| [1] |
SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71( 3): 209- 249. DOI: 10.3322/caac.21660. |
| [2] |
BLECHACZ B, MISHRA L. Hepatocellular carcinoma biology[J]. Recent Results Cancer Res, 2013, 190: 1- 20. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-16037-0_1. |
| [3] |
CHEN CY, SHYU AB. AU-rich elements: Characterization and importance in mRNA degradation[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 1995, 20( 11): 465- 470. DOI: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89102-1. |
| [4] |
LIU H, ZHENG W, SONG Z. circDlgap4 alleviates cerebral ischaemic injury by binding to AUF1 to suppress oxidative stress and neuroinflammation[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2022, 59( 5): 3218- 3232. DOI: 10.1007/s12035-022-02796-5. |
| [5] |
CHEN LY, LINGNER J. AUF1/HnRNP D RNA binding protein functions in telomere maintenance[J]. Mol Cell, 2012, 47( 1): 1- 2. DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.06.031. |
| [6] |
ULLMER W, SEMLER BL. Direct and indirect effects on viral translation and RNA replication are required for AUF1 restriction of enterovirus infections in human cells[J]. mBio, 2018, 9( 5): e01669- e01618. DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01669-18. |
| [7] |
MOORE AE, CHENETTE DM, LARKIN LC, et al. Physiological networks and disease functions of RNA-binding protein AUF1[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2014, 5( 4): 549- 564. DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1230. |
| [8] |
WU QC, LI JH, WANG B, et al. Significance of the expression levels of GPC-3 and AUF1 in cancer tissue in the evaluation of pathological stage and prognosis of patients with esophageal cancer[J]. Clin Misdiagnosis Mistherapy, 2023, 9( 10): 44- 48.
吴其琛, 李俊海, 王博, 等. 癌组织中GPC-3、AUF1表达水平对食管癌患者病理分期及预后评估的意义[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2023, 9( 10): 44- 48.
|
| [9] |
CHANDRASHEKAR DS, BASHEL B, BALASUBRAMANYA SAH, et al. UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses[J]. Neoplasia, 2017, 19( 8): 649- 658. DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002. |
| [10] |
CHANDRASHEKAR DS, KARTHIKEYAN SK, KORLA PK, et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform[J]. Neoplasia, 2022, 25: 18- 27. DOI: 10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001. |
| [11] |
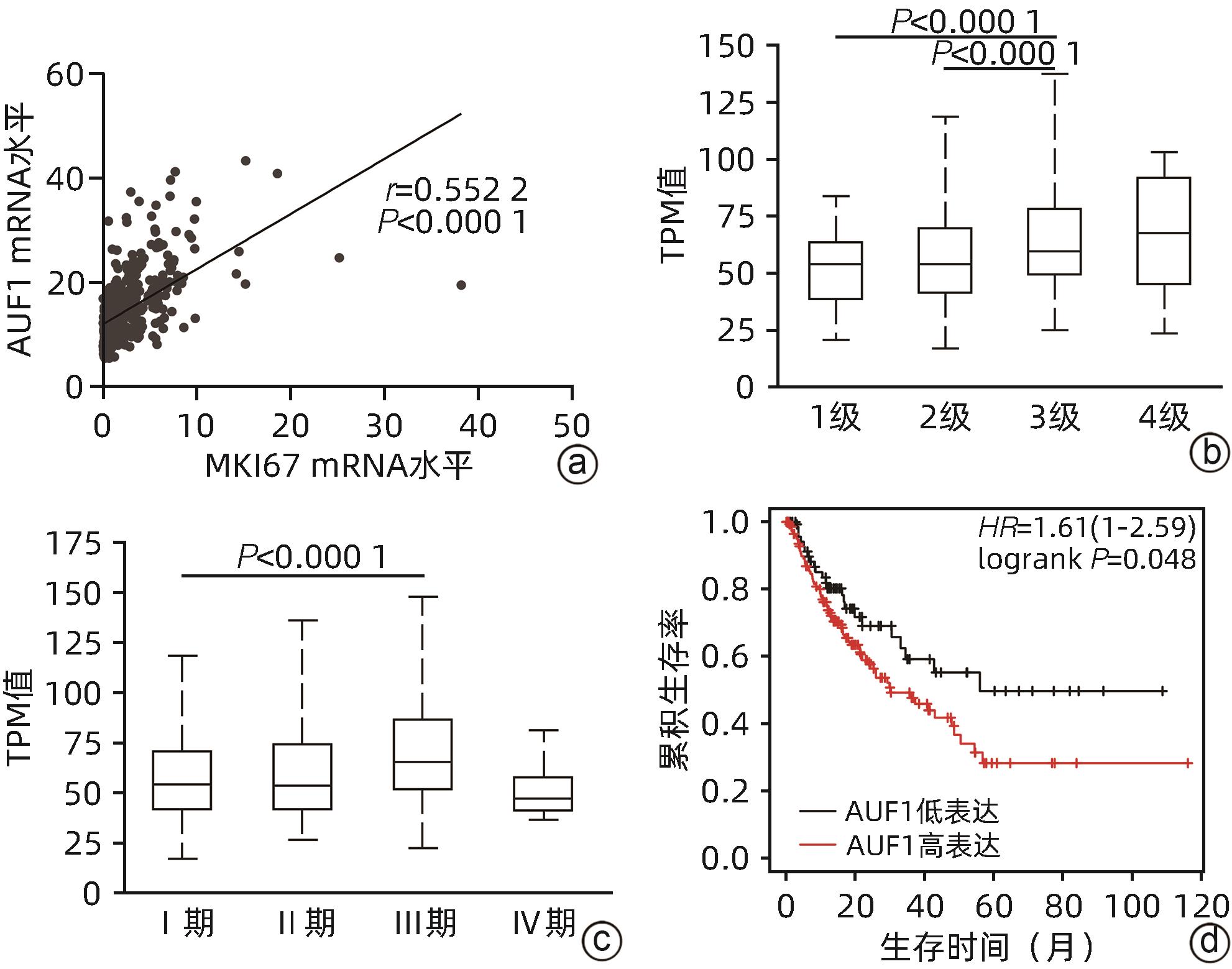
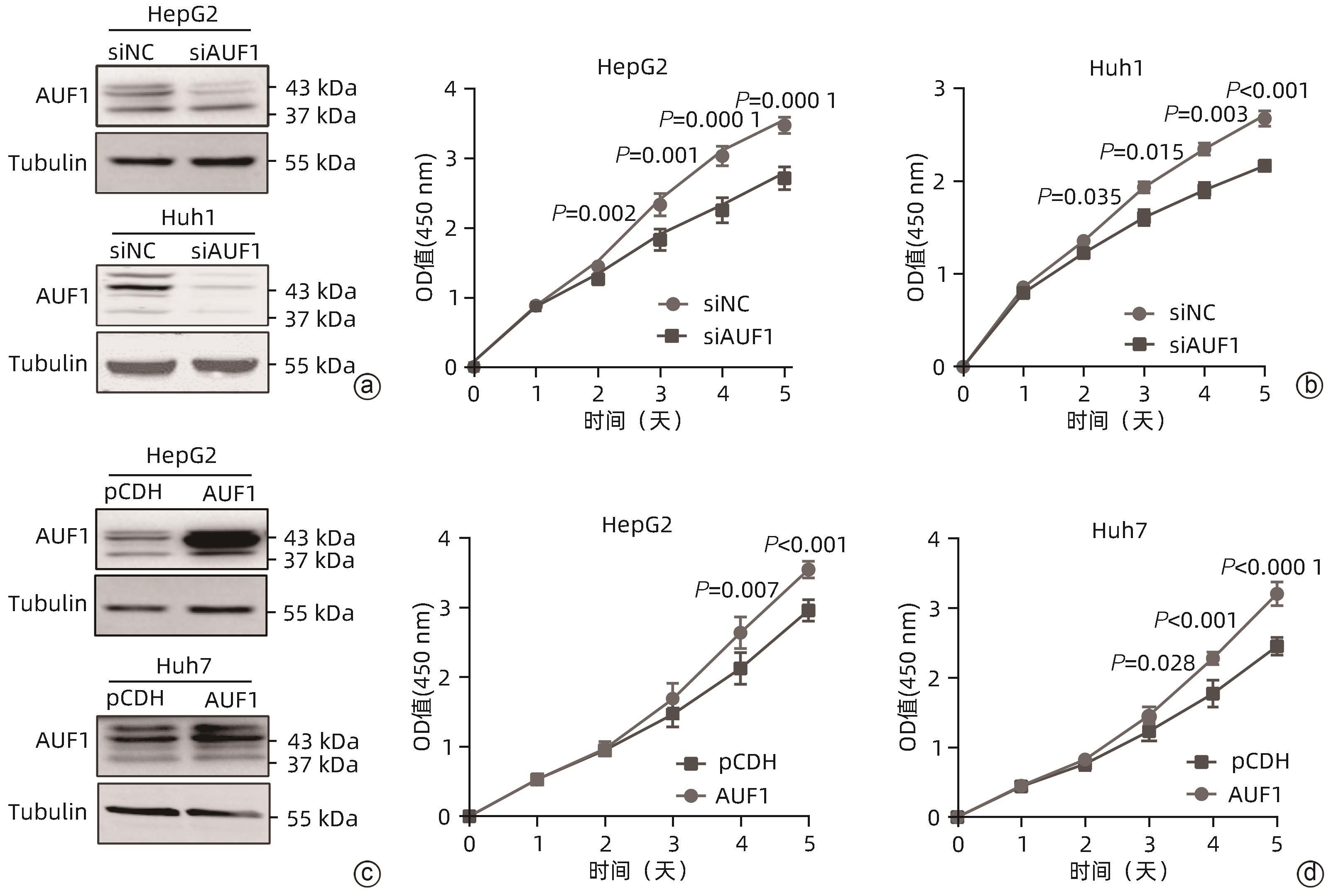
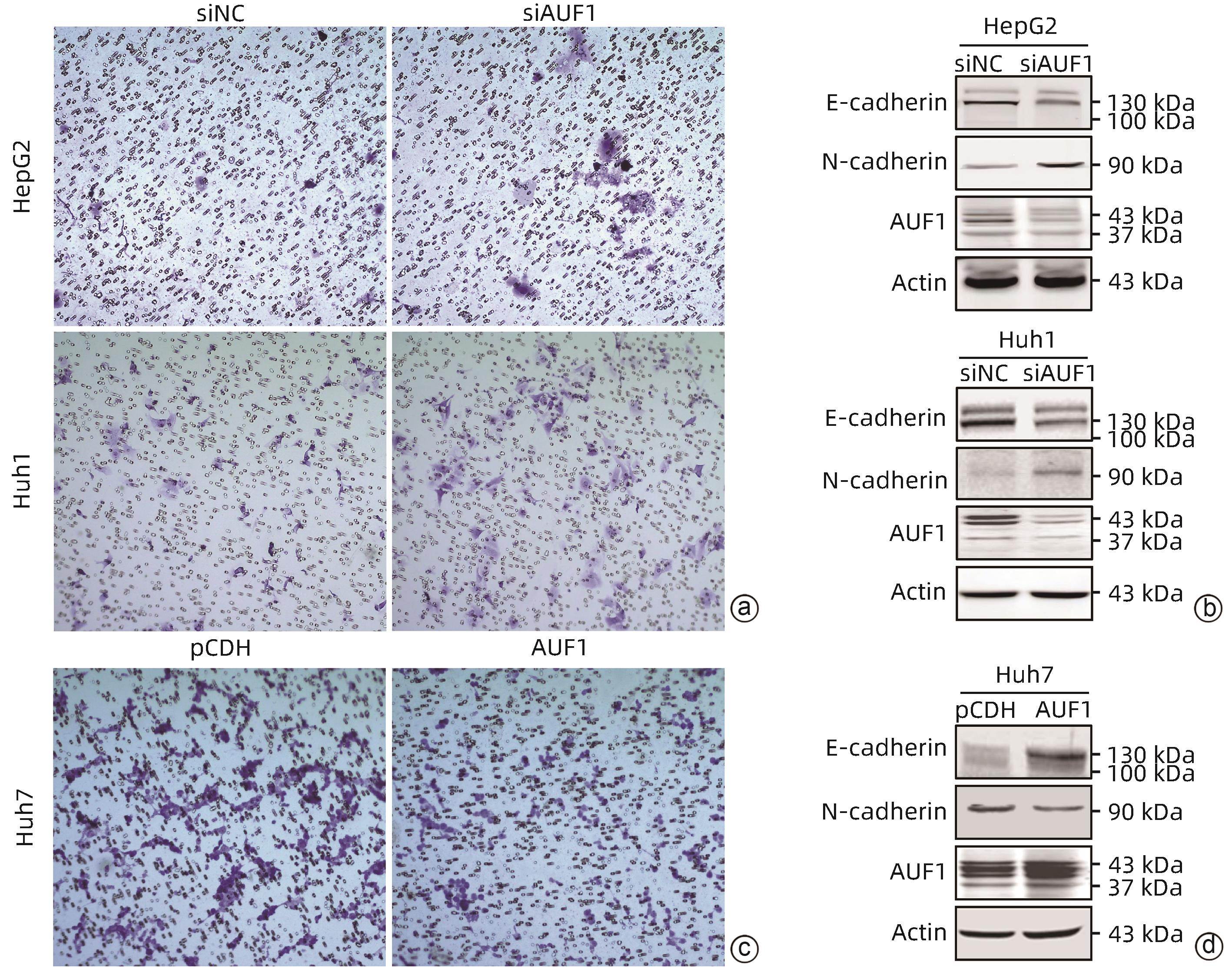
ZHANG T, GUAN GW, ZHANG J, et al. E2F1-mediated AUF1 upregulation promotes HCC development and enhances drug resistance via stabilization of AKR1B10[J]. Cancer Sci, 2022, 113( 4): 1154- 1167. DOI: 10.1111/cas.15272. |
| [12] |
KIM D, PERTEA G, TRAPNELL C, et al. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions[J]. Genome Biol, 2013, 14( 4): R36. DOI: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-4-r36. |
| [13] |
LIAO Y, SMYTH GK, SHI W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30( 7): 923- 930. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. |
| [14] |
ROBINSON MD, MCCARTHY DJ, SMYTH GK. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26( 1): 139- 140. DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. |
| [15] |
YANG YZ, KANG P, GAO J, et al. AU-binding factor 1 expression was correlated with metadherin expression and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Tumour Biol, 2014, 35( 3): 2747- 2751. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-013-1362-2. |
| [16] |
DANG H, TAKAI A, FORGUES M, et al. Oncogenic activation of the RNA binding protein NELFE and MYC signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017, 32( 1): 101- 114. e 8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.06.002. |
| [17] |
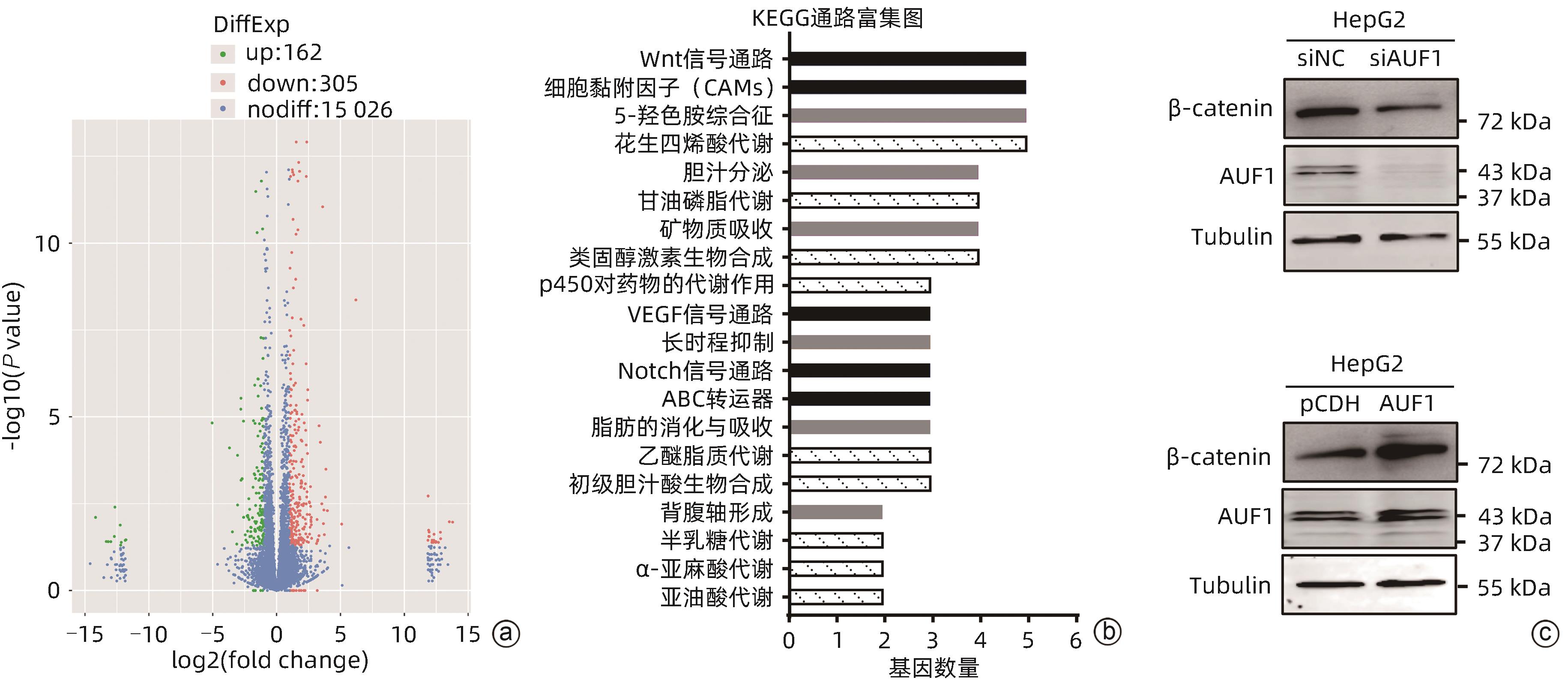
JUNG YS, STRATTON SA, LEE SH, et al. TMEM9-v-ATPase activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling via APC lysosomal degradation for liver regeneration and tumorigenesis[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73( 2): 776- 794. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31305. |
| [18] |
LACHENMAYER A, ALSINET C, SAVIC R, et al. Wnt-pathway activation in two molecular classes of hepatocellular carcinoma and experimental modulation by sorafenib[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2012, 18( 18): 4997- 5007. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2322. |
| [19] |
QU JY, LIU XT, LI J, et al. AKR1B10 promotes proliferation of breast cancer cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Chin J Cell Mol Immunol, 2019, 35( 12): 1094- 1100.
屈佳肴, 刘香婷, 李佳, 等. 醛酮还原酶家族1成员B10(AKR1B10)通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路促进乳腺癌细胞增殖[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2019, 35( 12): 1094- 1100.
|







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: