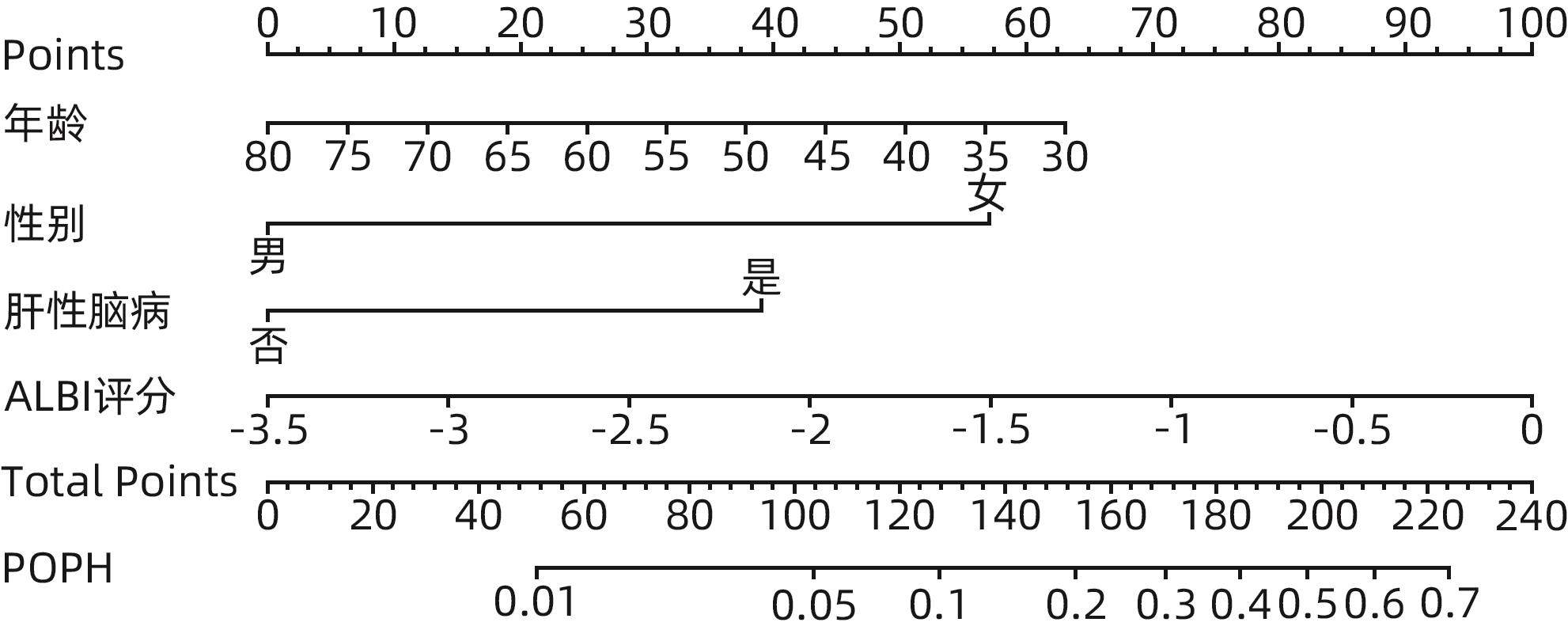
| [1] |
KHADERI S, KHAN R, SAFDAR Z, et al. Long-term follow-up of portopulmonary hypertension patients after liver transplantation[J]. Liver Transpl, 2014, 20( 6): 724- 727. DOI: 10.1002/lt.23870. |
| [2] |
GBD Cirrhosis Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5( 3): 245- 266. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. |
| [3] |
JOSE A, SHAH SA, ANWAR N, et al. Pulmonary vascular resistance predicts mortality and graft failure in transplantation patients with portopulmonary hypertension[J]. Liver Transpl, 2021, 27( 12): 1811- 1823. DOI: 10.1002/lt.26091. |
| [4] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Chinese guidelines on the management of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 11): 2408- 2425. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.11.006. |
| [5] |
MCLAUGHLIN VV, ARCHER SL, BADESCH DB, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association developed in collaboration with the American College of Chest Physicians; American Thoracic Society, Inc.; and the Pulmonary Hypertension Association[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2009, 53( 17): 1573- 1619. DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.01.004. |
| [6] |
TU Y, LI X, CHEN MJ, et al. Value of platelet count and related scoring models in predicting the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 6): 1308- 1312. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.06.009. |
| [7] |
WANG L, FENG YM, MA XW, et al. Diagnostic efficacy of noninvasive liver fibrosis indexes in predicting portal hypertension in patients with cirrhosis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12( 8): e0182969. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182969. |
| [8] |
MA LJ, HE C. The relationship between APRI and S index and Child Pugh in patients with hepatitis B cirrhosis[J]. Chin Hepatol, 2019, 24( 4): 448- 449. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2019.04.032. |
| [9] |
KAWUT SM, KROWKA MJ, TROTTER JF, et al. Clinical risk factors for portopulmonary hypertension[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48( 1): 196- 203. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22275. |
| [10] |
CASTAÑO G, SOOKOIAN S. Female sex and autoimmune hepatitis and the risk of portopulmonary hypertension[J]. Hepatology, 2008, 48( 6): 2090. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22599. |
| [11] |
DUBROCK HM, CARTIN-CEBA R, CHANNICK RN, et al. Sex differences in portopulmonary hypertension[J]. Chest, 2021, 159( 1): 328- 336. DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.07.081. |
| [12] |
ROBERTS KE, FALLON MB, KROWKA MJ, et al. Genetic risk factors for portopulmonary hypertension in patients with advanced liver disease[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2009, 179( 9): 835- 842. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200809-1472OC. |
| [13] |
AL-NAAMANI N, KROWKA MJ, FORDE KA, et al. Estrogen signaling and portopulmonary hypertension: The pulmonary vascular complications of liver disease study(PVCLD2)[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 2): 726- 737. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31314. |
| [14] |
SHAO YM, YIN X, QIN TT, et al. Prevalence and associated factors of portopulmonary hypertension in patients with portal hypertension: A case-control study[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 5595614. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5595614. |
| [15] |
KAWAGUCHI T, HONDA A, SUGIYAMA Y, et al. Association between the albumin-bilirubin(ALBI) score and severity of portopulmonary hypertension(PoPH): A data-mining analysis[J]. Hepatol Res, 2021, 51( 12): 1207- 1218. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13714. |
| [16] |
JOHNSON PJ, BERHANE S, KAGEBAYASHI C, et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33( 6): 550- 558. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.9151. |
| [17] |
FUJITA K, OURA K, YONEYAMA H, et al. Albumin-bilirubin score indicates liver fibrosis staging and prognosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. Hepatol Res, 2019, 49( 7): 731- 742. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13333. |
| [18] |
YAMASHITA Y, UMEMURA T, KIMURA T, et al. Prognostic utility of albumin-bilirubin grade in Japanese patients with primary biliary cholangitis[J]. JHEP Rep, 2022, 5( 4): 100662. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100662. |
| [19] |
WANG J, ZHANG ZP, YAN XM, et al. Albumin-Bilirubin(ALBI) as an accurate and simple prognostic score for chronic hepatitis B-related liver cirrhosis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51( 8): 1172- 1178. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2019.01.011. |
| [20] |
WANG YY, ZHONG JH, SU ZY, et al. Albumin-bilirubin versus Child-Pugh score as a predictor of outcome after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Br J Surg, 2016, 103( 6): 725- 734. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.10095. |
| [21] |
BAJAJ JS, RIDLON JM, HYLEMON PB, et al. Linkage of gut microbiome with cognition in hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2012, 302( 1): G168- G175. DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00190.2011. |
| [22] |
JAIN L, SHARMA BC, SHARMA P, et al. Serum endotoxin and inflammatory mediators in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2012, 44( 12): 1027- 1031. DOI: 10.1016/j.dld.2012.07.002. |
| [23] |
CHEN YH, YUAN W, MENG LK, et al. The role and mechanism of gut microbiota in pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Nutrients, 2022, 14( 20): 4278. DOI: 10.3390/nu14204278. |
| [24] |
ISHIDA K, NAMISAKI T, MURATA K, et al. Accuracy of fibrosis-4 index in identification of patients with cirrhosis who could potentially avoid variceal screening endoscopy[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9( 11): 3510. DOI: 10.3390/jcm9113510. |



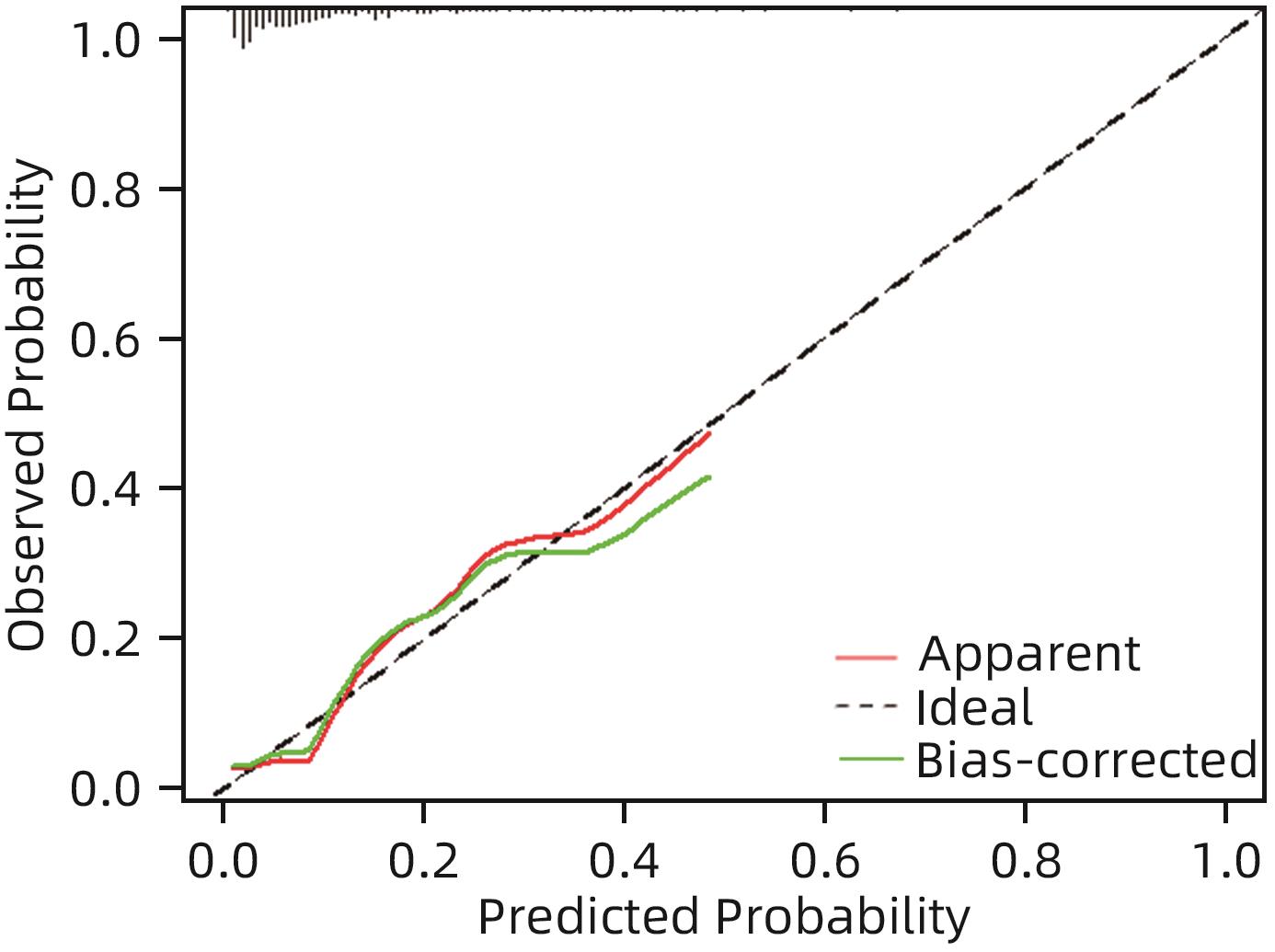




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: