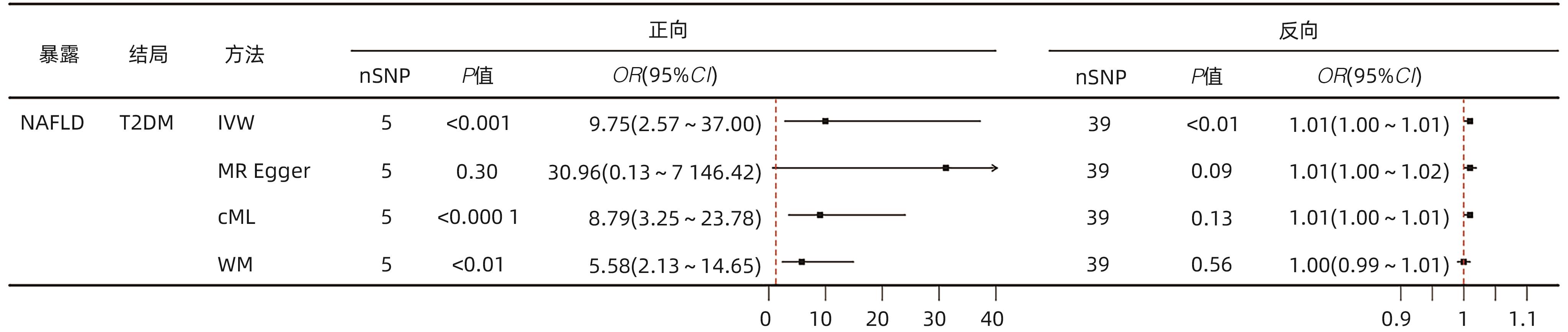
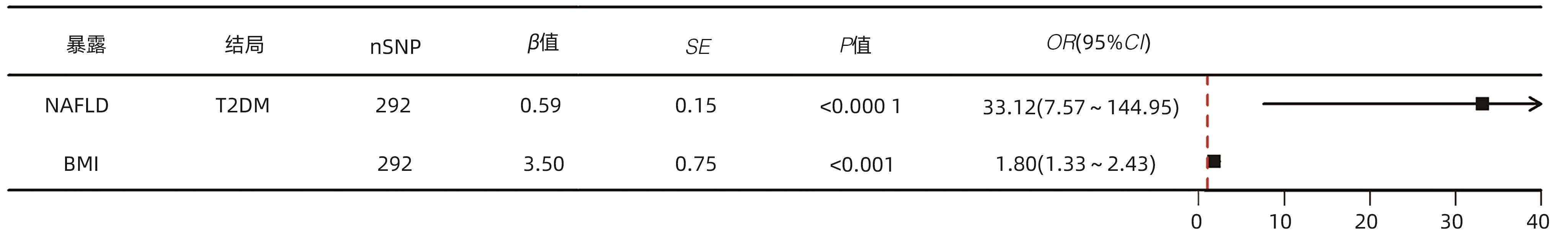
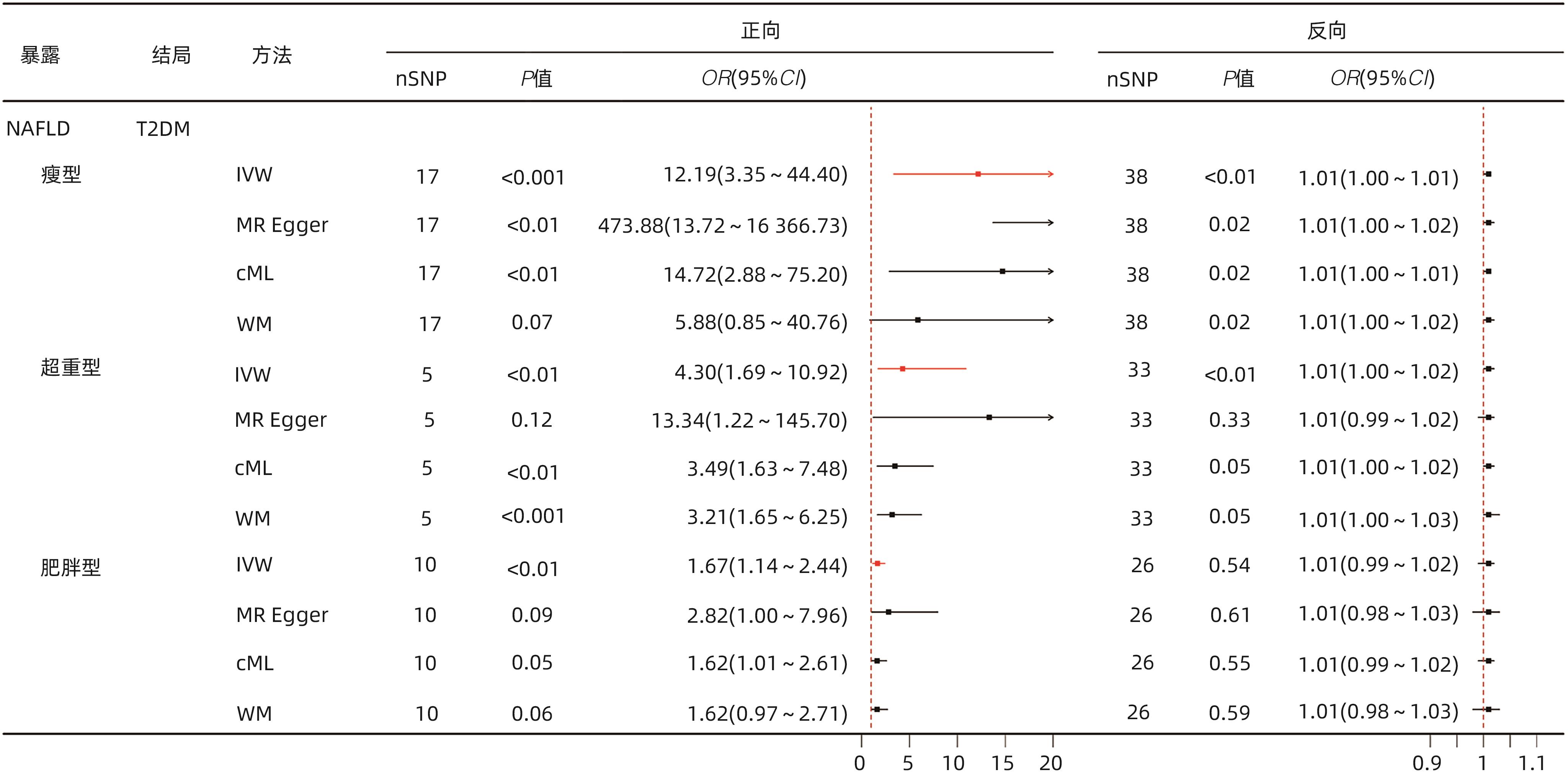
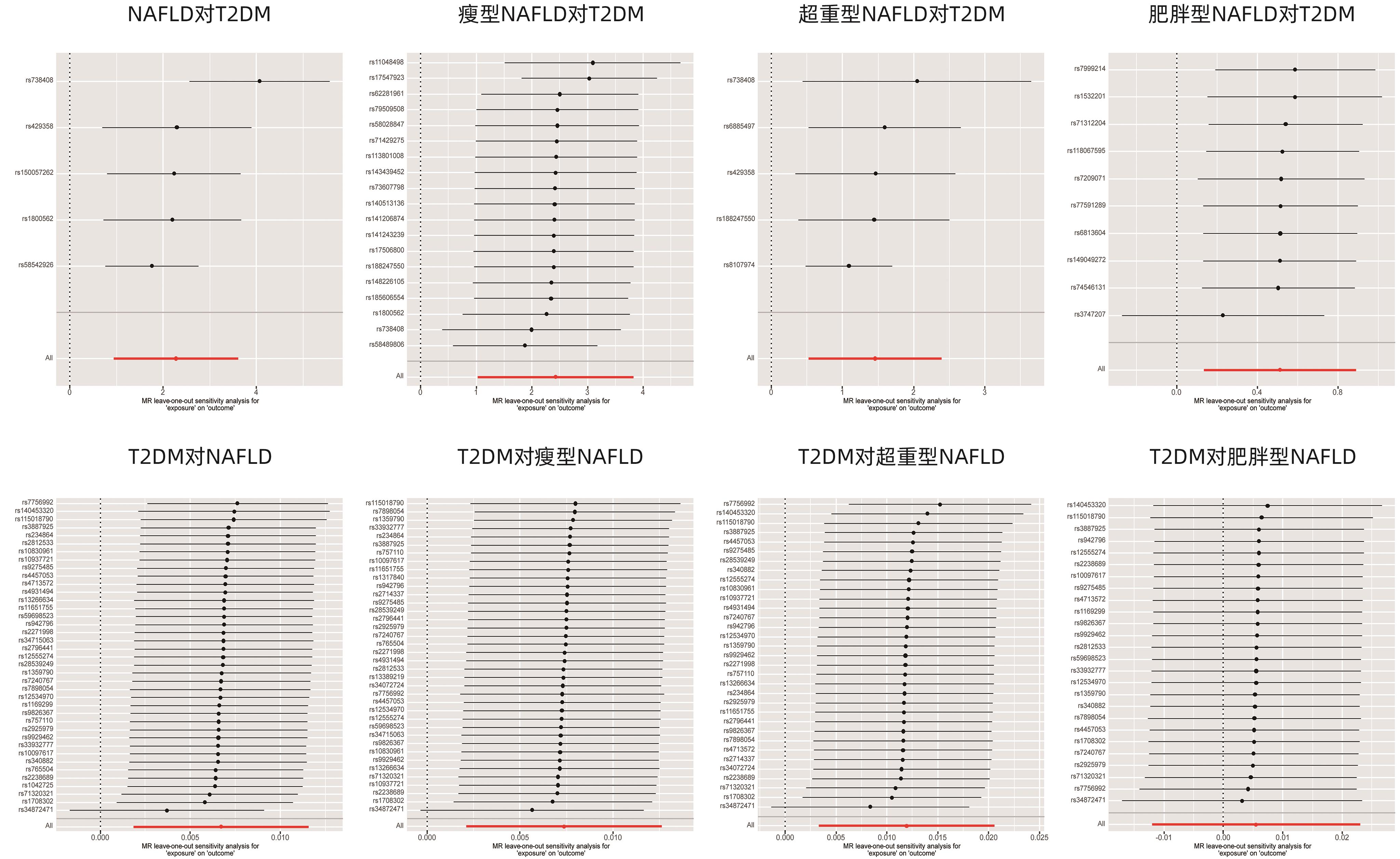
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
RIAZI K, AZHARI H, CHARETTE JH, et al. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 7( 9): 851- 861. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. |
| [3] |
LI L, LIU DW, YAN HY, et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 21 cohort studies[J]. Obes Rev, 2016, 17( 6): 510- 519. DOI: 10.1111/obr.12407. |
| [4] |
NABI O, LAPIDUS N, BOURSIER J, et al. Lean individuals with NAFLD have more severe liver disease and poorer clinical outcomes(NASH-CO Study)[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 78( 1): 272- 283. DOI: 10.1097/HEP.0000000000000329. |
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
TANG A, NG CH, PHANG PH, et al. Comparative burden of metabolic dysfunction in lean NAFLD vs non-lean NAFLD-A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21( 7): 1750- 1760. e 12. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.06.029. |
| [7] |
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas(10th ed)[M]. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2022.
|
| [8] |
YOUNOSSI ZM, GOLABI P, PRICE JK, et al. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.03.006.[ Online ahead of print] |
| [9] |
CAO LM, AN Y, LIU HY, et al. Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Med, 2024, 22( 1): 101. DOI: 10.1186/s12916-024-03315-0. |
| [10] |
GAO YT, ZHAO TY, SONG SN, et al. Lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: A literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2023, 200: 110699. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110699. |
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
SEKULA P, FABIOLA GRECO M, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess causality using observational data[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2016, 27( 11): 3253- 3265. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2016010098. |
| [13] |
FERENCE BA, HOLMES MV, SMITH GD. Using Mendelian randomization to improve the design of randomized trials[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2021, 11( 7): a040980. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040980. |
| [14] |
SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: The STROBE-MR statement[J]. JAMA, 2021, 326( 16): 1614- 1621. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2021.18236. |
| [15] |
SUN ZW, PAN XC, TIAN AW, et al. Genetic variants in HFE are associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals[J]. JHEP Rep, 2023, 5( 7): 100744. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2023.100744. |
| [16] |
O’CONNOR MJ, SCHROEDER P, HUERTA-CHAGOYA A, et al. Recessive genome-wide meta-analysis illuminates genetic architecture of type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes, 2022, 71( 3): 554- 565. DOI: 10.2337/db21-0545. |
| [17] |
YENGO L, SIDORENKO J, KEMPER KE, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2018, 27( 20): 3641- 3649. DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddy271. |
| [18] |
HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data[J]. PLoS Genet, 2017, 13( 11): e1007081. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007081. |
| [19] |
BURGESS S, SCOTT RA, TIMPSON NJ, et al. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: A blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2015, 30( 7): 543- 552. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-015-0011-z. |
| [20] |
BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44( 2): 512- 525. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyv080. |
| [21] |
XUE HR, SHEN XT, PAN W. Constrained maximum likelihood-based Mendelian randomization robust to both correlated and uncorrelated pleiotropic effects[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2021, 108( 7): 1251- 1269. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.05.014. |
| [22] |
BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent estimation in Mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted Median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40( 4): 304- 314. DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21965. |
| [23] |
SANDERSON E, DAVEY SMITH G, WINDMEIJER F, et al. An examination of multivariable Mendelian randomization in the single-sample and two-sample summary data settings[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2019, 48( 3): 713- 727. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyy262. |
| [24] |
BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2017, 32( 5): 377- 389. DOI: 10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x. |
| [25] |
VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases[J]. Nat Genet, 2018, 50( 5): 693- 698. DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7. |
| [26] |
BOWDEN J, SPILLER W, DEL GRECO M F, et al. Improving the visualization, interpretation and analysis of two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization via the Radial plot and Radial regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2018, 47( 6): 2100. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyy265. |
| [27] |
BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO M F, MINELLI C, et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: Moving beyond the NOME assumption[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2019, 48( 3): 728- 742. DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyy258. |
| [28] |
BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from Mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants[J]. Epidemiology, 2017, 28( 1): 30- 42. DOI: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000559. |
| [29] |
Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease Group, Hepatology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2010, 2( 4): 43- 48. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7380.2010.04.013.
|
| [30] |
LIU ZP, ZHANG Y, GRAHAM S, et al. Causal relationships between NAFLD, T2D and obesity have implications for disease subphenotyping[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73( 2): 263- 276. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.006. |
| [31] |
NI XT, TONG C, HALENGBIEKE A, et al. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2023, 206: 110993. DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110993. |
| [32] |
MANTOVANI A, BYRNE CD, BONORA E, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Care, 2018, 41( 2): 372- 382. DOI: 10.2337/dc17-1902. |
| [33] |
MANTOVANI A, PETRACCA G, BEATRICE G, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident diabetes mellitus: An updated meta-analysis of 501 022 adult individuals[J]. Gut, 2021, 70( 5): 962- 969. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322572. |
| [34] |
KOSMALSKI M, ŚLIWIŃSKA A, DRZEWOSKI J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or type 2 diabetes mellitus-the chicken or the egg dilemma[J]. Biomedicines, 2023, 11( 4): 1097. DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11041097. |
| [35] |
KHAN RS, BRIL F, CUSI K, et al. Modulation of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatology, 2019, 70( 2): 711- 724. DOI: 10.1002/hep.30429. |
| [36] |
ZHANG XY, LIU Y, WANG WL, et al. Diagnosis and evaluation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. J Clin Hepatol, 2023, 39( 8): 1780- 1788. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2023.08.003. |
| [37] |
ESLAM M, VALENTI L, ROMEO S. Genetics and epigenetics of NAFLD and NASH: Clinical impact[J]. J Hepatol, 2018, 68( 2): 268- 279. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.003. |
| [38] |
LIU DJ, PELOSO GM, YU HJ, et al. Exome-wide association study of plasma lipids in>300, 000 individuals[J]. Nat Genet, 2017, 49( 12): 1758- 1766. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3977. |
| [39] |
BESSONE F, RAZORI MV, ROMA MG. Molecular pathways of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development and progression[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76( 1): 99- 128. DOI: 10.1007/s00018-018-2947-0. |
| [40] |
MALONE JI, HANSEN BC. Does obesity cause type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM)? Or is it the opposite?[J]. Pediatr Diabetes, 2019, 20( 1): 5- 9. DOI: 10.1111/pedi.12787. |
| [41] |
YE Q, ZOU BY, YEO YH, et al. Global prevalence, incidence, and outcomes of non-obese or lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 5( 8): 739- 752. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30077-7. |
| [42] |
PINGITORE P, ROMEO S. The role of PNPLA3 in health and disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, 2019, 1864( 6): 900- 906. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.06.018. |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
SMITH GI, POLIDORI DC, YOSHINO M, et al. Influence of adiposity, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic triglyceride content on insulin kinetics[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130( 6): 3305- 3314. DOI: 10.1172/JCI136756. |
| [45] |
TOBARI M, HASHIMOTO E, TANIAI M, et al. Characteristics of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis among lean patients in Japan: Not uncommon and not always benign[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 34( 8): 1404- 1410. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.14585. |
| [46] |
PETTA S, CIMINNISI S, DI MARCO V, et al. Sarcopenia is associated with severe liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 45( 4): 510- 518. DOI: 10.1111/apt.13889. |
| [47] |
ZHOU XM, YU XY, SONG ZY. Clinical characteristics and management of lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Chin J Health Manag, 2024, 18( 3): 236- 240. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115624-20230803-00047. |
| [48] |
LI N, XANG W, WU SL, et al. Association between the lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of incident type 2 diabetes in a healthy population of Northwest China: A retrospective cohort study with a 2-year follow-up period[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14: 1173757. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1173757. |
| [49] |
FRACANZANI AL, PETTA S, LOMBARDI R, et al. Liver and cardiovascular damage in patients with lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and association with visceral obesity[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 15( 10): 1604- 1611. e 1. DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.04.045. |



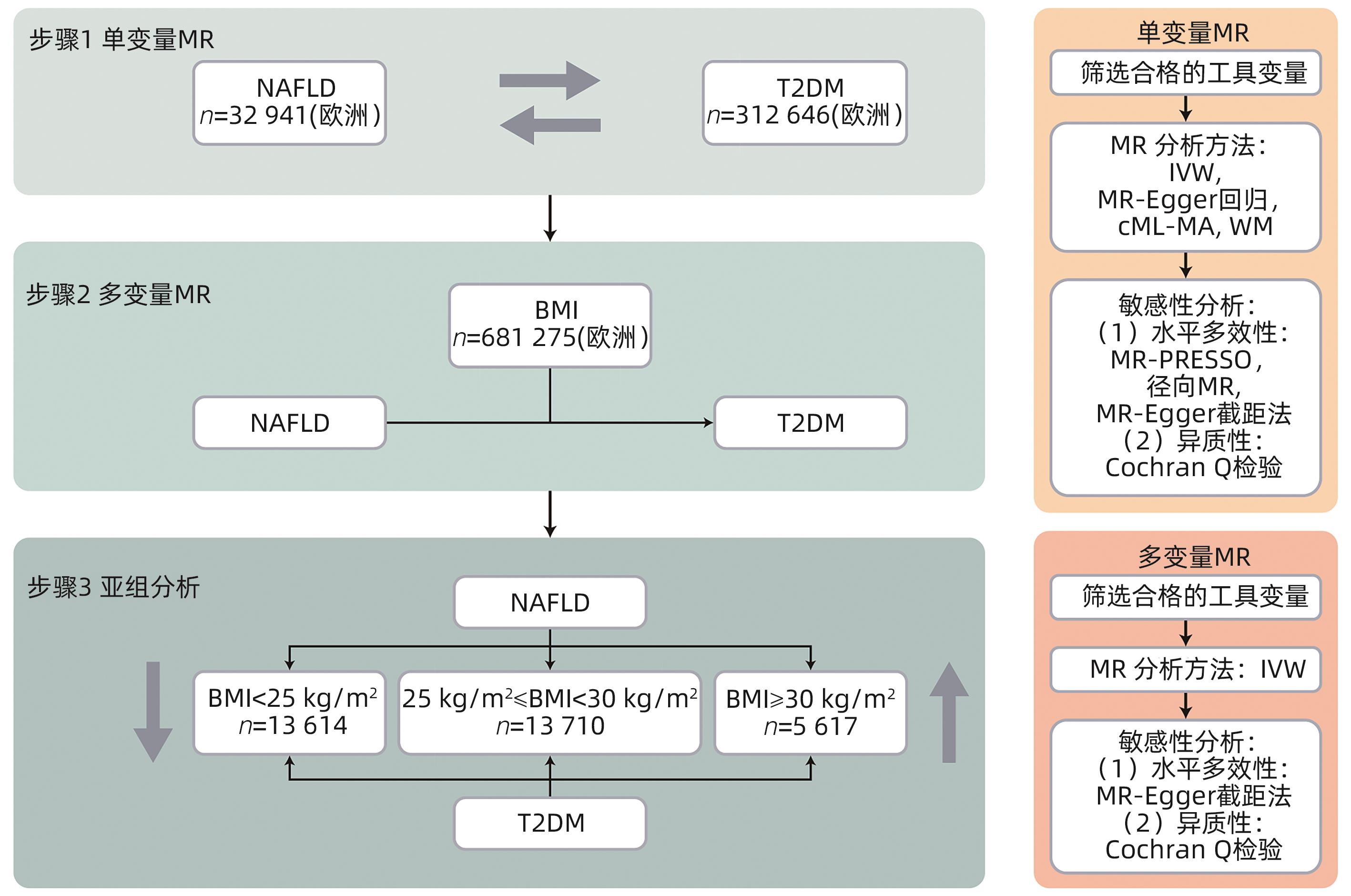




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: