012. |
| [13] |
CHEN R, KANG R, TANG D. The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2022, 54( 2): 91- 102. DOI: 10.1038/s12276-022-00736-w. |
| [14] |
FANG P, DOU B, LIANG J, et al. Quercetin reduces oxidative stress and apoptosis by inhibiting HMGB1 and its translocation, thereby alleviating liver injury in ACLF rats[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2021, 2021: 2898995. DOI: 10.1155/2021/2898995. |
| [15] |
HOU W, WEI X, LIANG J, et al. HMGB1-induced hepatocyte pyroptosis expanding inflammatory responses contributes to the pathogenesis of acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF)[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 7295- 7313. DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S336626. |
| [16] |
NI YA, CHEN H, NIE H, et al. HMGB1: An overview of its roles in the pathogenesis of liver disease[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2021, 110( 5): 987- 998. DOI: 10.1002/JLB.3MR0121-277R. |
| [17] |
RASZEJA-WYSZOMIRSKA J, NIEWIŃSKI G, GRACZYŃSKA A, et al. Clinical implication of plasma CD163 in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Transplant Proc, 2022, 54( 4): 1011- 1016. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.02.048. |
| [18] |
NIELSEN MC, HVIDBJERG GANTZEL R, CLÀRIA J, et al. Macrophage activation markers, CD163 and CD206, in acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Cells, 2020, 9( 5). DOI: 10.3390/cells9051175. |
| [19] |
TRIANTAFYLLOU E, WOOLLARD KJ, MCPHAIL M, et al. The role of monocytes and macrophages in acute and acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 2948. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02948. |
| [20] |
ZHAO R, WU W, ZHOU Z, et al. Prognostic utility of novel biomarkers in acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF) associated with hepatitis B: A multicenter prospective study[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49( 1): 42- 50. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13251. |
| [21] |
GRONBAK H, RODGAARD-HANSEN S, AAGAARD NK, et al. Macrophage activation markers predict mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis without or with acute-on-chronic liver failure(ACLF)[J]. J Hepatol, 2016, 64( 4): 813- 822. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.11.021. |
| [22] |
WANG Y, CHEN C, QI J, et al. Altered PGE2-EP2 is associated with an excessive immune response in HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Transl Med, 2019, 17( 1): 93. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-1844-0. |
| [23] |
HANGAI S, AO T, KIMURA Y, et al. PGE2 induced in and released by dying cells functions as an inhibitory DAMP[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113( 14): 3844- 3849. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1602023113. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: