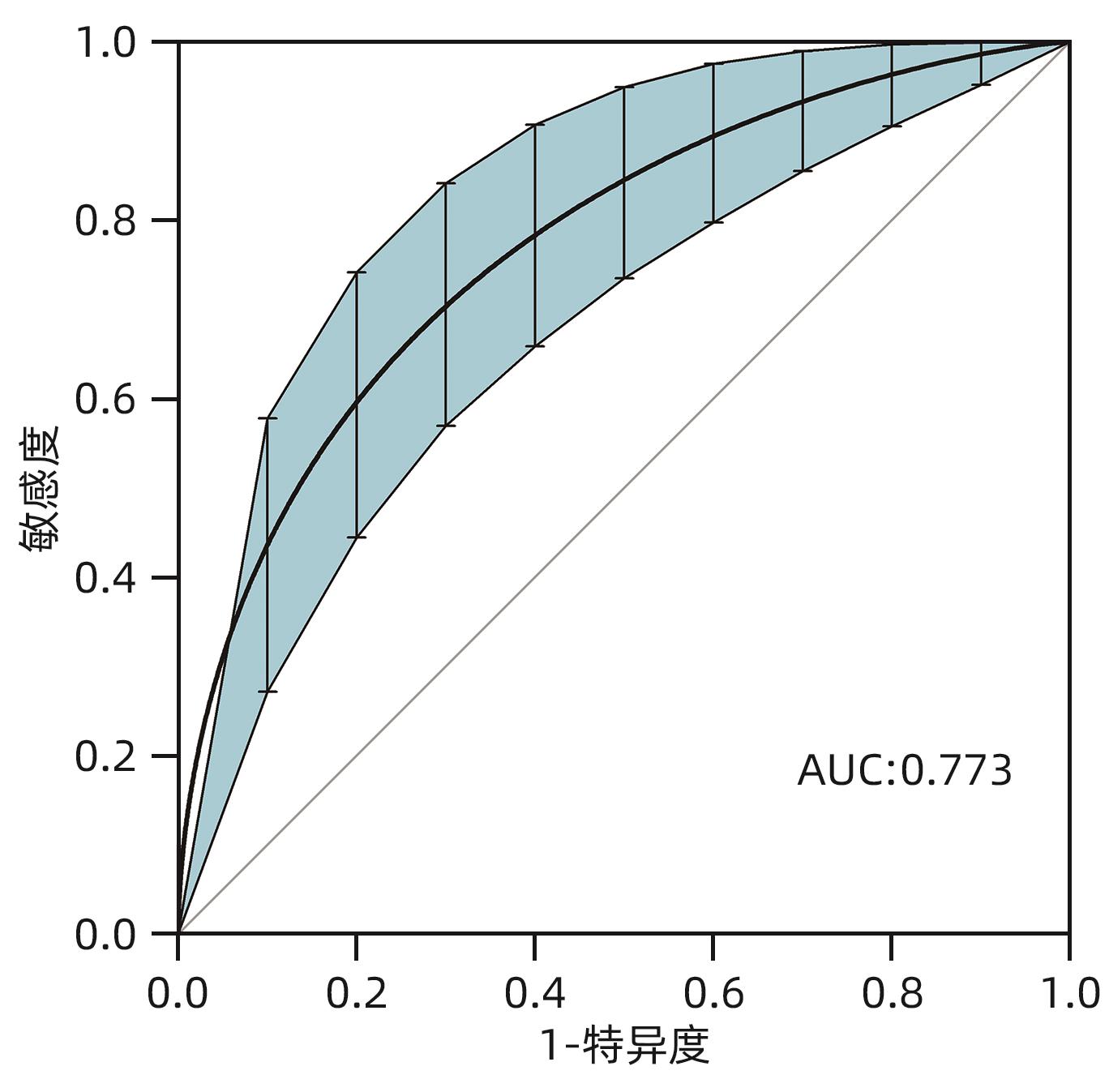
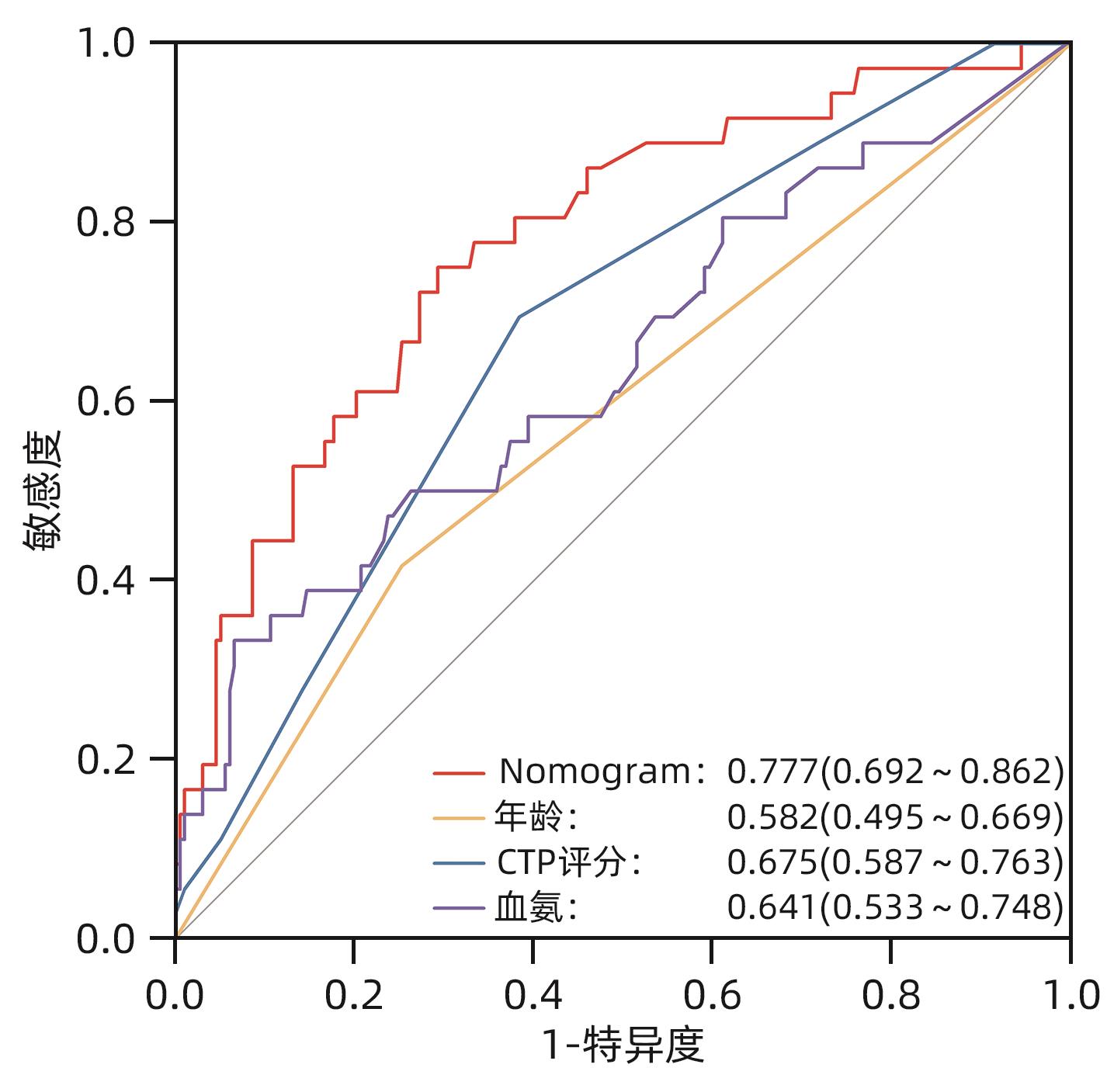
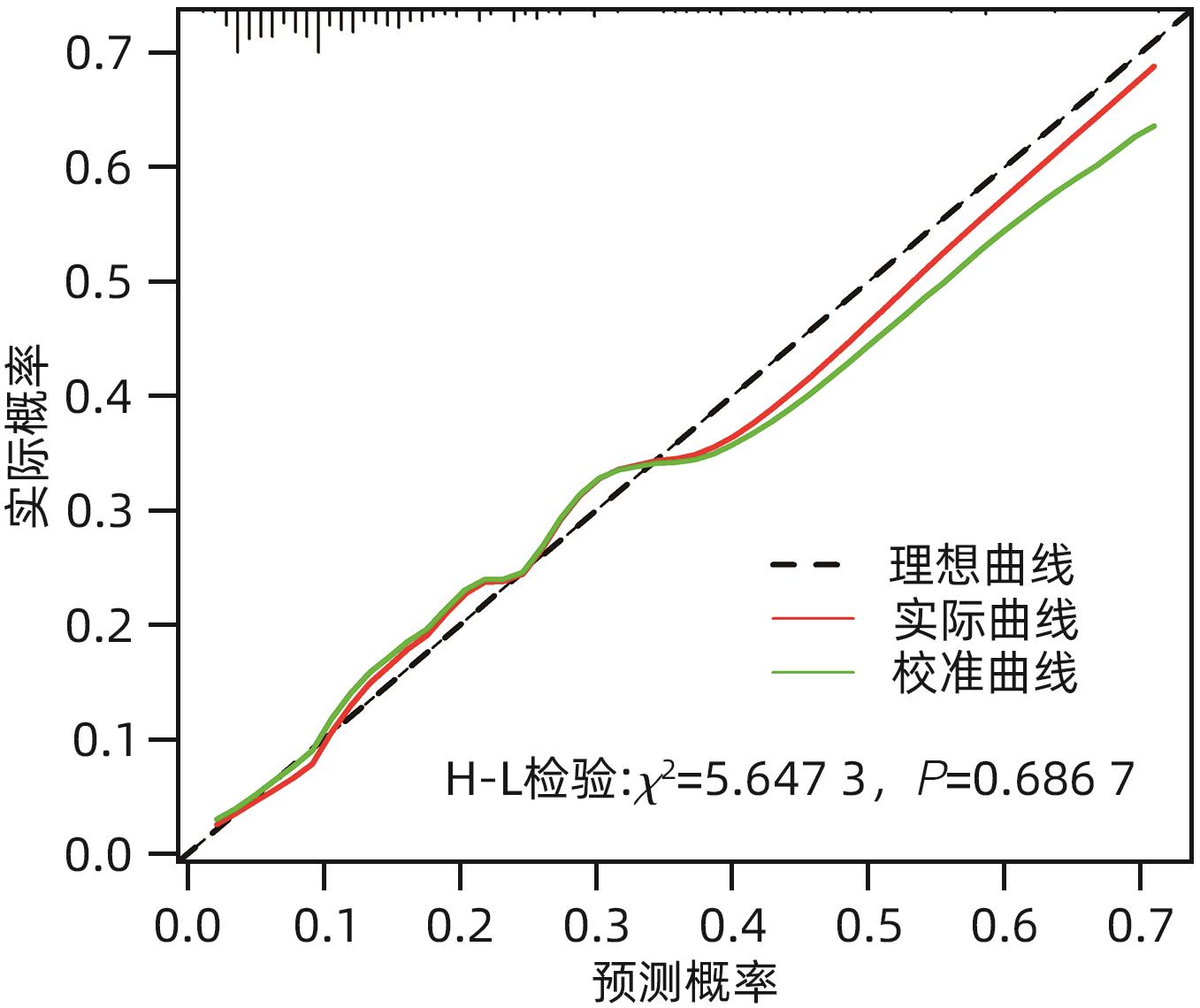
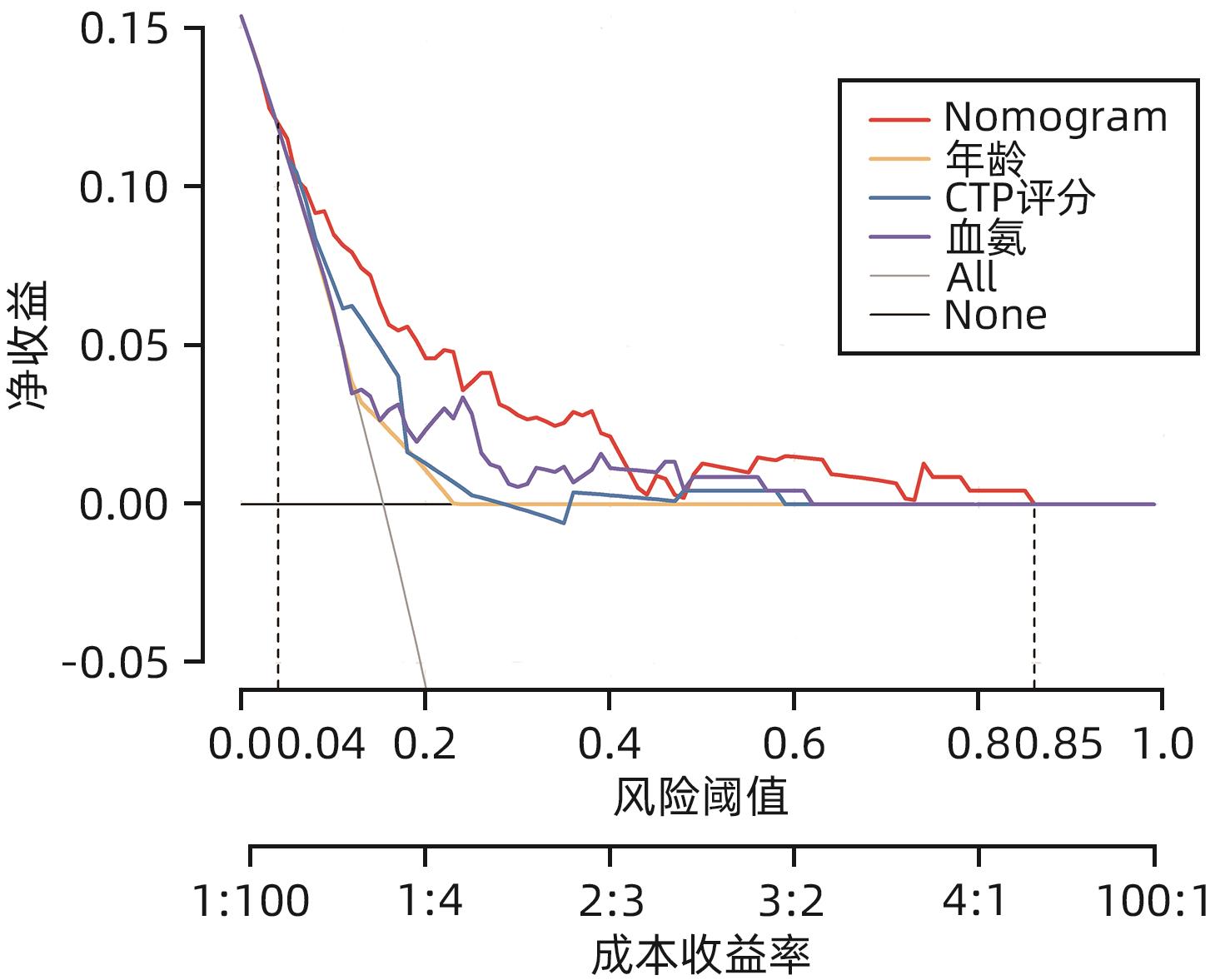
| [1] |
BOIKE JR, THORNBURG BG, ASRANI SK, et al. North American practice-based recommendations for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in portal hypertension[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 20( 8): 1636- 1662. e 36. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.07.018. |
| [2] |
de FRANCHIS R, BAVENO VI FACULTY. Expanding consensus in portal hypertension: Report of the Baveno VI Consensus Workshop: Stratifying risk and individualizing care for portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2015, 63( 3): 743- 752. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.05.022. |
| [3] |
LYU Y, FAN DM, HAN GH. Application status and future prospect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in gastroesophageal variceal bleeding in liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 6): 1229- 1233. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.06.004. |
| [4] |
ZHANG K, LIU JL, LIU YL, et al. To observe the clinical effect of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt guided by 3D model constructed by CT thin-layer scanning data computer in the treatment of cirrhotic portal hypertension complicated with gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 6): 655- 656, 660. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.06.28. |
| [5] |
CHEN GH, WANG GC, ZHANG CQ. Current status of research on hepatic encephalopathy after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2021, 37( 5): 1201- 1204. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2021.05.047. |
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
The Chinese College of Interventionalists. CCI clinical practice guidelines: Management of TIPS for portal hypertension(2019 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2694- 2699. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.010. |
| [8] |
ZHOU NS, ZHANG J, MA XM, et al. The study of unplanned readmission within 31 days after being discharged in one general third-level grade A hospital in Beijing[J]. Chin Hosp Manag, 2010, 30( 4): 18- 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5329.2010.04.008. |
| [9] |
General Office of the Ministry of Health. Notice on printing and distributing the indicators of medical quality management and control in tertiary general hospitals(2011 edition)[EB/OL].( 2011-01-27)[ 2023-11-10]. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm. http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2011-01/27/content_1793358.htm |
| [10] |
HAN Q. Analysis of types of diseases, days of interval and influencing factors of unplanned re-admission patients within 31 days after discharge[J]. Chin Nurs Res, 2020, 34( 16): 2862- 2867. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2020.16.010. |
| [11] |
SARWAR A, WEINSTEIN JL, NOVACK V, et al. Causes and rates of 30-day readmissions after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2020, 215( 1): 235- 241. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.19.21732. |
| [12] |
SHENG S, HUANG Y. Establishment and validation of the interactive nomogram model for all-cause readmission within 90-days in patients with heart failure[J]. Chin J Integr Med Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis, 2023, 21( 16): 2909- 2915. DOI: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2023.16.002. |
| [13] |
CHEN XY, LI K, WANG X, et al. Establishment of prediction model of unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in elderly patients receiving total knee arthroplasty[J]. Pract Geriatr, 2023, 37( 8): 772- 776. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2023.08.005. |
| [14] |
MA L, WANG ZX, LUO B. Predictive value of HALP index for unplanned readmission within 30 days after discharge in elderly patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Pract J Card Cereb Pneumal Vasc Dis, 2024, 32( 2): 20- 23. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1008-5971.2024.00.028. |
| [15] |
ZHANG JQ, WANG ZC, YANG JY, et al. Construction and validation of the risk prediction model for secondary hepatic encephalopathy in patients with chronic hepatitis B and cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2023, 28( 8): 916- 920, 931. DOI: 10.14000/j.cnki.issn.1008-1704.2023.08.011. |
| [16] |
PUGH RN, MURRAY-LYON IM, DAWSON JL, et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices[J]. Br J Surg, 1973, 60( 8): 646- 649. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. |
| [17] |
LI H, XIA ZB, XIAO NJ, et al. Current research status of prognostic models for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 5): 1191- 1196. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.05.030. |
| [18] |
LIU ZL, FAN ZP, LIU YL, et al. Value of Model for End-Stage Liver Disease and Child-Turcotte-Pugh score in predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatic sinus obstruction syndrome associated with Gynura segetum(Lour.) Merr[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2020, 36( 11): 2462- 2466. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.11.013. |
| [19] |
ZHANG F, LIU B, SHI YQ, et al. Analysis of risk factors for hepatic encephalopathy in patients with liver cirrhosis with upper gastrointestinal bleeding[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Dig, 2018, 26( 11): 934- 937. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-038X.2018.11.10. |
| [20] |
LOCKWOOD AH. Blood ammonia levels and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2004, 19( 3-4): 345- 349. DOI: 10.1023/b: mebr.0000043980.74574.eb.
|
| [21] |
VILSTRUP H, AMODIO P, BAJAJ J, et al. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver[J]. Hepatology, 2014, 60( 2): 715- 735. DOI: 10.1002/hep.27210. |
| [22] |
BROWN JR, ALONSO A, MAZIMBA S, et al. Improved 30 day heart failure rehospitalization prediction through the addition of device-measured parameters[J]. ESC Heart Failure, 2020, 7( 6): 3762- 3771. DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12956. |
| [23] |
GLANCE LG, KELLERMANN AL, OSLER TM, et al. Hospital readmission after noncardiac surgery: the role of major complications[J]. JAMA Surg, 2014, 149( 5): 439- 445. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2014.4. |



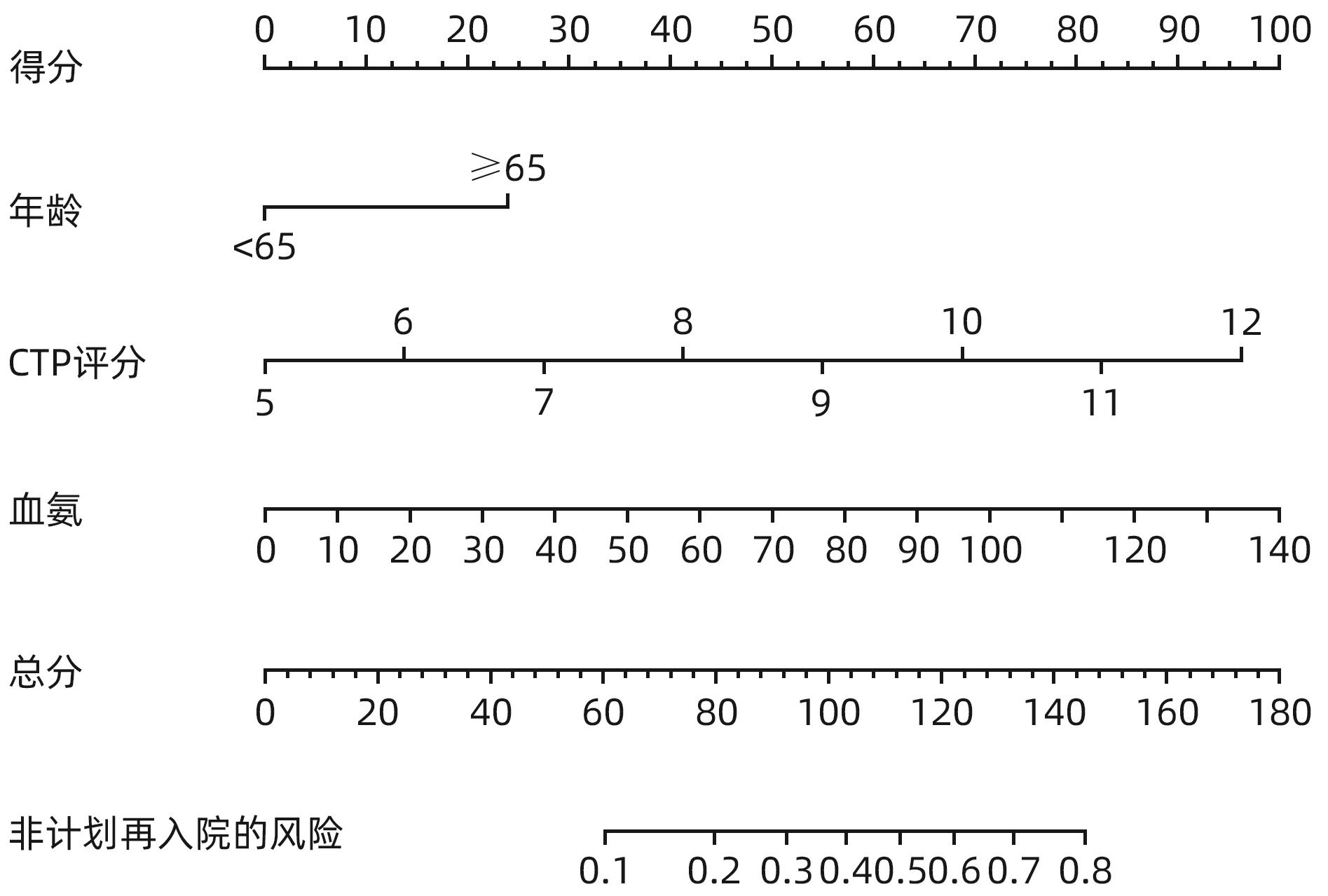




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: