| [1] |
BAI SL, YING DJ. Systematic anatomy[M]. 9th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2018.
柏树令, 应大君. 系统解剖学[M]. 9版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018.
|
| [2] |
China Anti-Cancer Association Committee of Liver Cancer. Guidelines for holistic integrative management of liver cancer(2022 abridged version)[J]. Chin J Clin Oncol, 2022, 49( 17): 865- 873. DOI: 10.12354/j.issn.1000-8179.2022.20220942. |
| [3] |
General Office of National Health Commission. Standard for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer(2022 edition)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2022, 38( 2): 288- 303. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2022.02.009. |
| [4] |
Bureau of Medical Administration, Nationsl Health Commiaaion of the People’s Republic of China. Standardization for diagnosis and treatment of primary hepatic carcinom(2019 edition)[J]. Chin J Pract Surg, 2020, 40( 2): 121- 138. DOI: 10.19538/j.cjps.issn1005-2208.2020.02.01. |
| [5] |
DUTTA K, CHANDRA S, GOURISARIA MK. Early-stage detection of liver disease through machine learning algorithms[M]// Advances in Data and Information Sciences. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2022: 155- 166. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-16-5689-7_14. |
| [6] |
BOATENG EY, ABAYE DA. A review of the logistic regression model with emphasis on medical research[J]. J Data Anal Inf Process, 2019, 7( 4): 190- 207. DOI: 10.4236/jdaip.2019.74012. |
| [7] |
NAYAK S, GOURISARIA MK, PANDEY M, et al. Prediction of heart disease by mining frequent items and classification techniques[C]// 2019 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems(ICCS). Madurai, India. IEEE, 2019: 607- 611. DOI: 10.1109/ICCS45141.2019.9065805. |
| [8] |
PEREIRA S, MEIER R, MCKINLEY R, et al. Enhancing interpretability of automatically extracted machine learning features: Application to a RBM-Random Forest system on brain lesion segmentation[J]. Med Image Anal, 2018, 44: 228- 244. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2017.12.009. |
| [9] |
ÇAMLICA Z, TIZHOOSH HR, KHALVATI F. Medical image classification via SVM using LBP features from saliency-based folded data[C]// 2015 IEEE 14th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications(ICMLA). Miami, FL, USA. IEEE, 2015: 128- 132. DOI: 10.1109/ICMLA.2015.131. |
| [10] |
MARUYAMA T, HAYASHI N, SATO Y, et al. Comparison of medical image classification accuracy among three machine learning methods[J]. J Xray Sci Technol, 2018, 26( 6): 885- 893. DOI: 10.3233/XST-18386. |
| [11] |
NAEEM S, ALI A, QADRI S, et al. Machine-learning based hybrid-feature analysis for liver cancer classification using fused(MR and CT) images[J]. Appl Sci, 2020, 10( 9): 3134. DOI: 10.3390/app10093134. |
| [12] |
MAO B, MA JD, DUAN SB, et al. Preoperative classification of primary and metastatic liver cancer via machine learning-based ultrasound radiomics[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31( 7): 4576- 4586. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-07562-6. |
| [13] |
WANG XH, GUO HF, YIN XP, et al. Classification of colorectal liver metastases and hepatocellular carcinoma lesions based on CT-radiomics[J]. Beijing Biomed Eng, 2021, 40( 6): 551- 556. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2021.06.001. |
| [14] |
ZHANG J, LI D, FENG YY, et al. Comparison of support vector machine algorithm and diffusion weighted imaging in differentiating small hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules[J]. Chin Comput Med Imag, 2022, 28( 4): 366- 371. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5741.2022.04.008. |
| [15] |
ANWAR SM, MAJID M, QAYYUM A, et al. Medical image analysis using convolutional neural networks: A review[J]. J Med Syst, 2018, 42( 11): 226. DOI: 10.1007/s10916-018-1088-1. |
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
WANG W, LIANG D, CHEN Q, et al. Medical image classification using deep learning[M]∥ Deep learning in healthcare: paradigms and applications, Cham: Springer, 2020: 33- 51. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-32606-7_3. |
| [18] |
WANG SH, HAN XJ, DU J, et al. Saliency-based 3D convolutional neural network for categorising common focal liver lesions on multisequence MRI[J]. Insights Imaging, 2021, 12( 1): 173. DOI: 10.1186/s13244-021-01117-z. |
| [19] |
TAKENAGA T, HANAOKA S, NOMURA Y, et al. Multichannel three-dimensional fully convolutional residual network-based focal liver lesion detection and classification in Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI[J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2021, 16( 9): 1527- 1536. DOI: 10.1007/s11548-021-02416-y. |
| [20] |
LI WY. A kind of research on lesions detection in liver CT images based on convolutional neural network[D]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2019.
李文雅. 一种基于卷积神经网络的肝脏CT图像病灶检测问题研究[D]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2019.
|
| [21] |
MA JM. Application of artificial intelligence based on deep learning in magnetic resonance imaging of early liver cancer[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2020.
马举铭. 基于深度学习的人工智能在早期肝癌磁共振影像的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2020.
|
| [22] |
WU DL. Detection of small lesions in liver CT images based on improved Faster R-CNN[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022.
吴德蓝. 基于改进Faster R-CNN的肝脏CT图像小病灶检测[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022.
|
| [23] |
CHEN X. Research on liver lesion classification algorithm based on weakly-labeled CT images[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020.
陈效. 弱标注CT图像中肝脏病灶分类算法研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.
|
| [24] |
ADAMS R, BISCHOF L. Seeded region growing[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 1994, 16( 6): 641- 647. DOI: 10.1109/34.295913. |
| [25] |
LEE SU, YOON CHUNG S, PARK RH. A comparative performance study of several global thresholding techniques for segmentation[J]. Comput Vis Graph Image Process, 1990, 52( 2): 171- 190. DOI: 10.1016/0734-189x(90)90053-x. |
| [26] |
OSHER S, FEDKIW R, PIECHOR K. Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces[J]. Appl Mech Rev, 2004, 57( 3): B15.
|
| [27] |
VORONTSOV E, ABI-JAOUDEH N, KADOURY S. Metastatic liver tumor segmentation using texture-based omni-directional deformable surface models[C]//YOSHIDA H, NÄPPI J, SAINI S. International MICCAI Workshop on Computational and Clinical Challenges in Abdominal Imaging. Cham: Springer, 2014: 74- 83.
|
| [28] |
RAJ A, JAYASREE M. Automated liver tumor detection using Markov random field segmentation[J]. Procedia Technol, 2016, 24: 1305- 1310. DOI: 10.1016/j.protcy.2016.05.126. |
| [29] |
SHIMIZU A, NARIHIRA T, FURUKAWA D, et al. Ensemble segmentation using AdaBoost with application to liver lesion extraction from a CT volume[J]. MIDAS J, 2008. DOI: 10.54294/wrtw01. |
| [30] |
ZHANG RZ, ZHAO L, LOU WT, et al. Automatic segmentation of acute ischemic stroke from DWI using 3-D fully convolutional DenseNets[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37( 9): 2149- 2160. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2821244. |
| [31] |
HESAMIAN MH, JIA WJ, HE XJ, et al. Deep learning techniques for medical image segmentation: Achievements and challenges[J]. J Digit Imaging, 2019, 32( 4): 582- 596. DOI: 10.1007/s10278-019-00227-x. |
| [32] |
RAZZAK MI, NAZ S, ZAIB A. Deep learning for medical image processing: Overview, challenges and future[EB/OL]. 2017: arXiv: 1704. 06825. http://arxiv.org/abs/1704.06825. http://arxiv.org/abs/1704.06825 |
| [33] |
BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2017, 39( 12): 2481- 2495. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615. |
| [34] |
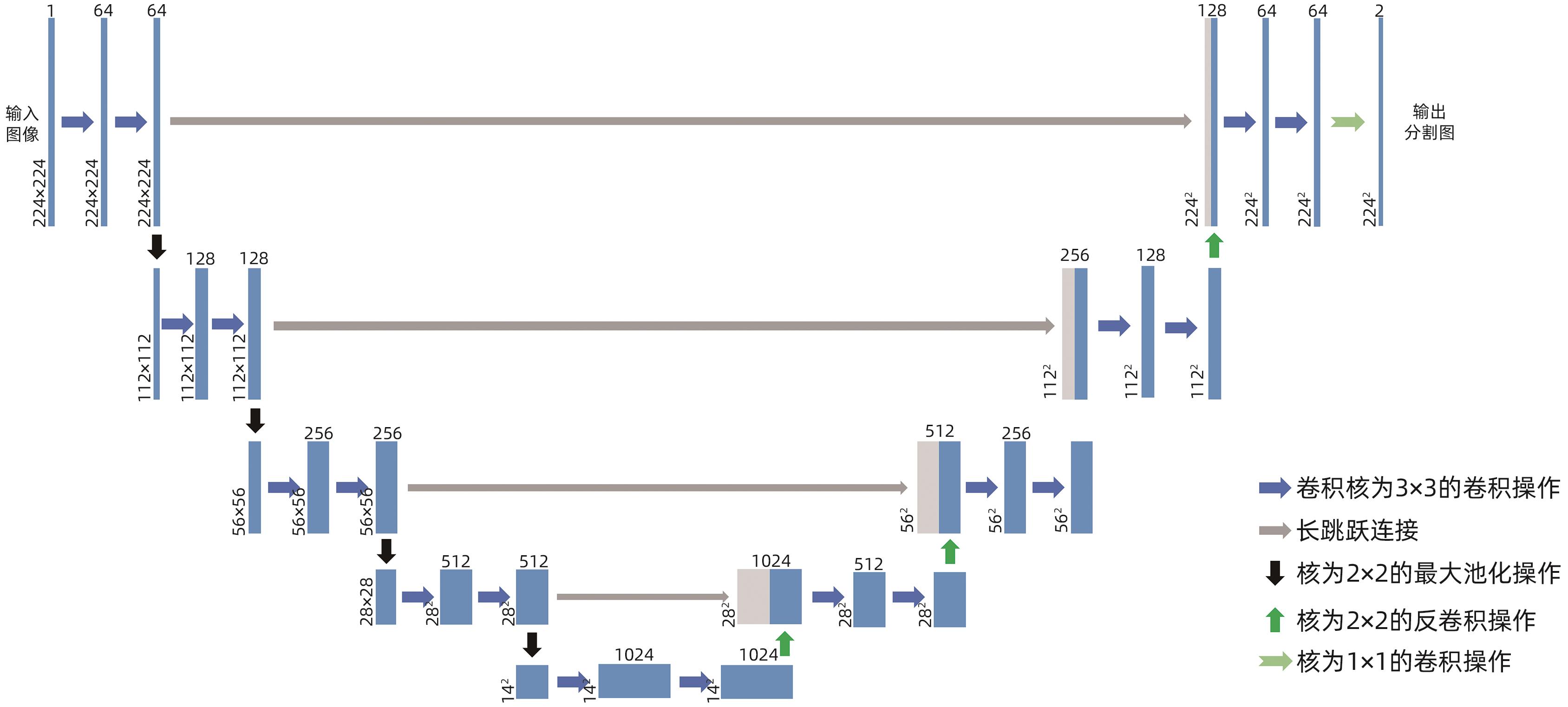
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[EB/OL]. 2015: arXiv: 1505. 04597. http://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597. http://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597 |
| [35] |
DONG X, ZHOU YZ, WANG LT, et al. Liver cancer detection using hybridized fully convolutional neural network based on deep learning framework[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 129889- 129898. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3006362. |
| [36] |
GAO F. Liver tumor image segmentation and MVI prediction based on feature learning[D]. Zhengzhou: Information Engineering University, 2022.
高飞. 基于特征学习的肝脏肿瘤图像分割与MVI预测[D]. 郑州: 战略支援部队信息工程大学, 2022.
|
| [37] |
GHONIEM RM. A novel bio-inspired deep learning approach for liver cancer diagnosis[J]. Information, 2020, 11( 2): 80. DOI: 10.3390/info11020080. |
| [38] |
ALMOTAIRI S, KAREEM G, AOUF M, et al. Liver tumor segmentation in CT scans using modified SegNet[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20( 5): 1516. DOI: 10.3390/s20051516. |
| [39] |
ALIRR OI. Deep learning and level set approach for liver and tumor segmentation from CT scans[J]. J Appl Clin Med Phys, 2020, 21( 10): 200- 209. DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13003. |
| [40] |
SEO H, HUANG C, BASSENNE M, et al. Modified U-net(mU-net) with incorporation of object-dependent high level features for improved liver and liver-tumor segmentation in CT images[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39( 5): 1316- 1325. DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2948320. |
| [41] |
CHEN YL, WANG K, LIAO XY, et al. Channel-unet: A spatial channel-wise convolutional neural network for liver and tumors segmentation[J]. Front Genet, 2019, 10: 1110. DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01110. |
| [42] |
XI XF, WANG L, SHENG VS, et al. Cascade U-ResNets for simultaneous liver and lesion segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 68944- 68952. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985671. |
| [43] |
XIAO XJ, QIANG Y, ZHAO JJ, et al. Segmentation of liver lesions without contrast agents with radiomics-guided densely UNet-nested GAN[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 2864- 2878. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047429. |
| [44] |
ZHANG Y, JIANG BX, WU J, et al. Deep learning initialized and gradient enhanced level-set based segmentation for liver tumor from CT images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 76056- 76068. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988647. |
| [45] |
ZHANG C, HUA QQ, CHU YY, et al. Liver tumor segmentation using 2.5D UV-Net with multi-scale convolution[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2021, 133: 104424. DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104424. |
| [46] |
BILIC P, CHRIST P, LI HB, et al. The liver tumor segmentation benchmark(LiTS)[J]. Med Image Anal, 2023, 84: 102680. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102680. |
| [47] |
SOLER L, HOSTETTLER A, AGNUS V, et al. 3D image reconstruction for comparison of algorithm database: A patient specific anatomical and medical image database[DB]. France: Institut de Recherche contre les Cancers de l’Appareil Digestif(IRCAD), 2010. https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01/. https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3d-ircadb-01/ |
| [48] |
Image Big Data Artificial Intelligence Working Committee of Chinese Society of Radiology Chinese Medical Association, Abdominal Group of Chinese Society of Radiology Chinese Medical Association, Magnetic Resonance Imaging Group of Chinese Society of Radiology Chinese Medical Association. Expert consensus on the focal liver lesion annotation of CT and MRI(2020)[J]. Chin J Radiol, 2020, 54( 12): 1145- 1152. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20200706-00893. |







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: