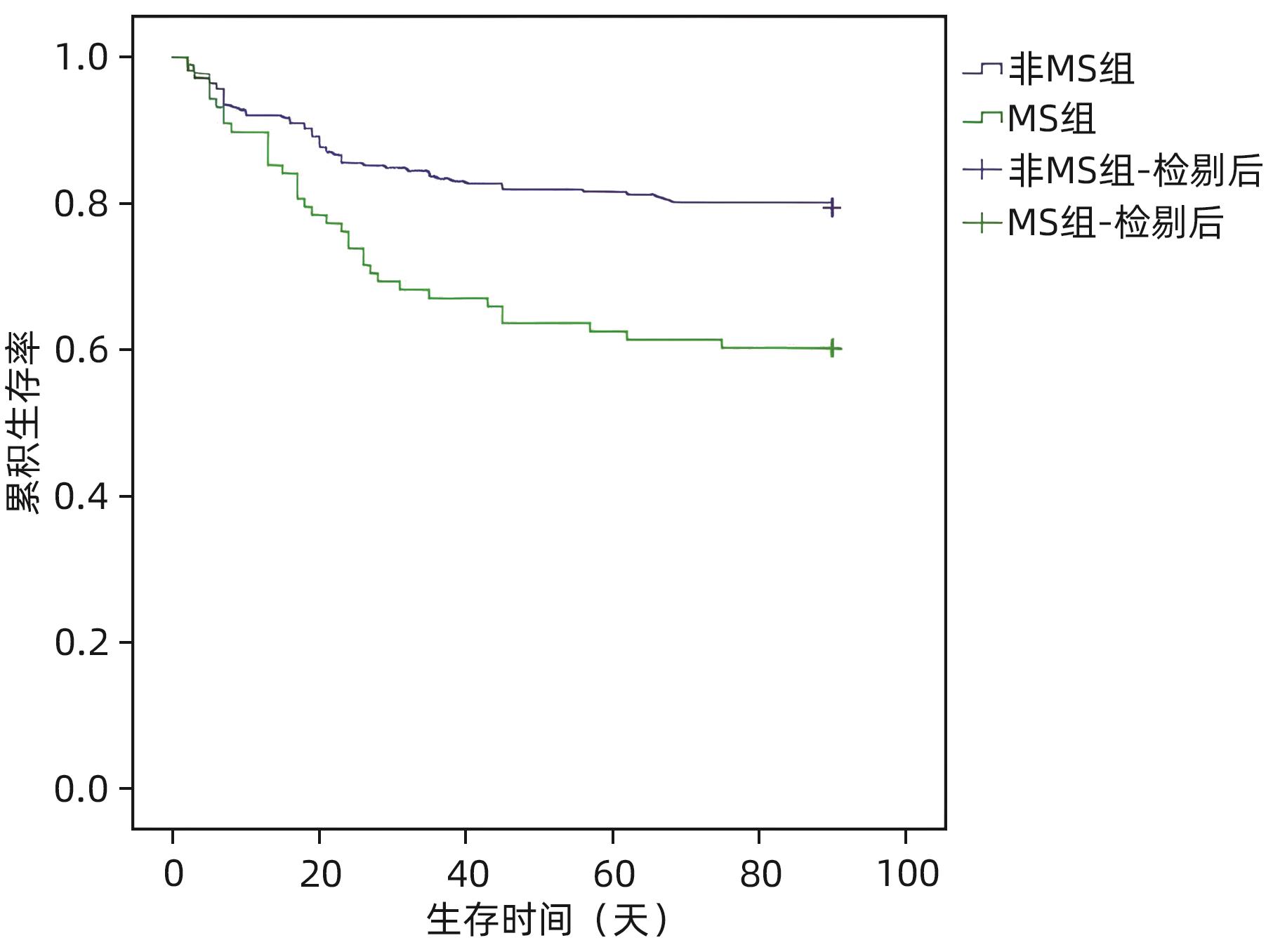
| [1] |
Liver Failure and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases, Chinese Medical Association; Severe Liver Disease and Artificial Liver Group, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of liver failure(2018)[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 1): 38- 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.01.007. |
| [2] |
CHEN MJ, LI X, TANG SH. Advances in multi-dimensional assessment of liver function in the prognosis of patients with liver failure[J]. Clin J Med Offic, 2023, 51( 9): 901- 903, 907. DOI: 10.16680/j.1671-3826.2023.09.05. |
| [3] |
ASRANI S, SIMONETTO D, KAMATH P. Acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2015, 13( 12): 2128- 39. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.008. |
| [4] |
MEZZANO G, JUANOLA A, CARDENAS A, et al. Global burden of disease: Acute-on-chronic liver failure, a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Gut, 2022, 71( 1): 148- 155. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322161. |
| [5] |
BERZIGOTTI A, GARCIA-TSAO G, BOSCH J, et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for clinical decompensation in patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2011, 54( 2): 555- 561. DOI: 10.1002/hep.24418. |
| [6] |
SARIN SK, CHOUDHURY A, SHARMA MK, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: Consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver(APASL): An update[J]. Hepatol Int, 2019, 13( 4): 353- 390. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-019-09946-3. |
| [7] |
Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese Society of Infectious Disease, Chinese Medical Association. The guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: 2019 version[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2019, 35( 12): 2648- 2669. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2019.12.007. |
| [8] |
Metabolic Syndrome Research Collaboration Group, Diabetes Branch, Chinese Medical Association. Recommendations on metabolic syndrome, diabetes branch, Chinese Medical Association[J]. Chin J Diabetes, 2004, 12( 3): 5- 10.
中华医学会糖尿病学分会代谢综合征研究协作组. 中华医学会糖尿病学分会关于代谢综合征的建议[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2004, 12( 3): 5- 10.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
FAHED G, AOUN L, ZERDAN M BOU, et al. Metabolic syndrome: Updates on pathophysiology and management in 2021[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23( 2): 786. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23020786. |
| [11] |
LAM DW, LEROITH D, FEINGOLD KR, et al. Metabolic syndrome[R]. Endotext. MDText.com, Inc, 2000.
|
| [12] |
HIRODE G, WONG RJ. Trends in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in the United States, 2011-2016[J]. JAMA, 2020, 323( 24): 2526- 2528. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.4501. |
| [13] |
SETO WK. Chronic hepatitis B and metabolic risk factors: A call for rigorous longitudinal studies[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25( 3): 282- 286. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i3.282. |
| [14] |
REN HN, WANG JN, GAO Y, et al. Metabolic syndrome and liver-related events: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2019, 19( 1): 40. DOI: 10.1186/s12902-019-0366-3. |
| [15] |
DIAO YT, HU DQ, HU X, et al. The role of metabolic factors and steatosis in treatment-Naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B and normal alanine aminotransferase[J]. Infect Dis Ther, 2022, 11( 3): 1133- 1148. DOI: 10.1007/s40121-022-00629-5. |
| [16] |
DUSEJA A, DE A, TANEJA S, et al. Impact of metabolic risk factors on the severity and outcome of patients with alcohol-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. Liver Int, 2021, 41( 1): 150- 157. DOI: 10.1111/liv.14671. |
| [17] |
ENGIN A. The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 960: 221- 245. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_9. |
| [18] |
PARADIS V, PERLEMUTER G, BONVOUST F, et al. High glucose and hyperinsulinemia stimulate connective tissue growth factor expression: A potential mechanism involved in progression to fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Hepatology, 2001, 34( 4 Pt 1): 738- 744. DOI: 10.1053/jhep.2001.28055. |
| [19] |
PERGOLA GD, PANNACCIULLI N. Coagulation and fibrinolysis abnormalities in obesity[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2002, 25( 10): 899- 904. DOI: 10.1007/BF03344054. |
| [20] |
LAAT-KREMERS RD, CASTELNUOVO AD, van der VORM L, et al. Increased BMI and blood lipids are associated with a hypercoagulable state in the moli-sani cohort[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 897733. DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.897733. |



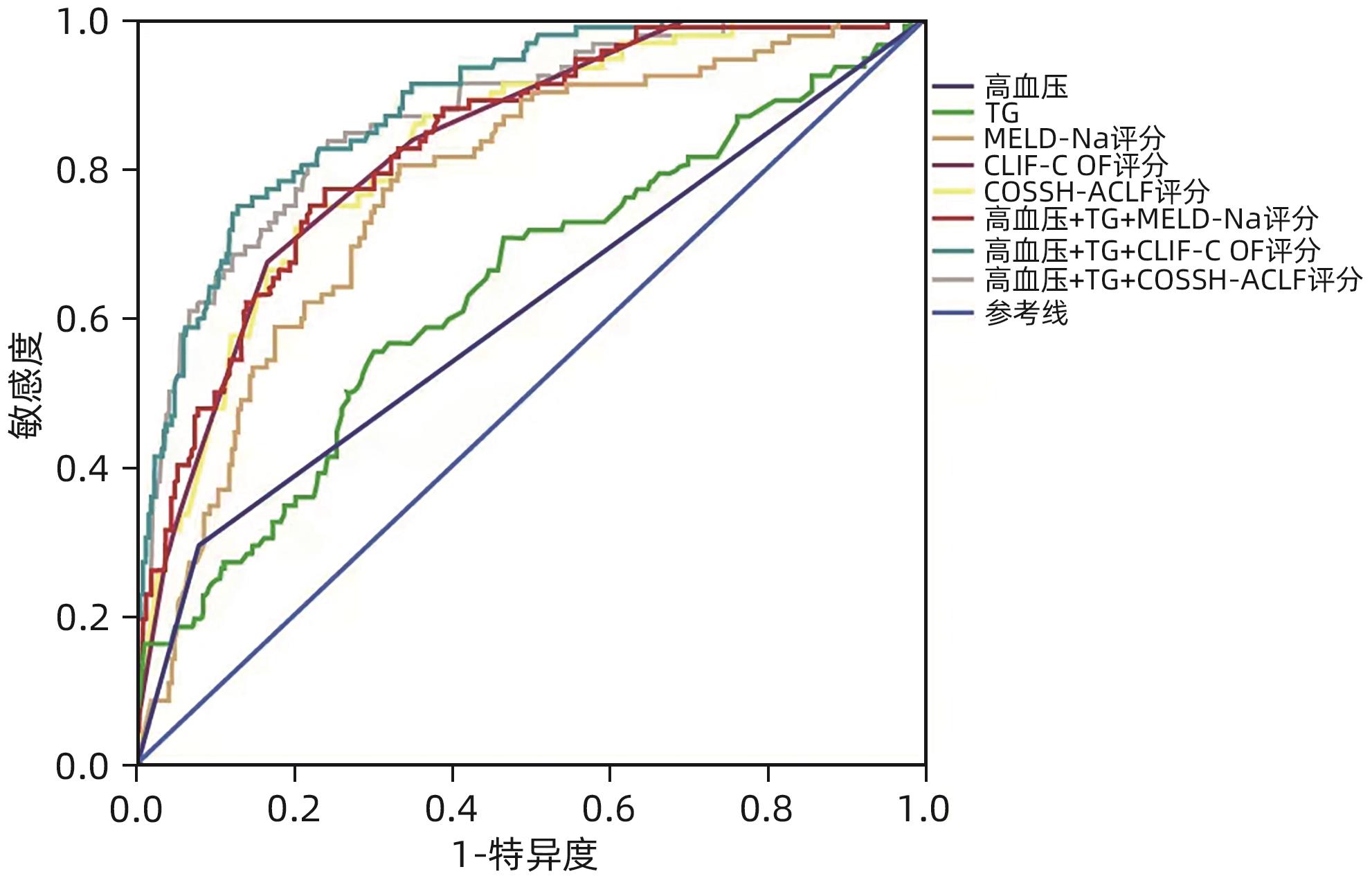




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: