| [1] |
|
| [2] |
WANG H, MEN PX, XIAO YF, et al. Hepatitis B infection in the general population of China: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2019, 19( 1): 811. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-019-4428-y. |
| [3] |
LOK AS, MCMAHON BJ, BROWN RS Jr, et al. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis B viral infection in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 63( 1): 284- 306. DOI: 10.1002/hep.28280. |
| [4] |
CHEN CF, LEE WC, YANG HI, et al. Changes in serum levels of HBV DNA and alanine aminotransferase determine risk for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterology, 2011, 141( 4): 1240- 1248. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.06.036. |
| [5] |
KIM GA, HAN S, CHOI GH, et al. Moderate levels of serum hepatitis B virus DNA are associated with the highest risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 51( 11): 1169- 1179. DOI: 10.1111/apt.15725. |
| [6] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis B(2022 version)[J]. Chin J Infect Dis, 2023, 41( 1): 3- 28. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311365-20230220-00050. |
| [7] |
TERRAULT NA, LOK ASF, MCMAHON BJ, et al. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67( 4): 1560- 1599. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29800. |
| [8] |
YIN GQ, LI J, ZHONG B, et al. New therapeutic options for persistent low-level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: Increase of entecavir dosage[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27( 8): 666- 676. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i8.666. |
| [9] |
LU FM, FENG B, ZHENG SJ, et al. Current status of the research on low-level viremia in chronic hepatitis B patients receiving nucleos(t)ide analogues[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 6): 1268- 1274. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.06.007. |
| [10] |
SUN YM, WU XN, ZHOU JL, et al. Persistent low level of hepatitis B virus promotes fibrosis progression during therapy[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18( 11): 2582- 2591. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.001. |
| [11] |
YANG J, CHOI WM, SHIM JH, et al. Low level of hepatitis B viremia compared with undetectable viremia increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with untreated compensated cirrhosis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2023, 118( 6): 1010- 1018. DOI: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002181. |
| [12] |
SUN FR, LIU ZF, WANG BY. Correlation between low-level viremia and hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma and recurrence: A retrospective study[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21( 1): 1103. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08483-3. |
| [13] |
LIU SN, GUO XF, WU DR, et al. Construction of clinical evidence grading system of TCM intervention based on evidence-based medicine principles[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med, 2023, 43( 8): 911- 915.
刘少南, 郭新峰, 吴大嵘, 等. 基于循证医学原则的中医干预类临床证据分级系统的构建[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2023, 43( 8): 911- 915.
|
| [14] |
ZENG XT, LIU H, CHEN X, et al. Meta-analysis series IV: Quality evaluation tools for observational research[J]. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med, 2012, 4( 4): 297- 299. DOI: 10.3969/j.1674-4055.2012.04.004. |
| [15] |
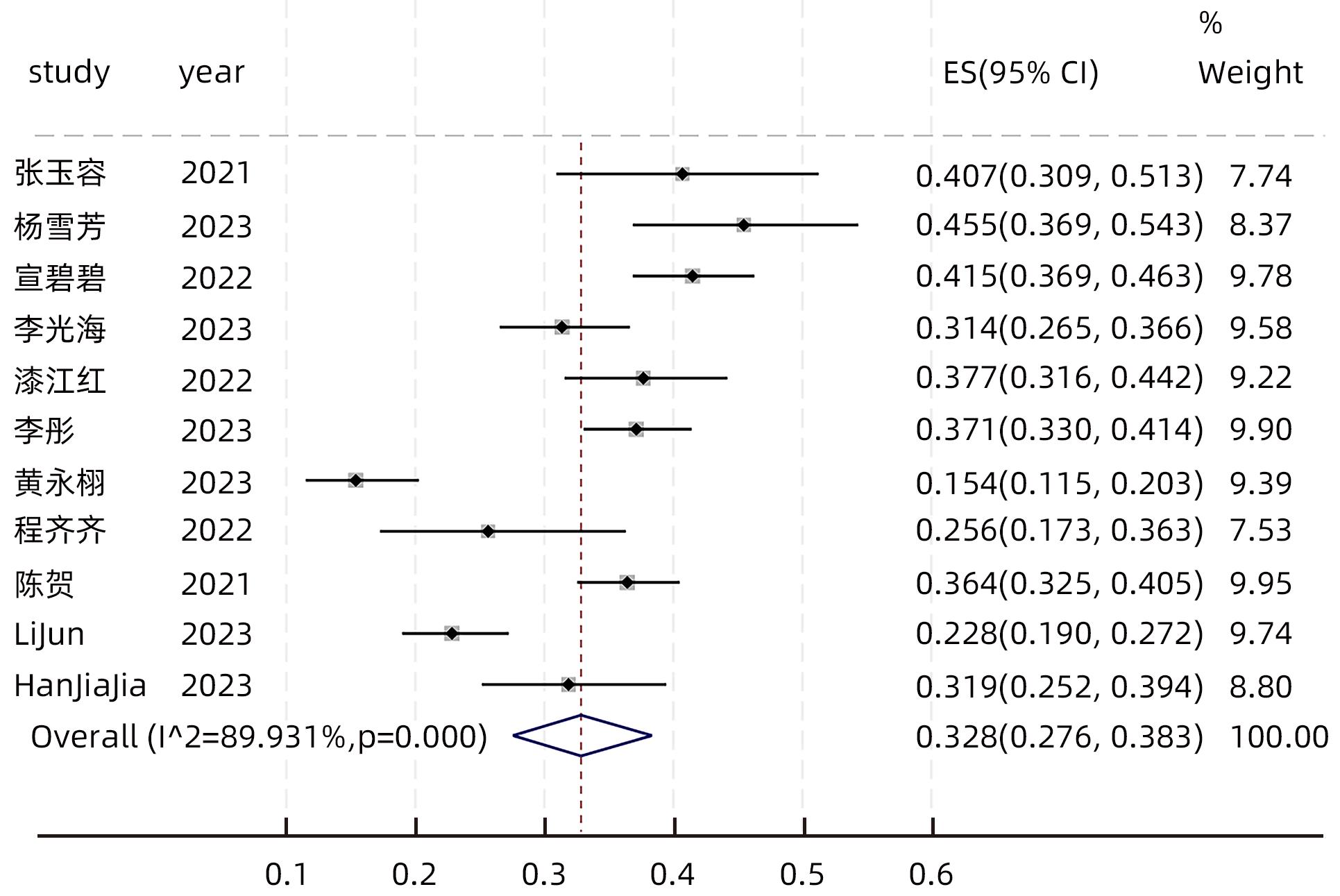
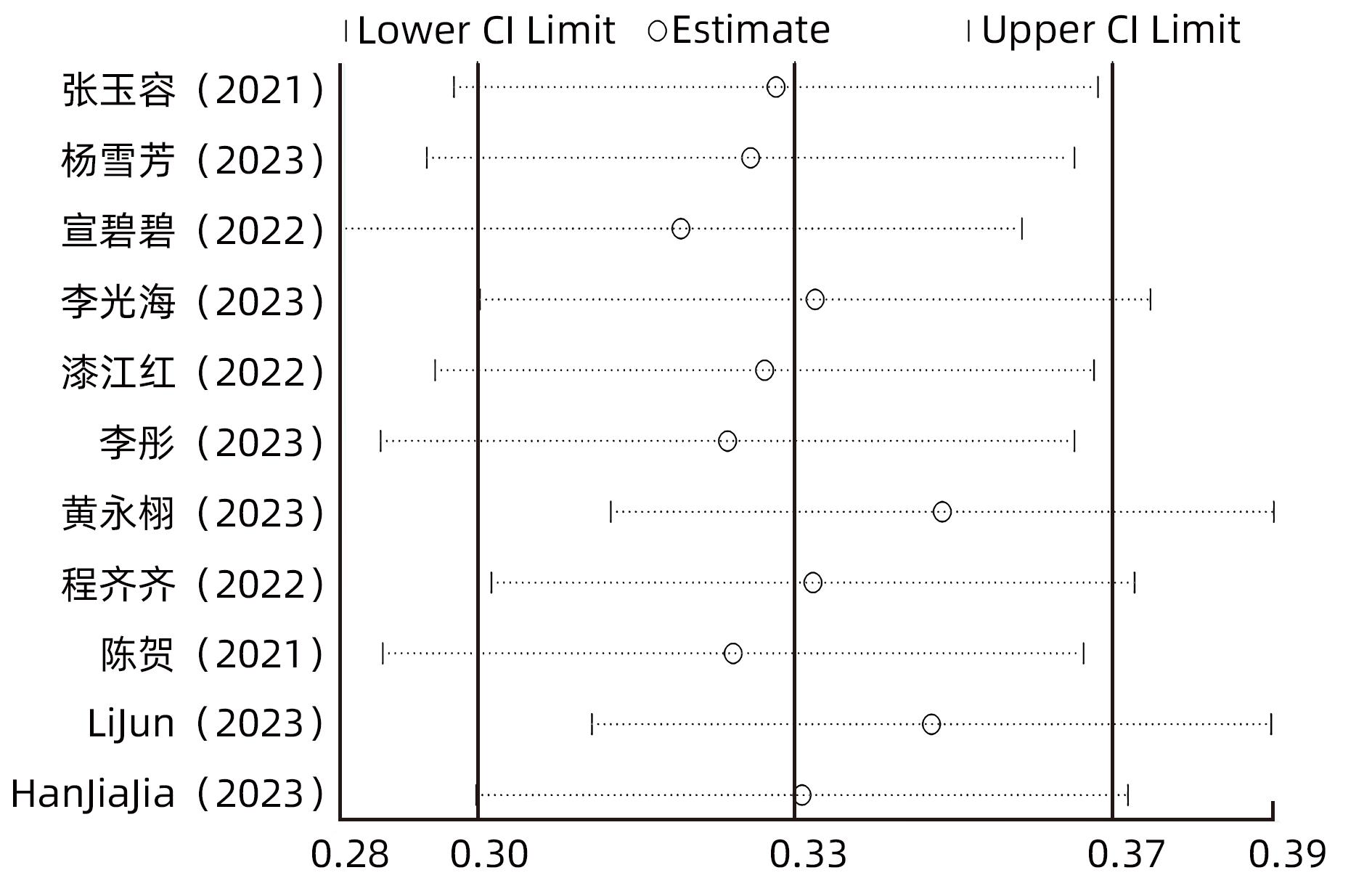
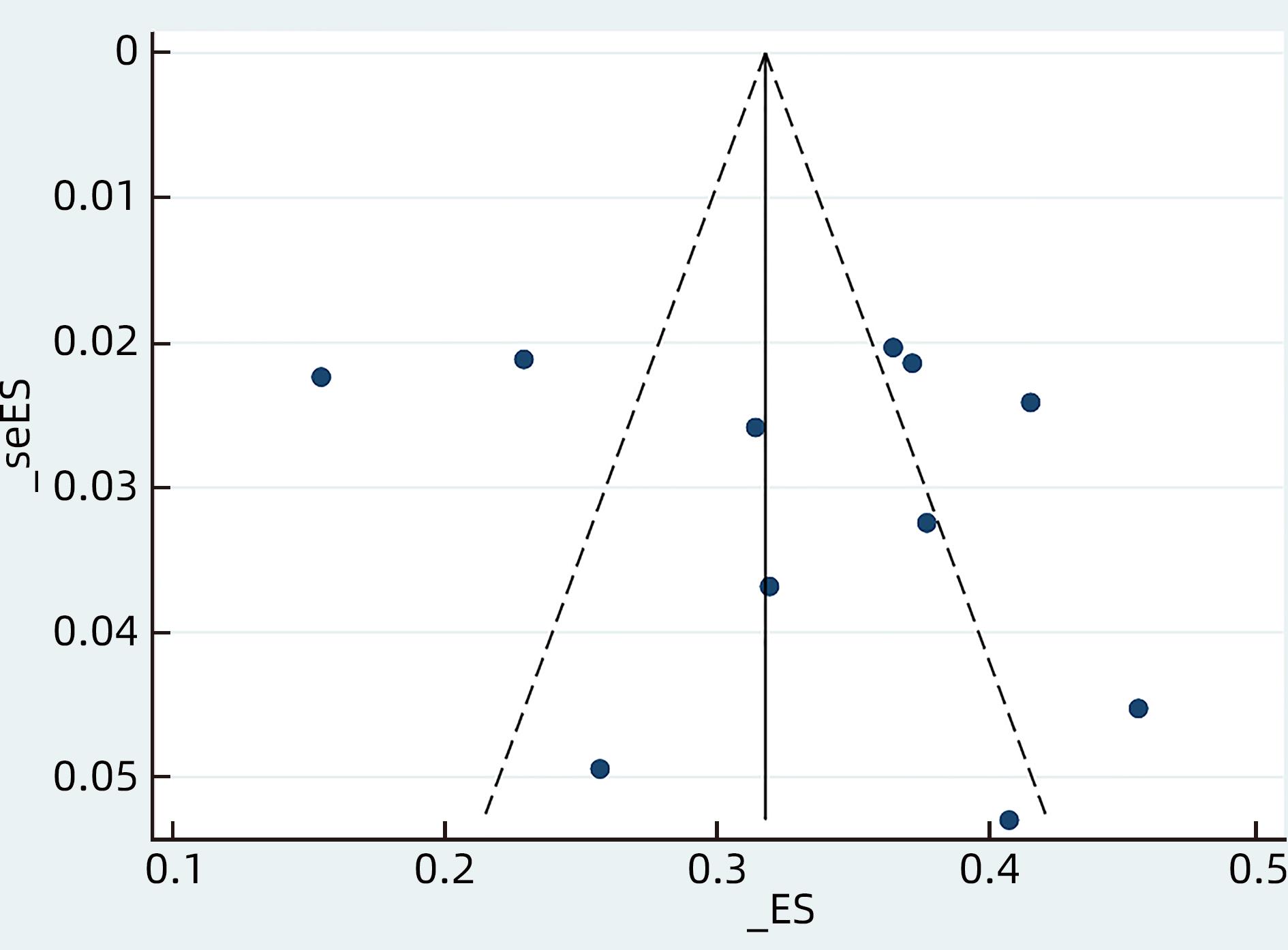
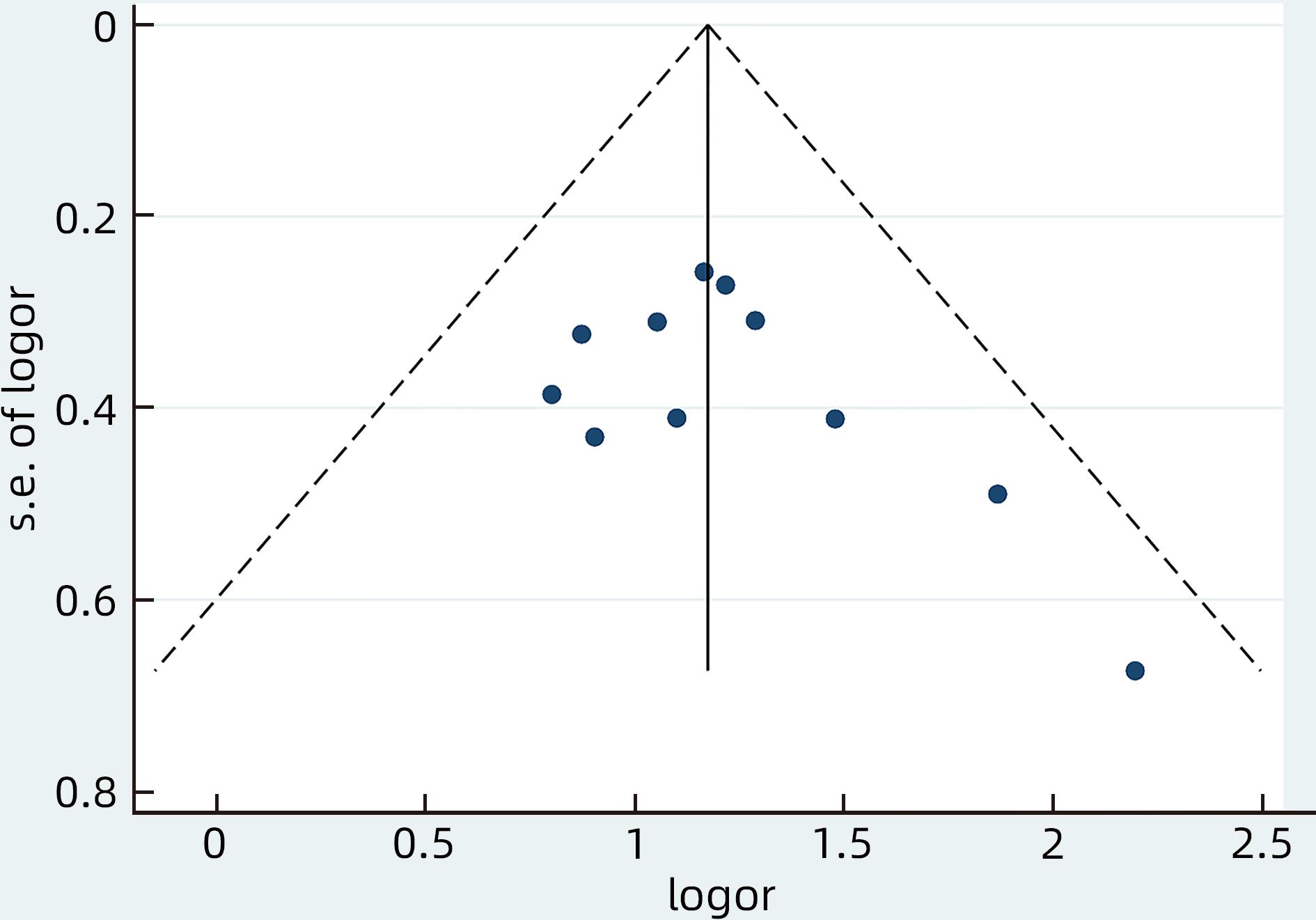
ZHANG YR. Profile of low level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2021.
张玉容. 慢性乙型肝炎患者低病毒血症状况研究[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2021.
|
| [16] |
YANG XF, XU Y, ZHANG BT, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and risk factors of low level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B after treatment[J]. Chin J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 32( 3): 276- 281. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5709.2023.03.008. |
| [17] |
XUAN BB, XU YH, DU ZC, et al. Influencing factors for low-level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B liver cirrhosis and its association with the progression of liver inflammation and liver fibrosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 10): 2252- 2259. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.10.011. |
| [18] |
LI GH, SUN L. Risk factors of low level viremia in chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleosides(acids)[J]. Med Health, 2023( 2): 165- 168.
李光海, 孙龙. 核苷(酸)类药物治疗慢性乙型肝炎低病毒血症危险因素分析[J]. 医药卫生, 2023( 2): 165- 168.
|
| [19] |
QI JH. Analysis of influencing factors of hypoviremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B and liver cirrhosis[J]. J Front Med, 2022, 12( 35): 52- 54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1752.2022.35.015. |
| [20] |
LI T, KONG Y, LIU YY, et al. Demographic characteristics and associated influencing factors in treated patients with chronic hepatitis B with hypoviremia: A single-center retrospective cross-sectional study[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2023, 31( 1): 42- 48. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20220121-00039. |
| [21] |
HUANG YX, CHEN C, BAO ZH, et al. Influencing factors of low-level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with Entecavir[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 3): 320- 324. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2023.03.015. |
| [22] |
CHENG QQ, YANG LX, CAI TP, et al. Influencing factors for low-level viremia and their dynamic changes in patients with chronic hepatitis B treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues for the first time[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 12): 2716- 2722. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.12.008. |
| [23] |
CHEN H, FU JJ, LI L, et al. Influencing factors for low-level viremia in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with long-term entecavir antiviral therapy[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 3): 556- 559. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.03.011. |
| [24] |
LU JH, ZHANG CN, HE PY, et al. Risk factors for very low-level viremia in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A single-center retrospective study[J]. Liver Res, 2022, 6( 1): 39- 44. DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2022.02.001. |
| [25] |
LI J, DONG XQ, CAO LH, et al. Factors associated with persistent positive in HBV DNA level in patients with chronic Hepatitis B receiving entecavir treatment[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2023, 13: 1151899. DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1151899. |
| [26] |
HAN JJ, GUO YF, ZHANG XY, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of low-level viremia in chronic hepatitis B patients after long-term therapy with nucleos(t)ide analogs[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2023, 34( 1): 53- 61. DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2023.21978. |
| [27] |
LEE SB, JEONG J, PARK JH, et al. Low-level viremia and cirrhotic complications in patients with chronic hepatitis B according to adherence to entecavir[J]. Clin Mol Hepatol, 2020, 26( 3): 364- 375. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0012. |
| [28] |
AGARWAL K, BRUNETTO M, SETO WK, et al. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68( 4): 672- 681. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.11.039. |
| [29] |
PAVLOVIC V, YANG L, CHAN HLY, et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a(40 kD) stopping rules in chronic hepatitis B: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data[J]. Antivir Ther, 2019, 24( 2): 133- 140. DOI: 10.3851/IMP3304. |
| [30] |
LU JH, YANG L, YE LH, et al. Clinical significance of HBsAg quantitative detection in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Mod J Integr Tradit Chin West Med, 2020, 29( 33): 3674- 3678. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2020.33.007. |
| [31] |
HOOFNAGLE JH, DI BISCEGLIE AM. Serologic diagnosis of acute and chronic viral hepatitis[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 1991, 11( 2): 73- 83. DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1040426. |
| [32] |
ZHANG XJ, WU R, HUANG W, et al. Clinical study of hepatitis B virus RNA in different HBeAg states in chronic hepatitis B[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol, 2023, 33( 3): 257- 260.
张晓晶, 武瑞, 黄伟, 等. 乙型肝炎病毒RNA在慢性乙型病毒性肝炎不同HBeAg状态下的临床研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2023, 33( 3): 257- 260.
|
| [33] |
LEE WM, KING WC, JANSSEN HLA, et al. Hepatitis B e antigen loss in adults and children with chronic hepatitis B living in North America: A prospective cohort study[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2021, 28( 11): 1526- 1538. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13591. |
| [34] |
LAU GKK, WANG FS. Uncover the immune biomarkers underlying hepatitis B e antigen(HBeAg) seroconversion: A need for more translational study[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56( 4): 753- 755. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.12.006. |
| [35] |
WANG CT, ZHANG YF, SUN BH, et al. Models for predicting hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in response to interferon-α in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2015, 21( 18): 5668- 5676. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5668. |
| [36] |
GENG MF, LI YX, GAO FY, et al. A scoring model predicts hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogs: Real-world clinical practice[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2017, 62: 18- 25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.06.016. |
| [37] |
HUDU SA, NIAZLIN MT, NORDIN SA, et al. Quantitative hepatitis B e antigen: A better predictor of hepatitis B virus DNA than quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen[J]. Clin Lab, 2018, 64( 4): 443- 449. DOI: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2017.170916. |
| [38] |
ZHANG C, LIU YQ, LI JW, et al. Dose-response relationship between qAnti-HBc and liver inflammation in chronic hepatitis B with normal or mildly elevated alanine transaminase based on liver biopsy[J]. J Med Virol, 2022, 94( 8): 3911- 3923. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27779. |
| [39] |
WANG XM, GAO XZ, WU RH, et al. Serum qAnti-HBc combined with ALT and HBsAg predicts significant hepatic inflammation in HBeAg-positive immune active patients[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37( 9): 1806- 1814. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15881. |
| [40] |
LI J, MAO RC, LI XL, et al. A novel noninvasive index for the prediction of moderate to severe fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2018, 50( 5): 482- 489. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2017.12.028. |
| [41] |
XIE YD, LI MH, OU XJ, et al. IP10 and anti-HBc can predict virological relapse and HBsAg loss in chronic hepatitis B patients after nucleos(t)ide analog discontinuation[J]. Dig Dis, 2023, 41( 6): 922- 931. DOI: 10.1159/000533515. |
| [42] |
YU XG, DENG JK, HE XH, et al. Performance verification and clinical evaluation of HBV DNA high-sensitivity detection kit[J]. J Mol Diagn Ther, 2019, 11( 2): 111- 116. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6929.2019.02.009. |
| [43] |
XIE L, LIU GW, GUO HJ. Analysis of the correlation between HBV DNA load level and hepatitis B hepatocellular carcinoma indicators and the effect on the outcome[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Liver Dis, 2023, 33( 10): 925- 929. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2023.010.014. |
| [44] |
LI J, BI YH, HUANG YH, et al. Consistency and the value of high-sensitivity and conventional fluorescence quantitative PCR in different viral load in patients with chronic hepatitis B[J]. J Trop Med, 2023, 23( 2): 198- 202. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3619.2023.02.013. |
| [45] |
LONG L, ZHANG Q, XIONG Y, et al. Application of high-sensitivity hepatitis B virus-DNA testing in the monitoring of antiviral therapy in patients with low-level viremia[J]. Guizhou Med J, 2022, 46( 8): 1182- 1183, 1186. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2022.08.002. |
| [46] |
GISH RG, GIVEN BD, LAI CL, et al. Chronic hepatitis B: Virology, natural history, current management and a glimpse at future opportunities[J]. Antiviral Res, 2015, 121: 47- 58. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2015.06.008. |
| [47] |
SUN FL, XIA W, OUYANG YL. Research progress on detection methods for hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2023, 30( 5): 366- 373. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13817. |
| [48] |
PARK HD. Current status of clinical application of point-of-care testing[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2021, 145( 2): 168- 175. DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2020-0112-RA. |
| [49] |
TIAN Y, FAN ZH, XU L, et al. CRISPR/Cas13a-assisted rapid and portable HBV DNA detection for low-level viremia patients[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2023, 12( 1): e2177088. DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2023.2177088. |
| [50] |
LIU LP, WU XP, CAI TP, et al. Analysis of efficacy and factors influencing sequential combination therapy with tenofovir alafenamide fumarate after treatment with entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with low-level viremia[J]. Chin J Hepatol, 2023, 31( 2): 118- 125. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501113-20221019-00507. |
| [51] |
ISHIDO S, TAMAKI N, UCHIHARA N, et al. Switching from entecavir to tenofovir alafenamide for maintaining complete virological response in chronic hepatitis B[J]. JGH Open, 2023, 7( 8): 567- 571. DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12950. |
| [52] |
SANAI FM, ALJAWAD M, ALGHAMDI AS, et al. Long-term health and economic benefits of switching to tenofovir alafenamide versus continuing on entecavir in chronic hepatitis B patients with low-level viremia in Saudi Arabia[J]. Saudi J Gastroenterol, 2024, 30( 1): 23- 29. DOI: 10.4103/sjg.sjg_170_23. |
| [53] |
CHOI J, KIM HJ, LEE J, et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients treated with entecavir vs tenofovir for chronic hepatitis B: A Korean nationwide cohort study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2019, 5( 1): 30- 36. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4070. |
| [54] |
DUSHEIKO G. Will we need novel combinations to cure HBV infection?[J]. Liver Int, 2020, 40( Suppl 1): 35- 42. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14371. |
| [55] |
GROSSI G, VIGANÒ M, LOGLIO A, et al. Hepatitis B virus long-term impact of antiviral therapy nucleot(s)ide analogues(NUCs)[J]. Liver Int, 2017, 37( Suppl 1): 45- 51. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13291. |
| [56] |
PAPATHEODORIDIS GV, IDILMAN R, DALEKOS GN, et al. The risk of hepatocellular carcinoma decreases after the first 5 years of entecavir or tenofovir in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis B[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66( 5): 1444- 1453. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29320. |
| [57] |
ALLARD NL, MACLACHLAN JH, DEV A, et al. Adherence in chronic hepatitis B: Associations between medication possession ratio and adverse viral outcomes[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2020, 20( 1): 140. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01219-w. |
| [58] |
SHIN JW, JUNG SW, LEE SB, et al. Medication nonadherence increases hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhotic complications, and mortality in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with entecavir[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2018, 113( 7): 998- 1008. DOI: 10.1038/s41395-018-0093-9. |
| [59] |
TAO YC, WANG ML, ZHANG DM, et al. Optimal drug administration manner would rescue partial virological response in chronic hepatitis B patients with entecavir or tenofovir treatment[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2020, 27( 7): 731- 738. DOI: 10.1111/jvh.13275. |
| [60] |
WANG CH, CHANG KK, LIN RC, et al. Consolidation period of 18 months no better at promoting off-treatment durability in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment than a 12-month period: A prospective randomized cohort study[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2020, 99( 18): e19907. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019907. |
| [61] |
BOGLIONE L, CUSATO J, CARITI G, et al. Role of HBsAg decline in patients with chronic hepatitis B HBeAg-negative and E genotype treated with pegylated-interferon[J]. Antiviral Res, 2016, 136: 32- 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.10.011. |
| [62] |
HANSEN BE, BUSTER EH, STEYERBERG EW, et al. Prediction of the response to peg-interferon-alfa in patients with HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B using decline of HBV DNA during treatment[J]. J Med Virol, 2010, 82( 7): 1135- 1142. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.21778. |
| [63] |
GAO P, LUO YP, LI JF, et al. Effects of hepatitis B virus on Th17, Treg and Th17/Treg ratio in different alanine aminetransferase stages[J]. J Peking Univ Health Sci, 2022, 54( 2): 272- 277. DOI: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.02.012. |
| [64] |
LAN YT, WANG ZL, TIAN P, et al. Treg/Th17 imbalance and its clinical significance in patients with hepatitis B-associated liver cirrhosis[J]. Diagn Pathol, 2019, 14( 1): 114. DOI: 10.1186/s13000-019-0891-4. |
| [65] |
LIU NQ, LIU B, ZHANG L, et al. Recovery of circulating CD56 dim NK cells and the balance of Th17/Treg after nucleoside analog therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B and low levels of HBsAg[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 62: 59- 66. DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.043. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: